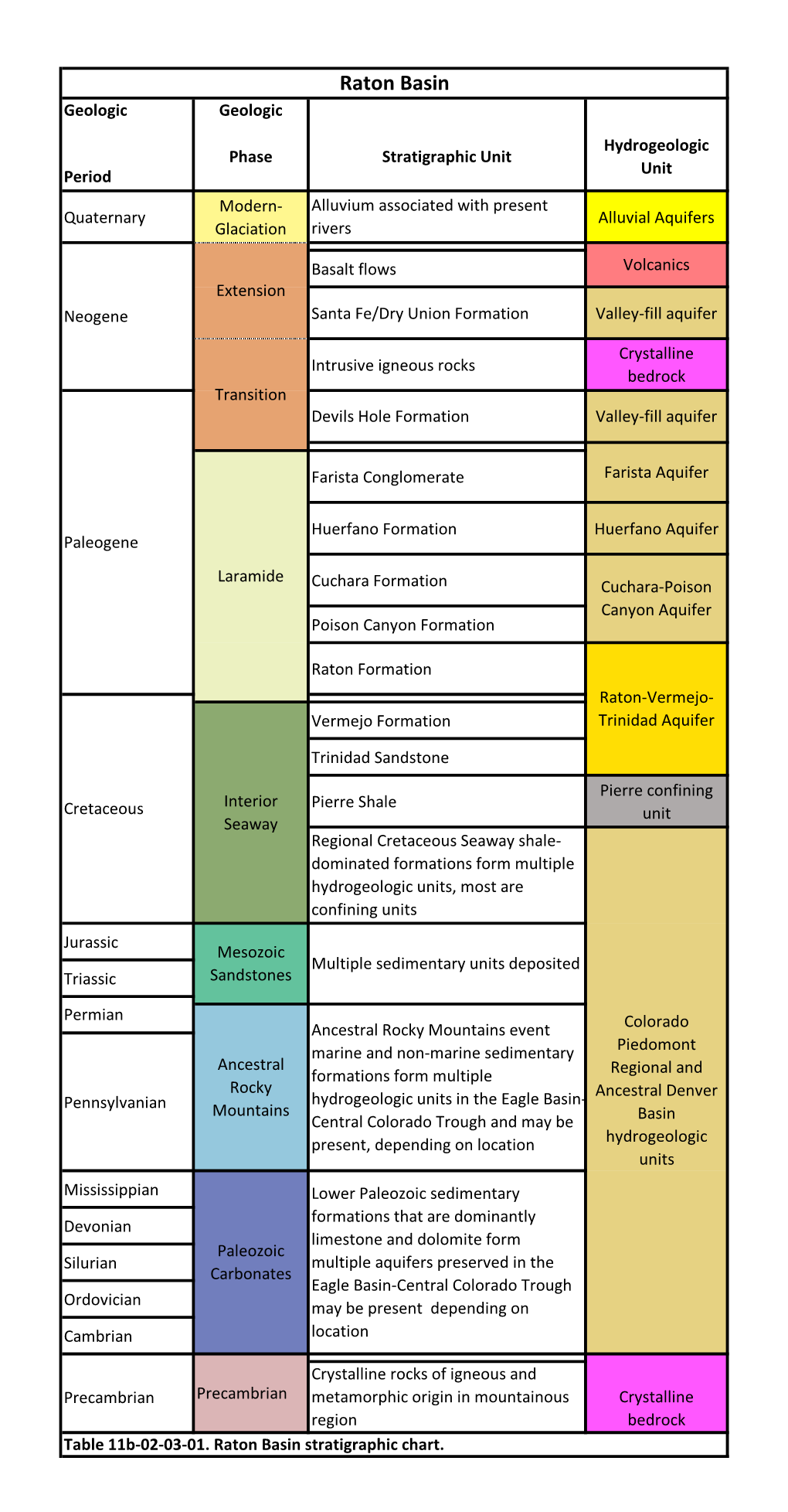
Raton Basin Stratigraphic Chart
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Chapter SR a SUMMARY of TERTIARY COAL RESOURCES OF
Chapter SR A SUMMARY OF TERTIARY COAL RESOURCES OF THE RATON BASIN, COLORADO AND NEW MEXICO By R.M. Flores and L.R. Bader in U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1625-A Contents Introduction...........................................................................................................................SR-1 Stratigraphy...........................................................................................................................SR-2 Depositional Environments...............................................................................................SR-5 Description of Coal Zones.................................................................................................SR-7 Coal Quality..........................................................................................................................SR-9 Original Resources............................................................................................................SR-12 Production History............................................................................................................SR-13 Coal-bed Methane..............................................................................................................SR-15 Conclusions.........................................................................................................................SR-17 References...........................................................................................................................SR-19 Figures SR-1. Map showing the geology -

