(73) Assignee If Its of the Sawengy
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Anti-Inflammatory and Immune Regulatory Actions of Naja Naja
toxins Review Anti-Inflammatory and Immune Regulatory Actions of Naja naja atra Venom Shu-Zhi Wang 1,2 and Zheng-Hong Qin 3,* 1 Institute of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China; [email protected] 2 Hunan Province Cooperative Innovation Center for Molecular Target New Drug Study, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China 3 Department of Pharmacology and Laboratory of Aging and Nervous Diseases, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Translational Research and Therapy for Neuro-Psycho-Diseases, Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Preventive and Translational Medicine for Geriatric Diseases, College of Pharmaceutical Science, Soochow University, Suzhou 215123, China * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel./Fax: +86-512-65882071 Received: 23 December 2017; Accepted: 24 February 2018; Published: 28 February 2018 Abstract: Naja naja atra venom (NNAV) is composed of various proteins, peptides, and enzymes with different biological and pharmacological functions. A number of previous studies have reported that NNAV exerts potent analgesic effects on various animal models of pain. The clinical studies using whole venom or active components have confirmed that NNAV is an effective and safe medicine for treatment of chronic pain. Furthermore, recent studies have demonstrated that NNAV has anti-inflammatory and immune regulatory actions in vitro and in vivo. In this review article, we summarize recent studies of NNAV and its components on inflammation and immunity. The main new findings in NNAV research show that it may enhance innate and humoral immune responses while suppressing T lymphocytes-mediated cellular immunity, thus suggesting that NNAV and its active components may have therapeutic values in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. -

Rope Parasite” the Rope Parasite Parasites: Nearly Every Au�S�C Child I Ever Treated Proved to Carry a Significant Parasite Burden
Au#sm: 2015 Dietrich Klinghardt MD, PhD Infec4ons and Infestaons Chronic Infecons, Infesta#ons and ASD Infec4ons affect us in 3 ways: 1. Immune reac,on against the microbes or their metabolic products Treatment: low dose immunotherapy (LDI, LDA, EPD) 2. Effects of their secreted endo- and exotoxins and metabolic waste Treatment: colon hydrotherapy, sauna, intes4nal binders (Enterosgel, MicroSilica, chlorella, zeolite), detoxificaon with herbs and medical drugs, ac4vaon of detox pathways by solving underlying blocKages (methylaon, etc.) 3. Compe,,on for our micronutrients Treatment: decrease microbial load, consider vitamin/mineral protocol Lyme, Toxins and Epigene#cs • In 2000 I examined 10 au4s4c children with no Known history of Lyme disease (age 3-10), with the IgeneX Western Blot test – aer successful treatment. 5 children were IgM posi4ve, 3 children IgG, 2 children were negave. That is 80% of the children had clinical Lyme disease, none the history of a 4cK bite! • Why is it taking so long for au4sm-literate prac44oners to embrace the fact, that many au4s4c children have contracted Lyme or several co-infec4ons in the womb from an oVen asymptomac mother? Why not become Lyme literate also? • Infec4ons can be treated without the use of an4bio4cs, using liposomal ozonated essen4al oils, herbs, ozone, Rife devices, PEMF, colloidal silver, regular s.c injecons of artesunate, the Klinghardt co-infec4on cocKtail and more. • Symptomac infec4ons and infestaons are