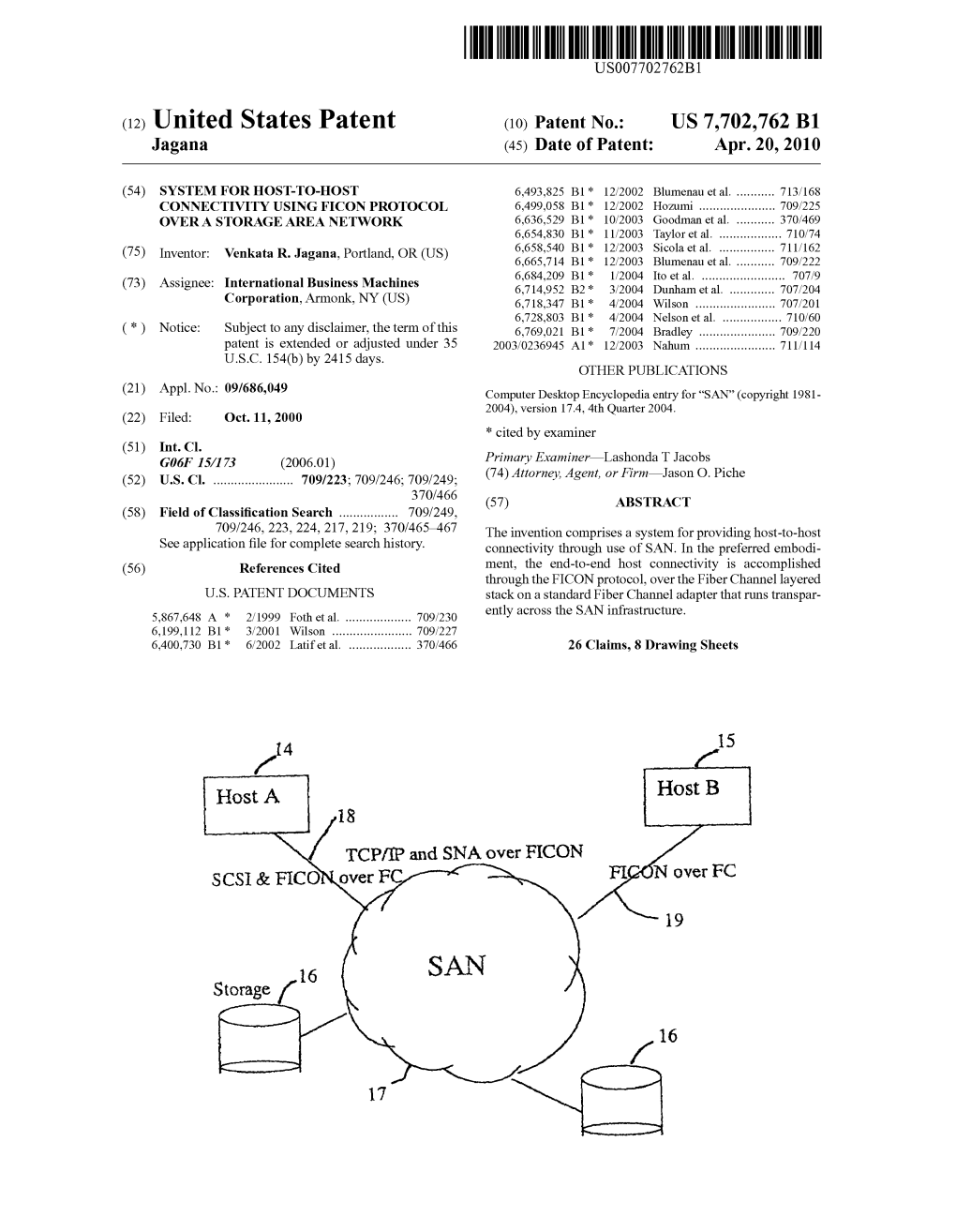
TCP/IP and SNA Over FICON SCSI & Ficonover FC FICON Over FC 19
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

