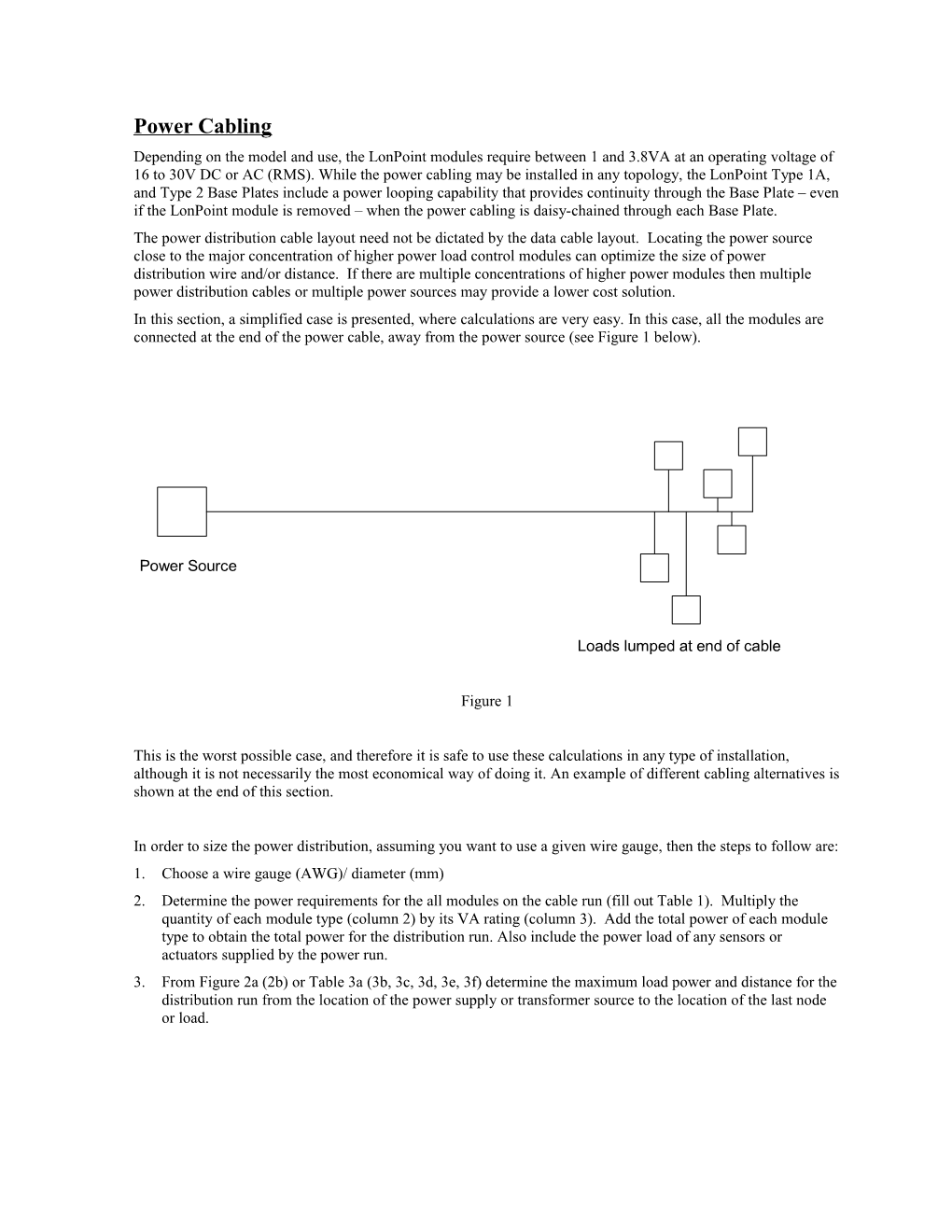
Power Cabling Depending on the model and use, the LonPoint modules require between 1 and 3.8VA at an operating voltage of 16 to 30V DC or AC (RMS). While the power cabling may be installed in any topology, the LonPoint Type 1A, and Type 2 Base Plates include a power looping capability that provides continuity through the Base Plate – even if the LonPoint module is removed – when the power cabling is daisy-chained through each Base Plate. The power distribution cable layout need not be dictated by the data cable layout. Locating the power source close to the major concentration of higher power load control modules can optimize the size of power distribution wire and/or distance. If there are multiple concentrations of higher power modules then multiple power distribution cables or multiple power sources may provide a lower cost solution. In this section, a simplified case is presented, where calculations are very easy. In this case, all the modules are connected at the end of the power cable, away from the power source (see Figure 1 below).
