1
Business Finance Name ______Examination Three Spring 2002
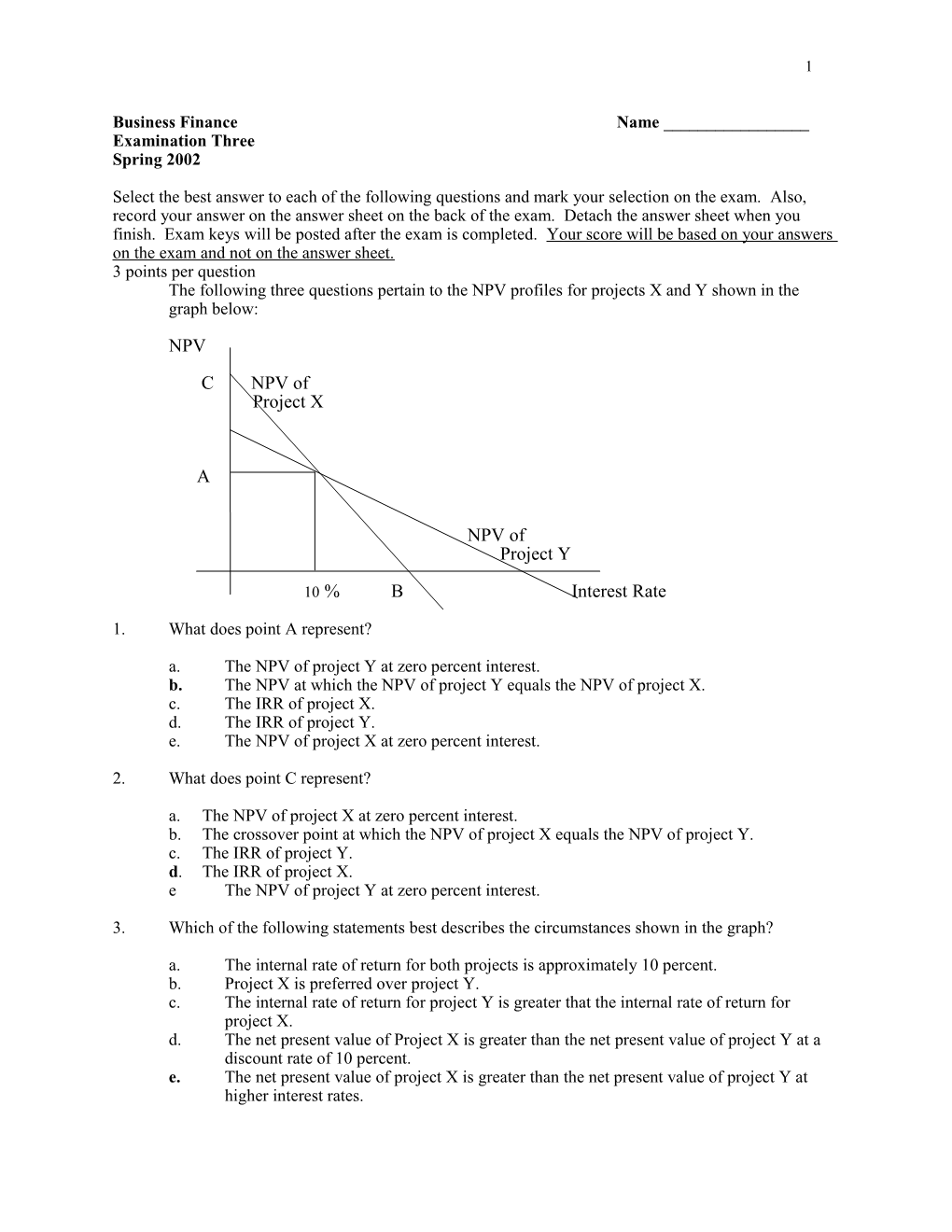
Select the best answer to each of the following questions and mark your selection on the exam. Also, record your answer on the answer sheet on the back of the exam. Detach the answer sheet when you finish. Exam keys will be posted after the exam is completed. Your score will be based on your answers on the exam and not on the answer sheet. 3 points per question The following three questions pertain to the NPV profiles for projects X and Y shown in the graph below:
NPV C NPV of Project X
A
NPV of Project Y
10 % B Interest Rate
1. What does point A represent?
a. The NPV of project Y at zero percent interest. b. The NPV at which the NPV of project Y equals the NPV of project X. c. The IRR of project X. d. The IRR of project Y. e. The NPV of project X at zero percent interest.
