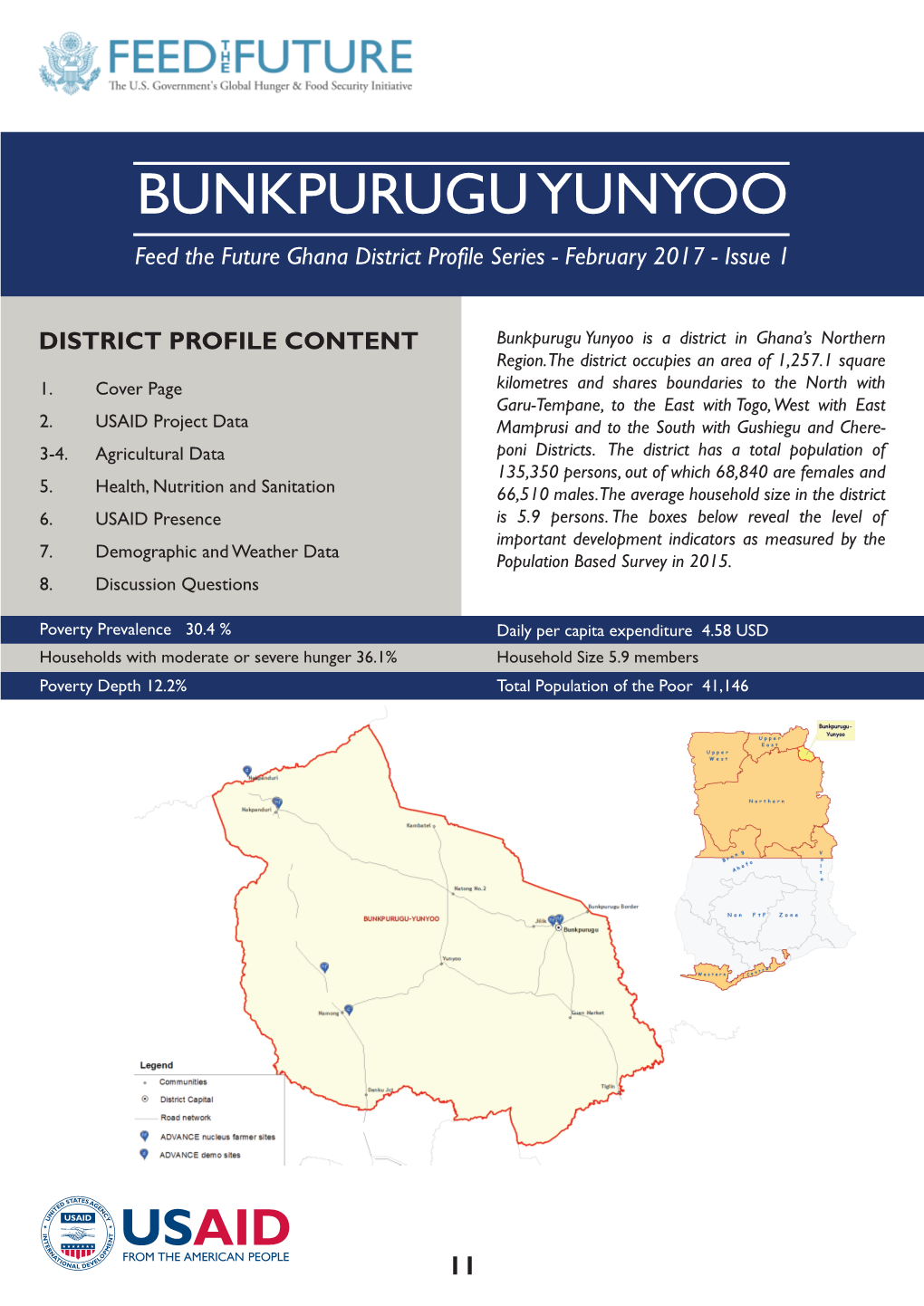
BUNKPURUGU YUNYOO Feed the Future Ghana District Profile Series - February 2017 - Issue 1
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Ownership and Access to Land in Urban Mamprugu, Northern Ghana
Journal of Poverty, Investment and Development - An Open Access International Journal Vol.3 2014 Ownership and Access to Land in Urban Mamprugu, Northern Ghana Sagre Bambangi1 and Abdulai Abubakari2 Abstract This paper explores land ownership and access to land in the urban areas of Mamprugu in the Northern Region of Ghana. An overview of the system of land ownership and access in the rural areas for both residential and agricultural purposes has been used as a background for the understanding of the changes provoked by urbanization. The information used was qualitative through key informant interviews, observation and group discussions. The study revealed that land ownership and access in the traditional rural context was often in tranquility and rarely encountered conflicts. Occasional conflicts arising from the traditional rural arrangements were often easier to resolve. Also, the financial costs have been considered to be within the means of the average family or household in the locality. However, it was observed that access to land by women in the traditional framework subtly deprived women because of the patrilineal system of inheritance and the role assigned to women by the society. In the urban context, land ownership and access is in transition with a combination of traditional and modern institutions in land administration for residential and public infrastructure purposes. The study observed increasing incidence of land disputes in Mamprugu as urbanization progresses. It is recommended that the three district assemblies in Mamprugu in collaboration with the traditional authorities initiate a joint programme to address causes of the emerging problems in the few urban settlements. -

