G10B: Autonomic Innervation of the GI Tract (Dr. Albertine)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Variations of Thoracic Splanchnic Nerves and Its Clinical Implications
Int. J. Morphol., 23(3):247-251, 2005. Variations of Thoracic Splanchnic Nerves and its Clinical Implications Variaciones de los Nervios Esplácnicos Torácicos y sus Implicancias Clínicas *Tony George Jacob; ** Surbhi Wadhwa; ***Shipra Paul & ****Srijit Das JACOB, G. T.; WADHWA, S.; PAUL, S. & DAS, S. Variations of thoracic splanchnic nerves and its clinical implications. Int. J. Morphol., 23(3):247-251, 2005. SUMMARY:The present study reports an anomalous branching pattern of the thoracic sympathetic chain. At the level of T3 ganglion, an anomalous branch i.e accessory sympathetic chain (ASC) descended anteromedial to the main sympathetic chain (MSC). The MSC and the ASC communicated with each other at the level of T9, T10 and T11 ganglion, indicating the absence of classical pattern of greater, lesser and least splanchnic nerves on the right side. However, on the left side, the sympathetic chain displayed normal branching pattern. We opine that the ASC may be representing a higher origin of greater splanchnic nerve at the level of T3 ganglion and the branches from MSC at T9, T10 and T11 ganglion may be the lesser and least splanchnic nerves, which further joined the ASC (i.e presumably the greater splanchnic nerve) to form a common trunk. This common trunk pierced the right crus of diaphragm to reach the right suprarenal plexus after giving few branches to the celiac plexus. Awareness and knowledge of such anatomical variants of thoracic sympathetic chain may be helpful to surgeons in avoiding any incomplete denervation or preventing any inadvertent injury during thoracic sympathectomy. KEY WORDS: Splanchnic nerves; Sympathetic chain; Trunk thoracic; Ganglion. -

Anatomical Planes in Rectal Cancer Surgery
DOI: 10.4274/tjcd.galenos.2019.2019-10-2 Turk J Colorectal Dis 2019;29:165-170 REVIEW Anatomical Planes in Rectal Cancer Surgery Rektum Kanser Cerrahisinde Anatomik Planlar Halil İbrahim Açar, Mehmet Ayhan Kuzu Ankara University Faculty of Medicine, Department of General Surgery, Ankara, Turkey ABSTRACT This review outlines important anatomical landmarks not only for rectal cancer surgery but also for pelvic exentration. Keywords: Anorectal anatomy, pelvic anatomy, surgical anatomy of rectum ÖZ Pelvis anatomisini derleme halinde özetleyen bu makale rektum kanser cerrahisi ve pelvik ezantrasyon için önemli topografik noktaları gözden geçirmektedir. Anahtar Kelimeler: Anorektal anatomi, pelvik anatomi, rektumun cerrahi anatomisi Introduction Surgical Anatomy of the Rectum The rectum extends from the promontory to the anal canal Pelvic Anatomy and is approximately 12-15 cm long. It fills the sacral It is essential to know the pelvic anatomy because of the concavity and ends with an anal canal 2-3 cm anteroinferior intestinal and urogenital complications that may develop to the tip of the coccyx. The rectum contains three folds in after the surgical procedures applied to the pelvic region. the coronal plane laterally. The upper and lower are convex The pelvis, encircled by bone tissue, is surrounded by the to the right, and the middle is convex to the left. The middle main vessels, ureters, and autonomic nerves. Success in the fold is aligned with the peritoneal reflection. Intraluminal surgical treatment of pelvic organs is only possible with a projections of the lower boundaries of these folds are known as Houston’s valves. Unlike the sigmoid colon, taenia, good knowledge of the embryological development of the epiploic appendices, and haustra are absent in the rectum. -

