United States Patent [111 3,557,305
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

And Others Signal Transmission and Delivery Between Head-End and Office of Telecommunications
DOCUMENT RESUME ED 084 875 EM 011 699 AUTHOR Chadwick, Russell B.; And Others TITLE Signal Transmission and Delivery Between Head-End and Subscriber TerminalS. A Survey of Technical Requirements for Broadband Cable Teleservices. Volume Three. INSTITUTION Office of Telecommunications (DOC), Washington, D.C. PUB DATE Jul 73 NOTE 226p.; See Also EM 011 495 through EM 011 500 EDRS PRICE MF-$0.65 HC-$9.87 DESCRIPTORS *Cable Television; Communications; *Media Technology; *Technical Reports; Technological Advancement; *Technology; *Telecommunication IDENTIFIERS *Broadband Cable Teleservices; CATV; FCC; Federal Communications Commission; Head End; National Cable Television Association; NCTA; Subscriber Terminals ABSTRACT Technical factors involved in the delivery of broadband information between a cable television (CATV) system head-end and subscriber terminals are discussed. Recommendations pertaining to the need for research in specified areas are given and a review of the system's hardware is provided, including details about device noise and distortion characteristics. A treatment of various types of trucking systems, including two-way configurations, is presented and attention is devoted to the applications of advanced communications techniques, encompassing digital transrissiop, multiple-access systems, and signal transmission via optical waveguides. The report concludes with a review and listing of standards and tests for the delivery system, including those set by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) and the National Cable Television Association.(NCTA).(Author) A SURVEY OF TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS FOR BROADBAND CABLE TELESERVICES VOLUME 3 VOLUME 3 SIGNAL TRANSMISSION AND DELIVERY BETWEEN HEAD-END AND SUBSCRIBER TERMINALS RUSSELL B. CHADWICK RICHARD A. CHANDLER ROBERT L. GALLAWA LOCKETT E. WOOD 4S-St OF CO4, U.S. -