Cretaceous–Paleogene Plant Extinction and Recovery in Patagonia
Paleobiology, 46(4), 2020, pp. 445–469 DOI: 10.1017/pab.2020.45 Featured Article Cretaceous–Paleogene plant extinction and recovery in Patagonia Elena Stiles , Peter Wilf, Ari Iglesias, María A. Gandolfo, and N. Rubén Cúneo Abstract.—The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K/Pg) extinction appears to have been geographically heteroge- neous for some organismal groups. Southern Hemisphere K/Pg palynological records have shown lower extinction and faster recovery than in the Northern Hemisphere, but no comparable, well-con- strained Southern Hemisphere macrofloras spanning this interval had been available. Here, macrofloral turnover patterns are addressed for the first time in the Southern Hemisphere, using more than 3500 dicot leaves from the latest Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) and the earliest Paleocene (Danian) of Argentine Patagonia. A maximum ca. 90% macrofloral extinction and ca. 45% drop in rarefied species richness is esti- mated across the K/Pg, consistent with substantial species-level extinction and previously observed extir- pation of host-specialized leaf mines. However, prior palynological and taxonomic studies indicate low turnover of higher taxa and persistence of general floral composition in the same sections. High species extinction, decreased species richness, and homogeneous Danian macrofloras across time and facies resemble patterns often observed in North America, but there are several notable differences. When com- pared with boundary-spanning macrofloras at similar absolute paleolatitudes (ca. 50°S or 50°N) from the Williston Basin (WB) in the Dakotas, both Maastrichtian and Danian Patagonian species richnesses are higher, extending a history of elevated South American diversity into the Maastrichtian. Despite high spe- cies turnover, our analyses also reveal continuity and expansion of leaf morphospace, including an increase in lobed and toothed species unlike the Danian WB. -

Geology of the Northern Perth Basin, Western Australia
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233726107 Geology of the northern Perth Basin, Western Australia. A field guide Technical Report · June 2005 CITATIONS READS 15 1,069 4 authors: Arthur John Mory David Haig Government of Western Australia University of Western Australia 91 PUBLICATIONS 743 CITATIONS 61 PUBLICATIONS 907 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE Stephen Mcloughlin Roger M. Hocking Swedish Museum of Natural History Geological Survey of Western Australia 143 PUBLICATIONS 3,298 CITATIONS 54 PUBLICATIONS 375 CITATIONS SEE PROFILE SEE PROFILE Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects: Lower Permian bryozoans of Western Australia View project Late Palaeozoic palynology of Dronning Maud Land, Antarctica View project All content following this page was uploaded by Stephen Mcloughlin on 05 May 2017. The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file. All in-text references underlined in blue are added to the original document and are linked to publications on ResearchGate, letting you access and read them immediately. Department of Industry and Resources RECORD GEOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN PERTH 2005/9 BASIN, WESTERN AUSTRALIA — A FIELD GUIDE by A. J. Mory, D. W. Haig, S. McLoughlin, and R. M. Hocking Geological Survey of Western Australia GEOLOGICAL SURVEY OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA Record 2005/9 GEOLOGY OF THE NORTHERN PERTH BASIN, WESTERN AUSTRALIA — A FIELD GUIDE by A. J. Mory, D. W. Haig1, S. McLoughlin2, and R. M. Hocking 1 School of Earth and Geographical Sciences, The University of Western Australia 2 School of Natural Resource Sciences, Queensland University of Technology Perth 2005 MINISTER FOR STATE DEVELOPMENT Hon. -