Autonomic Nervous System
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 1 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 2 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 3 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 4 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 5 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 6 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 7 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 8 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PAGE 9 REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The autonomic nervous system controls the activity of _?_. (a) smooth muscle (b) cardiac muscle (c) glands (d) all of these (e) none of these 2. All preganglionic and postganglionic autonomic neurons are _?_ neurons. (a) somatic efferent (b) visceral efferent (c) somatic afferent (d) visceral afferent (e) association neurons 3. Which neurotransmitter is released at the synapses between preganglionic and postganglionic autonomic neurons ? (a) epinephrine (b) norepinephrine (c) acetylcholine (d) serotonin (e) oxytocin 4. All preganglionic sympathetic neurons are located in: (a) the lateral horn of the spinal cord of spinal cord segments T1-L2 (b) brainstem nuclei (c) intramural (terminal) ganglia (d) paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic chains (e) prevertebral ganglia 5. All preganglionic parasympathetic neurons are located in _?_. (a) prevertebral ganglia (b) the lateral horn of spinal cord segments T1-L2 (c) sympathetic chain ganglia (d) intramural ganglia (e) brainstem nuclei and spinal cord segments S2-S4 6. Prevertebral and paravertebral ganglia contain _?_. (a) preganglionic sympathetic neurons (b) preganglionic parasympathetic neurons (c) postganglionic sympathetic neurons (d) postganglionic parasympathetic neurons (e) all of these 7. The otic, ciliary, submandibular and pterygopalatine ganglia are located in the head region and contain _?_. (a) preganglionic sympathetic neurons (b) preganglionic parasympathetic neurons (c) postganglionic sympathetic neurons (d) postganglionic parasympathetic neurons (e) none of these 8. -

Of the Pediatric Mediastinum
MRI of the Pediatric Mediastinum Dianna M. E. Bardo, MD Director of Body MR & Co-Director of the 3D Innovation Lab Disclosures Consultant & Speakers Bureau – honoraria Koninklijke Philips Healthcare N V Author – royalties Thieme Publishing Springer Publishing Mediastinum - Anatomy Superior Mediastinum thoracic inlet to thoracic plane thoracic plane to diaphragm Inferior Mediastinum lateral – pleural surface anterior – sternum posterior – vertebral bodies Mediastinum - Anatomy Anterior T4 Mediastinum pericardium to sternum Middle Mediastinum pericardial sac Posterior Mediastinum vertebral bodies to pericardium lateral – pleural surface superior – thoracic inlet inferior - diaphragm Mediastinum – MR Challenges Motion Cardiac ECG – gating/triggering Breathing Respiratory navigation Artifacts Intubation – LMA Surgical / Interventional materials Mediastinum – MR Sequences ECG gated/triggered sequences SSFP – black blood SE – IR – GRE Non- ECG gated/triggered sequences mDIXON (W, F, IP, OP), eTHRIVE, turbo SE, STIR, DWI Respiratory – triggered, radially acquired T2W MultiVane, BLADE, PROPELLER Mediastinum – MR Sequences MRA / MRV REACT – non Gd enhanced Gd enhanced sequences THRIVE, mDIXON, mDIXON XD Mediastinum – Contents Superior Mediastinum PVT Left BATTLE: Phrenic nerve Vagus nerve Structures at the level of the sternal angle Thoracic duct Left recurrent laryngeal nerve (not the right) CLAPTRAP Brachiocephalic veins Cardiac plexus Aortic arch (and its 3 branches) Ligamentum arteriosum Thymus Aortic arch (inner concavity) Trachea Pulmonary -