Power Source
Loads lumped at end of cable
Figure 1
This is the worst possible case, and therefore it is safe to use these calculations in any type of installation, although it is not necessarily the most economical way of doing it. An example of different cabling alternatives is shown at the end of this section.
In order to size the power distribution, assuming you want to use a given wire gauge, then the steps to follow are: 1. Choose a wire gauge (AWG)/ diameter (mm) 2. Determine the power requirements for the all modules on the cable run (fill out Table 1). Multiply the quantity of each module type (column 2) by its VA rating (column 3). Add the total power of each module type to obtain the total power for the distribution run. Also include the power load of any sensors or actuators supplied by the power run. 3. From Figure 2a (2b) or Table 3a (3b, 3c, 3d, 3e, 3f) determine the maximum load power and distance for the distribution run from the location of the power supply or transformer source to the location of the last node or load.
Power Requirements Module type Number of Power Total Power on modules on per distribution power module run. distribution run. DO-10 3.8 VA (w/outputs fully loaded) DO-10 1 VA (w/outputs lightly loaded) DI-10 1 VA
AI-10 2.9 VA (two-wire mode) AI-10 0.9 VA (all modes except 2-wire mode) AO-10 2.4 VA
Scheduler 1.6 VA
Router 1 VA
Other loads on the same wire ?
Total
Table 1: Power Consumption Requirements per cable run Finding the maximum distance and total power Locate the curve for the wire size you want to use in the graphs below. For each point on a given curve, you can read the maximum load power and maximum distance for the wire run.
Figure 2a: Maximum Load Power vs. Distance and Wire Gauge (AWG) 100
90
80 ) A V
( 70
r e w
o 60 P
d a
o 50 L
m
u 40 m i x
a 30 M 20 18 16 14 12 20 22
10
0 0 100 200 300 400 500 Distance (Meters)
Figure 2b: Maximum Load Power vs. Distance and Wire Diameter (mm) 100
90
80 ) A V
( 70
r e w
o 60 P
d a
o 50 L
m
u 40 m i x
a 30 M 0.8 1 1.3 1.6 2 20 0.5 0.65
10
0 0 100 200 300 400 500 Distance (Meters) Wire Gauge Load Power (VA) (AWG) Feet Meters 10 15 20 25 30 40 55 75 100 130 180 16 5 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 33 10 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 20 20 49 15 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 20 18 18 66 20 22 22 22 22 22 22 22 20 18 18 16 82 25 22 22 22 22 22 22 20 18 18 16 16 98 30 22 22 22 22 22 20 20 18 16 16 14 115 35 22 22 22 22 22 20 18 18 16 16 14 131 40 22 22 22 22 20 20 18 16 16 14 14 148 45 22 22 22 22 20 20 18 16 16 14 12 164 50 22 22 22 20 20 18 18 16 14 14 12 180 55 22 22 22 20 20 18 16 16 14 14 12 197 60 22 22 20 20 20 18 16 16 14 12 12 230 70 22 22 20 20 18 18 16 14 14 12 246 75 22 22 20 18 18 16 16 14 12 12 262 80 22 20 20 18 18 16 16 14 12 12 279 85 22 20 20 18 18 16 14 14 12 12 295 90 22 20 20 18 18 16 14 14 12 312 95 22 20 18 18 18 16 14 14 12 361 110 22 20 18 18 16 16 14 12 12 377 115 20 20 18 18 16 14 14 12 12 394 120 20 20 18 16 16 14 14 12 459 140 20 18 18 16 16 14 12 12 492 150 20 18 16 16 16 14 12 12 591 180 20 18 16 16 14 14 12 623 190 18 18 16 14 14 12 12 673 205 18 16 16 14 14 12 12 738 225 18 16 16 14 14 12 787 240 18 16 14 14 14 12 935 285 18 16 14 14 12 12 1001 305 16 16 14 12 12 1181 360 16 14 14 12 12 1247 380 16 14 12 12 12 1493 455 16 14 12 12 1509 460 14 14 12 12 1640 500 14 12 12
