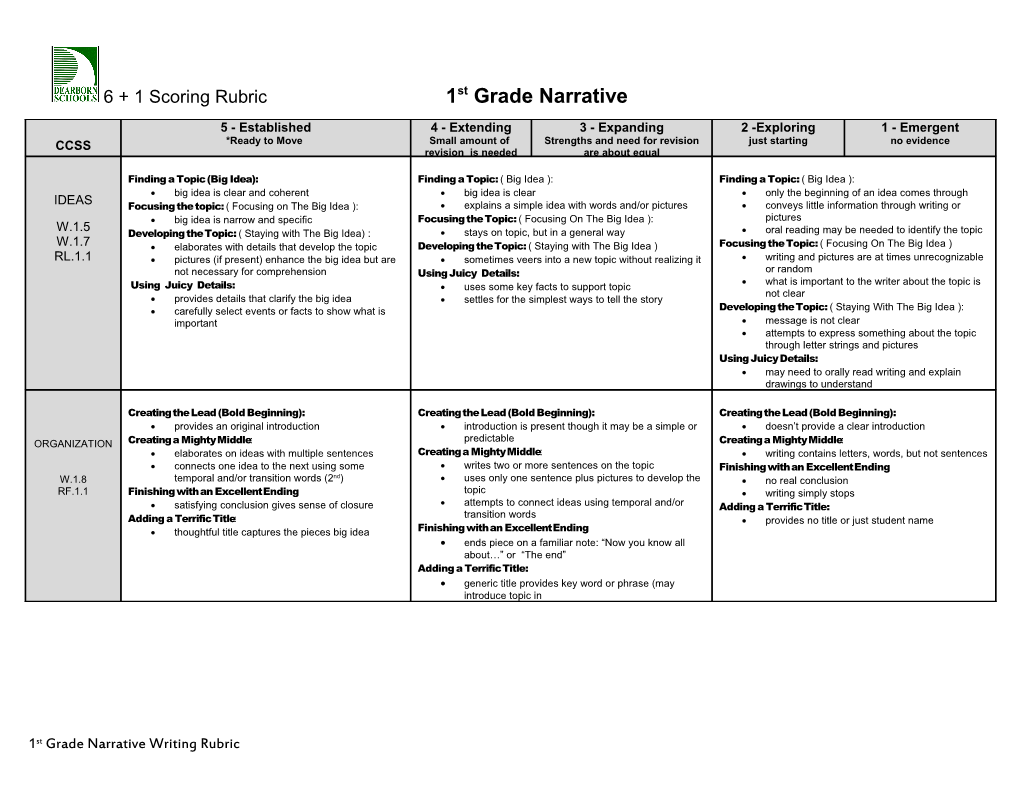
6 + 1 Scoring Rubric 1st Grade Narrative 5 - Established 4 - Extending 3 - Expanding 2 -Exploring 1 - Emergent CCSS *Ready to Move Small amount of Strengths and need for revision just starting no evidence revision is needed are about equal
Finding a Topic (Big Idea): Finding a Topic: ( Big Idea ): Finding a Topic: ( Big Idea ): big idea is clear and coherent big idea is clear only the beginning of an idea comes through IDEAS Focusing the topic: ( Focusing on The Big Idea ): explains a simple idea with words and/or pictures conveys little information through writing or big idea is narrow and specific Focusing the Topic: ( Focusing On The Big Idea ): pictures W.1.5 Developing the Topic: ( Staying with The Big Idea) : stays on topic, but in a general way oral reading may be needed to identify the topic W.1.7 elaborates with details that develop the topic Developing the Topic: ( Staying with The Big Idea ) Focusing the Topic: ( Focusing On The Big Idea ) RL.1.1 pictures (if present) enhance the big idea but are sometimes veers into a new topic without realizing it writing and pictures are at times unrecognizable or random not necessary for comprehension Using Juicy Details: what is important to the writer about the topic is Using Juicy Details: uses some key facts to support topic not clear provides details that clarify the big idea settles for the simplest ways to tell the story carefully select events or facts to show what is Developing the Topic: ( Staying With The Big Idea ): important message is not clear attempts to express something about the topic through letter strings and pictures Using Juicy Details: may need to orally read writing and explain drawings to understand
Creating the Lead (Bold Beginning): Creating the Lead (Bold Beginning): Creating the Lead (Bold Beginning): provides an original introduction introduction is present though it may be a simple or doesn’t provide a clear introduction predictable ORGANIZATION Creating a Mighty Middle: Creating a Mighty Middle: elaborates on ideas with multiple sentences Creating a Mighty Middle: writing contains letters, words, but not sentences connects one idea to the next using some writes two or more sentences on the topic Finishing with an Excellent Ending W.1.8 temporal and/or transition words (2nd) uses only one sentence plus pictures to develop the no real conclusion RF.1.1 Finishing with an Excellent Ending topic writing simply stops attempts to connect ideas using temporal and/or satisfying conclusion gives sense of closure Adding a Terrific Title: transition words Adding a Terrific Title: provides no title or just student name thoughtful title captures the pieces big idea Finishing with an Excellent Ending ends piece on a familiar note: “Now you know all about…” or “The end” Adding a Terrific Title: generic title provides key word or phrase (may introduce topic in
1st Grade Narrative Writing Rubric 5 - Established 4 - Extending 3 - Expanding 2 -Exploring 1 - Emergent CCSS *Ready to Move Small amount of Strengths and need for revision just starting no evidence revision is needed are about equal
Establishing a Tone: (Expressing a Feeling ): Establishing a Tone: ( Expressing a Feeling ): Establishing a Tone: (Expressing a Feeling ): cares about the topic and it shows attempts to speak to the audience, but it is mostly unsure how the writer feels about the topic VOICE speaks to the intended audience generic Communicating the Purpose: ( Sparkle And Pizzazz ) Communicating the Purpose: ( Sparkle And Pizzazz ) Communicating the Purpose: (Sparkle And Pizzazz ): reasons for creating the piece are unclear Informational writing reflects strong commitment informational writing shows some engagement with Creating a Connection to the Audience: ( Reaching Out to topic; communicates why the topic is important topic W.1.5 The Reader ) Creating a Connection to the Audience: ( Reaching Out W.1.7 Creating a Connection to the Audience Reaching Out no awareness of audience RF.1.4 The Reader ): The Reader ) copied writing from another source mindful of the audience; wants the reader to “get attempts to create a connection Saying Things in New Ways: it” Saying Things in New Ways voice does not pop out Saying Things in New Ways: creates 1-2 moments that catch the reader’s pictures and words are predictable Expresses ideas in new ways attention
