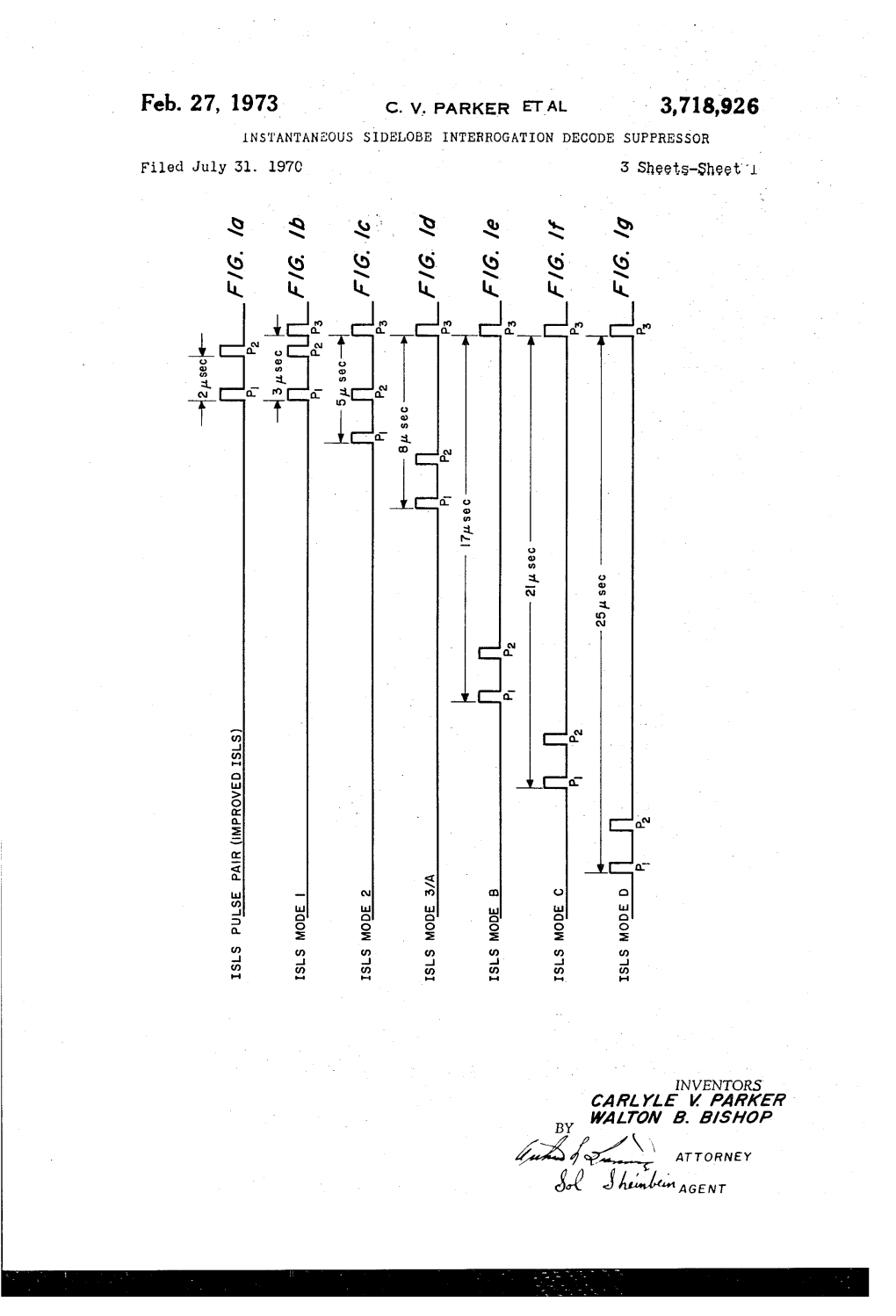
Feb. 27, 1973 C. V. Parker ETAL 3,718,926 INSTANTANEOUS SIDELOBE INTERROGATION DECODE SUPPRESSOR Filed July 3L
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Communications-Electronics (C-E) Managers
DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE Air Force Qualification Training Headquarters US Air Force Package 2EXXX-201LB Washington DC 20330-1680 1 October 1999 COMMUNICATIONS- ELECTRONICS (C-E) MANAGER’S HANDBOOK 1. This Air Force Qualification Training Package (AFQTP) has been developed to provide information on Communications Electronics (C-E) systems likely to be encountered by senior NCOs as they assume C-E management responsibilities. 2. Review Air Force publishing bulletins and AFIND 8 to identify available training materials. 3. Maintain this AFQTP IAW AFIs 36-2201 and 36-2233. Routine changes will be accomplished via page changes and urgent changes will be disseminated via message. Submit recommended AFQTP improvements/ corrections to the 81 TRSS Qualification Training Flight (81 TRSS/TSQS), 601 D Street, Keesler AFB MS 39534-2229. BY ORDER OF THE SECRETARY OF THE AIR FORCE OFFICIAL JOHN W. HANDY, Lieutenant General, USAF Deputy Chief of Staff/Installations and Logistics 1 Atch Handbook ____________ Supersedes AFQTP 300X0-201LB, dated 21 Nov 1996 OPR: HQ USAF/LGMM OCR: 81 TRSS/TSQA DISTRIBUTION: F TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE Resource constraints in the Air Force are impacting the availability of our most valuable resource - manpower. This condition which will continue to exist in the future, makes it essential for the work force to be effectively trained to perform duties within each level of an Air Force Specialty (AFS). This handbook is another tool that will enable the Air Force and each MAJCOM to place the needed emphasis on total career field training. This handbook is identified as a mandatory training requirement in several Career Field Training Education Plan. -

