Cerebral Palsy
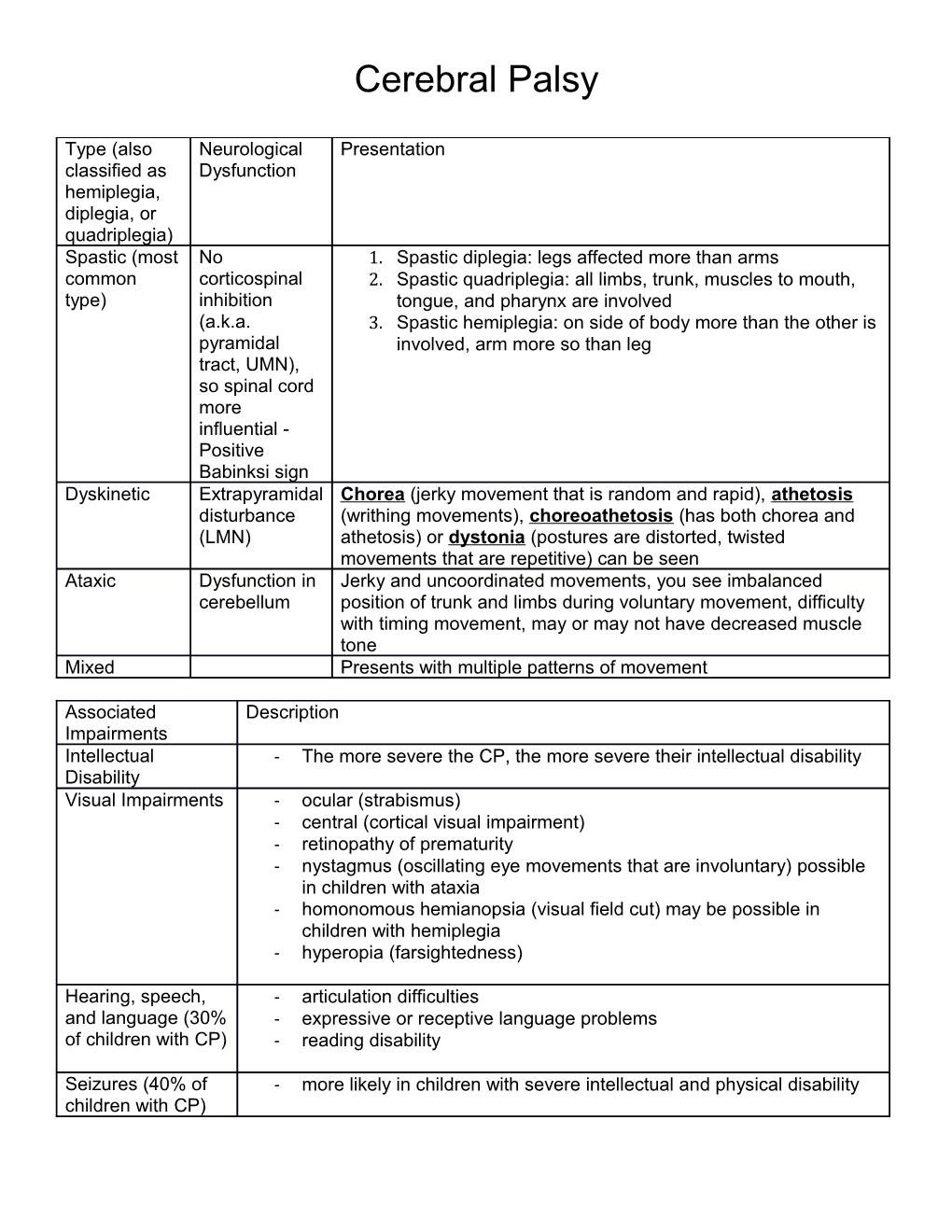
Type (also Neurological Presentation classified as Dysfunction hemiplegia, diplegia, or quadriplegia) Spastic (most No 1. Spastic diplegia: legs affected more than arms common corticospinal 2. Spastic quadriplegia: all limbs, trunk, muscles to mouth, type) inhibition tongue, and pharynx are involved (a.k.a. 3. Spastic hemiplegia: on side of body more than the other is pyramidal involved, arm more so than leg tract, UMN), so spinal cord more influential - Positive Babinksi sign Dyskinetic Extrapyramidal Chorea (jerky movement that is random and rapid), athetosis disturbance (writhing movements), choreoathetosis (has both chorea and (LMN) athetosis) or dystonia (postures are distorted, twisted movements that are repetitive) can be seen Ataxic Dysfunction in Jerky and uncoordinated movements, you see imbalanced cerebellum position of trunk and limbs during voluntary movement, difficulty with timing movement, may or may not have decreased muscle tone Mixed Presents with multiple patterns of movement
Associated Description Impairments Intellectual - The more severe the CP, the more severe their intellectual disability Disability Visual Impairments - ocular (strabismus) - central (cortical visual impairment) - retinopathy of prematurity - nystagmus (oscillating eye movements that are involuntary) possible in children with ataxia - homonomous hemianopsia (visual field cut) may be possible in children with hemiplegia - hyperopia (farsightedness)
Hearing, speech, - articulation difficulties and language (30% - expressive or receptive language problems of children with CP) - reading disability
Seizures (40% of - more likely in children with severe intellectual and physical disability children with CP) Cerebral Palsy Feeding and - hypotonia growth problems - weak suck - poor coordination of swallow - tonic bite reflex - hyperactive gag reflex - tongue thrust - gastroesophageal reflux - constipation
Osteopenia - reduced bone density = weak bones - increased risk of fractures
Intervention Purpose Neurodevelopmental Therapy (NDT) - to help the child develop more typical movement patterns - includes positioning, therapeutic handling, play - goal is to normalize tone and improve movement control during activity
Constraint-induced therapy (a.k.a. forced-use - for children with CP hemiplegia therapy) - constrain involved side to force use of less involved side Physical exercise (such as dancing, swimming, - strengthen muscles and bones playing more physical games) - improve motor skills - prevent the development of contractures
Orthotic devices - ankle-foot orthosis (AFO) to stabilize foot and allow for stretch to Achilles tendon - resting hand splint to hold the thumb abducted and wrist in neutral or slightly extended to prevent deformity
Positioning (seating) devices - seating systems designed for the child to prevent contractures and joint deformities as a result of the spasticity
Casting - to reduce or inhibit tone - made for UEs or Les - can be used for immobilization for stability during weight-bearing activity - casts position spastic muscles so they are lengthened and stretched gently - serial casting can be used to slowly increase range of motion if there is a Cerebral Palsy contracture already present
Adaptive Equipment - crutches (forearm Lofstrand crutches) - walkers (posterior walker) - wheelchairs with solid seat/back - wheelchair with trunk supports - wheelchair with tray - wheelchair with high back that can tilt 10-15 degrees - seating cushions for wheelchair - molded inserts for wheelchair - power wheelchairs - supportive strollers - car seat or car bed
Assistive Technology - computers - artificial speech - articifical sight - iPad - Wii