FICON Native Implementation and Reference Guide
Front cover FICON Native Implementation and Reference Guide Architecture, terminology, and topology concepts Planning, implemention, and migration guidance Realistic examples and scenarios Bill White JongHak Kim Manfred Lindenau Ken Trowell ibm.com/redbooks International Technical Support Organization FICON Native Implementation and Reference Guide October 2002 SG24-6266-01 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page vii. Second Edition (October 2002) This edition applies to FICON channel adaptors installed and running in FICON native (FC) mode in the IBM zSeries procressors (at hardware driver level 3G) and the IBM 9672 Generation 5 and Generation 6 processors (at hardware driver level 26). © Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2001, 2002. All rights reserved. Note to U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights -- Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Notices . vii Trademarks . viii Preface . ix The team that wrote this redbook. ix Become a published author . .x Comments welcome. .x Chapter 1. Overview . 1 1.1 How to use this redbook . 2 1.2 Introduction to FICON . 2 1.3 zSeries and S/390 9672 G5/G6 I/O connectivity. 3 1.4 zSeries and S/390 FICON channel benefits . 5 Chapter 2. FICON topology and terminology . 9 2.1 Basic Fibre Channel terminology . 10 2.2 FICON channel topology. 12 2.2.1 Point-to-point configuration . 14 2.2.2 Switched point-to-point configuration . 15 2.2.3 Cascaded FICON Directors configuration. 16 2.3 Access control. 18 2.4 Fibre Channel and FICON terminology. -

Cisco MDS 9250I Multiservice Fabric Switch for IBM an Optimized Solution for Departmental and Branch-Office Sans As Well As Large-Scale Sans
IBM Systems Data Sheet Cisco MDS 9250i Multiservice Fabric Switch for IBM An optimized solution for departmental and branch-office SANs as well as large-scale SANs Cisco MDS 9250i Multiservice Fabric Switch for IBM® System Highlights Storage® is an optimized platform for deploying high-performance SAN extension solutions, distributed intelligent fabric services and ●● ●●Provide 16 Gbps connectivity in a cost-effective multiprotocol connectivity for both open systems and high-densit y Fibre Channel switch mainframe environments. With a compact form factor and advanced ●● ●●Enable storage area network (SAN) con- capabilities normally available only on director-class switches, solidation with integrated multiprotocol MDS 9250i is an ideal solution for departmental and remote branch- support office SANs as well as large-scale SANs in conjunction with the ●● ●●Deliver high-p erformance Fibre Channel Cisco MDS 9710 Multilayer Director. over IP (FCIP) and fast disaster recovery ●● ●●Support hardware-bas ed virtual fabric MDS 9250i offers up to 40 16 Gbps Fibre Channel ports, two isolation with virtual SANs (VSANs) and 10 Gigabit Ethernet IP storage services ports and eight 10 Gigabit Fibre Channel routing with Inter-V SAN routing (IVR) Ethernet Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) ports in a fixed, two- rack-unit (2RU) form factor. MDS 9250i connects to existing native Fibre ●● ●●Enable cost- effective, high- performing Channel networks, protecting current investments in storage networks. Fibre Channel and FCIP connectivity for open systems and mainframe environments Main features and benefits ●● ●●Cisco Data Mobility Manager (DMM) as a MDS 9250i provides unique multiservice and multiprotocol functions in distributed fabric service a compact 2RU form factor. -

IBM System Z9 Enterprise Class
The server built to help optimize your resources throughout the enterprise IBM System z9 Enterprise Class A “classic” might just be the best Today’s market finds that business needs are changing, and having a com petitive advantage isn’t always about having more or being bigger, but more about being smarter and responding faster to change and to your clients. Often, being reactive to change has led to infrastructures with mixed technolo gies, spread across an enterprise, that are complex and difficult to control and costly to manage. Integration of appli cations and data is limited and difficult. Using internal information to make insightful decisions for the company Highlights can be difficult because knowing you are using the “best” data—that which is ■ Strengthening the role of the ■ Continued improvement in most current and complete—may not mainframe as the data hub of IBM FICON® performance and be possible. the enterprise throughput In many situations, investments have ■ New versatile capacity settings ■ On demand innovative tech been made in disparate technologies designed to optimize capacity nologies to help meet ever- that may fall short of meeting their and cost changing business demands goals. Merging information from one branch to another may not be possible ■ IBM System z9™ Integrated and so company direction is set with Information Processor (IBM zIIP) is designed to improve resource optimization and lower the cost of eligible work only a portion of the data at hand, and help achieve advanced I/O function and But data management can be a big in a global economy that can really hurt. -