The Dagbon Chieftaincy Crisis
GOVERNANCE AND SECURITY IN GHANA: THE DAGBON CHIEFTAINCY CRISIS SIPRI/OSI African Security and Governance Project WEST AFRICA CIVIL SOCIETY INSTITUTE SIPRI/OSI African Security and Governance Project The Dagbon Chieftaincy Crisis iii WEST AFRICA CIVIL SOCIETY INSTITUTE WEST AFRICA CIVIL SOCIETY INSTITUTE About WACSI The West Africa Civil Society Institute (WACSI) was created by the Open Society Initiative for West Africa (OSIWA) to reinforce the capacities of civil society in the region. The Institute was established to bridge the institutional and operational gaps within civil society. Vision: To strengthen civil society organisations as strategic partners for the promotion of democracy, good governance and national development in the sub region. Mission: The objective of the Institute is to strengthen the institutional and technical capacities of CSOs in the formulation of policies, the implementation and promotion of democratic values and principles in West Africa. The role of WACSI is to serve as a resource centre for training, research, experience sharing and dialogue for CSOs in West Africa. The Institute makes its plea through policy dialogue to discuss current issues affecting West African States. Reference documents are regularly published by the Institute and distributed to policy makers. www.wacsi.org About SIPRI SIPRI is an independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament. Established in 1966, SIPRI provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public. SIPRI was established on the basis of a decision by the Swedish Parliament and receives a substantial part of its funding in the form of an annual grant from the Swedish Government. -

Ghana Gazette
GHANA GAZETTE Published by Authority CONTENTS PAGE Facility with Long Term Licence … … … … … … … … … … … … 1236 Facility with Provisional Licence … … … … … … … … … … … … 201 Page | 1 HEALTH FACILITIES WITH LONG TERM LICENCE AS AT 12/01/2021 (ACCORDING TO THE HEALTH INSTITUTIONS AND FACILITIES ACT 829, 2011) TYPE OF PRACTITIONER DATE OF DATE NO NAME OF FACILITY TYPE OF FACILITY LICENCE REGION TOWN DISTRICT IN-CHARGE ISSUE EXPIRY DR. THOMAS PRIMUS 1 A1 HOSPITAL PRIMARY HOSPITAL LONG TERM ASHANTI KUMASI KUMASI METROPOLITAN KPADENOU 19 June 2019 18 June 2022 PROF. JOSEPH WOAHEN 2 ACADEMY CLINIC LIMITED CLINIC LONG TERM ASHANTI ASOKORE MAMPONG KUMASI METROPOLITAN ACHEAMPONG 05 October 2018 04 October 2021 MADAM PAULINA 3 ADAB SAB MATERNITY HOME MATERNITY HOME LONG TERM ASHANTI BOHYEN KUMASI METRO NTOW SAKYIBEA 04 April 2018 03 April 2021 DR. BEN BLAY OFOSU- 4 ADIEBEBA HOSPITAL LIMITED PRIMARY HOSPITAL LONG-TERM ASHANTI ADIEBEBA KUMASI METROPOLITAN BARKO 07 August 2019 06 August 2022 5 ADOM MMROSO MATERNITY HOME HEALTH CENTRE LONG TERM ASHANTI BROFOYEDU-KENYASI KWABRE MR. FELIX ATANGA 23 August 2018 22 August 2021 DR. EMMANUEL 6 AFARI COMMUNITY HOSPITAL LIMITED PRIMARY HOSPITAL LONG TERM ASHANTI AFARI ATWIMA NWABIAGYA MENSAH OSEI 04 January 2019 03 January 2022 AFRICAN DIASPORA CLINIC & MATERNITY MADAM PATRICIA 7 HOME HEALTH CENTRE LONG TERM ASHANTI ABIREM NEWTOWN KWABRE DISTRICT IJEOMA OGU 08 March 2019 07 March 2022 DR. JAMES K. BARNIE- 8 AGA HEALTH FOUNDATION PRIMARY HOSPITAL LONG TERM ASHANTI OBUASI OBUASI MUNICIPAL ASENSO 30 July 2018 29 July 2021 DR. JOSEPH YAW 9 AGAPE MEDICAL CENTRE PRIMARY HOSPITAL LONG TERM ASHANTI EJISU EJISU JUABEN MUNICIPAL MANU 15 March 2019 14 March 2022 10 AHMADIYYA MUSLIM MISSION -ASOKORE PRIMARY HOSPITAL LONG TERM ASHANTI ASOKORE KUMASI METROPOLITAN 30 July 2018 29 July 2021 AHMADIYYA MUSLIM MISSION HOSPITAL- DR. -

