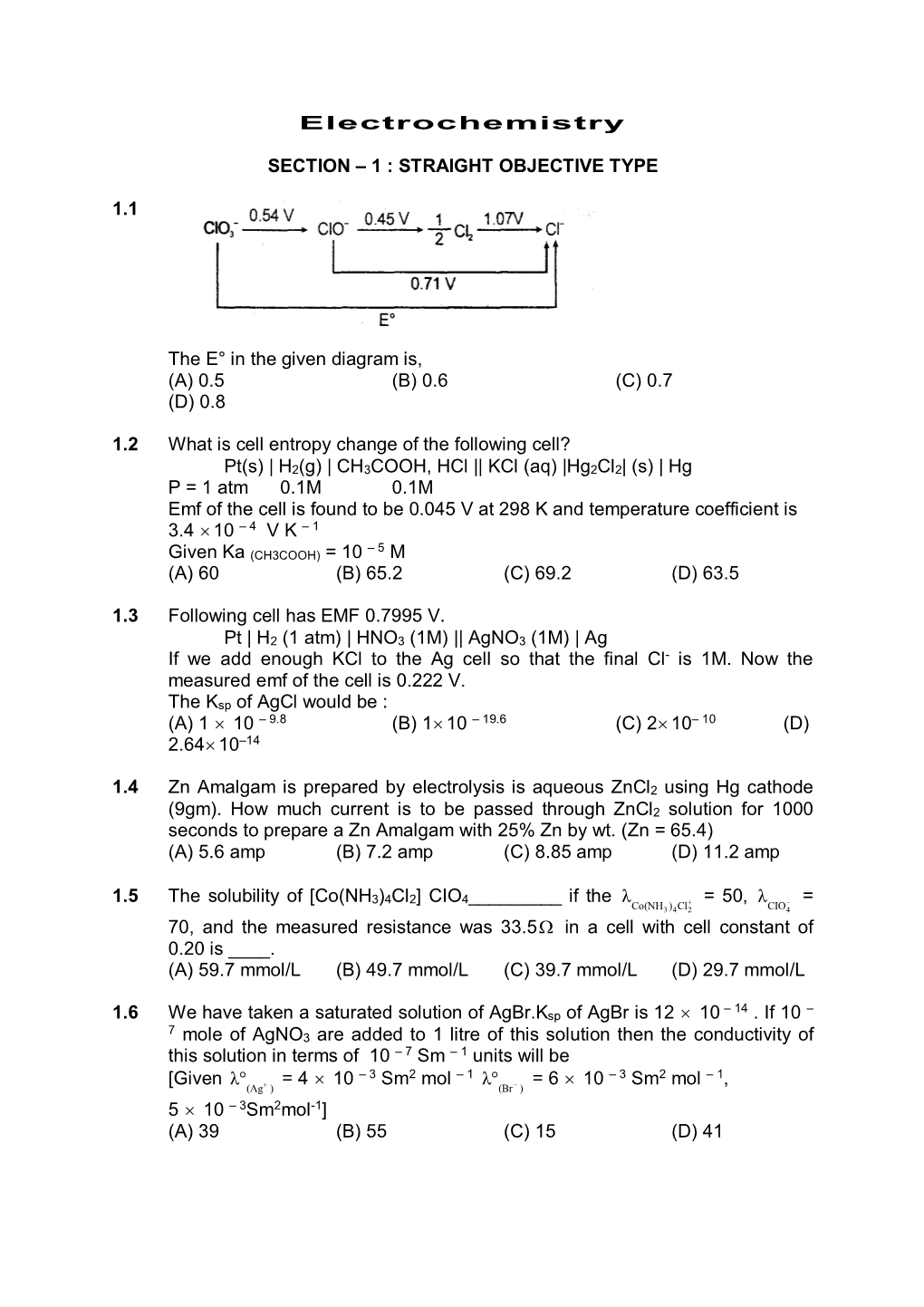
Electrochemistry SECTION
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Electrowinning of Tellurium by Means of PLS Modelling
2009:056 MASTER'S THESIS Optimisation of Influential Factors in Electrowinning of Tellurium by Means of PLS Modelling Seyed Mohammad Khosh Khoo Sany Luleå University of Technology Master Thesis, Continuation Courses Minerals and Metallurgical Engineering Department of Chemical Engineering and Geosciences Division of Process Metallurgy 2009:056 - ISSN: 1653-0187 - ISRN: LTU-PB-EX--09/056--SE Optimisation of Influential Factors in Electrowinning of Tellurium by Means of PLS Modelling Master Thesis By: Seyed Mohammad Khoshkhoo Sany [email protected] Supervisors: Prof. Åke Sandström (Luleå University of Technology) Dr. Nils Johan Bolin (Boliden Mineral AB) Abstract Electrowinning of tellurium is a relatively simple process that can be carried out effectively by employing the existing technology. In order to obtain tellurium with the least amount of impurities, the effects of three main factors were studied, namely current density, free concentration of caustic soda and initial concentration of tellurium. Five elements were chosen as the main impurities: Ag, Bi, Cd, Ni and Pb. A series of 17 experiments arranged in a CCF (central composite faced-centred) design has been carried out and the results were fitted using PLS (partial least squares) method. The effect of free caustic concentration was found to be the most important of the three parameters studied. Current density was also important, yielding the least amount of impurities at high current densities. Tellurium concentration had the smallest effect of the three parameters studied. From the model, current densities of 330-350 A/m2, tellurium concentrations of 90-120 g/l and free sodium hydroxide concentration of around 120 g/l are suggested as optimal conditions for obtaining the purest tellurium. -