Troubleshooting FICON
Send documentation comments to [email protected] CHAPTER 16 Troubleshooting FICON Fibre Connection (FICON) interface capabilities enhance the Cisco MDS 9000 Family by supporting both open systems and mainframe storage network environments. Inclusion of Control Unit Port (CUP) support further enhances the MDS offering by allowing in-band management of the switch from FICON processors. This chapter includes the following sections: • FICON Overview, page 16-1 • FICON Configuration Requirements, page 16-6 • Initial Troubleshooting Checklist, page 16-7 • FICON Issues, page 16-9 FICON Overview The Cisco MDS 9000 Family supports the Fibre Channel, FICON, iSCSI, and FCIP capabilities within a single, high-availability platform. Fibre Channel and FICON are different FC4 protocols and their traffic are independent of each other. If required, devices using these protocols can be isolated using VSANs. The Cisco SAN-OS FICON feature supports high-availability, scalability, and SAN extension technologies including VSANs, IVR, FCIP, and PortChannels. Tip When you create a mixed environment, place all FICON devices in one VSAN (other than the default VSAN) and segregate the FCP switch ports in a separate VSAN (other than the default VSAN). This isolation ensures proper communication for all connected devices. You can implement FICON on the following switches: • Any switch in the Cisco MDS 9500 Series. • Any switch in the Cisco MDS 9200 Series (including the Cisco MDS 9222i Multiservice Modular Switch). • Cisco MDS 9134 Multilayer Fabric Switch. • MDS 9000 Family 18/4-Port Multiservice Module. Cisco MDS 9000 Family Troubleshooting Guide, Release 3.x OL-9285-05 16-1 Chapter 16 Troubleshooting FICON FICON Overview Send documentation comments to [email protected] Note The FICON feature is not supported on Cisco MDS 9120, 9124 or 9140 switches, the 32-port Fibre Channel switching module, Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem or Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeCenter. -

IBM Z Connectivity Handbook
Front cover IBM Z Connectivity Handbook Octavian Lascu John Troy Anna Shugol Frank Packheiser Kazuhiro Nakajima Paul Schouten Hervey Kamga Jannie Houlbjerg Bo XU Redbooks IBM Redbooks IBM Z Connectivity Handbook August 2020 SG24-5444-20 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page vii. Twentyfirst Edition (August 2020) This edition applies to connectivity options available on the IBM z15 (M/T 8561), IBM z15 (M/T 8562), IBM z14 (M/T 3906), IBM z14 Model ZR1 (M/T 3907), IBM z13, and IBM z13s. © Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2020. All rights reserved. Note to U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights -- Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Notices . vii Trademarks . viii Preface . ix Authors. ix Now you can become a published author, too! . xi Comments welcome. xi Stay connected to IBM Redbooks . xi Chapter 1. Introduction. 1 1.1 I/O channel overview. 2 1.1.1 I/O hardware infrastructure . 2 1.1.2 I/O connectivity features . 3 1.2 FICON Express . 4 1.3 zHyperLink Express . 5 1.4 Open Systems Adapter-Express. 6 1.5 HiperSockets. 7 1.6 Parallel Sysplex and coupling links . 8 1.7 Shared Memory Communications. 9 1.8 I/O feature support . 10 1.9 Special-purpose feature support . 12 1.9.1 Crypto Express features . 12 1.9.2 Flash Express feature . 12 1.9.3 zEDC Express feature . 13 Chapter 2. Channel subsystem overview . 15 2.1 CSS description . 16 2.1.1 CSS elements . -

IBM System Z9 109 Technical Introduction
Front cover IBM System z9 109 Technical Introduction Hardware description Software support Key functions Bill Ogden Jose Fadel Bill White ibm.com/redbooks International Technical Support Organization IBM System z9 109 Technical Introduction July 2005 SG24-6669-00 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page vii. First Edition (July 2005) This edition applies to the initial announcement of the IBM System z9 109. © Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2005. All rights reserved. Note to U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights -- Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Notices . vii Trademarks . viii Preface . ix The authors . ix Become a published author . ix Comments welcome. .x Chapter 1. Introduction. 1 1.1 Evolution . 2 1.2 z9-109 server highlights . 3 1.3 zSeries comparisons. 4 1.4 z9-109 server models and processor units . 6 1.5 Upgrades. 6 1.6 Considerations . 7 Chapter 2. Hardware overview . 9 2.1 System frames . 10 2.2 Books . 10 2.3 MCM . 12 2.4 Processor units . 13 2.4.1 PU characterizations. 14 2.5 Memory . 14 2.6 I/O interfaces. 15 2.7 I/O cages and features . 16 2.7.1 Physical I/O connections. 18 2.7.2 Coupling connections . 20 2.7.3 Cryptographic functions . 20 2.8 Time functions. 21 2.8.1 Sysplex Timer . 21 2.8.2 Server Time Protocol (STP) . 22 2.9 Hardware Storage Area . 22 2.10 System control . 22 2.11 HMC and SE . -

