(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Before Legendary Coach Bill Parcells
Coach Bill Parcells ACG interviews a renowned coach whose road to Super Bowl victories began at West Point. B Y J OHN I NGOLDSBY efore legendary Coach Bill Parcells goldsby , Parcells discusses how his experience Army for South Carolina, and then Cahill be - won two Super Bowls with the New coaching at the academies helped form the came the head coach, and fortunately I was York Giants, he was an assistant foundation that led to his unprecedented able to get a job with him. coach at Army and head coach at Air NFL success. BForce. His natural coaching talent ACG How did you end up getting the job and military discipline combined to What years did you coach at West with Coach Cahill? ACG make him the most famous turnaround artist Point , and who was head coach PARCELLS: I was already coaching for in NFL history. After leading the Giants “from when you were linebackers coach ? about three years in the Midwest, starting at worst to first ,” Parcells took his coaching tal - PARCELLS : I was at Army from 19 66 a Division 3 school named Hastings College T N I O ents to the New England Patriots, New York through ’ 69, and Tom Cahill, who coinciden - in Nebraska as a part-time job . Then I went P T S E W Jets and Dallas Cowboys, and then to the tally was my high school coach in New Jersey, back to my alma mater, Wichita State at the T A Y M Miami Dolphins ’ front office , bringing each took a job at West Point as the freshman time, and was there for a few years, and then E D A C of these franchises back from the dead . -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,359,192 B2 Issa Et Al