The Diaphragm
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Regional anatomy McClellan, George 1896 Vol. 1 Jefferson Medical Books and Notebooks November 2009 The Diaphragm Follow this and additional works at: https://jdc.jefferson.edu/regional_anatomy Part of the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine Commons Let us know how access to this document benefits ouy Recommended Citation "The Diaphragm" (2009). Regional anatomy McClellan, George 1896 Vol. 1. Paper 13. https://jdc.jefferson.edu/regional_anatomy/13 This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Jefferson Digital Commons. The Jefferson Digital Commons is a service of Thomas Jefferson University's Center for Teaching and Learning (CTL). The Commons is a showcase for Jefferson books and journals, peer-reviewed scholarly publications, unique historical collections from the University archives, and teaching tools. The Jefferson Digital Commons allows researchers and interested readers anywhere in the world to learn about and keep up to date with Jefferson scholarship. This article has been accepted for inclusion in Regional anatomy McClellan, George 1896 Vol. 1 by an authorized administrator of the Jefferson Digital Commons. For more information, please contact: [email protected]. 320 THE DIAPHRAGJ1I. The nerves from the four upp e1' ganglia are quite small, and pass inward to join the cardiac and posterior pulmonary plexuses. The nerves from the six lower ganglia constitute the greater, the lesser, and the smaller splanchnic nerves. The great splanchnic nerue is composed of the most numerous filaments from the fifth, sixth, seventh, eighth, ninth, and tenth ganglia, which combine into a single trunk, and, passing through the crus of the diaphragm on the corresponding side, join the solar, renal, and supra-renal plexuses. -

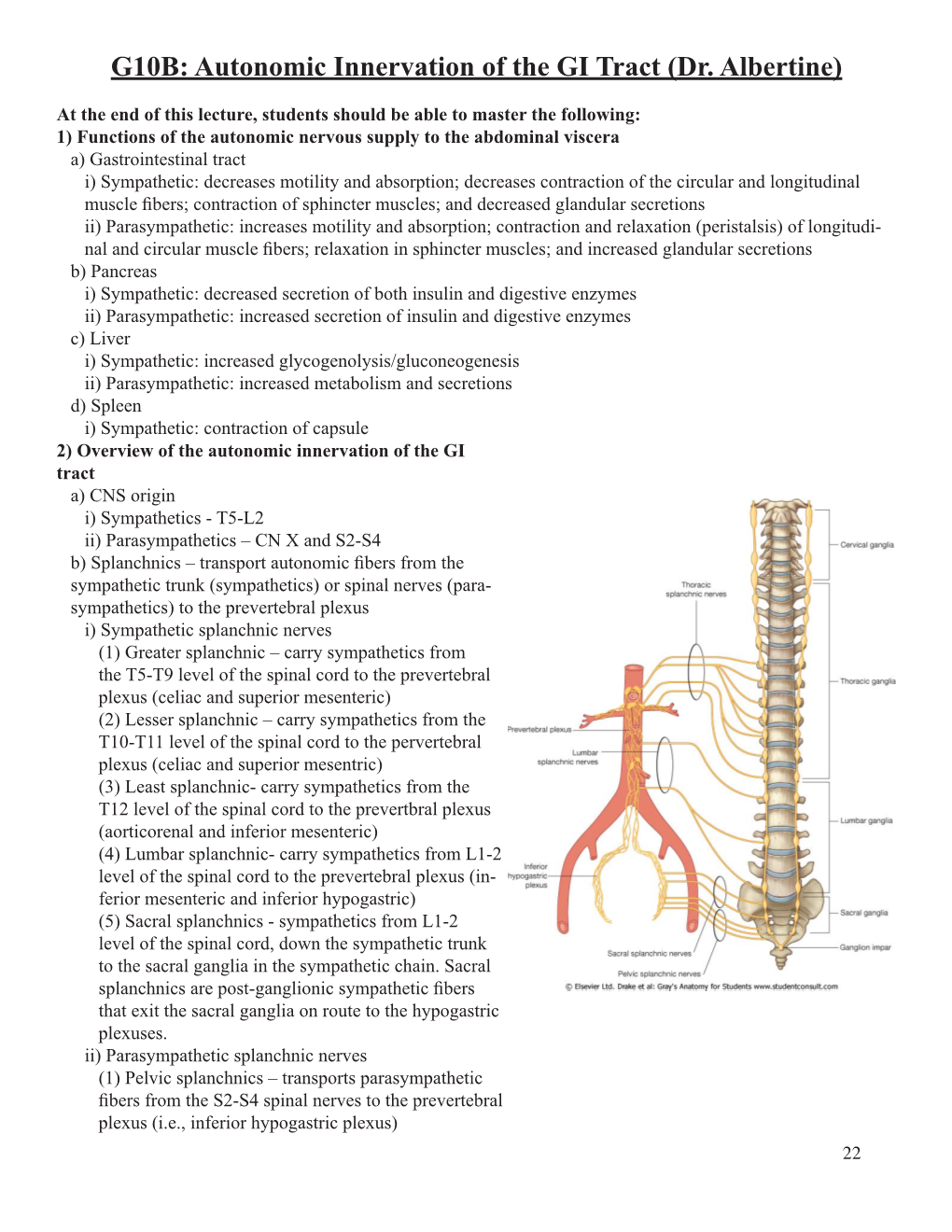
Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Brain Spinal Cord Sensory Division Motor Division Somatic Nervou
Autonomic Nervous System Organization of Nervous System: Nervous system Integration Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system (CNS) (PNS) Motor Sensory output input Brain Spinal cord Motor division Sensory division (Efferent) (Afferent) “self governing” Autonomic Nervous System Somatic Nervous System (Involuntary; smooth & (Voluntary; skeletal muscle) cardiac muscle) Stability of internal environment depends largely on this system Marieb & Hoehn – Figure 14.2 Autonomic Nervous System Ganglion: Comparison of Somatic vs. Autonomic: A group of cell bodies located in the PNS Cell body Effector location NTs organs Effect CNS Single neuron from CNS to effector organs ACh + Stimulatory Heavily myelinated axon Somatic NS Somatic Skeletal muscle ACh = Acetylcholine Two-neuron chain from CNS to effector organs CNS ACh Ganglion NE Postganglionic axon Preganglionic axon (unmyelinated) (lightly myelinated) Sympathetic + Stimulatory Autonomic NS Autonomic or inhibitory CNS Ganglion (depends ACh ACh on NT and NT receptor Smooth muscle, Type) Postganglionic glands, cardiac Preganglionic axon axon muscle Parasympathetic (lightly myelinated) (unmyelinated) NE = Norepinephrine 1 Autonomic Nervous System Organization of Nervous System: Nervous system Integration Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system (CNS) (PNS) Motor Sensory output input Brain Spinal cord Motor division Sensory division (Efferent) (Afferent) Autonomic Nervous System Somatic Nervous System (Involuntary; smooth & (Voluntary; skeletal muscle) cardiac muscle) Sympathetic division -