Geologic Studies of the Platte River, South-Central Nebraska and Adjacent Areas—Geologic Maps, Subsurface Study, and Geologic History
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Publications of the US Geological Survey US Geological Survey 2005 Geologic Studies of the Platte River, South-Central Nebraska and Adjacent Areas—Geologic Maps, Subsurface Study, and Geologic History Steven M. Condon Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usgspubs Part of the Earth Sciences Commons Condon, Steven M., "Geologic Studies of the Platte River, South-Central Nebraska and Adjacent Areas—Geologic Maps, Subsurface Study, and Geologic History" (2005). Publications of the US Geological Survey. 22. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/usgspubs/22 This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the US Geological Survey at DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln. It has been accepted for inclusion in Publications of the US Geological Survey by an authorized administrator of DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln. Geologic Studies of the Platte River, South- Central Nebraska and Adjacent Areas—Geologic Maps, Subsurface Study, and Geologic History Professional Paper 1706 U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Geologic Studies of the Platte River, South-Central Nebraska and Adjacent Areas—Geologic Maps, Subsurface Study, and Geologic History By Steven M. Condon Professional Paper 1706 U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey U.S. Department of the Interior Gale A. Norton, Secretary U.S. Geological Survey Charles G. Groat, Director Version 1.0, 2005 This publication and any updates to it are available online at: http://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/pp1706/ Manuscript approved for publication, March 3, 2005 Text edited by James W. Hendley II Layout and design by Stephen L. -

International Ocean Discovery Program Expedition 369 Scientific
International Ocean Discovery Program Expedition 369 Scientific Prospectus Australia Cretaceous Climate and Tectonics Tectonic, paleoclimate, and paleoceanographic history of the Mentelle Basin and Naturaliste Plateau at southern high latitudes during the Cretaceous Richard Hobbs Brian Huber Co-Chief Scientist Co-Chief Scientist Department of Earth Sciences Department of Paleobiology, MRC-121 Durham University Smithsonian Institution Durham DH1 3LE Washington DC 20013 United Kingdom USA Kara A. Bogus Expedition Project Manager/Staff Scientist International Ocean Discovery Program Texas A&M University 1000 Discovery Drive College Station TX 77845 USA Publisher’s notes This publication was prepared by the JOIDES Resolution Science Operator (JRSO) at Texas A&M University (TAMU) as an account of work performed under the International Ocean Discovery Program (IODP). Funding for IODP is provided by the following international partners: National Science Foundation (NSF), United States Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT), Japan European Consortium for Ocean Research Drilling (ECORD) Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST), People’s Republic of China Korea Institute of Geoscience and Mineral Resources (KIGAM) Australia-New Zealand IODP Consortium (ANZIC) Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES), India Coordination for Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES), Brazil Portions of this work may have been published in whole or in part in other IODP documents or publications. This IODP Scientific Prospectus is based on precruise JOIDES Resolution Facility advisory panel discussions and scientific input from the designated Co-Chief Scientists on behalf of the drilling proponents. During the course of the cruise, actual site operations may indicate to the Co-Chief Scientists, the Staff Scientist/Expedition Project Manager, and the Operations Superintendent that it would be scientifically or operationally advantageous to amend the plan detailed in this prospectus. -