WORD Choosing Strong Verbs: ( Choosing Zippy Verbs ): Choosing Strong Verbs: ( Choosing Zippy Verbs ): Choosing Strong Verbs: ( Choosing Zippy Verbs ): CHOICE uses many “action words” uses verbs correctly, but not many action verbs unsure how to use verbs lively verbs add energy uses forms of “to be” almost exclusively neglects verbs or uses them incorrectly Selecting “Just Right” Words: ( Picking “ Just Right Selecting “Just Right” Words: ( Picking “ Just Right” Selecting “ Just Right” Words: ( Picking “ Just Right” L.1.4 “Words ): Words ): Words ): L.1.5 uses words and/or phrases that catch the reader’s attempts to use a word and/or phrase that is catchy uses simple words and/or letter strings L.1.6 attention most words and phrases are basic Stretching for Never-Before-Tried Words: RF.1.3 selects words carefully related to the topic Stretching for Never-Before-Tried Words: only uses known words (name, high frequency Stretching for Never-Before-Tried Words: attempts to use new words, but mostly settle for the words, words from the walls, etc.) tries new words to communicate clearly first word that comes to mind Choosing Words to Create Meaning: chooses best word over the first word Choosing Words to Create Meaning: misuses words making it difficult for the reader to Choosing Words to Create Meaning: uses basic language to explain or tell, which makes understand uses everyday words well it hard for the reader to get a clear picture uses descriptive language to explain or tell occasionally misuses words
Building Complete Sentences: Building Complete Sentences: Building Complete Sentences: SENTENCE carefully crafts sentences that are varied and uses mostly simple, grammatically correct sentences struggles with sentence construction FLUENCY grammatically correct sentence fragments are unintentional and may Starting Sentences in Different Ways: sentence fragments add to the flow of the piece disrupt the flow of the piece begins each line the same way Starting Sentences in Different Ways: Starting Sentences in Different Ways: repeats familiar words and letters L.1.1 begins sentences in a variety of ways most sentences begin the same way Varying Sentence Lengths: L.1.2 Varying Sentence Lengths: Varying Sentence Lengths: most words stand alone L.1.6 creates sentences of various lengths; some short most sentences are of equal length (follow the same Making Smooth Sounding Sentences: RF.1.4 and some long pattern) reading aloud is a challenge Making Smooth Sounding Sentences: longer sentences may go on and on only the writer can read the piece with any sense piece is easy to read aloud Making Smooth Sounding Sentences: of continuity may attempt to use conjunctions to connect ideas some sentences read smoothly, others are choppy or awkward piece can be read aloud without too much trouble
1st Grade Narrative Writing Rubric 2 5 - Established 4 - Extending 3 - Expanding 2 -Exploring 1 - Emergent CCSS *Ready to Move Small amount of Strengths and need for revision just starting no evidence revision is needed are about equal
Spelling: ( Spelling Well ): Spelling: ( Spelling Well ): Spelling: ( Spelling Well ): CONVENTIONS spells high frequency words correctly, and less spells simple high frequency words correctly or uses letter strings and/or pre-phonetic spelling familiar words phonetically phonetically L.1.2 Capitalizing Correctly: RF.1.2 spelling doesn’t impede the reader unfamiliar words present a challenge shows no control over the use of capitals RF.1.3 Capitalizing Correctly: Capitalizing Correctly: Punctuating Effectively: ( Punctuating Powerfully ): uses basic capitalization rules with consistency mostly capitalizes the first words in a sentence and neglects punctuation or uses punctuation (beginning of a sentence, proper names, pronoun sometimes proper nouns and the pronoun I incorrectly I) Punctuating Effectively: ( Punctuating Powerfully ): Applying Basic Grammar:: Punctuating Effectively: ( Punctuating Powerfully ): inconsistent use of end marks limited writing makes it difficult to determine what uses end marks correctly and sometimes Applying Basic Grammar: the writer knows about grammar and usage creatively mistakes in grammar and usage are throughout the Applying Basic Grammar: piece, but can be easily corrected shows control in applying the basic rules of * Upon obtaining a 5 in all traits, proceed on to the 2nd-3rd Grade Narrative Writing Rubric. Adapted by Dearborn Public Schools from Ruth Culham’s “6 Traits of Writing” and the English Language Arts Common Core State Standards
1st Grade Narrative Writing Rubric 3