A Spatio-Thematic Analysis of Violent Conflicts in Northern Ghana Between 2007 and 2013
conflict & communication online, Vol. 15, No. 2, 2016 www.cco.regener-online.de ISSN 1618-0747 Patrick Osei-Kufuor, Stephen B Kendie & Kwaku Adutwum Boakye Conflict, peace and development: A spatio-thematic analysis of violent conflicts in Northern Ghana between 2007 and 2013 Kurzfassung: Der vorliegende Aufsatz enthält Informationen und Landkarten zur räumlichen und zeitlichen Dynamik gewaltförmiger Konflikte im Norden Ghanas und fokussiert deren Struktur, Ursachen und Entwicklungstand. Die primären Daten der Studie wurden in ausgewählten Konfliktherden erhoben und dienen zur Validierung der sekundären Informationen, die den Berichten zweier nationaler Tageszeitungen entnommen wurden. Infolge seiner großen ethnischen Heterogenität und des Kampfes um Anerkennung und Dominanz zwischen den ethnischen Gruppen liegen die Konfliktzonen hauptsächlich in der östlichen Region Nord-Ghanas. Konfliktursachen sind Ethnizität, Häuptlingschaft, Religion, Politik, Urbanisierung, Verteilungskämpfe und der Kampf um Anerkennung. Viele der Konflikte sind nach wie vor ungelöst. Da sie den Akzent mehr auf die Auslöser der Gewalt denn auf die tiefer liegenden Streitfragen gelegt haben, blieb Vermittlungsversuchen im Allgemeinen nur ein kurzfristiger Stabilisierungserfolg beschieden. Für einen dauerhaften Frieden im Norden Ghanas müssen Regierung und Zivilgesellschaft den strukturellen Konfliktursachen größere Aufmerksamkeit schenken. Die Nationalversammlung der Häuptlinge muss Regeln und Praktiken und Bräuche der Weitergabe von Autorität kodifizieren. Um Grenzen festzuschreiben und Konflikte um Land und Boden zu reduzieren, muss der Staat die Vergabe von Landtiteln vorantreiben. Abstract: This study provides in text and in maps the spatial and temporal dynamics of violent conflicts in Northern Ghana focusing on their structure, causes and status. Primary data was collected from identified conflict hotspots to validate secondary information collected from two national dailies. -