almost always the result of a high body burden of glyphosate, mercury and aluminum - against the bacKdrop of epigene4c injuries (epimutaons) suffered in the womb or from our ancestors( trauma, vaccine adjuvants, worK place related lead, aluminum, herbicides etc., electromagne4c radiaon exposures etc.) • Most symptoms are caused by a confused upregulated immune system (molecular mimicry) Toxins from a toxic environment enter our system through damaged boundaries and membranes (gut barrier, blood brain barrier, damaged endothelium, etc.). -

Amphiphilic B-Sheet Cobra Cardiotoxin Targets Mitochondria and Disrupts Its Network
CORE Metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk Provided by Elsevier - Publisher Connector FEBS 29626 FEBS Letters 579 (2005) 3169–3174 Amphiphilic b-sheet cobra cardiotoxin targets mitochondria and disrupts its network Chia-Hui Wang, Wen-guey Wu* Department of Life Sciences, Institute of Bioinformatics and Structural Biology, National Tsinghua University, 101, Section 2, Kuang Fu Road, Hsinchu 30013, Taiwan Received 29 March 2005; revised 2 May 2005; accepted 2 May 2005 Available online 23 May 2005 Edited by Maurice Montal brane is likely to be involved in the CTX-induced perturbation Abstract Recent advance in understanding the role of toxin proteins in controlling cell death has revealed that pro-apoptotic of cytosolic calcium homeostasis and hypercontracture in rat viral proteins targeting mitochondria contain amphiphilic a-heli- ventricular myocytes [5,10]; however, evidence indicating ces with pore-forming properties. Herein, we describe that the that CTX may target intracellular organelle within the cell is pore-forming amphiphilic b-sheet cardiotoxins (or cytotoxins, lacking. CTXs) from Taiwan cobra (Naja atra) also target mitochondrial A large number of protein toxins from bacteria and virus membrane after internalization and act synergistically with have been extensively studied in order to understand their CTX-induced cytosolic calcium increase to disrupt mitochondria mechanism of action as well as of intracellular membrane network. It is suggested that CTX-induced fragmentation of trafficking [11–13]. For instance, cholera toxin and related mitochondria play a role in controlling CTX-induced necrosis AB5-subunit bacterial toxin have been shown to follow a of myocytes and cause severe tissue necrosis in the victims. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0191272 A1 Stemmer Et Al
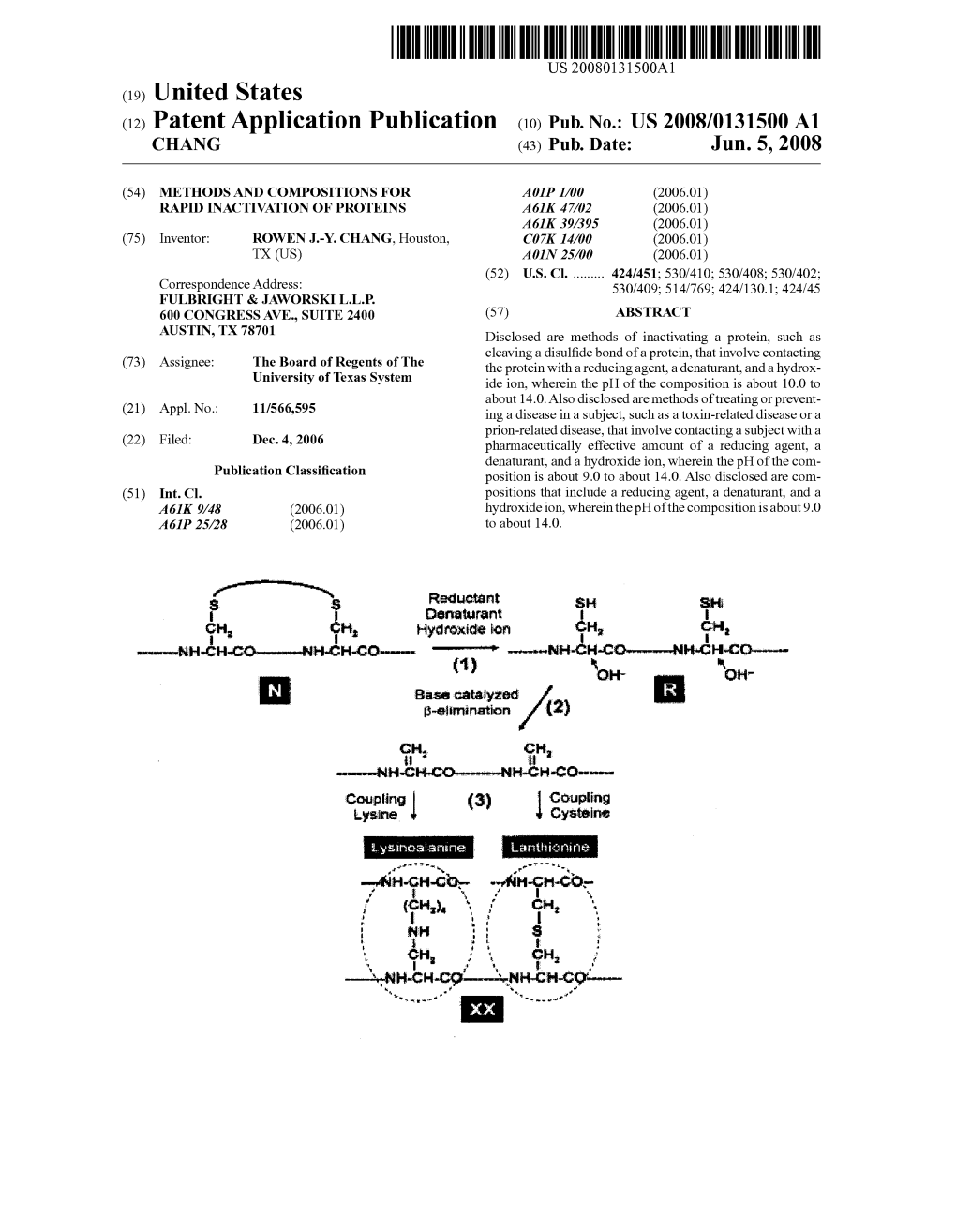
US 200701.91272A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0191272 A1 Stemmer et al. (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 16, 2007 (54) PROTEINACEOUS PHARMACEUTICALS Publication Classification AND USES THEREOF (76) Inventors: Willem P.C. Stemmer, Los Gatos, CA (51) Int. Cl. (US); Volker Schellenberger, Palo A6II 38/16 (2006.01) Alto, CA (US); Martin Bader, C40B 40/08 (2006.01) Mountain View, CA (US); Michael C40B 40/10 (2006.01) Scholle, Mountain View, CA (US) C07K I4/47 (2006.01) (52) U.S. Cl. ................. 514/12: 435/7.1: 435/6; 530/324 Correspondence Address: WILSON SONSN GOODRCH & ROSAT 650 PAGE MILL ROAD (57) ABSTRACT PALO ALTO, CA 94304-1050 (US) (21) Appl. No.: 11/528,927 The present invention provides cysteine-containing scaf folds and/or proteins, expression vectors, host cell and (22) Filed: Sep. 27, 2006 display systems harboring and/or expressing such cysteine containing products. The present invention also provides Related U.S. Application Data methods of designing libraries of Such products, methods of (60) Provisional application No. 60/721,270, filed