Cre|4|L-Feuhis ATTORNEYS Nov
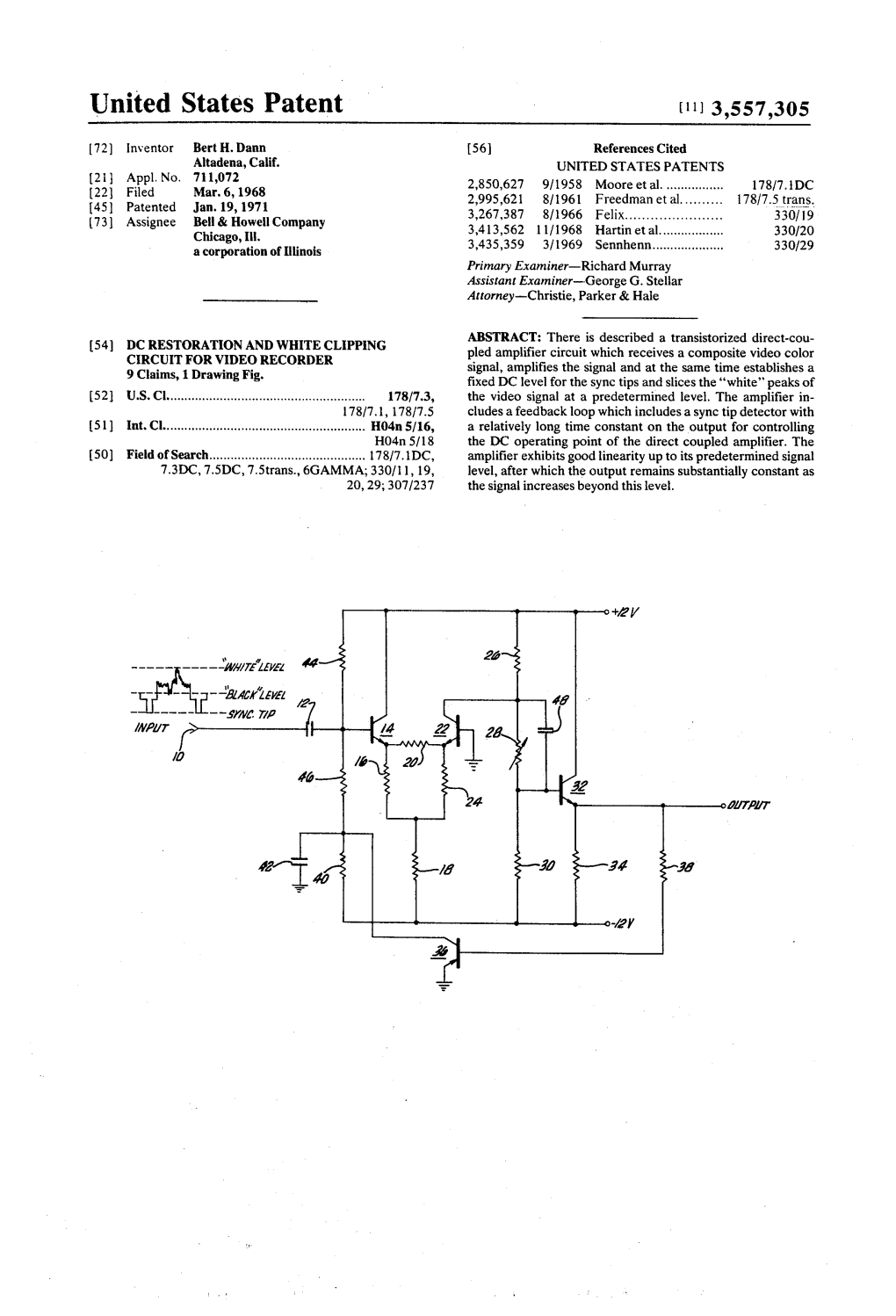
Nov. 28, 1961 M. V. SULLIVAN 3,011,018 HIGHLIGHT APERTURE CORRECTION SYSTEM Filed Sept. 26, 1956 3 Sheets-Sheet 1 NVENTOR MICHAEL V.SULL VAN cre|4|l-feuHIS ATTORNEYS Nov. 28, 1961 M. W. SULLIVAN 3,011,018 HIGHLIGHT APERTURE CORRECTION SYSTEM Filed Sept. 26, 1956 3 Sheets-Sheet 2 aa- ?-s? ? O ???? S I INVENTOR MICHAEL V. SULLIVAN -a?.--77. ? ????? ??? HIS AT TORNEYS Nov. 28, 1961 M. V. SULLIVAN 3,011,018 HIGHLIGHT APERTURE CORRECTION SYSTEM Filed Sept. 26, 1956 3 Sheets-Sheet 3 NVENTOR MiCHAEL V. SULLIVAN Y Cit...!!* His A ?????? la? 3,011,018 United States Patent Office Patented Nov. 28, 1961 3,011,018 FIG. 2 illustrates the waveform of the television pic HIGHLIGHT APERTURE CORRECTION SYSTEM ture signal at various points in the aperture equalization Michael V. Sullivan, Florham Park, N.J., assignor to system shown in FIG. 1; Columbia Broadcasting System, Inc., New York, N.Y., FIG. 3 is a circuit diagram of the input and white a corporation of New York clipper portions of the system shown in FIG. 1; Filed Sept. 26, 1956, Ser. No. 612,221 FIG. 4 is ? circuit diagram of the difference ampli 7 Claims. (Cl. 178-6) fier portion of the system shown in FIG. 1; and FIG. 5 is a circuit diagram of the summing amplifier This invention relates to television, and more particu and output portions of the system shown in FIG.1. larly to a new and improved aperture equalization O Referring first to the block diagram of FIG. 1 and method and means for correcting aperture distortion in the graphic representations of the signal waveform of the highlight regions of the television picture, without FIG.2, a television picture information signal as illus increasing the high frequency noise which is inherent in trated in FIG. -