Table 2a: Determine wire gauge (AWG) given distance and load power Load Power (VA) Wire Gauge (AWG) Feet Meters 12 14 16 18 20 22 33 10 1053 662 416 262 164 103 66 20 526 331 208 131 82 51 98 30 351 220 138 87 54 34 131 40 263 165 104 65 41 25 164 50 210 132 83 52 32 20 197 60 175 110 69 43 27 17 230 70 150 94 59 37 23 14 262 80 131 82 52 32 20 12 295 90 117 73 46 29 18 11 328 100 105 66 41 26 16 10 361 110 95 60 37 23 14 9 394 120 87 55 34 21 13 8 427 130 81 50 32 20 12 7 459 140 75 47 29 18 11 7 492 150 70 44 27 17 10 6 525 160 65 41 26 16 10 6 558 170 61 38 24 15 9 6 591 180 58 36 23 14 9 5 623 190 55 34 21 13 8 5 656 200 52 33 20 13 8 5 689 210 50 31 19 12 7 4 722 220 47 30 18 11 7 4 755 230 45 28 18 11 7 4 787 240 43 27 17 10 6 4 820 250 42 26 16 10 6 4 853 260 40 25 16 10 6 3 886 270 39 24 15 9 6 3 919 280 37 23 14 9 5 3 951 290 36 22 14 9 5 3 984 300 35 22 13 8 5 3 1017 310 33 21 13 8 5 3 1050 320 32 20 13 8 5 3 1083 330 31 20 12 7 4 3 1115 340 30 19 12 7 4 3 1148 350 30 18 11 7 4 2 1181 360 29 18 11 7 4 2 1214 370 28 17 11 7 4 2 1247 380 27 17 10 6 4 2 1280 390 27 16 10 6 4 2 1312 400 26 16 10 6 4 2 1345 410 25 16 10 6 4 2 1378 420 25 15 9 6 3 2 1411 430 24 15 9 6 3 2 1444 440 23 15 9 5 3 2 1476 450 23 14 9 5 3 2 1509 460 22 14 9 5 3 2 1542 470 22 14 8 5 3 2 1575 480 21 13 8 5 3 2 1608 490 21 13 8 5 3 2 1640 500 21 13 8 5 3 2
Table 2b: Determine load power, given distance and wire gauge (AWG) Distance Wire Size (AWG) (Meters) VA 12 14 16 18 20 22 5 1859 1169 735 462 291 183 10 930 585 368 231 145 91 15 620 390 245 154 97 61 20 465 292 184 116 73 46 25 372 234 147 92 58 37 30 310 195 123 77 48 30 35 266 167 105 66 42 26 40 232 146 92 58 36 23 45 207 130 82 51 32 20 50 186 117 74 46 29 18 55 169 106 67 42 26 17 60 155 97 61 39 24 15 65 143 90 57 36 22 14 70 133 84 53 33 21 13 75 124 78 49 31 19 12 80 116 73 46 29 18 11 85 109 69 43 27 17 11 90 103 65 41 26 16 10 95 98 62 39 24 15 10 100 93 58 37 23 15 9 105 89 56 35 22 14 9 110 85 53 33 21 13 8 115 81 51 32 20 13 8 120 77 49 31 19 12 8 125 74 47 29 18 12 7 130 72 45 28 18 11 7 135 69 43 27 17 11 7 140 66 42 26 17 10 7 145 64 40 25 16 10 6 150 62 39 25 15 10 6 155 60 38 24 15 9 6 160 58 37 23 14 9 6 165 56 35 22 14 9 6 170 55 34 22 14 9 5 175 53 33 21 13 8 5 180 52 32 20 13 8 5 185 50 32 20 12 8 5 190 49 31 19 12 8 5 195 48 30 19 12 7 5 200 46 29 18 12 7 5
Table 2c: Determine distance, given load power and wire gauge (AWG) Wire Dia. (mm) Power (VA) Feet Meters 4.8 9.6 16.8 24 36 48 72 96 144 192 240 16.4 5 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 19.7 6 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 23.0 7 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 0.80 26.2 8 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 1.00 29.5 9 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 0.80 1.00 39.4 12 