Ghana Poverty Mapping Report
ii Copyright © 2015 Ghana Statistical Service iii PREFACE AND ACKNOWLEDGEMENT The Ghana Statistical Service wishes to acknowledge the contribution of the Government of Ghana, the UK Department for International Development (UK-DFID) and the World Bank through the provision of both technical and financial support towards the successful implementation of the Poverty Mapping Project using the Small Area Estimation Method. The Service also acknowledges the invaluable contributions of Dhiraj Sharma, Vasco Molini and Nobuo Yoshida (all consultants from the World Bank), Baah Wadieh, Anthony Amuzu, Sylvester Gyamfi, Abena Osei-Akoto, Jacqueline Anum, Samilia Mintah, Yaw Misefa, Appiah Kusi-Boateng, Anthony Krakah, Rosalind Quartey, Francis Bright Mensah, Omar Seidu, Ernest Enyan, Augusta Okantey and Hanna Frempong Konadu, all of the Statistical Service who worked tirelessly with the consultants to produce this report under the overall guidance and supervision of Dr. Philomena Nyarko, the Government Statistician. Dr. Philomena Nyarko Government Statistician iv TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE AND ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ............................................................................. iv LIST OF TABLES ....................................................................................................................... vi LIST OF FIGURES .................................................................................................................... vii EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ........................................................................................................ -

Relevance of Indigenous Conflict Management Mechanisms: Evidence from Bunkpurugu-Yunyoo and Central Gonja Districts of Northern Region, Ghana
Relevance of Indigenous Conflict Management Mechanisms: Evidence from Bunkpurugu-Yunyoo and Central Gonja Districts of Northern Region, Ghana Mohammed Gadafi Ibrahim (Corresponding author) School for Development Studies, College of Humanities and Legal Studies, University of Cape Coast, Cape Coast, Ghana Email: [email protected] Joseph Kingley Adjei Department of Sociology and Anthropology, College of Humanities and Legal Studies, University of Cape Coast, Cape Coast, Ghana Joseph Agyanim Boateng School for Development Studies, College of Humanities and Legal Studies, University of Cape Coast, Cape Coast, Ghana DOI//http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/gjds.v16i1.2 ABSTRACT The Northern Region is witnessing protracted and relapsed conflicts, and attempts at resolving these largely through Western models, particularly the formal court system have not been successful. As such, this study explores the relevance of indigenous conflict management mechanisms in restoring enduring peace in theN orthern Region of Ghana. The study employed a multiple case study design. Data was collected from forty- three purposively selected respondents using interviews, focus group discussions, and observations. The results from thematic and cross-site analysis revealed that indigenous mechanisms have features of inclusive participatory approach at all levels of the conflict leading to acceptable outcomes. The traditional mechanisms have proven to be immediate and meaningful, accessible, and affordable. The use of local languages is well understood by all parties and processes and procedure are well attuned to local needs as they produce quick justice for the people. The development of a comprehensive programme to incorporate aspects of both the indigenous and western-centred judicial structures for the purposes of legitimacy of management outcomes is proposed. -

Volta Region
REGIONAL ANALYTICAL REPORT VOLTA REGION Ghana Statistical Service June, 2013 Copyright © 2013 Ghana Statistical Service Prepared by: Martin K. Yeboah Augusta Okantey Emmanuel Nii Okang Tawiah Edited by: N.N.N. Nsowah-Nuamah Chief Editor: Nii Bentsi-Enchill ii PREFACE AND ACKNOWLEDGEMENT There cannot be any meaningful developmental activity without taking into account the characteristics of the population for whom the activity is targeted. The size of the population and its spatial distribution, growth and change over time, and socio-economic characteristics are all important in development planning. The Kilimanjaro Programme of Action on Population adopted by African countries in 1984 stressed the need for population to be considered as a key factor in the formulation of development strategies and plans. A population census is the most important source of data on the population in a country. It provides information on the size, composition, growth and distribution of the population at the national and sub-national levels. Data from the 2010 Population and Housing Census (PHC) will serve as reference for equitable distribution of resources, government services and the allocation of government funds among various regions and districts for education, health and other social services. The Ghana Statistical Service (GSS) is delighted to provide data users with an analytical report on the 2010 PHC at the regional level to facilitate planning and decision-making. This follows the publication of the National Analytical Report in May, 2013 which contained information on the 2010 PHC at the national level with regional comparisons. Conclusions and recommendations from these reports are expected to serve as a basis for improving the quality of life of Ghanaians through evidence-based policy formulation, planning, monitoring and evaluation of developmental goals and intervention programs. -

