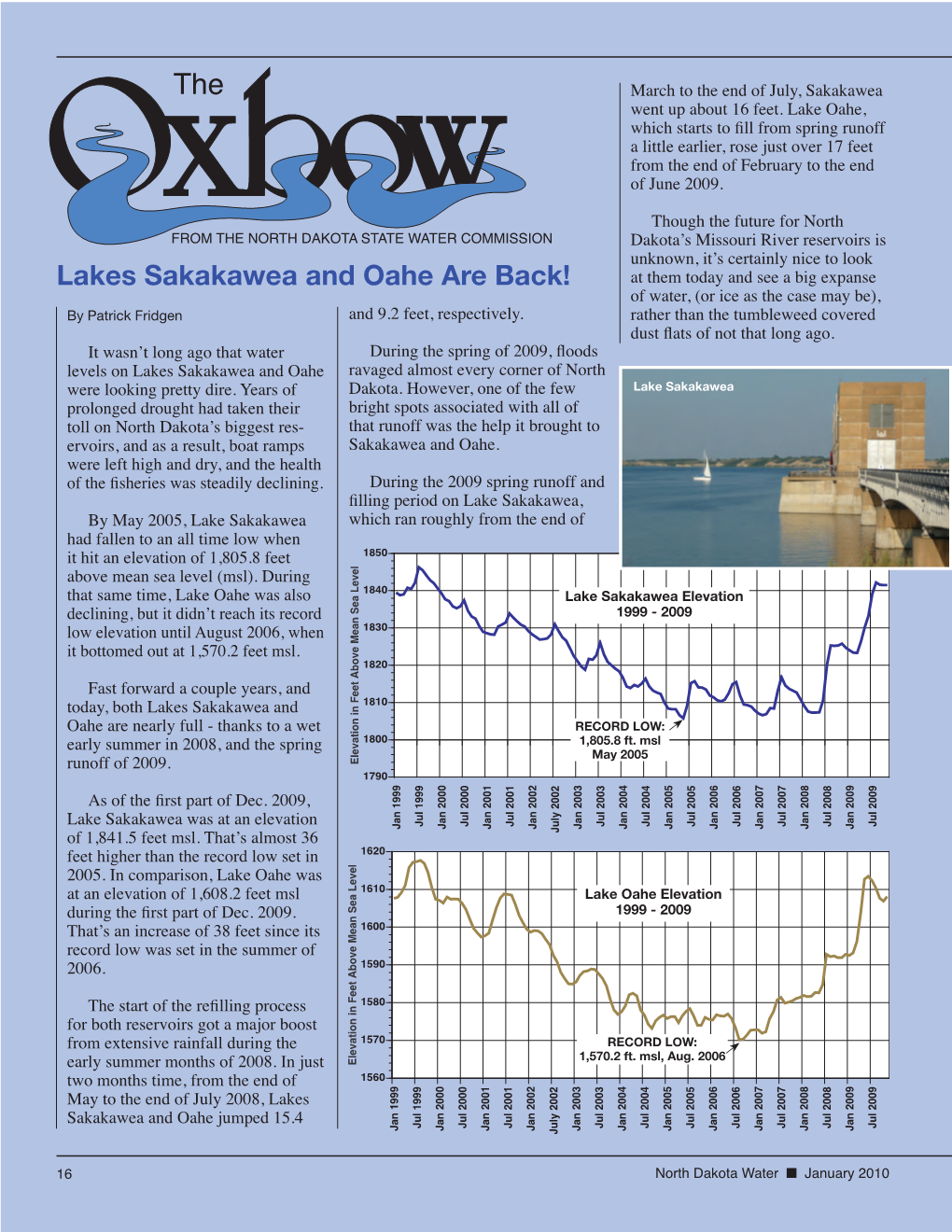
Lakes Sakakawea and Oahe Are Back! SWC A
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Today's Missouri River
DID YOU KNOW? The Missouri River is the longest river in North America. The Missouri is the world’s 15th- TODAY’S longest river. The Missouri has the nickname MISSOURI RIVER “Big Muddy,” because of the large The Missouri River has been an important resource for amount of silt that it carries. people living along or near it for thousands of years. As time went on and the corridor of the Missouri River was developed and populations increased, efforts have been There are approximately 150 fish made to control flows, create storage, and prevent flooding. species in the Missouri River, and As a result, six mainstem dams have been in place for more about 300 species of birds live in the than half a century, with the goal of bringing substantial Missouri River’s region. economic, environmental, and social benefits to the people of North Dakota and nine other states. The Missouri’s aquatic and riparian Since the building of the mainstem dams, it has been habitats also support several species realized that for all of the benefits that were provided, the of mammals, such as mink, river dams have also brought controversy. They have created otter, beaver, muskrat, and raccoon. competition between water users, loss of riparian habitat, impacts to endangered species, stream bank erosion, and delta formation - which are only a few of the complex issues The major dams built on the river related to today’s Missouri River management. were Fort Peck, Garrison, Oahe, Big Bend, Fort Randall, and Gavin’s Point. This educational booklet will outline the many benefits that the Missouri River provides, and also summarize some of the biggest issues that are facing river managers and residents within the basin today. -