Rare Earth Occurrences Proximal to the Cretaceous/Tertiary Boundary in the Raton Basin, South-Central Colorado*
Rare Earth Occurrences Proximal to the Cretaceous/Tertiary Boundary in the Raton Basin, South-central Colorado* Dr. H.T.Andersen1, Dr. Rex Bryan2, Mr. Thomas Gray3, & Dr. Dave Richers4 *Presented at the AiChe Conference, November 8-13, 2015, Salt Lake City, Utah 1 Digitus International, Golden, CO. 2 Tetra Tech, Inc., Golden, CO. 3 Tetra Tech, Inc., Golden, CO Abstract The Raton Coal Basin of Colorado and New Mexico is one of the premier coal basins where the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary can be viewed and samples of coals, tonsteins, and shaly materials proximal to this 1 boundary can be readily obtained. Near Trinidad, CO, extensive coal deposits exist that straddle this boundary. Further, the presence of near-by igneous features such as the Sangre de Cristo Mountains and associated dikes and sills provide a possible source of anomalous geochemical features found in the coals. Reconnaissance geochemical investigations utilizing a hand-held X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer (XRF) indicate that appreciable amounts of Ti, Zr, Y, and light rare-earth elements (REE) are present within the coals and coal partings near the boundary of the Cretaceous Vermejo Formation and the overlying Tertiary Raton Formation. In some instances, semi-quantitative determinations indicate elevated quantities of Y and light REE (hundreds of parts per million) are present in select raw coal samples in the area. Earlier studies of the REE content of coal samples in the basin were conducted by the USGS and presented in their CoalQual database. The results of the XRF spectroscopy corroborates the findings reported in that database. Altered kaolinitic pyroclastic ash is present in the basin that is interpreted to be in- part sourced from the Cretaceous/Tertiary (K-T) impact. -

Magmatic Evolution and Petrochemistry of Xenoliths Contained Within an Andesitic Dike of Western Spanish Peak, Colorado
Magmatic Evolution and Petrochemistry of Xenoliths contained within an Andesitic Dike of Western Spanish Peak, Colorado Thesis for Departmental Honors at the University of Colorado Ian Albert Rafael Contreras Department of Geological Sciences Thesis Advisor: Charles Stern | Geological Sciences Defense Committee: Charles Stern | Geological Sciences Rebecca Flowers | Geological Sciences Ilia Mishev | Mathematics April the 8th 2014 Magmatic Evolution and Petrochemistry of Xenoliths contained within an Andesitic Dike of Western Spanish Peak, Colorado Ian Albert Rafael Contreras Department of Geological Sciences University of Colorado Boulder Abstract The Spanish Peaks Wilderness of south-central Colorado is a diverse igneous complex which includes a variety of mid-Tertiary intrusions, including many small stocks and dikes, into Cretaceous and early Tertiary sediments. The focus of this thesis is to determine whether gabbroic xenoliths found within an andesitic dike on Western Spanish Peak were accidental or cognate, and their implications for the magma evolution of the area. A total of twelve samples were collected from a single radial dike, eleven of which were sliced into thin sections for petrological analyses. From the cut thin sections, six were chosen for electron microprobe analysis to determine mineral chemistry, and billets of ten samples were subject to ICP-MS analysis to determine bulk rock, trace element chemistry. Xenoliths were dominated by amphiboles, plagioclase feldspars, clinopyroxenes and opaques (Fe-Ti oxides) distributed in mostly porphyritic to equigranular textures. Pargasitic and kaersutitic amphiboles are present in both the xenoliths and the host dike. Additionally, plagioclase feldspars range from albite to labradorite, and clinopyroxenes range from augite to diopside. All xenoliths were found to be enriched in elements Ti, Sr, Cr and Mn compared to the host dike and other Spanish Peak radial dikes. -

Geological Survey Research 1961 Synopsis of Geologic and Hydrologic Results
Geological Survey Research 1961 Synopsis of Geologic and Hydrologic Results GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROFESSIONAL PAPER 424-A Geological Survey Research 1961 THOMAS B. NOLAN, Director GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROFESSIONAL PAPER 424 A synopsis ofgeologic and hydrologic results, accompanied by short papers in the geologic and hydrologic sciences. Published separately as chapters A, B, C, and D UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT PRINTING OFFICE, WASHINGTON : 1961 FOEEWOED The Geological Survey is engaged in many different kinds of investigations in the fields of geology and hydrology. These investigations may be grouped into several broad, inter related categories as follows: (a) Economic geology, including engineering geology (b) Eegional geologic mapping, including detailed mapping and stratigraphic studies (c) Eesource and topical studies (d) Ground-water studies (e) Surface-water studies (f) Quality-of-water studies (g) Field and laboratory research on geologic and hydrologic processes and principles. The Geological Survey also carries on investigations in its fields of competence for other Fed eral agencies that do not have the required specialized staffs or scientific facilities. Nearly all the Geological Survey's activities yield new data and principles of value in the development or application of the geologic and hydrologic sciences. The purpose of this report, which consists of 4 chapters, is to present as promptly as possible findings that have come to the fore during the fiscal year 1961 the 12 months ending June 30, 1961. The present volume, chapter A, is a synopsis of the highlights of recent findings of scientific and economic interest. Some of these findings have been published or placed on open file during the year; some are presented in chapters B, C, and D ; still others have not been pub lished previously. -