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 45.9 14 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.30 52.5 16 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 62.3 19 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.30 1.30 78.7 24 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 98.4 30 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 2.00 105.0 32 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 121.4 37 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.60 124.7 38 0.50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.30 1.60 2.00 160.8 49 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 164.0 50 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.30 1.60 2.00 190.3 58 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.30 1.60 213.3 65 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 229.7 70 0.50 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.60 242.8 74 0.50 0.65 0.80 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.60 246.1 75 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.30 1.60 2.00 255.9 78 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.00 1.30 1.60 321.5 98 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 324.8 99 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.60 328.1 100 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 2.00 347.8 106 0.50 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 383.9 117 0.50 0.65 1.00 1.00 1.30 1.60 403.5 123 0.50 0.65 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 429.8 131 0.50 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 479.0 146 0.50 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.60 488.8 149 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.60 492.1 150 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 2.00 547.9 167 0.65 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 613.5 187 0.65 0.80 1.30 1.30 1.60 646.3 197 0.65 1.00 1.30 1.30 1.60 652.9 199 0.65 1.00 1.30 1.60 1.60 656.2 200 0.65 1.00 1.30 1.60 2.00 810.4 247 0.65 1.00 1.30 1.60 925.2 282 0.80 1.00 1.30 1.60 958.0 292 0.80 1.00 1.60 1.60 981.0 299 0.80 1.30 1.60 1.60 984.3 300 0.80 1.30 1.60 2.00 1227.0 374 0.80 1.30 1.60 1400.9 427 1.00 1.30 1.60 1404.2 428 1.00 1.30 2.00 1620.7 494 1.00 1.30 1640.4 500 1.00 1.60 Table 2d: Determine wire diameter (mm) given distance and load power
Load Power (VA) Wire Diameter Feet Meters 2mm 1.6mm 1.3mm 1mm 0.8mm 0.65mm 0.5mm 33 10 971 621 410 242 155 102 60 66 20 485 310 205 121 77 51 30 98 30 323 207 136 80 51 34 20 131 40 242 155 102 60 38 25 15 164 50 194 124 82 48 31 20 12 197 60 161 103 68 40 25 17 10 230 70 138 88 58 34 22 14 8 262 80 121 77 51 30 19 12 7 295 90 107 69 45 26 17 11 6 328 100 97 62 41 24 15 10 6 361 110 88 56 37 22 14 9 5 394 120 80 51 34 20 12 8 5 427 130 74 47 31 18 11 7 4 459 140 69 44 29 17 11 7 4 492 150 64 41 27 16 10 6 4 525 160 60 38 25 15 9 6 3 558 170 57 36 24 14 9 6 3 591 180 53 34 22 13 8 5 3 623 190 51 32 21 12 8 5 3 656 200 48 31 20 12 7 5 3 689 210 46 29 19 11 7 4 2 722 220 44 28 18 11 7 4 2 755 230 42 27 17 10 6 4 2 787 240 40 25 17 10 6 4 2 820 250 38 24 16 9 6 4 2 