Bole District
BOLE DISTRICT Copyright © 2014 Ghana Statistical Service ii PREFACE AND ACKNOWLEDGEMENT No meaningful developmental activity can be undertaken without taking into account the characteristics of the population for whom the activity is targeted. The size of the population and its spatial distribution, growth and change over time, in addition to its socio-economic characteristics are all important in development planning. A population census is the most important source of data on the size, composition, growth and distribution of a country’s population at the national and sub-national levels. Data from the 2010 Population and Housing Census (PHC) will serve as reference for equitable distribution of national resources and government services, including the allocation of government funds among various regions, districts and other sub-national populations to education, health and other social services. The Ghana Statistical Service (GSS) is delighted to provide data users, especially the Metropolitan, Municipal and District Assemblies, with district-level analytical reports based on the 2010 PHC data to facilitate their planning and decision-making. The District Analytical Report for the Bole District is one of the 216 district census reports aimed at making data available to planners and decision makers at the district level. In addition to presenting the district profile, the report discusses the social and economic dimensions of demographic variables and their implications for policy formulation, planning and interventions. The conclusions and recommendations drawn from the district report are expected to serve as a basis for improving the quality of life of Ghanaians through evidence- based decision-making, monitoring and evaluation of developmental goals and intervention programmes. -

TOWARD INCLUSIVE AGRICULTURE- LED ECONOMIC TRANSFORMATION of the NORTHERN SAVANNAH ZONE of GHANA Lifting the Savannah, Lifting Ghana
TOWARD INCLUSIVE AGRICULTURE- LED ECONOMIC TRANSFORMATION OF THE NORTHERN SAVANNAH ZONE OF GHANA Lifting the Savannah, Lifting Ghana December 2016 Savannah Accelerated sada Development Authority ©2016-12 Savannah Accelerated Development Authority (SADA) Prepared by the Savannah Accelerated Development Authority (SADA) 2016-12 Savannah Accelerated Development Authority (SADA) Lamaseghu, Industrial Area, Tamale, Northern Region, Ghana House # 16, 5th Link, Cantonments, Opposite American Embassy, Accra, Ghana +233 372 028 997 [email protected] i FOREWORD The SADA Zone holds major agricultural promise that – when harnessed – will not only make the country highly secure and less dependent on imports, but more importantly transform the lives of the zone's inhabitants quite significantly -- the zone currently records lower performances in all major indices of socio-economic performance compared to the naonal average,” Charles Abugre, CEO, SADA. From Commercial Agriculture Investment Guide: The Northern Savannah Ecological Zone of Ghana, published by SADA. “The vision of SADA is to see a transformed Northern Savannah Ecological Zone; a place of opportunity and free from poverty. SADA aims to achieve this vision through coordinaon, collaboraon and facilitaon. SADA's key values are: Sustainability, Professionalism, Integrity and Accountability, Respect for Diversity and Gender, Impact, and Trust.” Charles Abugre, CEO, SADA. From Commercial Agriculture Investment Guide: The Northern Savannah Ecological Zone of Ghana, published by SADA. “The agricultural potenal of the SADA Zone, mainly its large-scale irrigaon possibilies, is largely untapped. The SADA Zone with at least 8 million unused or underulized ha of agricultural land with highly suitable soils, is open for a massive ulizaon of the regions land and water resources for large- scale irrigated farming, development of modern agro-industry value chains, including vegetable oils, rice, sugar, coon, cassava, shea, high value tree crops and vegetables among others. -

Newsletter Tel: +233-(0)30-2760781 | Fax: +233-(0)30-2760954
Japan International Cooperation Agency JICA Ghana Office, 2nd Floor, The Elizabeth, AnIgYe No. 68A, Senchi Link, Airport Residential Area, Accra P.O. Box 6402. Accra-North. GHANA newsletteR Tel: +233-(0)30-2760781 | Fax: +233-(0)30-2760954 Website: http//:www.jica.go.jp/ghana/english Issue no. 7 JAnuARY 2012»»» Published by Jiro Inamura FEATURE Education Upfront + »» FEATURE Pupils have deep Education understanding through JICA contributes to Quality a practical lesson Education in Ghana 02. Project Story Strengthening the Capacity of INSET Management 03. Exclusive Interview JICA Assists Ghanaian Teachers’ In-Service Training to go Nationwide 06. Project Story School Construction: Improving Access to Basic Education in Deprived Areas 06. Project Story Technical and Vocational Education and Training Support project Volunteers News 07. Volunteer’s Family Visits Ghana ANNOUNCEMENT 08. JICA Shop Rural Women’s Skills and JICA Contributes to Quality Education in Ghana Development Foundation (RWSDF) With barely four years left to work towards achieving the Millennium Development Growth and Development Agenda Goals (MDGs 2015). Ghana is largely on track to achieving the MDG 2 target for (GSGDA); of which the Education universal primary education (with over 80% of school-age children enrolled and Strategic Plan (ESP) 2010–2020 remaining in school). However, disparities between the national figures and those for influenced. the northern regions exist. Ghana is also on track to achieving the MDG 3 target for On-going projects include In-Service gender parity in primary education. Training (INSET) project (2009–2013), Education is the key and foundation of activities is the concept of Capacity School Construction Project, Advisor for economic growth and social development. -