Walleye Fishery Ecology in Lake Oahe of the Dakotas Eli Felts South Dakota State University
South Dakota State University Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2018 Walleye Fishery Ecology in Lake Oahe of the Dakotas Eli Felts South Dakota State University Follow this and additional works at: https://openprairie.sdstate.edu/etd Part of the Aquaculture and Fisheries Commons, and the Natural Resources Management and Policy Commons Recommended Citation Felts, Eli, "Walleye Fishery Ecology in Lake Oahe of the Dakotas" (2018). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. 2465. https://openprairie.sdstate.edu/etd/2465 This Dissertation - Open Access is brought to you for free and open access by Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange. It has been accepted for inclusion in Electronic Theses and Dissertations by an authorized administrator of Open PRAIRIE: Open Public Research Access Institutional Repository and Information Exchange. For more information, please contact [email protected]. WALLEYE FISHERY ECOLOGY IN LAKE OAHE OF THE DAKOTAS BY ELI FELTS A dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Doctor of Philosophy Major in Wildlife and Fisheries Sciences South Dakota State University 2018 iii ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This project was funded by the Federal Aid in Sport Fish Restoration Act Study number 1529 administered by South Dakota Department of Game, Fish, and Parks. Additional financial support was provided by the North Dakota Game and Fish Department. Staff of the South Dakota Department of Game, Fish and Parks and North Dakota Game and Fish Department completed the majority of the field work associated with this project. I want to especially thank Paul Bailey, Jason Barstad, Dave Fryda, Mike Greiner, Bob Hanten, Dan Jost, Jason Jungwirth, Russ Kinzer, Hilary Meyer, Kyle Potter, and Mike Smith for their efforts. -

Resolution No. 16-183-FF RESOLUTION of THE
Resolution No. 16-183-FF RESOLUTION OF THE GOVERNING BODY OF THE THREE AFFILIATED TRIBES OF THE FORT BERTHOLD INDIAN RESERVATION A Resolution Entitled, "Rescission ofResolution No. 16-127-CSB" WHEREAS, This Mandan Hidatsa and Arikara Nation (the "MHA Nation"), having accepted the Indian Reorganization Act of June 18, 1934 and the authority under said Act, and having adopted a Constitution and By-laws under said Act, and WHEREAS, The Constitution of the Nation generally authorizes and empowers the Tribal Business Council to engage in activities on behalf of and in the interest of the welfare and benefit of the Tribes and of the enrolled members thereof; and WHEREAS, Pursuant to Article III, Section 1 of its Constitution and By-Laws, the Tribal Business Council is the governing body of the MHA Nation; and WHEREAS, Pursuant to Article VI, Section 5(1) of said Constitution, the Tribal Business Council has the power to adopt resolutions regulating the procedures of the Tribal Council, its Agencies and Officials; and WHEREAS, The Tribal Business Council has authority to engage in activities on behalf of and for the welfare and benefit of the Tribes and of the enrolled members thereof; and WHEREAS, The Tribal Business Council approved Resolution No. 15-065-KH, entitled "Grant ofRight of Way" on April 16, 2015 and Resolution No. 16-127-CSB, entitled "Correction to Resolution No. 15-065-KH" on June 9, 20 16; and WHEREAS, Resolution No. 16-127 -CSB granted, for the first time, consent for right-of-way to Sacagawea Pipeline Company on Tract No. -