Tvtransmitter 2/O.2 Kw Band Lll with Modulation at a Fixed Lf :T
SIEMENS TVTransmitter 2/O.2 kW Band lll with modulation at a fixed lF :t Contents V l. Design ll. Features lll. Construction lV. Principles of Operation V. Electrical Data Vl. Scope ol Delivery rt v lssued by Bereich Bauelemente, Vertrieb, Balanstraße 73.8000 München 80 Terms of de lverv and riahts to chanse desisn reserved. l. Design fhe 2/O.2 kW VHF Band lll television transmitter consists Transmitter preamplifier stages up to an output power ot vof separate amplifier chains for the picture and sound approx. 1O W fitted with silicon transistors. signals with a combining network at the output. The pic- ture and sound pre stage with associated power supply Modulation at f ixed lF. is located in one cabinet together with the 2/0.2 kW out- For TV transmission in accordance with CCIR Recom- put stage with power supply and the diplexer in a second mendalions (625 lines, channel bandwidth 7 MHz). cabinet, the combining unit. lt is possible to house in picture this cabinet also some monitoring equipment. As Also available for FCC or OIRT standards. monitor, oscilloscope, switch point selector, sound de- modulator, Nyquist demodulator, but note this equipment Completely color-compatible for NTSC, PAL or SECAM is not part of the transmitter. standards. The standard version is designed for operation in accord- ance with the CCIR Recommendations (625 lines, T MHz channel bandwldth). lf required the transmitter can also be supplied to the FCC standard (525 lines, 6 MHz channel bandwidth), or OIRT standard (625 lines, S MHz channel lll. Construction For is fully bandwidth). -

Sony PMW 150 November 2012
Sony PMW 150 November 2012 EBU – Tech 3335 : Methods of measuring the imaging performance of television cameras for the purposes of characterising and setting Alan Roberts, November 2012 SUPPLEMENT 006 : Assessment of a Sony PMW 150 camera Tests have been conducted in line with EBU R.118. This document is a report of the results of the tests defined in Tech3335 and is not an endorsement of the product. Tests were made on a demonstration model of the Sony PMW-150 HDTV camcorder (serial number 61048) and it’s manual. Outwardly it appears to be very similar to the PMW EX1, and shares many features with it. The camera has an integral lens (Fuji, F/1.6, 20:1 4.1~82mm) and records only onto solid-state storage with two SxS slots. The lens has conventional 3-ring control, with manual or automatic operation, but the rings are all servo-driven and have no markings. It has 3 ⅓” COMS sensors of 1920x1080 pixels, and therefore should qualify as an HDTV camera. Recording HDTV uses MPEG2, 10-bit 4:2:2 1920x1080 at 50Mb/s, 8- bit 4:2:0 1920x1080 at 35Mb/s (with variable bit rate, maximum 35Mb/s), 8-bit 1440x1080 4:2:0 at 35Mb/s (VBR), 8-bit 1280x720 at 35Mb/s VBR, and 8-bit 1440x1080 at 25Mb/s VBR. All the 1080-line modes can be progressive or interlaced at frame rates from 23.976 to 29.97Hz, and 720P up to 60Hz. It can also record in standard SDTV modes, DVCAM. Note that the 50Mb/s mode cannot be used if recording is onto a SDHC card in an adaptor, it must be a proper SxS card (ExpressCard) or a XQD card in an adaptor for this mode. -

Pulsar MKII MN TV Modulator
Headend Systems Pulsar MKII™ (MN) – TV Modulator Description The Pulsar MKII™ (MN) device is a TV modulator used to convert baseband audio and video signals into RF output signals ready to go into your cable network. Thanks to built-in intelligence, all of its important parameters can be remotely controlled. Typical applications are in those cable TV distribution systems where high reliability, low maintenance and excellent price/performance ratio are of the highest priority. Features S Intelligent microprocessor controlled analog TV modulator S State-of-the-art frequency output S Fully agile converter 45 to 870 MHz S Intelligent video AGC S Full configuration and control via the ROSA™ Network Management System (NMS) S Auto RF level alignment in combination with Scientific-Atlanta’s LM 860™ network supervisor and ROSA NMS S Monitoring of modulation depth, audio deviation and over-modulation S Intelligent white clipper to prevent over-modulation S Front panel LCD and buttons for user-friendly control S A set of “plug ‘n play” options transforms the Pulsar MKII TV Modulator to suit any possible application S SAW filter for real adjacent channel operation S Built-in BTSC stereo encoder option Pulsar MKII (MN) – TV Modulator Specifications Interface Specifications Video inputs Connector BNC, 75 Level 1 Vpp (± 6 dB) Return loss O 30 dB Audio inputs Connector Screw terminal on quick-disconnect-plug Level -10 to 10 dBm for 25 kHz deviation Impedance 600 / 10 Balanced or unbalanced RF output Connector BNC, 75 (f-type optional) Return loss -

