Chapter 8. Two-Level Fractional Factorial Designs
Example 1. Five factors for an IC were investigated for improving the process yield. : aperture setting (small, large) exposure time ( below nominal, above nominal) development time (s, s) mask dimension (small, large) etch time ( min, min)
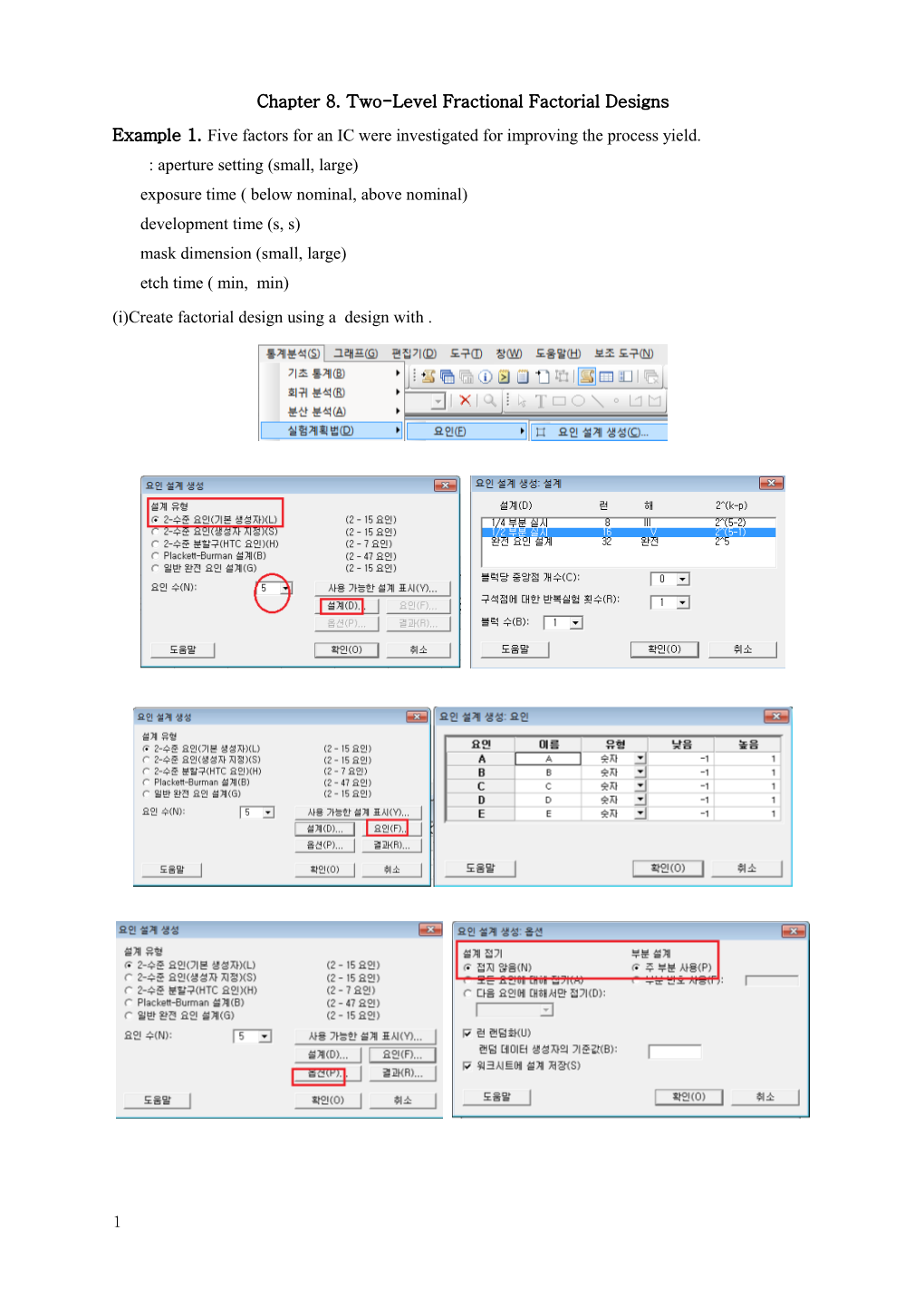
(i)Create factorial design using a design with .