Download File
March 2018 Study Report CHILD PROTECTION SECTION UNICEF Ghana Country Office March 2018 CHILD PROTECTION SECTION UNICEF Ghana Country Office Rapid Assessment on Child Protection related Attitude, Beliefs and Practices in Ghana @2018 March 2018 All rights reserved. This publication may be reproduced, as a whole or in part, provided that acknowledgement of the sources in made. Notification of such would be appreciated. Published by: UNICEF Ghana For further information, contact: UNICEF Ghana P.O. Box AN 5051, Accra-North, Ghana. Telephone: +233302772524; www.unicef.org/ghana These document was put together by Research and Development Division of the Ghana Health Service on behalf of UNICEF Ghana with financial support from the Government of Canada provided through Global Affairs Canada. The contents of the this document are the sole responsibility of research team. The contents don’t necessarily reflect the views and positions of UNICEF Ghana and Global Affairs Canada. Contents Acknowledgements 12 Executive Summary 13 Key Findings 14 Demographic characteristics of respondents 14 Belief and attitudes about child protection issues 14 Practices related to child protection 16 Conclusion 16 Recommendations 17 1. Introduction 20 1.1 Objectives 20 2. Methodology 22 2.1 Study sites 22 2.2 Sampling Frame for section of Enumeration Areas (EAs) 22 2.3 Allocation of EAs 22 2.4 Selection of communities, houses and households 23 2.5 Selection of individual respondents 23 2. 6 Data Collection Procedure 24 2. 7 Data Management and Analysis 24 2.8 Ethical -

UNICEF IWASH Project, Northern Region, Ghana: an Adapted Training Manual for Groundwater Development Groundwater Science Programme Open Report OR/11/047
UNICEF IWASH Project, Northern Region, Ghana: An Adapted Training Manual for Groundwater Development Groundwater Science Programme Open Report OR/11/047 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY GROUNDWATER SCIENCE PROGRAMME OPEN REPORT OR/11/047 UNICEF IWASH Project, Northern Region, Ghana: An Adapted Training Manual for Groundwater Development Ó Dochartaigh BÉ, Davies J, Beamish D and MacDonald AM Keywords Northern Region, Ghana, groundwater development, Voltaian Basin. Front cover Logging borehole chip samples using a colour chart Bibliographical reference Ó DOCHARTAIGH BÉ, DAVIES J, BEAMISH D AND MACDONALD AM. 2011. UNICEF IWASH Project, Northern Region, Ghana: An Adapted Training Manual for Groundwater Development. British Geological Survey Open Report, OR/11/047. 51pp. Copyright in materials derived from the British Geological Survey’s work is owned by the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and/or the authority that commissioned the work. You may not copy or adapt this publication without first obtaining permission. Contact the BGS Intellectual Property Rights Section, British Geological Survey, Keyworth, e-mail [email protected]. You may quote extracts of a reasonable length without prior permission, provided a full acknowledgement is given of the source of the extract. © NERC 2011. All rights reserved Keyworth, Nottingham British Geological Survey 2011 BRITISH GEOLOGICAL SURVEY The full range of our publications is available from BGS shops at British Geological Survey offices Nottingham, Edinburgh, London and Cardiff (Welsh publications only) see contact details below or shop online at www.geologyshop.com BGS Central Enquiries Desk Tel 0115 936 3143 Fax 0115 936 3276 The London Information Office also maintains a reference collection of BGS publications, including maps, for consultation.