US National Aviation Standard for the Mode Select Beacon System
DEPAF~TMENT OF TRANSPORTATION ORDER FE )ERAL.AVIATION ADMINISTRATION 6365.1A 1/3/83 SUBJ: U.S. NATIONAL AVIATION STANDARD FOR THE MODE SELECT BEACON SYSTEM (MODE S) 1. PURPOSE. This order establishes the U.S. National Aviation Standard for the *Mode Select Beacon System (Hode S) which defines the performance requirements of the Mode S system. * 2. DISTRIBUTION. The order is distributed to the director level in Washington with a division level distribution in the Acquisition and Materiel, Air Traffic, Program Engineering and Maintenance, and Systems Engineering Services, the Offices of Airworthiness, Flight Operations, and Budget; to the director level in the regions, with division level distribution in Air Traffic, Airway Facilities, and Flight Standards Divisions; to the director level at the Aeronautical Center with division level distribution to the FAA Depot; and to the director level at the FAA Technical Center with division level distribution in the Systems Test and Evaluation and Systems Simulation and Analysis Divisions. 3. CANCELLATION. Order 6365.1, u.s. National Aviation Standard for the Discrete Address Beacon System (DABS), dated December 9, 1980; is cancelled. 4 • BACKGROUND. * a. It was recognized in a study conducted for the Department of Transportation in 1968, that improvements would be required in the Air Traffic Control Radar Beacon System (ATCRBS) to support air traffic control through the 1990's. Also recognized was the need for a data link system to support enhanced automation with sufficient capacity to meet traffic growth through the same period. b. The concept that emerged was a discrete address beacon system with an integral data link. -

Student Comments
CHAPTER 8 IDENTIFICATION EQUIPMENT LEARNING OBJECTIVES After you finish this chapter , you should be able to do the following: 1. Describe a basic IFF system and how it operates. 2. Identify the AIMS MK XII IFF system components and explain their operation. 3. Explain the use of the AIMS MK XII equipment in a jamming environment and in emergency (Mode 4) operations. INTRODUCTION ATCRBS Air Traffic Control Radar Beacon System Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) is the system that IFF Identification Friend or Foe ships and stations use to identify friendly aircraft and MK XII Mark XII ships. Since hostile aircraft, with their fast speeds, pose S System a greater threat than ships, we will concentrate on aircraft IFF procedures. However, some of the IFF Today, all U.S. armed forces use the AIMS (Mark procedures also can be used for identifying ships. XII IFF) system, primarily to identify friendly units Basically, the ship or station desiring to know whether rapidly and positively. They also use AIMS for an approaching aircraft is friendly sends out a special tracking and controlling aircraft. In the military world, electronic signal in the direction of the aircraft. The high-speed aircraft present a critical problem in detection, identification, tracking, and evaluation. signal triggers an electronic response from an IFF Time is extremely critical when aircraft are transmitter in friendly aircraft. This response signal, in approaching at Mach (speed of sound) speeds. To turn, generates a coded symbol on the radar scope of provide ample time for initiating appropriate action, a the interrogating ship or station. -