The Neuroanatomy of Female Pelvic Pain
Chapter 2 The Neuroanatomy of Female Pelvic Pain Frank H. Willard and Mark D. Schuenke Introduction The female pelvis is innervated through primary afferent fi bers that course in nerves related to both the somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The somatic pelvis includes the bony pelvis, its ligaments, and its surrounding skeletal muscle of the urogenital and anal triangles, whereas the visceral pelvis includes the endopelvic fascial lining of the levator ani and the organ systems that it surrounds such as the rectum, reproductive organs, and urinary bladder. Uncovering the origin of pelvic pain patterns created by the convergence of these two separate primary afferent fi ber systems – somatic and visceral – on common neuronal circuitry in the sacral and thoracolumbar spinal cord can be a very dif fi cult process. Diagnosing these blended somatovisceral pelvic pain patterns in the female is further complicated by the strong descending signals from the cerebrum and brainstem to the dorsal horn neurons that can signi fi cantly modulate the perception of pain. These descending systems are themselves signi fi cantly in fl uenced by both the physiological (such as hormonal) and psychological (such as emotional) states of the individual further distorting the intensity, quality, and localization of pain from the pelvis. The interpretation of pelvic pain patterns requires a sound knowledge of the innervation of somatic and visceral pelvic structures coupled with an understand- ing of the interactions occurring in the dorsal horn of the lower spinal cord as well as in the brainstem and forebrain. This review will examine the somatic and vis- ceral innervation of the major structures and organ systems in and around the female pelvis. -