Fort Peck Draft
US Army Corps of Engineers Omaha District Draft Fort Peck Dam/Fort Peck Lake Project Montana Surplus Water Report Volume 1 Surplus Water Report Appendix A – Environmental Assessment August 2012 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK FORT PECK DAM/FORT PECK LAKE PROJECT, MONTANA SURPLUS WATER REPORT Omaha District U.S. Army Corps of Engineers August 2012 THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK Fort Peck Dam / Fort Peck Lake, Montana FORT PECK DAM/FORT PECK LAKE MONTANA SURPLUS WATER REPORT August 2012 Prepared By: The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Omaha District Omaha, NE Abstract: The Omaha District is proposing to temporarily make available 6,932 acre-feet/year of surplus water (equivalent to 17,816 acre-feet of storage) from the system-wide irrigation storage available at the Fort Peck Dam/Fort Peck Lake Project, Montana to meet municipal and industrial (M&I) water supply needs. Under Section 6 of the Flood Control Act of 1944 (Public Law 78-534), the Secretary of the Army is authorized to make agreements with states, municipalities, private concerns, or individuals for surplus water that may be available at any reservoir under the control of the Department. Terms of the agreements are normally for five (5) years, with an option for a five (5) year extension, subject to recalculation of reimbursement after the initial five (5) year period. This proposed action will allow the Omaha District to enter into surplus water agreements with interested water purveyors and to issue easements for up to the total amount of surplus water to meet regional water needs. -

D Nelson-Stastny Pred. Pallids
Appendix D Selected Introduced and Native Fish Species of the Missouri River in South Dakota and their Potential as Predators of Pallid Sturgeon Prepared for In Re: Missouri River System Litigation (03-MD- 01555)(and associated litigation) Prepared by Wayne Nelson-Stastny 20641 SD HWY 1806 SDGF&P Missouri River Fisheries Center Fort Pierre, South Dakota March 2004 Introduction This report discusses several native and introduced species to the Missouri River that have increased in abundance or have become important components of the fish community in the mainstem of the Missouri River in South Dakota. Because of the changes in the fish community, whether through increased abundance of a native species or stocking of a nonnative species, concern has been expressed regarding the potential impacts to native species, in particular predation on pallid sturgeon. Therefore, this report examines the reasons behind the changes to the fish community, the changes to the fish community itself, and individual species ecological characteristics. Lastly, the potential for predation of selected species is reviewed. General Change in Missouri River Four mainstem dams, Oahe, Big Bend, Fort Randall and Gavins Point, have dramatically changed the Missouri River that either passes through or borders South Dakota. The Missouri River was often referred to as the “Big Muddy” because of the turbid waters and sediment load. This characteristic was due in part to the two spring floods characteristic of the Missouri River that annually reorganized the river complex of chutes, side channels, back waters and sinuous main channel. A floodplain consisting of highly erodable soils and a relatively low gradient also added to the diversity of habitats and turbidity of the Missouri River (National Research Council 2002). -

In the United States District Court for the District of North Dakota
Case 1:16-cv-00304-DLH-CSM Document 26 Filed 09/13/16 Page 1 of 30 IN THE UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT FOR THE DISTRICT OF NORTH DAKOTA Paradigm Energy Partners, LLC, ) ) Plaintiff, ) ) ORDER GRANTING PLAINTIFF’S vs. ) MOTION FOR PRELIMINARY ) INJUNCTION Mark Fox, in his official capacity as ) Chairman of the Tribal Business Council ) of the Mandan, Hidatsa & Arikara Nation, ) Case No.: 1:16-cv-304 Chief Nelson Heart, in his official capacity ) as Chief of Police for the Mandan, Hidatsa ) & Arikara Nation, ) ) Defendants. ) I. BACKGROUND On August 19, 2016, the Plaintiff’s filed an “Emergency Motion for Temporary Restraining Order.” See Docket No. 4. The Plaintiff sought a temporary restraining order pursuant to Rule 65(b) of the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure, specifically requesting an order prohibiting the Defendants from interfering with the Plaintiff’s construction of two pipelines in McKenzie and Mountrail Counties, North Dakota. On August 22, 2016, the Defendants filed a motion to dismiss for lack of jurisdiction. See Docket No. 8. The Plaintiff filed a response in opposition to the Defendant’s motion on August 23, 2016. See Docket No. 9. On August 23, 2016, the Court issued an order granting the temporary restraining order. On August 30, 2016, the Defendants filed a motion to dissolve the temporary restraining order. See Docket No. 19. On August 31, 2016, the Plaintiff filed a response to the Defendant’s motion. See Docket No. 21. Thereafter, on September 1, 2016, a hearing was held in Bismarck, North Dakota, on the Plaintiff’s request for a preliminary 1 Case 1:16-cv-00304-DLH-CSM Document 26 Filed 09/13/16 Page 2 of 30 injunction. -
When You're on Your Own, We Are There with You
The Wright County 151stMonitor year Number 30 Thursday, July 23, 2020 $1.00 per copy Official newspaper of Wright County www.clarionnewsonline.com Supervisors Grassley finally hits Wright establish speed limit near County on 99 County Tour Agribusiness Park By Bridget Shileny Wright County Monitor Editor By Bridget Shileny As of Monday morning, the U.S. Senator Chuck Wright County Monitor Editor state tracker puts the county’s Grassley (IA-R) greeted people At the Monday morning case count at 415. McGrath last Thursday with elbow or meeting of the Wright County noted though that she received fist bumps. Grassley, who was Board of Supervisors, Jeremy a press release that morning that originally scheduled to be Abbas, Assistant to the test results have been backed up in the county in mid-March, County Engineer, presented at the state level, so she expects finally made his way to Wright two resolutions for the board the case count to rise, though not County last week as part of to consider. The first was to massively. She added that she his whirlwind tour of the state establish a speed limit on Clay was on a meeting last week with during a two-week recess from Avenue in the Agribusiness hospitals and other healthcare the Senate. Wright County was Park. The board approved a 25 entities about handling the his 27th county visited in two mph speed limit on the road flu season with COVID still weeks with two more planned between 320th Street and 330th a major concern. McGrath later last week. Street. -