Low-Cost Measurement for a Secondary Mode S Radar Transmitter
Low-Cost Measurement for a Secondary Mode S Radar Transmitter Angel Parra-Cerrada, Vicente Gonzalez-Posadas, Jose Luis Jimenez-Martin, Alvaro Blanco-del-Campo, Wilmar Hernandez, Senior Member, IEEE, and Carlos Calderon-Cordova Abstract—A low-cost, multiple-purpose, and high-precision MSSR [3]. However, these papers do not deal with the up-link timing test setup for the measurements of secondary signal of the MSSR taking into consideration the modulation Mode S radar transmission signal was proposed. The goal performances of this signal. This paper 34 shows a detailed was to fully guarantee compliance of the proposed transmitter under test with the really hard International Civil Aircraft analysis of the transmitted signal by an MSSR, allowing Organization requirements using traditional measurement us to verify compliance with International Standards and equipment, which was difficult or even impossible to ensure Recommended Practices [4]. This verification is made by using up to now. The low-cost structure proposed in this paper a exible user-controlled method that is independent of any allows the user to perform measurements independently of manufacturer of specific commercial test equipment, which the measurements performed by the pieces of test equipment shelled by the manufacturer of radar, which is a very important in many cases is the same as the manufacturer of the radar. aspect since the independence of the verifications is a mandatory This method guarantees that problems cannot be undetected requirement established by the safety standards of civil aviation. because of the same implementation of some hardware is used The proposed setup has been used to verify several transmitters in transmitter and test equipment. -

DABS/ATCRBS Transponder Bench Test Program
FAA-RD-73-160 Project Report ATC-25 DABS/ATCRBS Transponder Bench Testing Program J.R. Samson J.D. Welch E.R. Becotte E.A. Crocker H.D. Schofield 28 November 1973 Lincoln Laboratory MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY LEXINGTON, MASSACHUSETTS Prepared for the Federal Aviation Administration, Washington, D.C. 20591 This document is available to the public through the National Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA 22161 This document is disseminated under the sponsorship of the Department of Transportation in the interest of information exchange. The United States Government assumes no liability for its contents or use thereof. TECHNICAL REPORT STANDARD TIT LE?AGI 1. R.pe,t Ne. 2, Gov.rnm.nt Accession No. 3. Recipi.nl’s CotaleQ No. FAA-RD-73-160 4. ~,d. and Subtitl. 5. R.po,t Dole 28 Novem&r 1973 DARS/ATCRBS Transponder Wnch Tesfing ProWam 6. Per formtng OrQonizotien Code 9. Autho,(,) 8. Performing OrgenizaNon RePort No. J.R. Samson,J.D. Welch, E. R. Becotte, E.A. Grocker andH.D. Schofield P.TC-25 9, Performing Orgon+zation Neme and Address 10, Werk Unit No. Reject No. 034-241-012 Massachusettsbstitute of Tectiolou Lincok Laboratory II. contractor Gront No. P. 0. Box 73 DOT-FA 72wAI-261 Lexin@on, Massachtisetts 02173 13, Type of R.po,t and Period Covered 12. SPomsQrin9AgencyNow.o.d.Adir.ss fioject Report DepartmentofTransportation Federal Aviation AdmitisWation Systems Re8earch and DevelopmentService }4, SPonsoringAg6ncYCede... Washington,DC. 20591: 15, Supplemen,o,y Noles Tbework reported inthisdocummt%vas. Frfomedat Lincoln Laboratory, acenterf orre@earcho peratedby MassachusettsInstituteof TectioloW under"Air Force Contract Fl9628-73-C-OOO2; $6. -

Uc10x Installation Manual
UC10x Installation Manual UC100, UC101, UC102 and UC103 DRAFT 145 E Jewett Blvd STE 301 p. 509-493-XXXX [email protected] White Salmon, WA 98672 www.ucflight.com UC10x Installation Manual Contact Information Urban Canyon Flight, Inc. 145 E Jewett Blvd STE 301 White Salmon, WA 98672 U.S.A. Phone: (509) 493-XXXX - 8:00 AM – 5:00 PM (Pacific Time) Monday – Friday Urban Canyon Flight Technical Support available 7:00 AM – 4:00 PM (Pacific Time) Monday – Friday [email protected] Copyright ©2017 Urban Canyon Flight, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied, transmitted, disseminated or stored in any storage medium, for any purpose without the express written permission of Urban Canyon Flight Inc (“UCF”). UCF hereby grants permission to download a single copy of this manual and of any revision to this manual onto a hard drive or other electronic storage medium to be viewed for personal use, provided that such electronic or printed copy of this manual or revision must contain the complete text of this copyright notice and provided further that any unauthorized commercial distribution of this manual or any revision hereto is strictly prohibited. UCF reserves the right to revoke this permission at any time without cause, at which point the original manual and all electronic or hardcopies must be permanently deleted. Information in this document is subject to change without notice. UCF reserves the right to change or improve its products and to make changes in the content without obligation to notify any person or organization of such changes. -