Recommendation for Use Hofmann Voltameter for Educational Purposes
Glaswarenfabrik Tel. +49 (0) 9779 808 0 Karl Hecht Fax +49 (0) 9779 808 88 GmbH & Co KG Email: [email protected] Stettener Straße 22-24 Internet: www.assistent.eu 97647 Sondheim/Rhön VAT No. DE132198535 Germany Recommendation for use Hofmann voltameter for educational purposes Product number: 44285010 and 44286010 A water decomposition apparatus is used for the demonstration of electrolysis, i. e. for the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen by means of electric current. The apparatus is consisting of a glass tube with pear-shaped funnel and two lateral measuring tubes 60 ml : 0.2 ml with glass stopcocks. There are two versions available: Product number 44285010 Spare parts Glass part No. 44287010 Metal tripod 2 Clamps No. 40870010 2 Platinum electrodes No. 44288010 Product number 44286010 Spare parts Glass part No. 44287010 Metal tripod 2 Clamps No. 40870010 2 Carbon electrodes No. 44289010 Experimental setup and test procedure Attach the voltameter with two clamps to the support. Insert the carbon or platinum electrodes into the measuring tubes. The stoppers have to be firmly in position in order to avoid leakage of liquid. For safety reasons place the apparatus into a glass tray. Pour in the electrolyte through the funnel while stopcocks are both open to let the air escape. Close the stopcocks as soon as the electrolyte has reached the level of stopcock bores. Connect the electrodes and the pole terminals at the tripod by means of two short connecting cables. Connect a DC voltage source and supply with electrical energy. The required direct voltage is about 10 V to 20 V at max. -

3B Scientific® Physics
3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS Hofmann's Voltameter, S U58010 Instruction Sheet 11/08 ALF 1 Stand base with rod 2 Sockets 3 Gold leaf electrodes 4 Gas collection tube 5 Stop cock 6 Water reservoir 1. Safety instructions Since the conductivity of distilled water is too low electrolysis is carried out using dilute sulphuric acid The apparatus is made of glass. There is a risk of (c = 1 mol/l approx.). Students should always be breakage and resulting injury. informed of the dangers of the chemicals needed for • Handle the apparatus with care when carrying it the experiment. and make sure it is stable on the desk. • Carefully add the sulphuric acid to the water • Do not subject the glass components to while stirring. Never do this the other way round. mechanical stress. • Wear protective goggles when mixing the solution Hydrogen and oxygen form an explosive mixture. and when releasing the gases. • Never re-combine the gases in a test tube. Caution! Any acid that escapes can cause irreparable stains and holes in clothing. 1 2. Description 5. Example experiments Hofmann's voltameter is used for the electrolysis of 5.1 Investigation of the conductivity and composition water (converting electrical energy into chemical of water energy), quantitative determination of the resulting • Pour distilled water into the water reservoir with gases and confirmation of Faraday’s laws. both stopcocks open until both tubes are full. The apparatus consists of three vertical glass tubes Then close the stopcocks. connected to each other at the bottom. Taps at the • Turn on the power supply and observe the top ends of the outside tubes are closed whilst the electrodes. -