Hydropower Vision Chapter 2
Chapter 2: State of Hydropower in the United States Hydropower A New Chapter for America’s Renewable Electricity Source STATE OF HYDROPOWER 2 in the United States Photo from 65681751. Illustration by Joshua Bauer/NREL 70 2 Overview OVERVIEW Hydropower is the primary source of renewable energy generation in the United States, delivering 48% of total renewable electricity sector generation in 2015, and roughly 62% of total cumulative renewable generation over the past decade (2006-2015) [1]. The approximately 101 gigawatts1 (GW) of hydropower capacity installed as of 2014 included ~79.6 GW from hydropower gener ation2 facilities and ~21.6 GW from pumped storage hydro- power3 facilities [2]. Reliable generation and grid support services from hydropower help meet the nation’s require- ments for the electrical bulk power system, and hydro- power pro vides a long-term, renewable source of energy that is essentially free of hazardous waste and is low in carbon emissions. Hydropower also supports national energy security, as its fuel supply is largely domestic. % 48 HYDROPOWER PUMPED CAPACITY STORAGE OF TOTAL CAPACITY RENEWABLE GENERATION Hydropower is the largest renewable energy resource in the United States and has been an esta blished, reliable contributor to the nation’s supply of elec tricity for more than 100 years. In the early 20th century, the environmental conse- quences of hydropower were not well characterized, in part because national priorities were focused on economic development and national defense. By the latter half of the 20th century, however, there was greater awareness of the environmental impacts of dams, reservoirs, and hydropower operations. -

The Western Water Law and the Missouri River
The FROM THE NORTH DAKOTA STATE WATER COMMISSION Western Water Law and the Missouri River “…All other wealth falls into insignificance compared with that that which is to come from these lands from the pouring on them of the running streams of this country. Don’t let these streams get out of the possession of the people. If you fail in making a constitution in any other respect, fail not in this one. Take lessons from California and Colorado. Fix it in your constitution that no corporation – no body of men – no capital can get possessions and right to your waters. Hold the waters in the hands of the people.” Major John Wesley Powell (1889) 16 North Dakota Water n May 2013 By Steve Best “first in time – first in right” through the Missouri River. Thus, describes how this principal works. North Dakota’s Missouri River During the summer of 1889, the The first person, municipality, or water users do not rely on water first North Dakota Constitutional other entity, which applies for a stored behind the dams. Convention members were laying water use permit along a waterway the groundwork for what would for beneficial use, has priority over In spite of the fore-thought that officially become the State of North less senior water users in times the State Constitutional Convention Dakota that same year. On August when water is not as plentiful. had in 1889, the State of North 5, 1889, Major John Wesley Powell, Because North Dakota is a western Dakota is currently in conflict with Director of the US Geological water law state, it is important to the US Army Corps of Engineers Survey, delivered a speech before have the ability to appropriate water (Corps) over their proposed Surplus the Constitutional Convention from the Missouri River without Water Policy. -