Digital Avionics Systems Conference Results at That Time
CANDIDATE REQUIREMENTS FOR MULTILATERATION AND ADS-B SYSTEMS TO SERVE AS ALTERNATIVES TO SECONDARY RADAR PatrickJ. Martone, US DOT Volpe Center, Cambridge, MA George E. Tucker, NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA Abstract the ATCBI-6 secondary surveillance radar. These criteria were developed expressly for this The US Department of Transportation (DOT) evaluation. Volpe Center is currently involved in a National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Due to differences in the technologies, project to configure, deploy, and evaluate the comparing HITS and ATCBI-6 presents challenges. capabilities of a transponder multilateration and For example, radar measures target range and Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast azimuth, while multilateration measures time of (ADS-B) system that will perform aircraft tracking arrivals (TOAs) and provides a rectangular position, in the Gulf of Mexico offshore area. The and ADS-B utilizes GPS position. Assuming that Helicopter In-flight Tracking System (HITS) is the ground sites have the same coverage (which is being assessed for use in an offshore area where typically not the case), surveillance of a given several hundred petroleum industry helicopter volume using multilateration requires roughly three flights occur daily, and where there is currently times as many sites as SSR. On the other hand, little secondary surveillance radar coverage. There radar target report update rates are limited by the are also over-flights by aircraft to/from Mexico and radar antenna scan period (5 or 10 seconds), while CentraVSouth America. updates as frequent as once per second are achievable with multilateration. In contrast to the Although multilateration has been extensively requirements differences, testing procedures for tested for airport surface applications, there is SSR and multilateratiodADS-B are quite similar. -

Iff Operational Procedures Acp 160(E)
UNCLASSIFIED ACP 160(E) IFF OPERATIONAL PROCEDURES ACP 160(E) py when printed o c Uncontrolled SEPTEMBER 2014 UNCLASSIFIED UNCLASSIFIED ACP 160(E) FOREWORD 1. The Combined Communications-Electronics Board (CCEB) is comprised of the five member nations: Australia, Canada, New Zealand, United Kingdom and United States; and is the sponsoring authority for all Allied Communications Publications (ACPs). ACPs are raised and issued under common agreement between the member nations. 2. ACP 160(E), IFF Operational Procedures, is an UNCLASSIFIED Allied Communication Publication (ACP). Periodic accounting is not required. 3. This publication contains Allied military information official purposes only. 4. It is not permitted to copy or make extracts from this publication without consent of the Authorising Agency. 5. This ACP is to be maintained and amended in accordance with the provisions of ACP 198. py when printed o Uncontrolled c Uncontrolled i UNCLASSIFIED UNCLASSIFIED ACP 160(E) THE COMBINED COMMUNICATIONS-ELECTRONICS BOARD LETTER OF PROMULGATION FOR ACP 160(E) 1. The purpose of this Combined Communication Electronics Board (CCEB) Letter of Promulgation is to implement ACP 160(E) within the Armed Forces of the CCEB Nations. ACP 160(E) IFF Operational Procedures is an UNCLASSIFIED publication developed for Allied use and, under the direction of the CCEB Principals. It is promulgated for guidance, information, and use by the Armed Forces and other users of military communications facilities. 2. ACP 160(E) is effective on receipt for CCEB Nations and effective for NATO nations and Strategic Commands when promulgated by the NATO Military Committee (NAMILCOM). ACP 160(E) will supersede ACP 160(D), which shall be destroyed in accordance with national regulations. -

TECHNICAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN for a DISCRETE ADDRESS BEACON SYSTEM VOLUME I &X
Project Report ATC-4 Volume 1 Technical Development Plan for a Discrete Address Beacon System Volume 1 6 August 1971 Lincoln Laboratory MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY LEXINGTON, MASSACHUSETTS Prepared for the Federal Aviation Administration, Washington, D.C. 20591 This document is available to the public through the National Technical Information Service, Springfield, VA 22161 This document is disseminated under the sponsorship of the Department of Transportation in the interest of information exchange. The United States Government assumes no liability for its contents or use thereof. MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY LINCOLN LABORATORY DRAFT TECHNICAL DEVELOPMENT PLAN FOR A DISCRETE ADDRESS BEACON SYSTEM VOLUME I &x PROJECT REPORT ATC-4 (Air Traffic Control) 6 AUGUST 1971 All distribution of this document external to Lincoln Laboratory is under the control of the Federal’Aviation Administration. LEXINGTON MASSACHUSETTS CONTENTS VOLUME I I. Introduction I-l II. Issues II- 1 III. Design Options III- 1 IV. DABS Development Plan IV-1 V. Program Management V-l VOLUME II (Appendix) Task Descriptions A-l . 111 ABSTRACT The requirement for a Discrete Address Beacon System (DABS) was highlighted by the Department of Transportation Air Traffic Control Advisory Committee to provide improved surveillance and ground-air communications in support of air traffic control automation. This document presents a technical development plan for such a system; this plan was developed in close colaboration with FAA personnel in the Office of System Engineering Management and the Systems Research and Development Service. The DABS Technical Development Plan identifies the critical issues and technical options, presents a program for their resolution, followed by the development and . -

