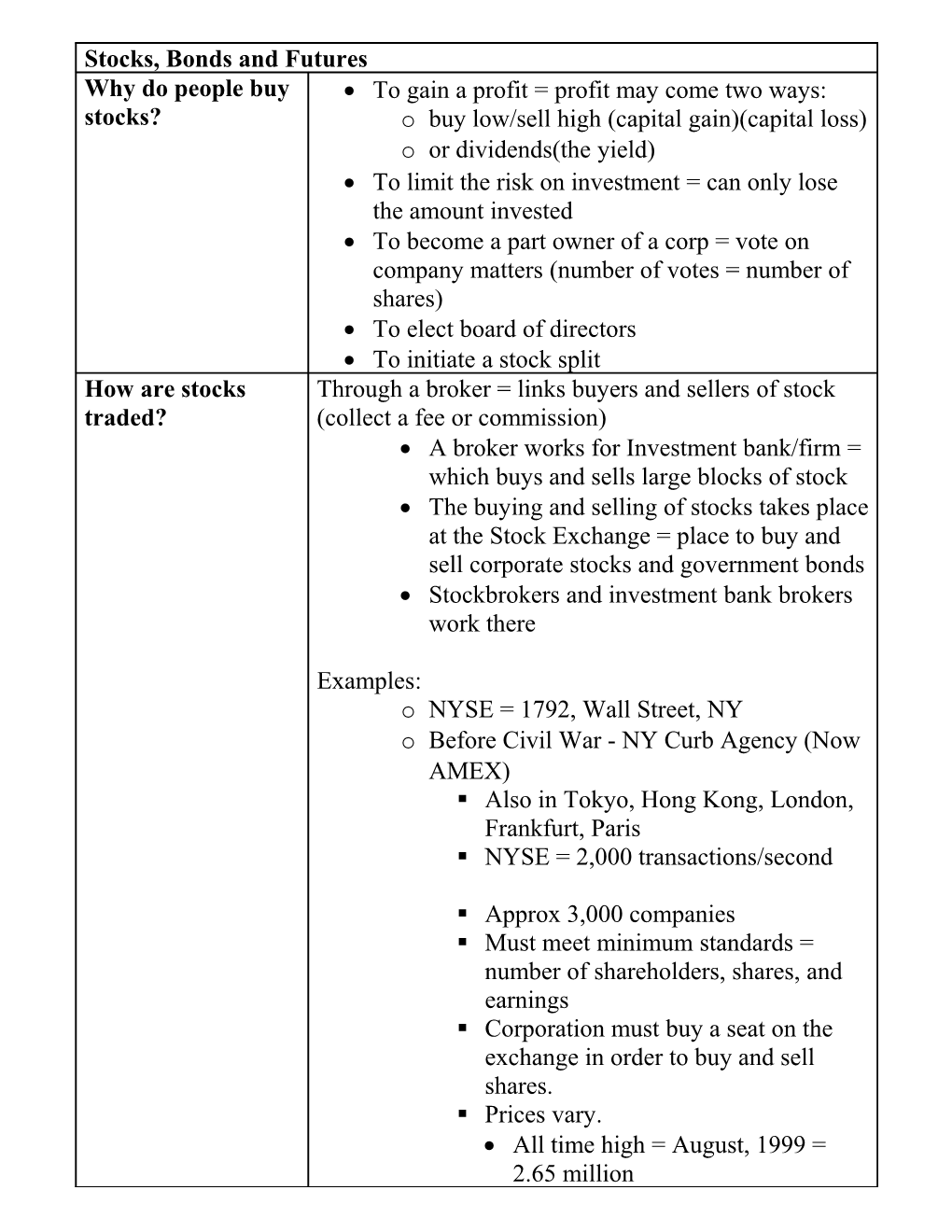
Stocks, Bonds and Futures Why do people buy To gain a profit = profit may come two ways: stocks? o buy low/sell high (capital gain)(capital loss) o or dividends(the yield) To limit the risk on investment = can only lose the amount invested To become a part owner of a corp = vote on company matters (number of votes = number of shares) To elect board of directors To initiate a stock split How are stocks Through a broker = links buyers and sellers of stock traded? (collect a fee or commission) A broker works for Investment bank/firm = which buys and sells large blocks of stock The buying and selling of stocks takes place at the Stock Exchange = place to buy and sell corporate stocks and government bonds Stockbrokers and investment bank brokers work there
Examples: o NYSE = 1792, Wall Street, NY o Before Civil War - NY Curb Agency (Now AMEX) . Also in Tokyo, Hong Kong, London, Frankfurt, Paris . NYSE = 2,000 transactions/second
. Approx 3,000 companies . Must meet minimum standards = number of shareholders, shares, and earnings . Corporation must buy a seat on the exchange in order to buy and sell shares. . Prices vary. All time high = August, 1999 = 2.65 million Low = 1871 = $2,750 o Over-the-Counter Market (OTC) o NASDAQ = Smaller corporations which can’t meet the standards of the NYSE o If too small for NASDAQ = broker may be able to deal directly with Corporation What Determines Shares typically traded in lots, or amounts, of 100 Stock Prices? Example: Seller asks for $38.12 per share Buyer offers $37.37 per share They may agree on something between the two This happens very quickly and 1000s of times per second
When many buyers compete for a scarce stock = price goes up When few buyers compete for a large supply = price goes down
So…demand affects stock prices.