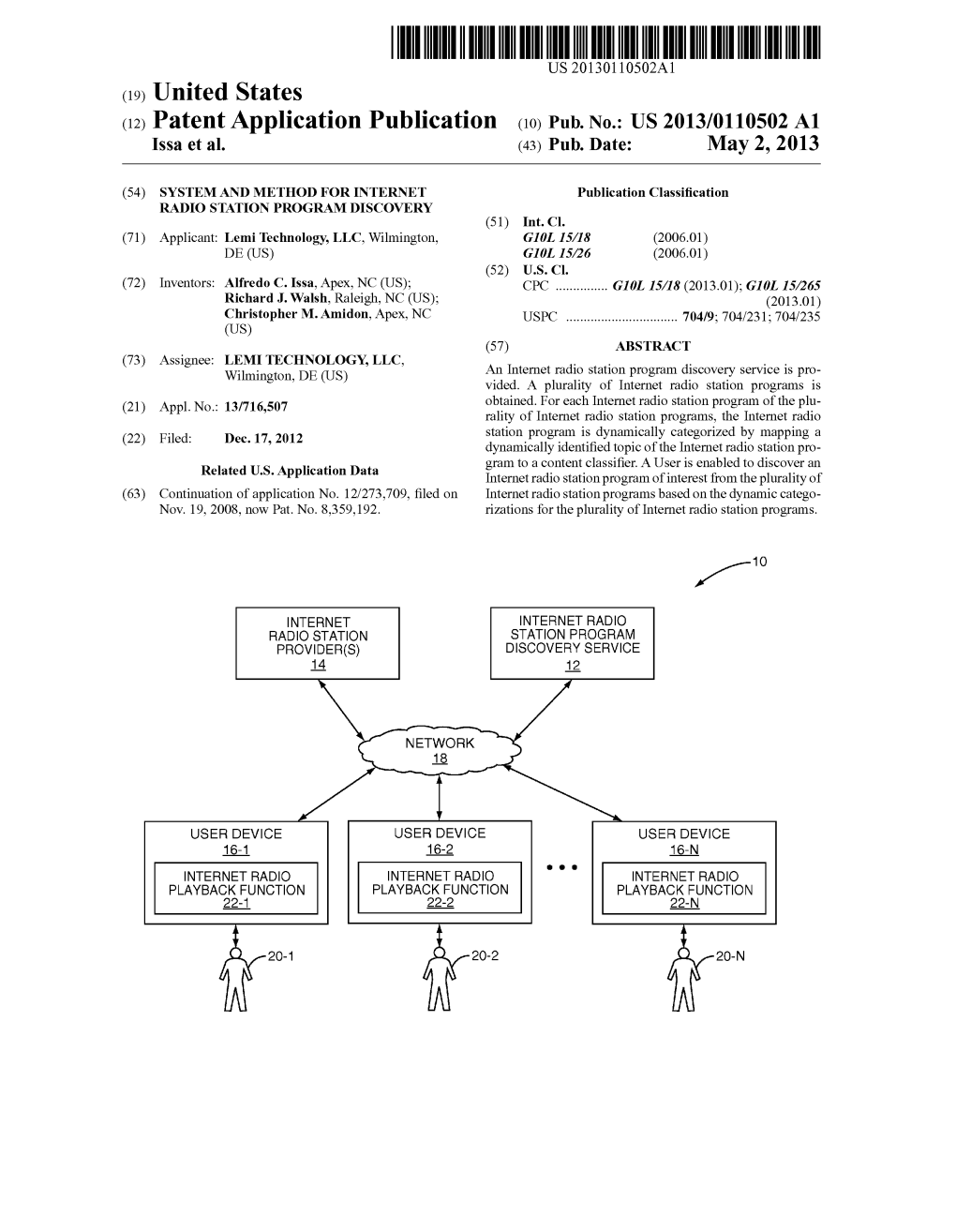
US00835.9192B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,359,192 B2 Issa et al. (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 22, 2013 (54) SYSTEMAND METHOD FOR INTERNET 5,579,537 A 11/1996 Takahisa RADIO STATION PROGRAM DISCOVERY 5,594,601 A 1/1997 Mimicket al. 5,654,719 A 8, 1997 Kunii 5,704,017 A 12/1997 Heckerman et al. (75) Inventors: Alfredo C. Issa, Apex, NC (US); 5,757,939 A 5/1998 Begeja et al. Richard J. Walsh, Raleigh, NC (US); 5,790,754 A 8, 1998 MoZer et al. Christopher M. Amidon, Apex, NC 5,812,937 A 9, 1998 Takahisa et al. 5,842,161 A 11/1998 Cohrs et al. (US) 5,864,753. A 1/1999 Morita et al. 5,872,747 A 2f1999 Johnson (73) Assignee: Lemi Technology, LLC, Portsmouth, 5,898,910 A 4/1999 Miyake et al. NH (US) (Continued) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 FOREIGN PATENT DOCUMENTS U.S.C. 154(b) by 663 days. EP O841180 A2 5, 1998 (Continued) (21) Appl. No.: 12/273,709 OTHER PUBLICATIONS (22) Filed: Nov. 19, 2008 Robert Ambrogi. "Full-text searching of podcasts.” http://www. (65) Prior Publication Data legaline.com/2006/01/full-text-searching-of-podcasts.html, Jan. 11, US 2010/O1248.92 A1 May 20, 2010 2006, copyright 2002-2008 Robert J. Ambrogi, 2 pages. (Continued) (51) Int. Cl. G06F 7/27 (2006.01) Primary Examiner — Qi Han (52) U.S. Cl. ....... 704/9: 704/3: 704/4; 704/10; 704/231; 704/251 (57) ABSTRACT (58) Field of Classification Search ................. -

Are You Astudent of Thegame?