The Sacral Parasympathetic Innervation of the Colon
THE SACRAL PARASYMPATHETIC INNERVATION OF THE COLON RUSSELL T. WOODBURNE Department of Anatomy, University of Michigan Hedical School, Ann Arbofi TWO FIGURES Autonomic nerves distribute by a variety of methods. They are recognized as components of all spinal and some cranial nerves, but they also have a strong tendency to exhibit a hitch-hiker relationship to arteries and to other nerves. The perivascular plexuses of the head and neck, and of the thorax and abdomen, are especially typical of peripheral sympa- thetic distribution. In the parasympathetic division, pre- ganglion& arising in the third, seventh, and ninth cranial nerves utilize the branches of the trigeminal nerve for pas- sage to the structure innervated. The vagus nerve is a main parasympathetic route to structures of the neck and chest and its terminal fibers end in the abdomen by mingling in the celiac plexus with sympathetic postganglionic fibers. In- testinal autonomies are perivascular for both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. St the brim of the pelvis the perivascular plexus of the aorta forms the hypogastric nerves which descend across the sacral promontory and dis- tribute to the pelvic viscera without following their blood vessels, With these predominantly sympathetic nerves, para- sympathetic fibers pass to the viscera of the pelvis and peri- neum, Anatomical description has recognized that the parasympa- thetic innervation of the descending and sigmoid portions of the large intestine is provided by components of the sacral parasympathetic roots from sacral nerves two, three, and four, which ascend from the pelvis to reach the colon. Implicit 67 68 RUSSELL T. WOODBURNE in most descriptions is an assumption that fibers of this char- acter ascend through the pelvic plexuses, mingle with the nerves of the abdominal portion of the hypogastric plexus, and distribute by means of the perivascular nerve plexuses along the inferior mesenteric artery and its branches. -

Autonomic Nervous System ANS 1 Introduction
Autonomic Nervous System ANS 1 Introduction Control the visceral function = arterial pressure = gastrointestinal motility and secretion = urinary bladder emptying = sweating = body temperature Sympathetic • Divisions of ANS : Division Parasympathetic Division ANS: Preganglionic fibers Postganglionic fibers The Autonomic nervous system Activated by centers located in: • -the spinal cord • - brain stem • - hypothalamus • - the limbic cortex • - The Autonomic nervous system operates by means of visceral reflexes - The efferent Autonomic signals are transmitted to the body through two major subdivisions called - The sympathetic nervous system . - The parasympathetic nervous system. Sympathetic Division Physiological Anatomy of the sympathetic nervous system - two para vertebral sympathetic chains of ganglia in sides of the spinal column - two pre vertebral ganglia inside the abdomen and nervous extending from the ganglia to the different internal organs - the sympathetic nervous originate in the spinal cord between the segments T1 - L2 and pass from here first in to the sympathetic chain and then to the tissues and organs The cell body of each pre ganglion nervous lies in the inter media lateral from of the spinal cord , and its fibers passes through an anterior root of the cord and the spinal nerve. The pre ganglion sympathetic fibers leave the nerve and pass into one of the ganglia of the sympathetic chain Sympathetic Ganglia: A - Paravertebral or Sympathetic chain ganglia B - Prevertebral or Collateral ganglia C - Terminal or Peripheral -

The Internal Thoracic (Mammary) Nerve A
Thorax: first published as 10.1136/thx.26.3.354 on 1 May 1971. Downloaded from Thorax (1971), 26, 354. The internal thoracic (mammary) nerve A. A. PEARSON and R. W. SAUTER Department of Anatomy, University of Oregon Medical School, Portland, Oregon, USA 97201 The internal thoracic (mammary) nerve is formed by contributions from the subclavian plexus and the phrenic nerve. It descends along the internal thoracic artery to the level of the seventh costal cartilage where it is lost. Some of its branches communicate with the intercostal nerves -and are thought to be distributed with these nerves. Others follow perforating and anterior mediastinal arteries. This study is based on human embryos and laboratory by the authors. Twenty-five human fetuses which were sectioned serially and prepared specimens which ranged in size from 12 to 111 with neurological stains. These include the mm crown-rump length were studied. protargol method of Bodian (1936), the silver The subclavian plexus is formed by fibres which method of Pearson and Whitlock (1949), and come from that portion of the sympathetic trunk other staining procedures developed in this and its ganglia which are located in the root of http://thorax.bmj.com/ on September 25, 2021 by guest. Protected copyright. FIG. 1. A composite drawing from cross-sections of a 47mm human fetus showing fibre bundles from the stellate ganglion passing to the internal thoracic nerve plexus and the phrenic nerve. Bodian method. x 51 approximately. 354 Thorax: first published as 10.1136/thx.26.3.354 on 1 May 1971. Downloaded from FIG. -