Sedimentation, Pedogenesis, and Paleoclimate Conditions in the Paleocene San Juan Basin, New Mexico, U.S.A
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Earth and Planetary Sciences ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 7-1-2016 Sedimentation, pedogenesis, and paleoclimate conditions in the Paleocene San Juan Basin, New Mexico, U.S.A. Kevin Hobbs Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalrepository.unm.edu/eps_etds Recommended Citation Hobbs, Kevin. "Sedimentation, pedogenesis, and paleoclimate conditions in the Paleocene San Juan Basin, New Mexico, U.S.A.." (2016). https://digitalrepository.unm.edu/eps_etds/104 This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the Electronic Theses and Dissertations at UNM Digital Repository. It has been accepted for inclusion in Earth and Planetary Sciences ETDs by an authorized administrator of UNM Digital Repository. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Kevin Michael Hobbs Candidate Earth and Planetary Sciences Department This dissertation is approved, and it is acceptable in quality and form for publication: Approved by the Dissertation Committee: Dr. Peter Fawcett, Chairperson Dr. Leslie McFadden Dr. Gary Weissmann Dr. Thomas Williamson i SEDIMENTATION, PEDOGENESIS, AND PALEOCLIMATE CONDITIONS IN THE PALEOCENE SAN JUAN BASIN, NEW MEXICO, U.S.A. by KEVIN MICHAEL HOBBS B.S., Geology, The University of the South, 2006 M.S., Geological Sciences, The University of Idaho, 2010 DISSERTATION Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Earth and Planetary Sciences The University of New Mexico Albuquerque, New Mexico July 2016 ii ACKNOWLEDMENTS I thank the following persons for professional help in the form of discussions, critique of ideas, or suggestions during the research and writing of this dissertation: From the Earth and Planetary Sciences Department: Viorel Atudorei, Adrian Brearley, Ben Burnett, Jeff Carritt, Laura Crossey, Magdalena Donahue, Maya Elrick, John Geissmann, Nick George, Karl Karlstrom, Bekah Levine, Grant Meyer, Corrinne Myers, Lyman Persico, Jane Selverstone, Zach Sharp, Mike Spilde. -

Geology of the Fox Hills Formation (Late Cretaceous
GEOLOGY OF THE FOX HILLS FORMATION (LATE CRETACEOUS) IN THE WILLISTON BASIN OF NORTH DAKOTA, WITH REFERENCE TO URANIUM POTENTIAL by A. M. CVANCARA UNNERSITY OF NORTIl DAKOTA DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY GRAND FORKS, NORTII DAKOTA 58202 REPORT OF INVESTIGATION NO. 5S NORTH DAKOTA GEOLOGICAL SURVEY E. A. Noble, State Geologist 1976 PREPARED FOR mE U.S. ENERGY RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT ADMINISTRATION GRAND JUNCTION OFFICE UNDER CONTRACT NO. AT(05-1)-1633 G1O-1633-1 CONTENTS ABSTRACT ~ag~ INTRODUCTION . 1 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS .... 1 MATERIALS AND METHODS 2 STRATIGRAPHY ......................... .. .. 2 Definition and relationship to other rock units .. 2 Distribution . .. 3 Lithology and sedimentary structures .. 3 Persistence of lithologic units ... .. 7 Contacts .. ... .. .. ., 7 Thickness . .. ... .. 8 STRUcrURE ... 8 PALEONTOLOGY . 9 Fossil groups . 9 Occurrence of fossils · ..... , 9 AGE AND CORRELATION 10 DEPOSITIONAL ENVIRONMENTS .............................. 10 URANIUM POTENTIAL . · 12 General . .. ., 12 Fox Hills Formation . 13 REFERENCES . · 14 ILLUSTRATIONS Figure Page 1. Fox Hills and adjacent Formations in North Dakota (modified from Carlson, 1973) . 4 2. Schematic stratigraphic column of Fox Hills Formation in North Dakota (modified slightly from Erickson, 1974, p. 144). The Linton Member was named by Klett and Erickson (1976). 5 Plate 1. Northwest-southeast cross section (Dunn to Sioux Counties) of Fox Hills Formation in southwestern North Dakota . (in pocket) 2. Southwest-northeast cross section (Bowman to Pierce Counties) of Fox Hills Formation in western North Dakota (in pocket) 3. Southwest-northeast cross section (Adams to Burleigh Counties) of Fox Hills Formation in southwestern North Dakota (in pocket) 4. Isopach map of Fox Hills Formation in North Dakota (in pocket) ABSTRACT model is followed for the deposition of Fox Hills sediments. -