C M Y K H6 SPECIALSPT 09-06-06 EZ EE H6 CMYK H6 Wednesday, September 6, 2006 R The Washington Post NFL 2006 1 2 3 3 5 EASIEST STRENGTH Chicago NFL Green Bay Seattle Minnesota N.Y. Jets QUIZ OF SCHEDULE FOR ’06 Opp. ’05: 114-142 115-141 117-139 117-139 119-137 Win pct.: .445 .449 .457 .457 .465 Are You a Student of the Game? You rifle through sports sections and magazines, you search the net, heaven knows you watch TV. But are you as hip to the the offseason happenings of the NFL as you think you are? Take our quiz and find out. Part 1: Name That Coach Nearly one-third of the league’s teams have new head coaches and the majority of them are hardly household faces. See if you can name them. We’ll give you four clues and, if the fourth isn’t a dead giveaway, you should probably move on to another sport. Hint: As a player, was named to the All-Monday Night team. Hint: As running backs coach at San Diego State, Hint: Knows all about winning Super Bowls — as a player. worked directly with future Hall of Famer Marshall Faulk. Hint: Attended Maryland State College (now the University of Maryland Hint: Inducted into Eastern Illinoi s University Hall of Fame in 2000. Eastern Shore). Hint: In first season as Giants offensive coordinator in 2000, Hint: Histeam’sowner—amanwhoisafashion visionary when it comes New York scored 328 points, the most in a decade. to the use of silver and black — regretted firing this coach in his first Hint: Has a strong affinity for Tuna. -

Active Statistical Leaders Heading Into 2001
“REAL” JOBS Pittsburgh Steelers quarterback TOMMY MADDOX once pitched insurance policies before he got a job throwing footballs. JOSE CORTEZ of the Kansas City Chiefs, the only NFL player in history born in El Salvador, was once a roofer. And everybody knows that 2001 NFL MVP KURT WARNER once stocked groceries. Indeed, a surprising number of NFL players had “real” jobs before they came into the league. “Football is a blue-collar man’s game,” says former Washington Redskins cornerback DARRELL GREEN. And maybe that’s why the league is filled with so many former “blue-collar” workers. Following is a list of “real jobs” previously held by some NFL players: PLAYER, TEAM CAREER(S) David Akers, Philadelphia Substitute teacher; waiter James Allen, Houston Worked at Houston recording studio Mitch Berger, St. Louis Pumped gas in Canada Jose Cortez, Kansas City Roofer Mark Dixon, Miami Golf course lawn maintenance Jay Feely, Atlanta Financial consultant Ray Jackson, Cincinnati Wal-Mart sporting goods employee Michael Lewis, New Orleans Budweiser truck driver Tommy Maddox, Pittsburgh Insurance salesman Fred McCrary, New England Corrections officer David Patten, New England Landscaper, electrician, truck loader Nathan Poole, Arizona Youth counselor Jeff Saturday, Indianapolis Electrical supply company Al Wallace, Carolina Public school assistant principal Kurt Warner, St. Louis Stocked groceries OTHER JOBS Football takes up a lot of their time, but that has not prevented a good number of NFL players from preparing for life after the game by jumping into some other lines of work even as they “moonlight” on the football field. For example, Philadelphia Eages cornerback TROY VINCENT – the 2002 Walter Payton NFL Man of the Year – is a full-fledged offseason entrepreneur. -

The New York Giants Football Helmet (13 Legendary Signers!)
The New York Giants Football Helmet (13 Legendary Signers!) Autographed by: Eli Manning, Phil Simms, Tom Coughlin, Bill Parcells, Lawrence Taylor, Odell Beckham Jr, YA Tittle, Tiki Barber, Justin Tuck, Harry Carson, Victor Cruz, Carl Banks and Michael Strahan that joined the NFL in 1925, and is the only one of that group still existing, as well as the league’s longest-establishedThe New York Giants team are ain NFC the EastNortheastern division team United within States. the The NFL. team The ranks Giants third were among one of all five NFL teams franchises with eight NFL titles: four in the pre–Super Bowl era (1927, 1934, 1938, 1956) and four since the advent of the Super Bowl (Super Bowls XXI (1986), XXV (1990), XLII (2007), and XLVI (2011)), along with more championship appearances than any other team, with 19 overall appearances. Throughout their history, the Giants have featured 28 Hall of Fame players, including NFL Most Valuable Player (MVP) award winners Mel Hein, Frank Gifford, Y. A. Tittle, and Lawrence Taylor. The team’s heated rivalry with the Philadelphia Eagles is the oldest of the NFC East rivalries, dating all the way back to 1933, and has been called the best rivalry in the NFL in the 21st century. authentic for life. This piece comes with an individually-numbered Certificate of Authenticity and is 100% guaranteed The New York Giants Football Helmet (13 Legendary Signers!) ITEM # __________ Opening Bid: $______________ Bid Increment: $______________ BIDDER NAME/PHONE NUMBER BID AMOUNT. -

15 Modern-Era Finalists for Hall of Fame Election Announced
For Immediate Release For More Information, Contact: January 11, 2013 Joe Horrigan at (330) 588-3627 15 MODERN-ERA FINALISTS FOR HALL OF FAME ELECTION ANNOUNCED Four first-year eligible nominees – Larry Allen, Jonathan Ogden, Warren Sapp, and Michael Strahan – are among the 15 modern-era finalists who will be considered for election to the Pro Football Hall of Fame when the Hall’s Selection Committee meets in New Orleans, La. on Saturday, Feb. 2, 2013. Joining the first-year eligible, are eight other modern-era players, a coach and two contributors. The 15 modern-era finalists, along with the two senior nominees announced in August 2012 (former Kansas City Chiefs and Houston Oilers defensive tackle Curley Culp and former Green Bay Packers and Washington Redskins linebacker Dave Robinson) will be the only candidates considered for Hall of Fame election when the 46-member Selection Committee meets. The 15 modern-era finalists were determined by a vote of the Hall’s Selection Committee from a list of 127 nominees that earlier was reduced to a list of 27 semifinalists, during the multi-step, year-long selection process. Culp and Robinson were selected as senior candidates by the Hall of Fame’s Seniors Committee. The Seniors Committee reviews the qualifications of those players whose careers took place more than 25 years ago. To be elected, a finalist must receive a minimum positive vote of 80 percent. The Pro Football Hall of Fame Selection Committee’s 17 finalists (15 modern-era and two senior nominees*) with their positions, teams, and years active follow: • Larry Allen – Guard/Tackle – 1994-2005 Dallas Cowboys; 2006-07 San Francisco 49ers • Jerome Bettis – Running Back – 1993-95 Los Angeles/St. -

GAME NOTES Patriots Vs
GAME NOTES Patriots vs. New York Jets– November 13, 2011 BRADY AND BELICHICK SURPASS MARINO AND SHULA FOR WINNINGEST COACH/QB TANDEM With today’s victory over the Jets, the Patriots’ quarterback-head coach tandem of Tom Brady and Bill Belichick (117) surpassed Pro Football Hall of Famers Dan Marino and Don Shula of Miami for the most wins by a quarterback-head coach duo in the Super Bowl era (since 1966). WINNINGEST COACH/QB TANDEMS SINCE 1970 (Regular Season Only – by victories) Quarterback/Head Coach Team W L T Pct. Tom Brady/Bill Belichick NE 117 35 0 .770 Dan Marino/Don Shula MIA 116 68 0 .630 Terry Bradshaw/Chuck Noll PIT 107 51 0 .601 WINNINGEST COACH/QB TANDEMS SINCE 1970 (Regular Season Only – by winning percentage) Quarterback/Head Coach Team W L T Pct. Tom Brady/Bill Belichick NE 117 35 0 .770 Ken Stabler/John Madden OAK 60 19 1 .756 Jim McMahon/Mike Ditka CHI 46 15 0 .754 Peyton Manning/Tony Dungy IND 73 24 0 .753 BILL BELICHICK TIES BILL PARCELLS WITH 183 CAREER WINS. Bill Belichick won his 183rd with the win against the Jets to tie Bill Pacrcells for ninth place on the NFL’s all-time list. Chuck Knox is eighth with 193 career wins. MOST WINS NFL COACHES Head Coach Team(s) Years of service Record 1. Don Shula BAL, MIA 33 347-173-6 2. George Halas Chicago 40 324-151-31 3. Tom Landry Dallas 29 270-178-6 4. Curly Lambeau GB,Cards, WAS 33 229-134-22 5. -

(330) 456-8207 15 Modern-Era Finalists F