Chemistry Unit: 4CH0 Paper: 2CR
Write your name here Surname Other names Centre Number Candidate Number Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Chemistry Unit: 4CH0 Paper: 2CR Wednesday 13 June 2018 – Morning Paper Reference Time: 1 hour 4CH0/2CR You must have: Total Marks Ruler, calculator Instructions • Use black ink or ball-point pen. • Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. • Answer all questions. • Answer the questions in the spaces provided – there may be more space than you need. • Show all the steps in any calculations and state the units. • Some questions must be answered with a cross in a box . If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box and then mark your new answer with a cross . Information • The total mark for this paper is 60. • The marks for each question are shown in brackets – use this as a guide as to how much time to spend on each question. Advice • Read each question carefully before you start to answer it. • Write your answers neatly and in good English. • Try to answer every question. • Check your answers if you have time at the end. Turn over P53147A ©2018 Pearson Education Ltd. *P53147A0120* 1/1/1/1/1/1/ DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA *P53147A0220* 2 Answer ALL questions. 1 The table shows some information about five gases. Formula Boiling point Gas of molecule in °C chlorine Cl2 –35 oxygen O2 –183 carbon monoxide CO –191 nitrogen N2 –196 DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA WRITE IN DO NOT hydrogen H2 –253 Choose gases from the table to answer this question. -

Electrolysis of Water - Wikipedia 1 of 15
Electrolysis of water - Wikipedia 1 of 15 Electrolysis of water Electrolysis of water is the decomposition of water into oxygen and hydrogen gas due to the passage of an electric current. This technique can be used to make hydrogen gas, a main component of hydrogen fuel, and breathable oxygen gas, or can mix the two into oxyhydrogen, which is also usable as fuel, though more volatile and dangerous. It is also called water splitting. It ideally requires a potential difference of 1.23 volts to split water. Simple setup for demonstration of Contents electrolysis of water at home History Principle Equations Thermodynamics Electrolyte selection Electrolyte for water electrolysis Pure water electrolysis Techniques Fundamental demonstration Hofmann voltameter Industrial High-pressure High-temperature An AA battery in a glass of tap water Alkaline water with salt showing hydrogen Polymer electrolyte membrane produced at the negative terminal Nickel/iron Nanogap electrochemical cells Applications Efficiency Industrial output Overpotential Thermodynamics https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrolysis_of_water Electrolysis of water - Wikipedia 2 of 15 See also References External links History Jan Rudolph Deiman and Adriaan Paets van Troostwijk used, in 1789, an electrostatic machine to make electricity which was discharged on gold electrodes in a Leyden jar with water.[1] In 1800 Alessandro Volta invented the voltaic pile, and a few weeks later the English scientists William Nicholson and Anthony Carlisle used it for the electrolysis of water. In 1806 -

We Would Like to Thank WSGC and Dr. William Farrow for Making This Project Possible 2015 WSGC Elijah High-Altitude Balloon Paylo
2015 WSGC Elijah High-Altitude Balloon Payload Project Final Report September 14, 2015 Ben Jensen1, Nate Klassen2, Woodrow Walker1, Scott Frazier3, Kai Swanson1, Taylor Davitz1 1Milwaukee School of Engineering, 2University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, 3University of Wisconsin- Milwaukee Abstract The purpose of this report is to discuss the research, development, and findings of several experiments performed on a high-altitude balloon payload platform. The team decided of the following five experiments to be performed during the flight: Oxygen Generation, Internal Heating, Speed of Sound Properties, Ozone Levels, and a new payload structure concept. The entire team was required to research and develop new skills to effectively design our experiments, including: Arduino programming, 3-D modeling/printing, soldering, launch equipment handling, and construction techniques. While the launch was successful, we did fall short of our overall goal in terms of data acquisition. The internship proved to be a rewarding introductory experience to real-world engineering. The project help us learn how to implement the entirety of the engineering process, using each person’s strengths to achieve an objective. Introduction The goal for the internship team was to research, design, and execute experiments aboard a high- altitude balloon platform. The team would collect and analyze data from each experiment. There were several constraints for the project, including budget, weight, and size. The team was given full control over what we wanted to research, and decided five upon concepts: Oxygen Generation, Internal Heating, Speed of Sound Properties, Ozone Levels, and a new payload structure concept. Oxygen Generation As the altitude increases, we see a corresponding decrease in air pressure. -