on Sep. screening Such libraries to yield entities exhibiting binding 27, 2005. Provisional application No. 60/721,188, specificities towards a target molecule. Further provided by filed on Sep. 27, 2005. Provisional application No. the invention are pharmaceutical compositions comprising 60/743,622, filed on Mar. 21, 2006. the cysteine-containing products of the present invention. Patent Application Publication Aug. 16, 2007 Sheet 1 of 46 US 2007/0191272 A1 Takara togra: Patent Application Publication Aug. 16, 2007 Sheet 2 of 46 US 2007/0191272 A1 FIG. -

Antitumoral Activity of Snake Venom Proteins: New Trends in Cancer Therapy
Hindawi Publishing Corporation BioMed Research International Volume 2014, Article ID 203639, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/203639 Review Article Antitumoral Activity of Snake Venom Proteins: New Trends in Cancer Therapy Leonardo A. Calderon,1 Juliana C. Sobrinho,1 Kayena D. Zaqueo,1 Andrea A. de Moura,1 Amy N. Grabner,1 Maurício V. Mazzi,2 Silvana Marcussi,3 Auro Nomizo,4 CarlaF.C.Fernandes,1 Juliana P. Zuliani,1 Bruna M. A. Carvalho,5 Saulo L. da Silva,5 Rodrigo G. Stábeli,1 and Andreimar M. Soares1 1 Centro de Estudos de Biomoleculas´ Aplicadas aSa` ude,´ CEBio, Fundac¸ao˜ Oswaldo Cruz, Fiocruz Rondoniaˆ e Departamento de Medicina, Universidade Federal de Rondonia,ˆ UNIR, Porto Velho, RO, Brazil 2 Fundac¸ao˜ Herm´ınio Ometto, UNIARARAS, Nucleo´ de Cienciasˆ da Saude-NUCISA,´ 13607-339 Araras, SP, Brazil 3 Departamento de Qu´ımica, Universidade Federal de Lavras, UFLA, 37200-000 Lavras, MG, Brazil 4 Departamento de Analises´ Cl´ınicas, Toxicologicas´ e Bromatologicas,´ Faculdade de Cienciasˆ Farmaceuticasˆ de Ribeirao˜ Preto, Universidade de Sao˜ Paulo, USP, Ribeirao˜ Preto, SP, Brazil 5 Departamento de Qu´ımica, Biotecnologia e Engenharia de Bioprocessos, Universidade Federal de Sao˜ Joao˜ del Rei, UFSJ, Campus Alto paraopeba, Ouro Branco, MG, Brazil Correspondence should be addressed to Andreimar M. Soares; [email protected] Received 20 September 2013; Revised 7 December 2013; Accepted 8 December 2013; Published 13 February 2014 Academic Editor: Fernando Albericio Copyright © 2014 Leonardo A. Calderon et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -

Privileged Frameworks from Snake Venom
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2015) 72:1939–1958 DOI 10.1007/s00018-015-1844-z Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences REVIEW Privileged frameworks from snake venom T. A. Reeks • B. G. Fry • P. F. Alewood Received: 17 December 2014 / Revised: 22 January 2015 / Accepted: 26 January 2015 / Published online: 19 February 2015 Ó Springer Basel 2015 Abstract Venom as a form of chemical prey capture is a Introduction key innovation that has underpinned the explosive ra- diation of the advanced snakes (Caenophidia). Small While venom in reptiles had a single, early evolution [1, 2], venom proteins are often rich in disulfide bonds thus it is at the base of the advanced snakes that it truly became facilitating stable molecular scaffolds that present key a key evolutionary innovation that underpinned the ex- functional residues on the protein surface. New toxin types plosive radiation of this lineage [3]. Snake venom is a are initially developed through the venom gland over-ex- complex mixture of enzymes, proteins and peptides. Many pression of normal body proteins, their subsequent gene of these toxin families have stable molecular scaffolds duplication and diversification that leads to neofunction- (Table 1). The toxins within the venom are a result of gene alisation as random