Brocade Fabric OS FICON Administrator's Guide
53-1003517-04 09 February 2016 Brocade Fabric OS FICON Administrator's Guide Supporting Fabric OS v7.4.0, Fabric OS 7.4.1 © 2016, Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Brocade, Brocade Assurance, the B-wing symbol, ClearLink, DCX, Fabric OS, HyperEdge, ICX, MLX, MyBrocade, OpenScript, VCS, VDX, Vplane, and Vyatta are registered trademarks, and Fabric Vision is a trademark of Brocade Communications Systems, Inc., in the United States and/or in other countries. Other brands, products, or service names mentioned may be trademarks of others. Notice: This document is for informational purposes only and does not set forth any warranty, expressed or implied, concerning any equipment, equipment feature, or service offered or to be offered by Brocade. Brocade reserves the right to make changes to this document at any time, without notice, and assumes no responsibility for its use. This informational document describes features that may not be currently available. Contact a Brocade sales office for information on feature and product availability. Export of technical data contained in this document may require an export license from the United States government. The authors and Brocade Communications Systems, Inc. assume no liability or responsibility to any person or entity with respect to the accuracy of this document or any loss, cost, liability, or damages arising from the information contained herein or the computer programs that accompany it. The product described by this document may contain open source software covered by the GNU General Public License or other open source license agreements. To find out which open source software is included in Brocade products, view the licensing terms applicable to the open source software, and obtain a copy of the programming source code, please visit http://www.brocade.com/support/oscd. -

Z9 BC System Overview Level 04A, April 2009
System z9 Business Class System Overview SA22-1083-04 Level 04a, April 2009 System z9 Business Class System Overview SA22-1083-04 Level 04a, April 2009 Level 04a, April 2009 Note Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Safety” on page | xiii, Appendix D, “Notices,” on page D-1, and IBM Systems Environmental Notices and User Guide, Z125-5823. Fifth Edition (April 2009) | This edition, SA22-1083-04, applies to the IBM® System z9® Business Class (z9® BC) server. This replaces | SA22-1083-03. Technical changes to the text are indicated by a vertical bar (|) to the left of the change. There may be a newer version of this document in a PDF file available on Resource Link™.Goto http://www.ibm.com/servers/resourcelink and click on Library on the navigation bar. A newer version is indicated by a lowercase, alphabetic letter following the form number suffix (for example: 00a, 00b, 01a, 01b). © Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2006, 2009. US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Level 04a, April 2009 Contents Figures............................ix Tables ............................xi Safety ............................xiii Safety Notices .........................xiii World Trade Safety Information ..................xiii Laser Safety Information .....................xiii Laser Compliance.......................xiii About this Publication .....................xv What is Included in this Publication .................xv -

Oracle's Storage Augments Mainframe Renaissance
Oracle’s Storage Augments Mainframe Renaissance Mainframe Storage Solutions Remain Best in Class September 2010 Report by Fred Moore, President of Horison Information Strategies, Delivering Continuing Innovations in Mainframe Storage Th Early Mainframes - 1964 System/360 was announced by IBM in April 1964 and is generally considered the first mainframe computer. More than any other computer development effort, the System/360 family of processors enabled companies to affordably integrate all of their data processing applications into a single management information system. The term “360” was actually chosen to show the versatile nature of the computer, which could cover a “360-degree radius” of business applications. At the time, it defined the mainframe as a system that could perform multiple tasks at the same time on one machine and it was now possible to perform one million instructions per second (1 MIPS). The System/360 was also designed to be compatible through all models so that work performed o any model in the 360 series could be ported to any other model. The System/360 could process online, batch and databases at the same time in a multi-programming mode so that the system was literally tailored to the specific customer's jobs. Until the introduction of the System/360 architecture, which introduced many of today’s storage management concepts, accessing large amounts of data had been very time consuming. System/360 greatly improved data storage and retrieval capabilities while providing management with real-time decision-making capabilities for the first time. 1 Mainframes in Transition – 1980s The mainframe was the predominant computing platform from its introduction in the mid-1960s until the mid 1980s. -