ए.सी. चालकता Absorption अवशोषण-गुणांक A
A absorption अवशोषण a. c. conductivity ए.सी. चालकता absorption अवशोषण-गुणांक a. c. interruption coefficient ए.सी. कावट absorption cross abandoned अवशोषण अनुथ परय, य section aberration परछेद वपथन access ablation तं अपरण access control अिभगम िनयंण ablative अपरक acceptable figure ablative liner वीकाय मान अपरक अतर absorption ablative material अवशोषण पैमदश अपरक पदाथ spectroscope abort वफल absorption अवशोषण तरंगमापी wavemeter abrasion अपघषण absorptivity अवशोषकता abrasion electrode अपघषण इलैोड abundance बाहुय, बहुलता abrasion test अपघषण परण academic शैक abrasiveness अपघषता accelerated aging वरत कालभावन absolute address िनरपे पता समुचय accelerated aging वरत कालभावन absolute gain िनरपे लध test परण absolute object िनरपे वतु मॉयूल accelerated life test module वरत आयु परण accelerating agent absolute pressure यथाथ दाब वरण कारक, वरणकार absolute system of acceleration िनरपे माक पित वरण unit acceleration limit absolute वरण सीमा िनरपे ताप, परम ताप acceleration temperature वरण संरण protection absolute time िनरपे काल acceleration stress absolute truth वरण ितबल परम सय acceleration absolute velocity वरण सता िनरपे वेग tolerance accelerator absolute weight िनरपे भार वरक, वरत absolute zero accelerograph परम शूय वरणलेखी, absorbed light अवशोषत काश एसलरोाफ़ absorbency accelerometer अवशोषणांक, अवशोषकता वरणमापी absorber acceptance angle अवशोषक वीकृित कोण absorbing boundary acceptance criterion अवशोषक परसीमा वीकृित कसौट, वीकृित absorbing अवशोषक घटक िनकष component acceptance absorptance वीकृित ितचयन अवशोषणांश sampling 2 acceptance acid-base वीकृित विनदश अल-ारसाय, अल- -

TV Transmitter 5/O.5 Kw Band Lll with Modulation at a Fixed Lf
SIEMENS TV Transmitter 5/O.5 kW Band lll with modulation at a fixed lF EEHT Contents l. Design ll. Features lll. Construction lV. Principles ol Operation V. Electrical Data Vl. Scope of Delivery lssued by Bereich Bauelemente, Vertrieb, 8000 München 80, Balanstraße 73 Terms of delivery and rishls lo chanqe desisn reserued- Transmitter preamplifier stages up to an output power l. Design of approx.5 W fitted with silicon transistors. The 5/0.5 kW VHF Band lll retevision transmitter with The electronic voltage regulators for the grid 1 and grid 2 combined picture/sound ampli{ication consists of the voltages are transistorized. 150/15 W picture/sound stage and rhe b/0.5 kW picrure/ lvlod sou nd tina I stage. ulation at fixed lF. For TV transmission in accordance The 150/15 W stage with associated power supplies with CCIR Recom- mendations (625 lines, is located in one cabinet, the 5/0.S kW stage with power channel bandwldth 7 MHz). suppljes in a second cabinet. Also available lor FCC or OIRT standards, if requested. The-standard version is designed for operation in accord- Completely color- comparible pAL ance for NTSC, or SECAM with the CCIR Recommendations (625 lines. T MHz standards. channel bandwidth). lf required the transmitter can also be supplied to the FCC standard (52b lines, 6 MHz channel bandwidth), or OIRT standard (625 lines, 8 MHz channel bandwidth). For these systems the transmitter is fully color-compatible to the NTSC, PAL or SECAM standards. lll. Construction (fig.2) Modulation at lixed lF assures the transmitter meets high quality requirements with excellent long,term stability. -