mutations modify their structure and duplication of proteins or peptides typically used elsewhere function. This process has led to preferentially selected in the body, with the copy being selectively expressed in (privileged) cysteine-rich scaffolds that enable the snake to the venom gland [4]. These genes are often amplified into build arrays of toxins many of which may lead to multi-gene families with diverse neofunctionalisation fol- therapeutic products and research tools. -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,846.445 B2 Schellenberger Et Al
USOO7846445B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,846.445 B2 Schellenberger et al. (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 7, 2010 (54) METHODS FOR PRODUCTION OF 5,176,502 A 1/1993 Sanderson et al. UNSTRUCTURED RECOMBINANT 5, 186,938 A 2/1993 Sablotsky et al. POLYMERS AND USES THEREOF 5,215,680 A 6/1993 D'arrigo 5,223,409 A 6/1993 Ladner et al. (75) Inventors: Volker Schellenberger, Palo Alto, CA 5,270,176 A * 12/1993 Dorschug et al. .......... 435/69.7 (US); Willem P. Stemmer, Los Gatos, 5,298,022 A 3, 1994 Bernardi CA (US); Chia-wei Wang, Santa Clara, 5,318.540 A 6, 1994 Athayde et al. CA (US); Michael D. Schole, Mountain 5,407,609 A 4/1995 Tice et al. View, CA (US); Mikhail Popkov, San 2. 3. E. 1 Diego, CA (US); Nathaniel C. Gordon, - - I oiszwillo et al. Campbell, CA (US); Andreas Crameri, 5,573,776 A 11, 1996 Harrison et al. Los Altos Hills, CA (US) 5,578,709 A 11/1996 WoiSZwillo s 5,599.907 A * 2/1997 Anderson et al. ........... 530,385 5,660,848 A 8, 1997 Moo-Youn (73) Assignee: suioperating, Inc., Mountain 5,756,115 A 5, 1998 NSW et al. iew, CA (US) 5,874,104 A 2/1999 Adler-moore et al. 5,916,588 A 6, 1999 P tal. (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this 5,942,252 A 8, 1999 p al patent is extended or adjusted under 35 5,965,156 A 10, 1999 Profitt et al. -

Toxines Et Fonctions Cholinergiques Neuronales Et Non Neuronales
Collection Rencontres en toxinologie © P. Marchot & J.-L. Boudier TTooxxiinneess eett ffoonnccttiioonnss cchhoolliinneerrggiiqquueess nneeuurroonnaalleess eett nnoonn nneeuurroonnaalleess Comité d’édition : Evelyne BENOIT, Françoise GOUDEY-PERRIERE, Pascale MARCHOT et Denis SERVENT Société Française pour l'Etude des Toxines Illustrations de couverture : En haut : Vue en microscopie électronique des synapses neuromusculaires du muscle triangulaire de sternum de souris (grossissement de 13 333 fois). Les pelotes noires sont générées par des molécules d’alpha-neurotoxine « à trois doigts », isolée d’un venin de cobra et radioiodée, fixées aux récepteurs nicotiniques de l’acétylcholine associés aux membranes post-synaptiques. (Copyright Pascale Marchot et Jean-Louis Boudier) En bas : Vue cristallographique du complexe de haute affinité formé entre (en jaune) cinq exemplaires d’une alpha- neurotoxine « à trois doigts », isolée d’un venin de cobra, et (en bleu) l’acetylcholine binding protein, protéine homopentamérique de mollusque aquatique et équivalent soluble du domaine extracellulaire de fixation des ligands du récepteur nicotinique de l’acétylcholine. (Copyright Pascale Marchot et Yves Bourne) Près de vingt ans de travaux menés par de nombreuses équipes au plan international relient ces deux images. Collection Rencontres en toxinologie La collection « Rencontres en toxinologie » est publiée à l’occasion des Colloques annuels « Rencontres en toxinologie » organisés par la Société Française pour l’Etude des Toxines (SFET). Les ouvrages parus de 2001 à 2007 ont été édités par Elsevier (Paris, France), puis par la Librairie Lavoisier (Cachan, France). A partir de 2008, ils seront édités par la SFET et diffusés sur le site http://www.sfet.asso.fr, en libre accès pour les auteurs et les lecteurs. -