2. What does point C represent?
a. The NPV of project X at zero percent interest. b. The crossover point at which the NPV of project X equals the NPV of project Y. c. The IRR of project Y. d. The IRR of project X. e The NPV of project Y at zero percent interest.
3. Which of the following statements best describes the circumstances shown in the graph?
a. The internal rate of return for both projects is approximately 10 percent. b. Project X is preferred over project Y. c. The internal rate of return for project Y is greater that the internal rate of return for project X. d. The net present value of Project X is greater than the net present value of project Y at a discount rate of 10 percent. e. The net present value of project X is greater than the net present value of project Y at higher interest rates. 2
4. Given the following bond quotes from the Wall Street Journal:
ATT 81/822 8.3 179 99 5/8 -3/8 ATT 81/824 8.3 210 100 -1/2 ATT 8.35s25 8.4 123 102 -3/8
What market rate of return is currently required on these long-term AT&T bonds?
a. 8.125 percent b. 8.35 percent c. 8.0 percent d. 8.3 percent e 8.4 percent
5. If the net present value of a proposed project is positive, then:
a. the internal rate of return for the project is equal to the required rate of return. b. the internal rate of return for the project is zero. c. the internal rate of return for the project is less than zero d. the internal rate of return for the project is less than the required rate of return. e. the internal rate of return for the project is greater than the required rate of return.
6. Everything else held constant, if the market interest rate for a newly issued bond rises:
a. The bond’s price will fall. b. The coupon rate of the bond falls. c. The par value of the bond falls. d. The maturity of the bond will increase. e. The yield-to-maturity of the bond falls.
7. The Net Present Value (NPV) is a preferred as a capital budgeting evaluation method over the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) because:
a. The Internal Rate of Return method does not consider the time value of money. b. The Internal Rate of Return method does not include all the cash flows that occur at the beginning of the project. c. The Internal Rate of Return method does not consider the overall project length. d. The Internal Rate of Return method disregards cashflows that occur at the end of the project. e. The Internal Rate of Return method assumes that the intermediate cash flows are reinvested at the Internal Rate of Return.
8. A traditional technique for valuing assets is:
D0(1+g) Value = ------(k - g). The use of this model requires that: a. The firm is publicly traded. b. The required rate of return (k) is greater than the growth rate (g). c. The growth rate (g) is positive. d. The dividend is constant over time. e The earnings of the firm are growing faster than the dividends. 3
9. The primary use of the modified internal rate of return (MIRR) is to:
a. Adjust for projects with unequal lives. b. Include all relevant expected cash flows. c. Eliminate the possibility of multiple rates of return. d. Eliminate the possibility of an unrealistic reinvestment rate assumption. e. Adjust for the relative scale of a project.
10. Which of the following would reduce the value of a share of stock if all other things were held constant?
a. An increase in the expected rate of growth in earnings and dividends. b. An increase in the firm’s payout ratio. c. An increase in the required rate of return on the security. d. An increase in the level of expected dividends e. All of the above would reduce the value of a share of stock.
8 points 11. The current market price of a Jones' Company bond is $938.83. A 15% coupon interest rate is paid semi-annually (that is, one-half of 15% every six months), and the par value is equal to $1,000. What is the YTM (on an annual basis) if the bonds mature 25 years from today?
A. 2 percent F. 8 percent B. 3 percent G. 10 percent C. 4 percent H. 12 percent D. 5 percent I. 14 percent E. 6 percent J. 16 percent
8 points 12. The XYZ Company recently issued a 30-year, 5.4 percent semiannual coupon bond at par. After four months, the market interest rates on similar bonds increased to 6 percent. At what price should the bonds sell?
A. $ 989.21 F. $ 951.52 B. $ 932.13 G. $ 935.22 C. $ 956.82 H. $ 916.97 D. $ 933.75 E. $ 964.62 4
10 points 13. Assume the firm has been growing at a 25% annual rate and is expected to continue to do so for 3 more years. At that time, growth is expected to slow to a constant 3% rate. The firm maintains a 40% payout ratio, and this year's retained earnings were $2.4 million. The firm's beta is 1.2, the risk-free rate is 8%, and the market risk premium is 9%. If the market is in equilibrium, what is the market value of the firm's common equity (1 million shares outstanding)?
