Name: ______Date: ______Period: ____ Evolution Test (Chapter 15 all, 16 all, 17-1 and 17-4) Test Date: ______To prepare for the test over Chapters 15-17, you should read the chapters, review your notes, study the warm ups, and any assignments we worked on during this time. Any words you do not know the meaning of, you should look up in the glossary of your book.
1. The founder of the Modern Scientific Theory of Evolution is considered to be ______. 2. Define Scientific Theory______3. Describe the following people’s influence on Darwin’s thinking and their major scientific contributions a. Charles Lyell
b. Thomas Malthus
4. Define the word species______. 5. How did speciation occur in the Galapagos finches? ______
6. Darwin’s Theory can be summarized by several statements. Describe each statement and give an example of each.
Statement Description Example Organisms differ and variations are inheritable
Organisms produce more offspring that can survive Survival of the Fittest
Descent with Modification
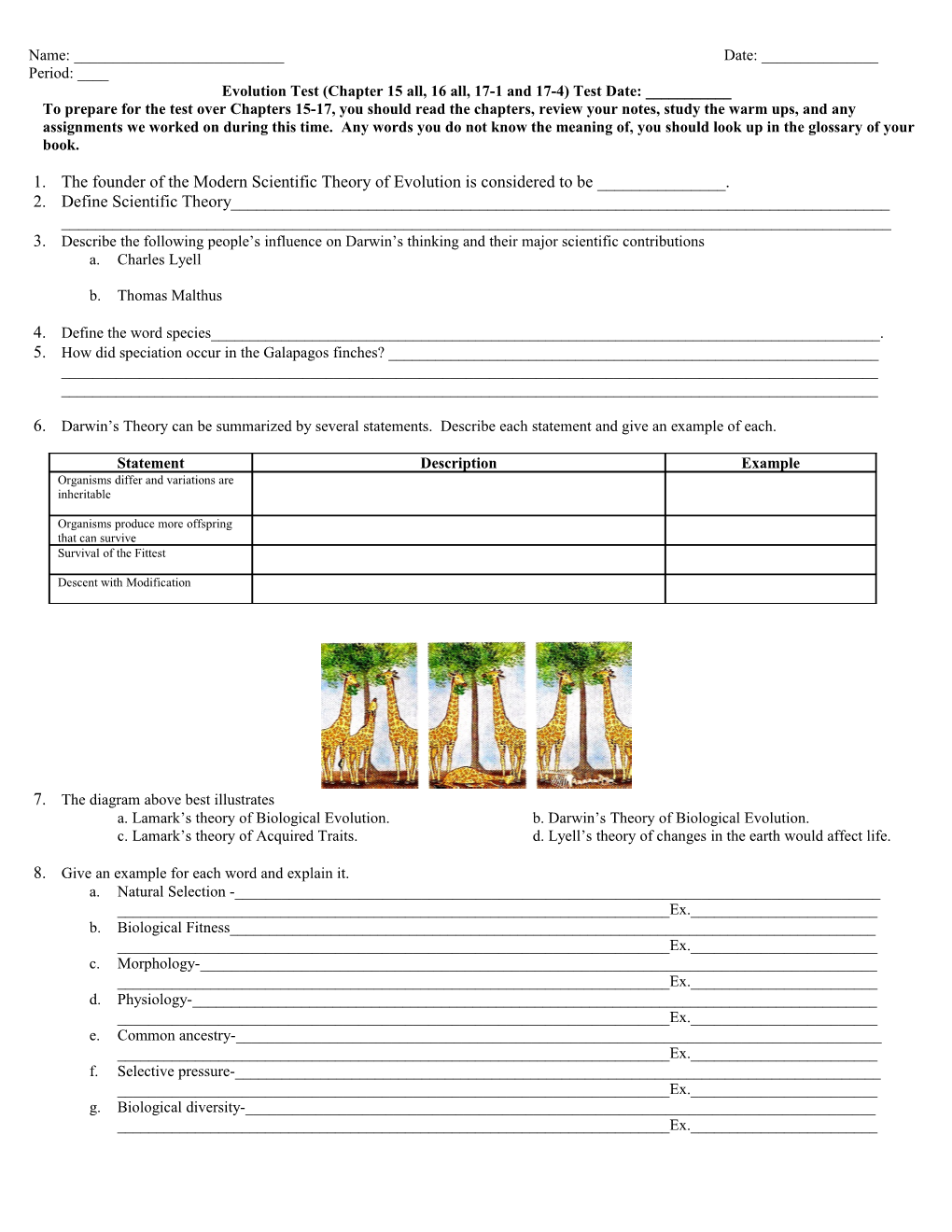
7. The diagram above best illustrates a. Lamark’s theory of Biological Evolution. b. Darwin’s Theory of Biological Evolution. c. Lamark’s theory of Acquired Traits. d. Lyell’s theory of changes in the earth would affect life.