Information Resources on the South American Camelids: Llamas, Alpacas, Guanacos, and Vicunas 2004-2008
NATIONAL AGRICULTURAL LIBRARY ARCHIVED FILE Archived files are provided for reference purposes only. This file was current when produced, but is no longer maintained and may now be outdated. Content may not appear in full or in its original format. All links external to the document have been deactivated. For additional information, see http://pubs.nal.usda.gov. United States Department of Information Resources on the Agriculture Agricultural Research South American Camelids: Service National Agricultural Llamas, Alpacas, Guanacos, Library Animal Welfare Information Center and Vicunas 2004-2008 AWIC Resource Series No. 12, Revised 2009 AWIC Resource Series No. 12, Revised 2009 United States Information Resources on the Department of Agriculture South American Agricultural Research Service Camelids: Llamas, National Agricultural Alpacas, Guanacos, and Library Animal Welfare Vicunas 2004-2008 Information Center AWIC Resource Series No. 12, Revised 2009 Compiled by: Jean A. Larson, M.S. Animal Welfare Information Center National Agricultural Library U.S. Department of Agriculture Beltsville, Maryland 20705 E-mail: [email protected] Web site: http://awic.nal.usda.gov Available online: http://www.nal.usda.gov/awic/pubs/Camelids/camelids.shtml Disclaimers Te U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, and where applicable, sex, marital status, familial status, parental status, religion, sexual orientation, genetic information, political beliefs, reprisal, or because all or a part of an individual’s income is derived from any public assistance program. (Not all prohibited bases apply to all programs.) Persons with disabilities who require alternative means for communication of program information (Braille, large print, audiotape, etc.) should contact USDA’s TARGET Center at (202) 720-2600 (voice and TDD). -

Neural Computation for Rehabilitation Animal Toxins and Their Advantages in Biotechnology and Pharmacology
BioMed Research International Animal Toxins and Their Advantages in Biotechnology and Pharmacology Guest Editors: S. L. Da Silva, E. G. Rowan, F. Albericio, R. G. Stábeli, NeuralL. A. Calderon, Computation and A. M. Soares for Rehabilitation Animal Toxins and Their Advantages in Biotechnology and Pharmacology BioMed Research International Animal Toxins and Their Advantages in Biotechnology and Pharmacology Guest Editors: S. L. Da Silva, E. G. Rowan, F. Albericio, R. G. Stabeli,´ L. A. Calderon, and A. M. Soares Copyright © 2014 Hindawi Publishing Corporation. All rights reserved. This is a special issue published in “BioMed Research International.” All articles are open access articles distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Contents Animal Toxins and Their Advantages in Biotechnology and Pharmacology,S.L.DaSilva,E.G.Rowan, F. Albericio, R. G. Stabeli,´ L. A. Calderon, and A. M. Soares Volume 2014, Article ID 951561, 2 pages Alkylation of Histidine Residues of Bothrops jararacussu Venom Proteins and Isolated Phospholipases A2: A Biotechnological Tool to Improve the Production of Antibodies,C.L.S.Guimaraes,˜ S. H. Andriao-Escarso,L.S.Moreira-Dill,B.M.A.Carvalho,D.P.Marchi-Salvador,N.A.Santos-Filho,˜ C. A. H. Fernandes, M. R. M. Fontes, J. R. Giglio, B. Barraviera, J. P. Zuliani, C. F. C. Fernandes, L. A. Calderon,´ R. G. Stabeli,´ F. Albericio, S. L. da Silva, and A. M. Soares Volume 2014, Article ID 981923, 12 pages Biochemical and Functional Characterization of Parawixia bistriata Spider Venom with Potential Proteolytic and Larvicidal Activities, Gizeli S. -