For Immediate Release For More Information, Contact: January 7, 2012 Joe Horrigan at (330) 456-8207 15 MODERN-ERA FINALISTS FOR HALL OF FAME ELECTION ANNOUNCED Two first-year eligible nominees – coach Bill Parcells and tackle Will Shields – are among the 15 modern-era finalists who will be considered for election to the Pro Football Hall of Fame when the Hall’s Selection Committee meets in Indianapolis, Ind. on Saturday, Feb. 4, 2012. Joining the first-year eligible, are 12 modern-era players and a contributor. The 15 modern-era finalists, along with the two senior nominees announced in August 2011 (former Pittsburgh Steelers cornerback Jack Butler and former Detroit Lions and Washington Redskins guard Dick Stanfel) will be the only candidates considered for Hall of Fame election when the 44-member Selection Committee meets. To be elected, a finalist must receive a minimum positive vote of 80 percent. Although technically a first-year eligible candidate, Parcells has been a finalist twice before (2001, 2002) following his announced retirement as head coach of the New York Jets in 1999. At the time the Hall of Fame By-Laws did not require a coach to be retired the now mandatory five seasons. Parcells returned to coach the Dallas Cowboys in 2003 and the five-year waiting period was in effect when he retired from coaching in 2006. The Pro Football Hall of Fame Selection Committee’s 17 finalists (15 modern-era and two senior nominees*) with their positions, teams, and years active follow: Jerome Bettis – Running Back – 1993-95 Los Angeles/St. -

Finding Aid to the Historymakers ® Video Oral History with Harry Carson
Finding Aid to The HistoryMakers ® Video Oral History with Harry Carson Overview of the Collection Repository: The HistoryMakers®1900 S. Michigan Avenue Chicago, Illinois 60616 [email protected] www.thehistorymakers.com Creator: Carson, Harry Title: The HistoryMakers® Video Oral History Interview with Harry Carson, Dates: September 1, 2016 Bulk Dates: 2016 Physical 10 uncompressed MOV digital video files (5:08:50). Description: Abstract: Football player Harry Carson (1953 - ) played for the New York Giants for thirteen years. A nine time Pro Bowler and Super Bowl champion, he was inducted into the Pro Football Hall of Fame in 2006. Carson was interviewed by The HistoryMakers® on September 1, 2016, in New York, New York. This collection is comprised of the original video footage of the interview. Identification: A2016_015 Language: The interview and records are in English. Biographical Note by The HistoryMakers® Football player Harry Carson was born on November 26, 1953 in Florence, South Carolina to Gladys Carson and Edgar Carson, Sr. He began playing football as a defensive end during his sophomore year at Wilson High School in Florence, where he also joined the Air Force Junior ROTC. In 1969, Carson transferred to the integrated McClenaghan High School, where he became a starting defensive end. Carson attended South Carolina State University in Orangeburg, South Carolina, where he was a four-year starter as a defensive lineman under Coach Willie Jeffries. Carson played a role in setting a college football record for the fewest points allowed in 1974. He graduated with his B.S. degree in education in fewest points allowed in 1974. -

DON SHULA All-Time Winner
THE COFFIN CORNER: Vol. 19, No. 2 (1997) DON SHULA All-Time Winner By Joe Horrigan In 1951, a rookie defensive back trying to earn a spot on the Cleveland Browns' training camp roster, caught the watchful eye of Head Coach Paul Brown. "Nice tackle Taseff!" barked the coach after witnessing the young defensive back's hard hit on fullback Marion Motley. The confident rookie-hopeful swiftly rose from the pile turned to his coach and announced, "The name is Shula. Shula," he repeated, "S-H-U-L-A!" Brown, undoubtedly stunned by the bold rookie's response, sarcastically replied, "I'll try to remember." No one that day could have possibly imagined that that confident rookie would eventually become the winningest coach in National Football League history and in the process make "Shula" a