Configuring FICON
Send documentation comments to [email protected] CHAPTER 28 Configuring FICON Fibre Connection (FICON) interface capabilities enhance the Cisco MDS 9000 Family by supporting both open systems and mainframe storage network environments. Inclusion of Control Unit Port (CUP) support further enhances the MDS offering by allowing in-band management of the switch from FICON processors. The fabric binding feature helps prevent unauthorized switches from joining the fabric or disrupting current fabric operations (see Chapter 38, “Configuring Fabric Binding”). The Registered Link Incident Report (RLIR) application provides a method for a switch port to send an LIR to a registered Nx port. This chapter includes the following sections: • About FICON, page 28-1 • FICON Port Numbering, page 28-7 • Configuring FICON, page 28-14 • Configuring FICON Ports, page 28-23 • FICON Configuration Files, page 28-32 • Port Swapping, page 28-36 • FICON Tape Acceleration, page 28-38 • Moving a FICON VSAN to an Offline State, page 28-40 • CUP In-Band Management, page 28-40 • Displaying FICON Information, page 28-42 • Default Settings, page 28-49 About FICON The FICON feature is not supported on: • Cisco MDS 9120 switches • Cisco MDS 9124 switches • Cisco MDS 9140 switches • The 32-port Fibre Channel switching module • Cisco Fabric Switch for HP c-Class BladeSystem • Cisco Fabric Switch for IBM BladeSystem Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide OL-16184-01, Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 3.x 28-1 Chapter 28 Configuring FICON About FICON Send documentation comments to [email protected] The Cisco MDS 9000 Family supports the Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP), FICON, iSCSI, and FCIP capabilities within a single, high availability platform. -

Brocade Fabric OS FICON Configuration Guide, 8.1.0
CONFIGURATION GUIDE Brocade Fabric OS FICON Configuration Guide, 8.1.0 Supporting Fabric OS 8.1.0 53-1004394-02 23 July 2018 Copyright © 2018 Brocade Communications Systems LLC. All Rights Reserved. Brocade and the stylized B logo are among the trademarks of Brocade Communications Systems LLC. Broadcom, the pulse logo, and Connecting everything are among the trademarks of Broadcom. The term "Broadcom" refers to Broadcom Inc. and/or its subsidiaries. Brocade, a Broadcom Inc. Company, reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products or data herein to improve reliability, function, or design. Information furnished by Brocade is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, Brocade does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of this information, nor the application or use of any product or circuit described herein, neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. The product described by this document may contain open source software covered by the GNU General Public License or other open source license agreements. To find out which open source software is included in Brocade products, view the licensing terms applicable to the open source software, and obtain a copy of the programming source code, please visit https://www.broadcom.com/support/fibre-channel-networking/tools/oscd. Brocade Fabric OS FICON Configuration Guide, 8.1.0 2 53-1004394-02 Contents Preface...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................7 -

Introduction to Storage Area Networks
SG24-5470- Introduction to Storage Area Networks Jon Tate Pall Beck Hector Hugo Ibarra Shanmuganathan Kumaravel Libor Miklas Redbooks International Technical Support Organization Introduction to Storage Area Networks December 2017 SG24-5470-08 Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on page ix. Ninth Edition (December 2017) This edition applies to the products in the IBM Storage Area Networks (SAN) portfolio. © Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 2017. All rights reserved. Note to U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights -- Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract with IBM Corp. Contents Notices . ix Trademarks . .x Preface . xi Authors. xii Now you can become a published author, too! . xiv Comments welcome. xiv Stay connected to IBM Redbooks . xiv Summary of changes. .xv December 2017, Ninth Edition . .xv Chapter 1. Introduction. 1 1.1 Networks . 2 1.1.1 The importance of communication . 2 1.2 Interconnection models . 2 1.2.1 The open systems interconnection model. 2 1.2.2 Translating the OSI model to the physical world. 4 1.3 Storage . 5 1.3.1 Storing data. 5 1.3.2 Redundant Array of Independent Disks . 6 1.4 Storage area networks . 11 1.5 Storage area network components . 13 1.5.1 Storage area network connectivity . 14 1.5.2 Storage area network storage. 14 1.5.3 Storage area network servers. 14 1.6 The importance of standards or models . 14 Chapter 2. Storage area networks . 17 2.1 Storage area networks . 18 2.1.1 The problem . 18 2.1.2 Requirements .