Hamamatsu C2741-03 Datasheet
Full-service, independent repair center -~ ARTISAN® with experienced engineers and technicians on staff. TECHNOLOGY GROUP ~I We buy your excess, underutilized, and idle equipment along with credit for buybacks and trade-ins. Custom engineering Your definitive source so your equipment works exactly as you specify. for quality pre-owned • Critical and expedited services • Leasing / Rentals/ Demos equipment. • In stock/ Ready-to-ship • !TAR-certified secure asset solutions Expert team I Trust guarantee I 100% satisfaction Artisan Technology Group (217) 352-9330 | [email protected] | artisantg.com All trademarks, brand names, and brands appearing herein are the property o f their respective owners. Find the Hamamatsu C2741-03 at our website: Click HERE INFRARED VIDICON CAMERA C2741-03 (Lens is optional) OUTLINE FEATURES The C2741-03 is a high-performance video camera G with various functions that have been developed for Sensitivity to 1800 (2200) nm image processing and measurement purposes. The camera has sensitivity to 1800 (2200) nm from a from visible wavelength region visible wavelength region. Compared with conventional G surveillance cameras, this camera excels in resolution, Image processing and image distortion, stability, etc. In addition, the camera can be connected to a real- measurement time image processor and measurement system, and G also to a personal computer for use with a video frame Contrast enhancement grabber board. function [Spectral Response Characteristics] 100 Using N2606 tube –1 10 Using N2606-06 tube Visible CCD Video Camera 10–2 10–3 10–4 Relative Sensitivity Infrared Camera –5 10 (C5840) 10–6 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 1600 1800 2000 2200 Wavelength (nm) Artisan Technology Group - Quality Instrumentation .. -

“Infinity” Camcorder This Document Is a Report of the Results of Tests That Are the Precursor of Those Described in the EBU Technical Document Tech3335
Thomson/Grass Valley DMC 1000 May 2009 Colorimetric and Resolution requirements of cameras Alan Roberts ADDENDUM 40 : Menu settings for Thomson/GV DMC1000 “Infinity” camcorder This document is a report of the results of tests that are the precursor of those described in the EBU technical document Tech3335. It is not an endorsement of the product. A one-day assessment was made on a sample of the DMC1000, Infinity camcorder (serial number 1FRMR), a multi-standard HDTV cam-corder with a Canon HA17x7.6 HD lens. It is a novel camera in many respects, and is the first HD cam-corder made under the Grass Valley name by Thomson. Physically, it resembles many other camcorders, the familiar digibeta size and layout, but it has a large lcd side panel with touch- screen controls for menu control, and records to a Rev-Pro hard drive and/or Compact Flash cards. It has excellent connectivity, including a standard HDMI connector for the viewfinder, and USB client and host connectors for downloading content from the recording media. Remote control is possible through a PDA application. It also has many features which make it suitable for multi-camera use in studio or location shooting. Although production models may well differ slightly from this sample, a full manual was available. Much of the content of this document is taken directly from that manual since there was insufficient time to test many of the innovatory features. Power consumption is 45 watts, a little high by modern standards, 49 watts when recording to RevPro. However, the power management and cooling system keep the camera cool to the touch, and acceptably quiet acoustically. -