Weighing Effects of Length Limits
1 1 E WWeighingeighing tthehe 0 1 EEffectsffects HT TABL G ooff LLengthength 9 WEI / LLimitsimits TH G Biologists pay special attention 8 to walleye on Devils Lake, Lake Sakakawea, the Garrison Reach of the Missouri River downstream of Garrison Dam, and Lake Oahe, WALLEYE LEN WALLEYE 7 annually assessing whether any of the common length limits would have a positive eff ect. 6 By Scott Gangl 5 Every summer, armed with nets and other sam- pling gear, fi sheries biologists navigate some of the state’s popular fi shing waters to assess the status and health of fi sh populations. 4 Once the data is summarized, analyzed and care- fully considered, the information provides the basis for State Game and Fish Department manage- ment decisions. Such as, how many fi sh to stock CRAIG BIHRLE or whether special regulations would enhance fi sh populations for anglers. 3 Select anglers routinely request special length Some North Dakota anglers regularly call for regulations, like “minimum,” “maximum,” “one- special length regulations, with the expectation that over,” or “slot” limits, with the expectation that protecting big fi sh or allowing small fi sh to grow protecting big fi sh or allowing small fi sh to grow will make the fi shing better. will make the fi shing better. While Department fi sheries managers seriously consider these regula- 2 tion requests, the data often doesn’t support the perception, so implementing a regulation would not achieve the desired results. 8 ND Outdoors May 2013 1 May 2013.indd 8 5/10/2013 1:01:16 PM Biologists pay special attention to walleye on Dev- food, teamed with a robust northern pike population, ils Lake, Lake Sakakawea, the Garrison Reach of the has also increased natural mortality. -

Ignorance of the Constitution Is Not Bliss: the Takings Clause Protects
IGNORANCE OF THE CONSTITUTION IS NOT BLISS: THE TAKINGS CLAUSE PROTECTS AGAINST THE STATE OF NORTH DAKOTA CLAIMING PRIVATE MINERALS UNDERNEATH LAKE SAKAKAWEA BY VIRTUE OF THE UNITED STATES ACQUIRING THE LAND FOR THE GARRISON DAM PROJECT JOSHUA A. SWANSON* ABSTRACT The government cannot flood private property by virtue of a man-made dam, or acquire such property for flood control purposes, and then claim that it owns the property. This principle is not nuanced, complex, or complicated. It is basic Constitutional law. It is a bedrock protection afforded landowners through the Takings Clause of the United States and North Dakota Constitu- tions. In cases of artificial, government-induced flooding, or the acquisition of private property for flood control purposes, state law lacks the power to transfer title to the government without compensation and a showing that the property is being taken for a public use. The Takings Clause is an unbreak- able shield protecting property owners from the government claiming their minerals through fiat, study, or legislation. The Takings Clause shields prop- erty owners like the Wilkinson family who lost their surface lands to the United States when it acquired the property for the Garrison Dam and Lake Sakakawea in the late 1950s but reserved the mineral interests. The State of North Dakota has no right, title, or claim to any of the minerals, like the Wil- kinsons’ mineral interests, underneath Lake Sakakawea. Given North Da- kota’s economic dependence on its land for agricultural and energy-related purposes, it is imperative that our courts protect landowners from ultra vires attempts by the State to eviscerate private property rights and claim that which is not theirs. -

Lewis and Clark Adventure Tour
Create Your Own Corps of Discovery Follow in the Footsteps of Lewis and Clark Legends are often described as “an extremely famous or notorious person, especially in a particular field.” Lewis and Clark and the Corps of Discovery are true legends. Sent off to claim uncharted territories and collect specimens and make friends with whomever they meet, the explorers hit the jackpot in North Dakota! The real adventure for Meriwether Lewis and William Clark began here, in what is now North Dakota. The explorers spent more consecutive days in North Dakota than any other state on the expedition, wintering near present-day Washburn at Fort Mandan. Two centuries later, you can see the same landscape at 28 locations recognized by the State Historical Society as significant to the Lewis and Clark Expedition. To experience this adventure for yourself, contact North Dakota Tourism at 1-800-435-5663 or visit www.ndtourism.com. Ask for a copy of Tourism’s Lewis & Clark Trail Guide, which highlights attractions and activities found along the trail in North Dakota. SITES TO SEE On-A-Slant Indian Village/Fort Abraham Lincoln State Park On-A-Slant Indian Village was occupied by Mandan Indians between 1650 and 1750. About 1,000 people lived in the village, but by the time of Lewis and Clark, most had been wiped out by smallpox. Today, reconstructed earthlodges overlook the Heart and Missouri rivers, giving a sense of scale and lifestyle. Each lodge is 30 to 40 feet in diameter and stands 10 to 12 feet high. A small museum offers a wonderful interpretive exhibit.