A. $13.10 million F. $18.42 million B. $20.75 million G. $14.18 million C. $15.44 million H. $19.50 million D. $17.47 million E. $12.15 million
10 points (5 points per section) 14. You are given the following data:
1. The risk-free rate is 4 percent. 2. The required return on the market is 15 percent. 3. The expected growth rate for the firm is 4 percent. 4. The last dividend paid was $2.00 per share. 5. Beta is 1.5.
A. At what price should the stock sell?
A. $30.30 F. $24.24 B. $18.91 G. $12.61 C. $25.21 H. $12.12 D. $18.18 E. $31.52
B. At what price should the stock sell if the following changes occur (assuming equilibrium before the changes were made)?
1. The inflation premium decreases by the amount of 0.5 percent. 2. An increased degree of risk aversion causes the required return on the market to go to 18 percent after adjusting for the changed inflation premium. 3. The expected growth rate increases to 5 percent. 4. Beta rises to 1.7.
A. $18.14 F. $21.60 B. $13.61 G. $12.96 C. $17.28 H. $22.68 D. $ 9.07 E. $ 8.64 5
8 points 15. Silicon Corp. recently issued 10-year, 15 percent coupon bonds at par value. Silicon's beta is 0.8; the optimal capital structure contains 45 percent debt/55 percent equity; and the marginal tax rate is 40 percent. If the expected return on the market is 18 percent and the treasury bill rate is 4 percent, estimate Silicon's weighted average cost of capital.
A. 13.95 percent F. 18.76 percent B. 20.89 percent G. 18.09 percent C. 11.06 percent H. 20.11 percent D. 11.79 percent E. 12.41 percent
8 points 16. If the required rate of return is 15 percent, what is the net present value of the project described below:
COST OF NEW EQUIPMENT $200,000 LIFE OF EQUIPMENT 10 YEARS SALVAGE VALUE $ 5,000 ANNUAL NET CASH FLOW $ 30,000
A. $-51,302 F. $-28,883 B. $-53,618 G. $-48,201 C. $-15,663 H. $-49,437 D. $-13,735 E. $-30,493 6
18 points (6 points per section) 17. Projects C has the following net cash flows: Year Project 0 -$7,000 1 3,000 2 2,000 3 1,500 4 4,000
A. If the required rate of return is 12 percent, what is the net present value for the project? A. $ 658.39 E. $ 683.47 B. $ 882.70 F. $ 920.81 C. $ 431.15 G. $ 477.77 D. $ 206.84 H. $ 156.33
B. What is the Internal Rate of Return for the project? A. 19.97 percent E. 21.48 percent B. 13.40 percent F. 15.75 percent C. 14.69 percent G. 18.95 percent D. 17.69 percent H. 13.15 percent
C. What is the profitability index for the project? A. 1.00 E. 1.18 B. 1.04 F. 1.22 C. 1.06 G. 1.29 D. 1.13 H. 1.34 7
Formula and Answer Sheet
Price = Cashflowt (1 + k)t
Price = Coupon(PVIFAK,N) + Par(PVIFK,N)
P0 = D0(1+gc)/(k-gc) k = (D0(1+gc)/P0) + gc
E(Ri) = RF + (E(RM) - RF)
Kre = Rf + (Rm - Rf) = (D0 (1 + g)/P0) + g EPS = (EBIT-I)(1-TR) shares Kne = (D0 (1 + g)/(P0(1 - F)) + g DOL = Q(P - VC) Ka = wdkd(1-tr) + wpkp + weke Q(P – VC) - FC
DTL = DOL x DFL DFL = EBIT EBIT - I DPS = EPS x payout ratio
NCFt NPV NPV = -C0 + ------EAA = ------(1+k)t PVIFA
NCFt C0 + NPV -C0 = ------PI = ------t (1+IRR) C0
BPre = Retained Earnings / we
1. ______3 pts 11. ______8 pts 2. ______3 pts 12. ______8 pts 3. ______3 pts 13. ______10 pts 4. ______3 pts 14.A ______5 pts 5. ______3 pts B ______5 pts 6. ______3 pts 15. ______8 pts 7. ______3 pts 16. ______8 pts 8. ______3 pts 17. A. ______6 pts 9. ______3 pts B. ______6 pts 10. ______3 pts C. ______6 pts