853 260 37 23 15 9 5 3 2 886 270 35 23 15 8 5 3 2 919 280 34 22 14 8 5 3 2 951 290 33 21 14 8 5 3 2 984 300 32 20 13 8 5 3 2 1017 310 31 20 13 7 5 3 1 1050 320 30 19 12 7 4 3 1 1083 330 29 18 12 7 4 3 1 1115 340 28 18 12 7 4 3 1 1148 350 27 17 11 6 4 2 1 1181 360 26 17 11 6 4 2 1 1214 370 26 16 11 6 4 2 1 1247 380 25 16 10 6 4 2 1 1280 390 24 15 10 6 3 2 1 1312 400 24 15 10 6 3 2 1 1345 410 23 15 10 5 3 2 1 1378 420 23 14 9 5 3 2 1 1411 430 22 14 9 5 3 2 1 1444 440 22 14 9 5 3 2 1 1476 450 21 13 9 5 3 2 1 1509 460 21 13 8 5 3 2 1 1542 470 20 13 8 5 3 2 1 1575 480 20 12 8 5 3 2 1 1608 490 19 12 8 4 3 2 1 1640 500 19 12 8 4 3 2 1 Table 2e: Determine load power, given distance and wire diameter (mm) Distance Wire Diameter (mm) (Meters) VA 2 1.6 1.3 1 0.8 0.65 0.5 5 1943 1243 821 486 311 205 121 10 971 622 410 243 155 103 61 15 648 414 274 162 104 68 40 20 486 311 205 121 78 51 30 25 389 249 164 97 62 41 24 30 324 207 137 81 52 34 20 35 278 178 117 69 44 29 17 40 243 155 103 61 39 26 15 45 216 138 91 54 35 23 13 50 194 124 82 49 31 21 12 55 177 113 75 44 28 19 11 60 162 104 68 40 26 17 10 65 149 96 63 37 24 16 9 70 139 89 59 35 22 15 9 75 130 83 55 32 21 14 8 80 121 78 51 30 19 13 8 85 114 73 48 29 18 12 7 90 108 69 46 27 17 11 7 95 102 65 43 26 16 11 6 100 97 62 41 24 16 10 6 105 93 59 39 23 15 10 6 110 88 57 37 22 14 9 6 115 84 54 36 21 14 9 5 120 81 52 34 20 13 9 5 125 78 50 33 19 12 8 5 130 75 48 32 19 12 8 5 135 72 46 30 18 12 8 4 140 69 44 29 17 11 7 4 145 67 43 28 17 11 7 4 150 65 41 27 16 10 7 4 155 63 40 26 16 10 7 4 160 61 39 26 15 10 6 4 165 59 38 25 15 9 6 4 170 57 37 24 14 9 6 4 175 56 36 23 14 9 6 3 180 54 35 23 13 9 6 3 185 53 34 22 13 8 6 3 190 51 33 22 13 8 5 3 195 50 32 21 12 8 5 3 200 49 31 21 12 8 5 3
Table 2f: Determine distance, given load power and wire diameter (mm) Power Source Ratings The power source rating requirements are determined by the sum of the power distribution cable runs attached to the power source. Example: Cable run A has 6 fully loaded DO-10 modules, as well as several actuators that take a total of 5VA. Cable run B has one Scheduler, one router, and 4 AO-10 modules, as well as one LonWorks-compatible controller that takes 3VA. The transformer size is calculated as the sum of all the loads on all the cable runs, plus the losses on the cable. In the worst case (all the loads and modules connected at the end of the cable run), the losses on the cable equal the power taken by the loads, therefore you must multiply the total by 2. Transformer power = (6x3.8VA + 5VA + 1.6VA + 1VA + 4x2.4VA + 3VA) x 2 = 86VA
Distributed Loading The numbers in Table 2a (2b, 2c, 2d, 2e, 2f) and Figure 2a (2b) were calculated for all the modules and loads connected at the end of the cable run. The requirements are eased if your installation has all the modules and loads evenly distributed along the power cable, and each node takes approximately the same power. Under that situation, as a rule of thumb, you can increase the total power sum obtained from the tables or graphs by a factor of 1.5, i.e. you will be able to connect more loads on a given cable length.