8. Give an example for each word and explain it. a. Natural Selection -______Ex.______b. Biological Fitness______Ex.______c. Morphology-______Ex.______d. Physiology-______Ex.______e. Common ancestry-______Ex.______f. Selective pressure-______Ex.______g. Biological diversity-______Ex.______
9. What adaptation does this organism have that makes it well-suited to its environment? ______10. What is the title of Darwin’s most famous publication? ______11. How could you identify if two organisms are members of the same species or different species? ______12. Name and explain the five major types of evidence that support the theory of biological evolution.
Name Description
13. Complete the following table.
Structures Identify whether the picture represents Why are they considered vestigial, homologous vestigial, homologous or analogous or analogous? structures. Letter C indicates the pelvic bone and the under developed legs in the Baleen whale.
1.______
Compare the two wings.
2.______Compare each shaded bone
3. ______
14. Which type of structure indicates common ancestry? ______
15. There are two sources of genetic variation. List and describe them. a. b.
16. What is the relative frequency of an allele in a population? ______
17. A change in allele frequencies over time leads to ______evolution. (Choose micro- or macro-)
18. What is a polygenic trait? (Review Chapter 16 and notes)
19. The distribution of a polygenic trait will form a ______- shaped curve, as shown to the right.
20. What is being plotted on the x- axis? ______and y- axes ______?
21. There are three kinds of selection on a polygenic trait. Look at the following graphs and identify i.Type of selection, ii. How is the population changing? a. b. c.
Type of Selection: ______Type of Selection______Type of Selection______How is the population changing? _____ How is the population changing?_____ How is the population changing?______22. Define speciation. ______
23. What kind of isolation must occur for speciation to take place? ______
24. What selective pressure created the different species of finches below? ______
25. Darwin hypothesized that the finches had come from a ______from the mainland and through the process called ______the birds developed specialized beaks to survive on different islands with different food sources.
26. Study the table above and identify the common name of the finch that most likely survive a major drought? ______27. There are three kinds of Reproductive Isolating Mechanisms. List and describe them. Give one example for each.
Reproductive Isolating Description Example Mechanism
Geographic
Temporal
Behavioral
28. ______are preserved remains of ancient organisms. 29. In ______dating scientists calculate the actual age of a fossil based on the amount of radioactive isotopes it contains.
30. Relative dating involves ______.
31. List two reasons organisms become extinct. a. ______b. ______32. Pattern of evolution in which long stable periods are interrupted by brief periods of more rapid change is called______.
33. ______is a process by which a single species evolves into many different forms over a period of time.
34. Define – Extinction______Ex.______35. Define- Convergent Evolution______Ex.______36. Define- Coevolution______Ex.______
35. According to Figure 14-4, the correct chronological order of organisms as they develop is _____. a. birds, dinosaurs, jawed fish, prokaryotes b. dinosaurs, jawed fish, birds, prokaryotes c. jawed fish, dinosaurs, prokaryotes, birds d. prokaryotes, jawed fish, dinosaurs, bird
36. What numbered layer of sediment contains the oldest fossils in the picture to the right? ______
3.
2.
1.