The Rocky Mountain Front, Southwestern USA
The Rocky Mountain Front, southwestern USA Charles E. Chapin, Shari A. Kelley, and Steven M. Cather New Mexico Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, Socorro, New Mexico 87801, USA ABSTRACT northeast-trending faults cross the Front thrust in southwest Wyoming and northern Range–Denver Basin boundary. However, Utah. A remarkable attribute of the RMF is The Rocky Mountain Front (RMF) trends several features changed from south to north that it maintained its position through multi- north-south near long 105°W for ~1500 km across the CMB. (1) The axis of the Denver ple orogenies and changes in orientation from near the U.S.-Mexico border to south- Basin was defl ected ~60 km to the north- and strength of tectonic stresses. During the ern Wyoming. This long, straight, persistent east. (2) The trend of the RMF changed from Laramide orogeny, the RMF marked a tec- structural boundary originated between 1.4 north–northwest to north. (3) Structural tonic boundary beyond which major contrac- and 1.1 Ga in the Mesoproterozoic. It cuts style of the Front Range–Denver Basin mar- tional partitioning of the Cordilleran fore- the 1.4 Ga Granite-Rhyolite Province and gin changed from northeast-vergent thrusts land was unable to penetrate. However, the was intruded by the shallow-level alkaline to northeast-dipping, high-angle reverse nature of the lithospheric fl aw that underlies granitic batholith of Pikes Peak (1.09 Ga) faults. (4) Early Laramide uplift north of the RMF is an unanswered question. in central Colorado. -

Co-Raton-Mesa-Nm.Pdf
D-5 I I I~ ..--- ~..,.....----~__O~~--- I I I UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR NATIONAL SE I I I I II I Cover painting "FISHERS PEAK" by Arthur Roy Mitchell, commissioned for the Denver Post's Collection of Western Art, reproduced through the courtesy of Palmer Hoyt, Editor. I I.1 I I SYNOPSIS NOT FOR FU~LIC l{ELEASJ Raton Mesa near Trinidad, Colorado, about 200 miles south of Denver, I is the highest, most scenic, impressive and accessible of a scattered group of lava-capped mesas straddling the eastern half of the Colorado- I New Mexico boundary. It and its highest part, Fishers Peak, are well I known landmarks dating back to the days of the Santa Fe Trail which~ traverses Raton Pass on its southwest flank, today crossed by an interstate high- I way. Three distinct, easily recognized vegetative zones, mostly forest, lay on its slopes; the Mesa top is a high mountain grassland. I Ancient lava flows covered portions of this region, the Raton I section of the Great Plains physiographic province, millions of years ago when the surface was much higher. These flows protected the mesas from subsequent erosion which has carried away the surrounding territory, • leaving Fishers Peak today towering 4,000 feet above the City of Trinidad. I Lavas at Capulin Mountain, a National Monument located nearby in New I Mexico, though at a lower elevation, are thought to be much more recent. Raton Pass was a strategic point on the Mountain Branch of the I Santa Fe Trail during the Mexican and Civil Wars, and to travelers past and present a clima~~ gateway to the southwest.