Degree's Final Thesis
DEGREE’S FINAL THESIS Thesis Title: Analysis and optimisation of radio spectrum pollution on 1030/1090 MHz bands associated with mode S transponders. Degree: Aerospace systems engineering AUTHOR: Borin Kaduk Aguilar DIRECTOR: Eduard Úbeda Farré DATE: 7th February 2021 Títol: Anàlisi i optimització de la pol·lució radio espectral en les bandes de 1030/1090 MHz associada als transponedors mode S. Autor: Borin Kaduk Aguilar Director: Eduard Úbeda Farré Data: 7 de Febrer del 2021 Resum La vigilància actual de les aeronaus es duu a terme amb un parell d’elements clau: el transponedor i l’interrogador. L’interrogador s’encarrega d’enviar senyals a l’aire per a detectar aeronaus i aquests, quan reben la senyal, transmeten una resposta que conté informació codificada en forma de polsos. Posteriorment la resposta serà processada pels mateixos interrogadors o antenes receptores, i amb el conjunt de respostes de diferents aeronaus i un teixit prou dens d’equips de recepció, podem arribar a vigilar tot el que succeeix a l’espai aeri. Aquest sistema col·laboratiu ha funcionat remarcablement bé des de la seva creació. Amb el temps, la tecnologia evoluciona i el número de vols creix, però les bandes de freqüència utilitzades romanen les mateixes. Com a conseqüència d’aquest creixement continu en un sistema basat en la utilització de dues bandes freqüencials fixes, trobem que en l’espai aeri apareixen cada vegada més i més missatges (interrogacions i respostes), arribant, en casos extrems, a la saturació del sistema de vigilància actual. Cal esmentar que amb l’avenç tecnològic hem pogut aportar solucions per a mitigar els problemes que han anat sorgint fins avui dia en quant a la vigilància aèria, com podrien ser el “garbling” o el “FRUIT”, però es tot un repte d’enginyeria aportar solucions contínues a un sistema que no para de créixer. -

TMÑ2004-213447 Cvr.P65
NASA/TM–2004-213447 Deployment and Evaluation of the Helicopter In-Flight Tracking System (HITS) Final Report Anastasios Daskalakis and Patrick Martone U.S. Department of Transportation Volpe Center, Cambridge, Massachusetts Sponsored by Advanced Air Transportation Technologies Project Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California December 2004 The NASA STI Program Office . in Profile Since its founding, NASA has been dedicated to the • CONFERENCE PUBLICATION. Collected advancement of aeronautics and space science. The papers from scientific and technical confer- NASA Scientific and Technical Information (STI) ences, symposia, seminars, or other meetings Program Office plays a key part in helping NASA sponsored or cosponsored by NASA. maintain this important role. • SPECIAL PUBLICATION. Scientific, technical, The NASA STI Program Office is operated by or historical information from NASA programs, Langley Research Center, the Lead Center for projects, and missions, often concerned with NASA’s scientific and technical information. The subjects having substantial public interest. NASA STI Program Office provides access to the NASA STI Database, the largest collection of • TECHNICAL TRANSLATION. English- aeronautical and space science STI in the world. language translations of foreign scientific and The Program Office is also NASA’s institutional technical material pertinent to NASA’s mission. mechanism for disseminating the results of its research and development activities. These results Specialized services that complement the STI are published by NASA in the NASA STI Report Program Office’s diverse offerings include creating Series, which includes the following report types: custom thesauri, building customized databases, organizing and publishing research results . even • TECHNICAL PUBLICATION. Reports of providing videos. completed research or a major significant phase of research that present the results of NASA For more information about the NASA STI programs and include extensive data or theoreti- Program Office, see the following: cal analysis.