But what affects demand for a stock? o Corporate finances good = “blue chip” stock Investor expectations = if investors think the price of a stock will go up = demand goes up = causing the price to go up o If investors think the price of a stock will go down = demand goes down = causing price to go down
Bull Market = Dow steadily rises for a period of time
Bear Market = Dow steadily falls for a period of time
External Forces = Sometimes things happen that are out of the control of buyers/sellers Example: Someone put poison in a few bottles of Tylenol capsules in 1982 Price for Johnson & Johnson stock fell Also…unemployment, inflation, interest rates, national election
Also…international events = revolutions, war terrorist attacks, etc Why should you Borrower: Earn yields (interest) consider buying bonds? Lender: Use money as capital What is good about Good safe way to save money and earn interest. corporate bonds? o Helps with the creation of capital. o Business expands. o Supply goes up. o Prices come down What is good about Even safer way to save money and earn interest. government bonds? Helps government meet its obligations. o Theoretically could relieve tax burden Why buy futures? In finance, a futures contract is a standardized contract, What are they traded on a futures exchange, to buy or sell a certain anyway? underlying instrument at a certain date in the future, at a pre-set price.
The future date is called the delivery date or final settlement date.
The pre-set price is called the futures price.
The price of the underlying asset on the delivery date is called the settlement price.
Regulation of the Securities Industry = Clayton Antitrust Act, 1914 Federal Securities Act, 1933 Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) for enforcement.
Prospectus = detailed fact sheet containing data on a company’s finances must be submitted Borrowing and Credit What is borrowing Borrowing is: It is the transfer of a specified amount on credit? of money from a lender to a borrower for a specified length of time. When a bank loans money to someone or some business, it amounts to the creation of money. o Say businessperson goes to the bank and asks to borrow $10,000. o Bank approves the loan and deposits $10,000 into the businessperson’s account. The money came out of the banks reserves (not counted in the money supply). o Now it is in a usable form. Businessperson can write checks, use cash, etc. Money has been created. Buying on credit Does not involve a direct exchange of money. Can pay for things without cash. Why do consumers •Paying a small amount every month makes large borrow money or purchases more affordable for many people. rely on credit? •Principal Interest Collateral – house in mortgage loan, car in car loan. •Installments – payments (longer the length of loan, the less per month – but the more interest will be paid) What is a Credit An estimation of the probability of you being able to rating? repay what you have borrowed Ability to pay Assets credit history What is a Credit It is a credit reporting service that businesses use to bureau? decided whetehr or not to loan or approve credit for you. Equifax What are Credit They are billed every 28 or 30 days terms? Includes Finance charge – total cost of credit Annual percentage rate (APR) – total cost of credit per year Usury – charging credit above the legal limit. What happens if May have to file Bankruptcy – legal declaration of you abuse credit? inability to pay debts. Remains on credit history for 14 years. How does Credit Use of credit helps satisfy many peoples’ wants impact the and needs. economy? Also stimulates economic growth by promoting economic stability. o One of the goals of the U.S. . Occurs when the output of goods and services increases per person . during a specified period of time. o Shows overhead How does credit Another goal of the U.S. promote stability? Occurs when employment is high and prices are stable Credit, when used responsibly, promotes high employment and stable prices How? As consumers use credit demand increases Production increases Employment increases
Supply now meets demand This is market EQUILIBRIUM!!