Ganglion of Impar Block
Ganglion of Impar Block A ganglion of impar block is safe and easy procedure used to treat visceral, pelvic, genital, perineal and anal pain. This injection is considered to be a type of sympathetic block that can be used in the treatment of sympathetically-mediated pain, pain secondary to malignancy, neuropathic pain and post- surgical pain. Patients who will benefit from this blockade will frequently present with vague and poorly localized pain in the “seat” region, which is burning in character and frequently accompanied by sensations of urgency with urination and/or defecation.[1] The target in the procedure is the ganglion of impar – also known as the ganglion of Walther or sacrococcygeal ganglion. It is a singular retroperitoneal structure located at the level of the sacrococcygeal junction (SCJ). There are 4 or 5 small sacral ganglia with the ganglion Impar being the most caudal segment of the confluence of the sacral sympathetic chain as it passes anteromedially over the sacrum. More specifically, the ganglion Impar is the terminal fusion of the 2 sacral sympathetic chains and is located with some anatomical variability between the SCJ and the lower segment of the first coccyx. The fusion of the 2 chains typically positions the ganglion midline, which makes it relatively easy to find. However, there is a wide range of variability in the anatomical location with respect to the SCJ.[2] This structure is of particular importance when considering patients who suffer from pain in the pelvic and perineal structures as it provides nociceptive and sympathetic supply to those regions. It receives afferent innervation from: Perineum Distal rectum Anus Distal urethra Distal vagina Vulva Coccyx Scrotum The block is performed by injecting a small amount of anesthetic onto the ganglion of impar, signals of the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and pain fibers are interrupted from multiple structures simultaneously, leading to dramatic pain relief. -

Sympathetic Control of Lower Esophageal Sphincter Function in the Cat: ACTION of DIRECT CERVICAL and SPLANCHNIC NERVE STIMULATION
Sympathetic Control of Lower Esophageal Sphincter Function in the Cat: ACTION OF DIRECT CERVICAL AND SPLANCHNIC NERVE STIMULATION Jacques Fournet, … , William J. Snape Jr., Sidney Cohen J Clin Invest. 1979;63(4):562-570. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI109337. The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of direct stimulation of the sympathetic nerves on the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) in the anesthetized cat. Neither unilateral nor bilateral cervical sympathectomy, or splanchnicectomy significantly modified basal LES pressure in animals with intact vagi, or animals having undergone bilateral cervical vagotomy. Electrical stimulation of the cut, peripheral, cervical sympathetic trunk increased mean arterial blood pressure, but had no effect on LES pressure or LES relaxation as induced by vagal stimulation. Stimulation of the central end of the cervical sympathetic trunk had no effect on LES pressure. Stimulation of the central end of the cut splanchnic nerve produced a decrease in LES pressure with a maximal response of 69.1±16.0% (mean±SEM). This inhibitory response was not modified by either propranolol or bilateral cervical vagotomy. Stimulation of the peripheral end of the cut, greater splanchnic nerve gave an increase in LES pressure with a maximal response of 38.2±7.19 mm Hg. Guanethidine, in the presence or absence of the adrenal glands, significantly augmented this excitatory response. This response was also slightly increased by phentolamine alone at 10 V, 1 Hz, but was not altered by propranolol. The excitatory response was completely antagonized by atropine or by trimethaphan camsylate. Stimulation of the peripheral end of the splanchnic nerve inhibited LES relaxation as induced by […] Find the latest version: https://jci.me/109337/pdf Sympathetic Control of Lower Esophageal Sphincter Function in the Cat ACTION OF DIRECT CERVICAL AND SPLANCHNIC NERVE STIMULATION JACQUES FOURNET, WILLIAM J.