Power Source
Evenly distributed equal loads Figure 3 Cable Temperature Effects The numbers in Table 2a (2b, 2c, 2d, 2e, 2f) and Figure 2a (2b) were calculated assuming that the average temperature of the wire is +55°C, although the temperature of individual segments of wire may be as high as 85°C. If the average ambient temperature is approximately 25°C, then, as a rule of thumb, you can increase the total power sum obtained from the tables or graphs by a factor of 1.1, i.e. you will be able to connect more loads on a given cable length. Note: If the power cabling is under-dimensioned, modules at the end of a cable run may not be able to start up, with the outputs of their switching power supplies breaking into oscillation. The modules that are unable to start will also take a higher amount of current, bringing down other neighboring nodes. Verify that the minimum specified voltage at the input of LonPoint modules is met.
Warning! It is important to note that a maximum of 16 Amperes can be passed through the internal jumpers on the Power terminals of a Type 1, Type 1A, and Type 2 Base Plate. This means that if the power wiring is looped in and out of the power terminals of the LonPoint Base Plates, the current load presented by all the LonPoint modules and any other devices powered by that circuit must be less than 16 Amperes, as shown in Figure 2a. If more than 16 Amperes must be supplied then the loop-through capability of the LonPoint Base Plate power terminals must not be used and the power cabling should be run in parallel, as shown in figure 2b. To calculate the maximum current, multiply the total number of load VA by 2 (to take into account the losses in the cable) and then divide by the source voltage (for example, 24VAC if that is the output of your transformer). Wiring example: Some alternatives The 2nd floor of a 10-floor building has a 500-foot run from the router interface of the backbone cable to a cluster of six DO-10 modules. What is the best power distribution architecture for this application? The possible architectures are: 1. One power source located at the router end of the network. 2. One power source located at the DO-10 cluster end of the network. 3. One power source located in the middle of the network. 4. Two power sources located at each end of the network. The objective is to determine the most cost-effective solution taking into consideration material and installation costs. In this example, we are not assuming that the cable size is already chosen, but we’ll try to optimize the topology and the cable gauge. Table 3 below is an analysis of each case, which allows you to calculate & compare the relative material / installation costs.
Figure Description Cable run load Power Wire size Transformer power wiring length size One power source 1 VA 9 ft 22 AWG, located at the router end 0.5mm 5a of the network 3 m 22.8VAx2 +1= 46.6VA 6x3.8VA 500 ft 16 AWG 1.3mm = 22.8VA 152 m One power source at the 6x3.8VA 9 ft 22 AWG, DO-10 cluster end of 0.5mm 5b the network = 22.8VA 3 m 22.8VA+1VAx2= 24.8VA 1 VA 500 ft 22 AWG 152 m 0.5mm One power source in the 1 VA 250 ft 22 AWG, middle of network 0.5mm 5c 76 m (22.8VA+1VA)x2= 47.6VA 6x3.8VA 250 ft 18 AWG, 1.0mm = 22.8VA 76 m Two power sources 9 ft 22 AWG located at each end of 0.5mm for 5d the network 1VA + 22.8VA 3 m router 1VA = 23.8VA & 22 AWG + 0.5mm for 22.8VA DO-10
Table 3 Router 6 x DI-10
Power Source Figure 5a
Router 6 x DI-10
Power Source Figure 5b
Router 6 x DI-10
Power Source Figure 5c
Router 6 x DI-10
Power Power Source Source Figure 5d