Wo 2007/038619 A2
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (43) International Publication Date PCT (10) International Publication Number 5 April 2007 (05.04.2007) WO 2007/038619 A2 (51) International Patent Classification: (74) Agents: WONG, Karen, K. et al.; WILSON SONSINI C40B 40/10 (2006.01) GOODRICH & ROSATI, 650 Page Mill Road, Palo Alto, CA 94304-1050 (US). (21) International Application Number: PCT/US2006/037713 (81) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every kind of national protection available): AE, AG, AL, AM, (22) International Filing Date: AT,AU, AZ, BA, BB, BG, BR, BW, BY, BZ, CA, CH, CN, 27 September 2006 (27.09.2006) CO, CR, CU, CZ, DE, DK, DM, DZ, EC, EE, EG, ES, FI, GB, GD, GE, GH, GM, HN, HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IS, JP, (25) Filing Language: English KE, KG, KM, KN, KP, KR, KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LT, LU, LV,LY,MA, MD, MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, (26) Publication Language: English NA, NG, NI, NO, NZ, OM, PG, PH, PL, PT, RO, RS, RU, SC, SD, SE, SG, SK, SL, SM, SV, SY, TJ, TM, TN, TR, (30) Priority Data: TT, TZ, UA, UG, US, UZ, VC, VN, ZA, ZM, ZW 60/721,270 27 September 2005 (27.09.2005) US 60/721,188 27 September 2005 (27.09.2005) US (84) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every 60/743,622 21 March 2006 (2 1.03.2006) US kind of regional protection available): ARIPO (BW, GH, GM, KE, LS, MW, MZ, NA, SD, SL, SZ, TZ, UG, ZM, (71) Applicant (for all designated States except US): AMU- ZW), Eurasian (AM, AZ, BY, KG, KZ, MD, RU, TJ, TM), NIX, INC. -
Molecular Model of Cytotoxin-1 from Naja Mossambica Mossambica Venom in Complex with Chymotrypsin
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/302458549 Molecular Model of Cytotoxin-1 from Naja mossambica mossambica Venom in Complex with Chymotrypsin Article in Rivista di biologia · December 2015 DOI: 10.1400/240197 CITATIONS READS 2 758 5 authors, including: Aisha Munawar Ashiq Hussain University of Engineering and Technology, Lahore Lahore University of Management Sciences 20 PUBLICATIONS 96 CITATIONS 25 PUBLICATIONS 322 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE Patrick Jack Spencer Instituto de Pesquisas Energéticas e Nucleares 63 PUBLICATIONS 690 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects: Characterization and evaluation of the immune response of the Tetanus toxin submitted to gamma irradiation by Cobalt-60 View project Biotechnology Patents in India - A timeline of 2000 and 2014 View project All content following this page was uploaded by Ashiq Hussain on 12 May 2016. The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file. THEORETICAL BIOLOGY FORUM 108 · 1-2/2015 PISA · ROMA FABRIZIO SERRA EDITORE MMXV Autorizzazione del Tribunale di Pisa n. 13 del 14 maggio 2012. Già registrata presso il Tribunale di Genova: registrazione n. 22/96 del 2 maggio 1996. Direttore responsabile: Fabrizio Serra * Amministrazione e abbonamenti Fabrizio Serra editore® Casella postale n. 1, succursale n. 8, I 56123 Pisa Uffici di Pisa: Via Santa Bibbiana 28, I 56127 Pisa, tel. +39 050542332, fax +39 050574888, [email protected] Uffici di Roma: Via Carlo Emanuele I, I 00185 Roma, tel. +39 0670493456, fax +39 0670476605, [email protected] * I prezzi ufficiali di abbonamento cartaceo e Online sono consultabili presso il sito Internet della casa editrice www.libraweb.net.