Biology • Environment • Chemistry MEMORABLE TEACHING MADE EASY!
3bscientific.com Biology • Environment • ChemistryBiology • Environment NATURAL SCIENCES NATURAL 3B SCIENTIFIC® NATURAL SCIENCES 3bscientific.com 9000953 EN MEMORABLE TEACHING MADE EASY! Dear customer, Discover the variety of possibilities for making your teaching even more memorable and exciting. We have assembled a wide range of products and experiments for you for teaching various course content in biology. We can offer you detailed models, high-quality preparations and realis- tic replicas that illustrate the structures of plants, animals, humans and the earth as well as numerous experiment sets to aid independent study, practicing and learning. From page 104 onwards, you can browse through the selection of products relating to the earth sciences, ecology and chemistry. These include models of the structure of the earth, rock collections, measuring equipment for water and soil analysis, molecule construction kits and chemical measuring instruments. New and worthy of particular mention are the powerful and comprehensive Coach 7 measuring and analysis software, the VinciLab data logger and the €lab lab interface, as well as the numerous sensors for the measurement of biological and chemical para- meters (page 152 onwards). Representing a further innovation in our range are the devices for neurophysiological studies on intact earthworms. You can find these on page 94 onwards. Let yourself be inspired by our wide range. It’s well worth a look! Our competent team will be happy to advise you personally and is looking forward to receiving your suggestions and orders! We look forward to hearing from you! The 3B Scientific team ›NEW IN ZOOLOGY Limbs of various mammals The dissected real limbs enable scientific comparison of the anatomy of the front or rear legs of selected mammals and allow conclusions to be drawn about their walking and running behavior. -

Answers Neatly and in Good English
Write your name here (Surname Other names ] Centre Number Candidate Number Pearson Edexcel International GCSE Chemistry Unit:4CHO Paper: 2CR Wednesday 13 June 201 8 - Morning Paper Reference Time: 1 hour 4CHO/2CR You must have: Total Marks Ruler, calculator ] Instructions • Use black ink or ball-point pen. • Fill in the boxes at the top of this page with your name, centre number and candidate number. • Answer all questions. • Answer the questions in the spaces provided - there may be more space than you need. • Show all the steps in any calculations and state the units. • Some questions must be answered with a cross in a box Kl. If you change your mind about an answer, put a line through the box N and then mark your new answer with a cross IX]. Information • The total mark for this paper is 60. • The marks for each question are shown in brackets - use this as a guide as to how much time to spend on each question. Advice • Read each question carefully before you start to answer it. • Write your answers neatly and in good English. • Try to answer every question. • Check your answers if you have time at the end. Turnover > P53147A ©2018 Pearson Education Ltd. 1/1/1/1/1/1/ P 5 3 1 A 1 2 0 Pearson 0 -?!"'1 s ® 0 s<|" s ^|s "51 s ^p 1^ £ x g 0 I .1 r~ s, -Is 0 °' u. §<» ^y SffllS C*J 5|s § s: m I <0 £ o|niS cn|i° ^4 s ^| s m 0 & ^1» g4 s ? ,'^ x in •V '[>. -

Electrodeposition Research
NAT'L INST OF STANDARDS & TECH R.I.C. All 101 888778 /National Bureau of Standards circular QC100 .U555 V529;1953 C.1 NBS-PUB-R 1947 •'>1 A 1 .. _ 1- • .. yil Ur U . ^ 4 1 'U tt mm, Co mm ere ureat) ;o UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE • Sinclair Weeks, Secretary NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS • A. V. Astin, Director Electrodeposition Research Proceedings of the NBS Semicentennial Symposium on Electrodeposition Research Held at the NBS on December 4-6, 1951 National Bureau of Standards Circular 529 Issued May 22, 1953 For sale by the Superintendent of Documents, U. S. Government Printing Office Washington 25, D. C. - Price 31-50 Buckram National Bureau of Standards AUG 2 8 1953 Sli5£ QC 100 0555 Foreword Electrodeposition processes have become an integral and important part of many industries—for example, the printing, metal refining, extractive metallurgy, hardware, automobile, and electronic indus- tries. This has come about largely as a result of extensive research in the field of electrodeposition, especially during the past 25 years. To encourage further research in this field, to present current re- search results and problems, and to facilitate the exchange of informa- tion, the National Bureau of Standards held the Symposium on Electrodeposition Research as the last of a series of twelve symposia conducted during the Bureau’s semicentennial in 1951. The papers presented at the Symposium are published in this volume. These papers represent a cross section of research currently being conducted in electrodeposition by industrial, university, and government labora- tories in Europe and the United States. -