name that no one would ever forget. His 347-173-6 record as head coach of the Miami Dolphins (1970-95) and before that the Baltimore Colts (1963-69) stands as the standard by which every past, present, and future NFL coach will be measured. Donald Francis Shula was born January 4, 1930, in Grand River, Ohio and was raised in Painesville, Ohio. Don was the youngest of three children when his mother, Mary, gave birth to triplets. "My dad was making $15 a week in a nursery so he had to find a befter paying job," recalled Shula. "He went on to work in the fisheries by the lake and as soon as I was big enough, I followed him there." Don's father, Dan, was by most accounts a quiet, hard-working man. -

105-107N110 Nyjets.Qxd:New York Jets-03R.Qxd
NEW YORK JETS CLUB OFFICIALS COACHING HISTORY Chairman and CEO: New York Titans 1960-62 Robert Wood Johnson IV (371-434-8) Team President: Neil Glat Records include postseason games Executive V.P./ General Manager: 1960-61 Sammy Baugh.............14-14-0 Mike Tannenbaum 1962 Clyde (Bulldog) Turner .....5-9-0 Assistant G.M.: Scott Cohen 1963-1973 Weeb Ewbank..............73-78-6 S.V.P., Programming and Media 1974-75 Charley Winner* ............9-14-0 Production: Bob Parente 1975 Ken Shipp........................1-4-0 S.V.P., Corporate Sales: Marc Riccio 1976 Lou Holtz**...................3-10-0 S.V.P., Consumer Sales and Services: 1976 Mike Holovak...................0-1-0 Rob Sullivan 1977-1982 Walt Michaels ...............41-49-1 Chief Financial Officer: Brian Friedman 1983-89 Joe Walton ..................54-59-1 Senior Counsel, Business and Legal 1990-93 Bruce Coslet................26-39-0 Affairs: Hymie Elhai 1994 Pete Carroll....................6-10-0 American Football Conference V.P., IT: Tom Murphy 1995-96 Rich Kotite.....................4-28-0 East Division V.P., Security: Steve Yarnell 1997-99 Bill Parcells..................30-20-0 Team Colors: Green and White Senior Personnel Executive: 2000 Al Groh............................9-7-0 1 Jets Drive Terry Bradway 2001-05 Herman Edwards.........41-44-0 Florham Park, New Jersey 07932 Assistant Director, Player Personnel: 2006-08 Eric Mangini ................23-26-0 Telephone (973) 549-4800 JoJo Wooden 2009-2011 Rex Ryan.....................32-22-0 Director, Pro Personnel: Brendan Prophett *Released after nine games in 1975 2012 SCHEDULE Pro Scout: Cole Hufnagel **Resigned after 13 games in 1976 PRESEASON Assistant Director, College Scouting: Aug. -

The Football Coach's Game Plan For
The Football Coach’s Game Plan for Leadership Table of Contents Part I – Interviews and Coaching Legend Profiles 1. Bill Parcells Coaching Philosophy 2. Jimmy Johnson on Creating a Winning Environment 3. Lou Holtz on Leadership 4. Urban Meyer on Turning Around a Program 5. Kirk Ferentz on Program Consistency 6. Frank Lenti on Motivating High School Athletes 7. Bill Walsh’s Super Bowl Success Philosophy 8. Mike Bellotti on Total Program Development Part II – Practice Plans and Mental Toughness Drills 9. Mental Game Keys for Quarterbacks 10. Mental Training at a D1 Football Power Part 1 11. Mental Training at a D1 Football Power Part 2 12. Urban Meyer’s On-Edge Teaching Style 13. Frank Lenti on Practice Organization 14. Seven Tips for Better Locker Room Speeches 15. A Revealing Analysis on Penalties 16. Football Visualization Criteria by Position 17. Prepare Your Team for Sudden Change 18. Pete Carroll’s Days of the Week Practice Focus 19. Chip Kelly’s Three Step Teaching Process 20. Six Tips on How Rookies Can Adjust 21. Belichick Uses Quizzes to Prepare Teams 22. Four Keys to Better Practice Communication 23. Five Questions to Evaluate Performance Part III – Athlete and Team Success Strategies 24. Seahawks Use Fine System to Motivate 25. Michigan State Seniors Speak Out 26. What Makes Tom Brady a Special Leader? 27. Clemson Players Use Movie Motivation 28. Josh Norman Gets Into Character to Motivate Himself 29. Urban Meyer’s Fast Impact on Ohio State 30. Saints Plan to Recover from Losses More Quickly 31. 49ers Adapt to the Millennial Generation 32.