1
(ii)Suppose that the experiment is performed in the run order so as to obtain the following data.
(iii)Fit a full model.
2
효과의 정규 확률도 (반응: yield, α = 0.05)
99 효과 유형 유의하지 않음 95 B 유의함
90 A 요인 이름 C 80 A A AB B B 70 C C 60 율 D D 50 분 E E 40 백 30 20
10 5
1 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 효과 Lenth의 PSE = 0.9375
(iv)Fit a reduced model.
3
(v)Plot the interaction between A and B.
yield에 대한 주효과도 적합 평균 A B C 50
40 균 평
의 30 d l e i y
20
10 -1 1 -1 1 -1 1
When B= -1, there is not much difference between the effect of A. However, if B=1, then A=1 has a much higher yield than A=-1. To get the maximum yield, we would use A=1 and B=1. From the main effect plot, C=1 gives a higher yield than C=-1.
(vi)Provide the contour plot.
4 yield 대 B, A의 등고선도 1.0 yield < 20 20 – 30 30 – 40 0.5 40 – 50 50 – 60 > 60
고정 값 C 1
B 0.0
-0.5
-1.0 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 A
Example 2. A quality improvement team uses a designed experiment to study the injection molding process so that shrinkage can be reduced. Six factors are considered: mold temperature screw speed
cycle time gate size holding pressure (i)Create factorial design using a .
5 (ii)Suppose that you get the following data after experiments. Enter the data in column C11
(iii)Test hypotheses
6
효과의 정규 확률도 (반응: 수축정도, α = 0.05)
99 효과 유형 유의하지 않음 95 B 유의함
90 A 요인 이름 AB 80 A 성형온도 B 나사속도 70 C 지속시간 60 율 D 사이클시간 50 분 E 게이트크기 40 백 F 지속압력 30 20
10 ABF 5 AD
1 0 10 20 30 40 효과 Lenth의 PSE = 0.9375
(iv)Find the reduced model.
7
Example 3. Design with I=ACE and I=BDE.
Example 4. A human performance analyst is conducting an experiment to study eye focus time and has built an apparatus in which several factors can be controlled during the test. : sharpness of vision 8 : distance from target to eye : target shape : illumination level : target size : target density : subject (i) Design
(ii)Suppose that you get the following data after experiments. Enter the data in column C12
9 (iii)Test hypotheses
효과의 정규 확률도 (반응: response, α = 0.05) 99 효과 유형 유의하지 않음 95 유의함 B 90 요인 이름 80 A A D B B 70 A C C 60 율 D D 50 분 E E 40 백 F F 30 G G 20
10 5
1 0 10 20 30 40 효과 Lenth의 PSE = 0.675
Plot shows that A, B, D effects are significant. However, is aliased with is aliased with and is aliased with . Therefore, it is not known if A,D, AD are significant or if A,B,D are significant.
(iv)To separate the main effects and the two-factor interactions, we use the full fold over design
Case 1. Adjust the current design.
10
11 효과의 정규 확률도 (반응: response, α = 0.05)
99 효과 유형 유의하지 않음 95 B 유의함
90 D 요인 이름 80 BD A A B B 70 C C 60 율 D D 50 분 E E 40 백 F F 30 G G 20
10 5 AF
1 0 10 20 30 40 효과 Lenth의 PSE = 0.75
Suppose that we do not consider the block effect in the model.
12 효과의 정규 확률도 (반응: response, α = 0.05)
99 효과 유형 유의하지 않음 95 B 유의함
90 D 요인 이름 BD 80 A A B B 70 C C 60 율 D D 50 분 E E 40 백 F F 30 G G 20
10 5
1 0 10 20 30 40 효과 Lenth의 PSE = 1.21875
Case 2. A new design is used.
13
(i)Suppose that you get the following data after experiments. Enter the data in column C12
(ii)Test hypotheses
14
효과의 정규 확률도 (반응: response, α = 0.05)
99 효과 유형 유의하지 않음 95 B 유의함
90 D 요인 이름 BD 80 A A B B 70 C C 60 율 D D 50 분 E E 40 백 F F 30 G G 20
10 5
1 0 10 20 30 40 효과 Lenth의 PSE = 1.21875
15