WO 2014/128300 Al 28 August 2014 (28.08.2014) P O P C T
(12) INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT) (19) World Intellectual Property Organization International Bureau (10) International Publication Number (43) International Publication Date WO 2014/128300 Al 28 August 2014 (28.08.2014) P O P C T (51) International Patent Classification: (81) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every C12P 5/02 (2006.01) C12M 1/00 (2006.01) kind of national protection available): AE, AG, AL, AM, C12M 1/107 (2006.01) C12M 1/34 (2006.01) AO, AT, AU, AZ, BA, BB, BG, BH, BN, BR, BW, BY, BZ, CA, CH, CL, CN, CO, CR, CU, CZ, DE, DK, DM, (21) Number: International Application DO, DZ, EC, EE, EG, ES, FI, GB, GD, GE, GH, GM, GT, PCT/EP2014/053545 HN, HR, HU, ID, IL, IN, IR, IS, JP, KE, KG, KN, KP, KR, (22) International Filing Date: KZ, LA, LC, LK, LR, LS, LT, LU, LY, MA, MD, ME, 24 February 2014 (24.02.2014) MG, MK, MN, MW, MX, MY, MZ, NA, NG, NI, NO, NZ, OM, PA, PE, PG, PH, PL, PT, QA, RO, RS, RU, RW, SA, (25) Filing Language: English SC, SD, SE, SG, SK, SL, SM, ST, SV, SY, TH, TJ, TM, (26) Publication Language: English TN, TR, TT, TZ, UA, UG, US, UZ, VC, VN, ZA, ZM, ZW. (30) Priority Data: 1303 156.2 22 February 2013 (22.02.2013) GB (84) Designated States (unless otherwise indicated, for every kind of regional protection available): ARIPO (BW, GH, (71) Applicant: KRAJETE GMBH [AT/AT]; Scharitzerstr. GM, KE, LR, LS, MW, MZ, NA, RW, SD, SL, SZ, TZ, 30, A-4020 Linz (AT). -

A Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Proton Transport Between the Electrolyte in a Reversible Fuel Cell and a Carbon- Based Hydrogen Storage
A THEORETICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL INVESTIGATION OF PROTON TRANSPORT BETWEEN THE ELECTROLYTE IN A REVERSIBLE FUEL CELL AND A CARBON- BASED HYDROGEN STORAGE A thesis submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy By Shahin Heidari College of Science, Engineering and Health RMIT University Melbourne, Victoria, Australia March 2017 1 DECLARATION I, Shahin Heidari, hereby submit the thesis entitled “a theoretical and experimental investigation of proton transport between the electrolyte in a reversible fuel cell and a carbon- based hydrogen storage” for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, and certify that except where due acknowledgement has been made, the work is that of the author alone; the work has not been submitted previously, in whole or in part, to qualify for any other academic award, and that the content of the thesis is the result of work that has been carried out since the official commencement date of the approved research program. Shahin Heidari March 2017 2 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I would like to acknowledge my senior supervisor, Professor John Andrews, for sharing his ideas and knowledge and supporting me in every step of my PhD journey. I would like to thank Professor Aliakbar Akbarzadeh and Doctor Abhijit date for giving me the opportunity of teaching and tutoring. I would like to thank all my friends and colleagues at RMIT University SAMME School and specifically Energy CARE group for their support. Many thanks also go to our hydrogen group at RMIT, specifically Dr. Amandeep Oberoi and Mr. Saeed Seif Mohammadi for sharing with me their knowledge in this field of study. -

The Electrochemistry of Sulphur and Its Ions In
THE ELECTROCHEMISTRY OF SULPHUR AND ITS IONS IN MOLTEN HAL IDES A THESIS submitted for the DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY in the UNIVERSITY OF LONDON • by PETER GEORGE DUDLEY, M.Phil., DIC, B.Sc.(Eng.), ARSM Department of Metallurgy and Materials Science Royal School of Mines Imperial College of Science and Technology September 1982 -i i- ABSTRACT The electrochemical behaviour of sulphur and its ions was examined in molten PbC£2, PbC&2-KCZ and PbCZ2-KCZ-NaCZsolvents. In particular the 2~ electrooxidation of the sulphide ion, S , was extensively studied at a variety of electrode substrates. Electrochemical studies were carried out in the temperature range 410-550°C by linear sweep voltammetry, chronoamperometry, steady-state I-V relationships, chronopotentiometry, controlled potential electrolysis and open circuit decay techniques. The electrooxidation of PbS was primarily observed at planar vitreous carbon and graphite electrodes, although the behaviour at platinum and gold electrodes was investigated for comparison. At vitreous carbon and graphite electrodes, two primary oxidation processes were observed corresponding to the reactions: (1) S2~ + S° + 2£' E s 0.45V wrt Ag/Ag+ and l + (2) 2S + 20T + S2Cz2 + 2e E s 0.97V wrt Ag/Ag The sulphur generated from reaction (1) under pulse conditions was shown to be reversible with respect to the electron transfer and to be diffusion controlled. However, at lower temperatures the oxidation process appears to be inhibited by the formation of a passive sulphur film. The nature and formation of sulphur films (at temperatures well below the boiling point of sulphur) on carbon, platinum and gold electrodes are discussed.