CEI INTERNATIONALE IEC INTERNATIONAL 244-5 Deuxième Édition STAN DARD Second Edition 1992-10
This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication NORME CEI INTERNATIONALE IEC INTERNATIONAL 244-5 Deuxième édition STAN DARD Second edition 1992-10 Méthodes de mesure applicables aux émetteurs radioélectriques Partie 5: Qualités de fonctionnement des émetteurs de télévision Methods of measurement for radio transmitters Part 5: Performance characteristics of television transmitters © CEI 1992 Droits de reproduction réservés — Copyright — all rights reserved Aucune partie de cette publication ne peut étre reproduite ni No part of this publication may be reproduced or utilized utilisée sous quelque forme que ce soit et par aucun procédé, in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, électronique ou mécanique, y compris la photocopie et les including photocopying and microfilm, without permission microfilms, sans laccord écrit de (éditeur. in writing from the publisher Bureau central de la Commission Electrotechnique Internationale 3, rue de Varembé Genève Suisse Téléfax: +41 22 919 0300 e-mail: inmallt IeC.Ch IEC web site http://www.iec.ch Commission Electrotechnique Internationale CODE PRIX X C International Electrotechnical Commission PRICE CODE IEC Meiw yHapOAHae 3nelsrpoTexHN4ecKaf KOMNCCNA • • Pour prix, voir catalogue en vigueur For price, see current catalogue This is a preview - click here to buy the full publication – 2 – 244-5 ©CEI SOMMAIRE Pages AVANT- PROPOS 6 INTRODUCTION 8 Articles 1 Domaine dapplication 10 2 Références normatives 10 2.1 Publications de la CEI 10 2.2 Publications du CCIR 12 3 Terminologie -

Camera Chains
TEE [VISION BROADOASTINO Camera Chains by Harold E. Ennes r II pRO 1 II II U18700 3828588 A Television Broadcasting Camera Chains by Harold E. Fennes HOWARD W. SAMS & CO., INC. THE BOBBS -MERRILL CO., INC. INDIANAPOLIS KANSAS CITY NEW YORK FIRST EDITION FIRST PRINTING -1971 Copyright © 1971 by Howard W. Sams & Co., Inc., Indianapolis, Indiana 46206. Printed in the United States of America. All rights reserved. Reproduction or use, without express permis- sion, of editorial or pictorial content, in any manner, is prohibited. No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the infor- mation contained herein. International Standard Book Number: 0- 672 -20833 -4 Library of Congress Catalog Card Number: 71- 157802 Preface The manufacturers of television camera chains normally provide instruc- tion manuals that range from preliminary (sketchy) data to elaborate coverage of circuit theory, operations, and maintenance of the specific equipment. Such manuals obviously cannot delve into certain training programs that are usually necessary before adequate comprehension of modern broadcast technology can be gained. It is the purpose of this book to provide the fundamental and advanced training that is necessary if full benefit is to be obtained from the infor- mation in modern instruction books. To do this most effectively, where possible, complete, detailed schematics have been avoided, and, instead, use has been made of block diagrams with simplified diagrams of indi- vidual blocks under discussion. The overall system concept is stressed so that the reader can more readily grasp the meaning of a specific circuit adjustment in terms of its effect on system performance. -

Television Systems Glossary of Television Terms
SECTION 318-015-000 AT&TCo Standard Issue 3, January 1972 TELEVISION SYSTEMS GLOSSARY OF TELEVISION TERMS CONTENTS PAGE 2. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS Abrasions (Film): Unwanted slight marks on the 1. GENERAL surface of film. 2. TERMS AND DEFINITIONS A-Scope: A cathode-ray oscilloscope arranged to present a display such that time is one coordinate 3. QUALITY ASSESSMENT SCALE 23 and signals appear as deflections in a direction perpendicular to the time scale (also called waveform monitor). Aspect Ratio: The numerical ratio of picture width to height. 1. GENERAL Audio (Webster's International): Of or pertaining 1.01 This section furnishes a list of terms presently to electric current and phenomena of frequencies used in the lineup, operation, and maintenance corresponding to normally audible sound waves. of Television Transmission Systems. Also included These frequencies are approximately 16 to 20,000 is the American Standards Association scale used Hz. In television parlance, audio is used to denote in the measurement of video signal levels. the sound portion of a television signal or system. 1.02 This section is reissued to include new Audio Channel: A channel capable of satisfactorily terminology. Since this is a general revision, transmitting audio signals. As a television term, arrows ordinarily used to indicate changes have audio channel refers to a channel transmitting the been omitted. audio signals which are generally, but not necessarily, associated with video signals. 1.03 Experience in providing television service has proven the need for common understanding Average Picture Level (APLJ: The average level and use of terms by all the Telephone and Broadcasting of the picture signal during active scanning time Companies.