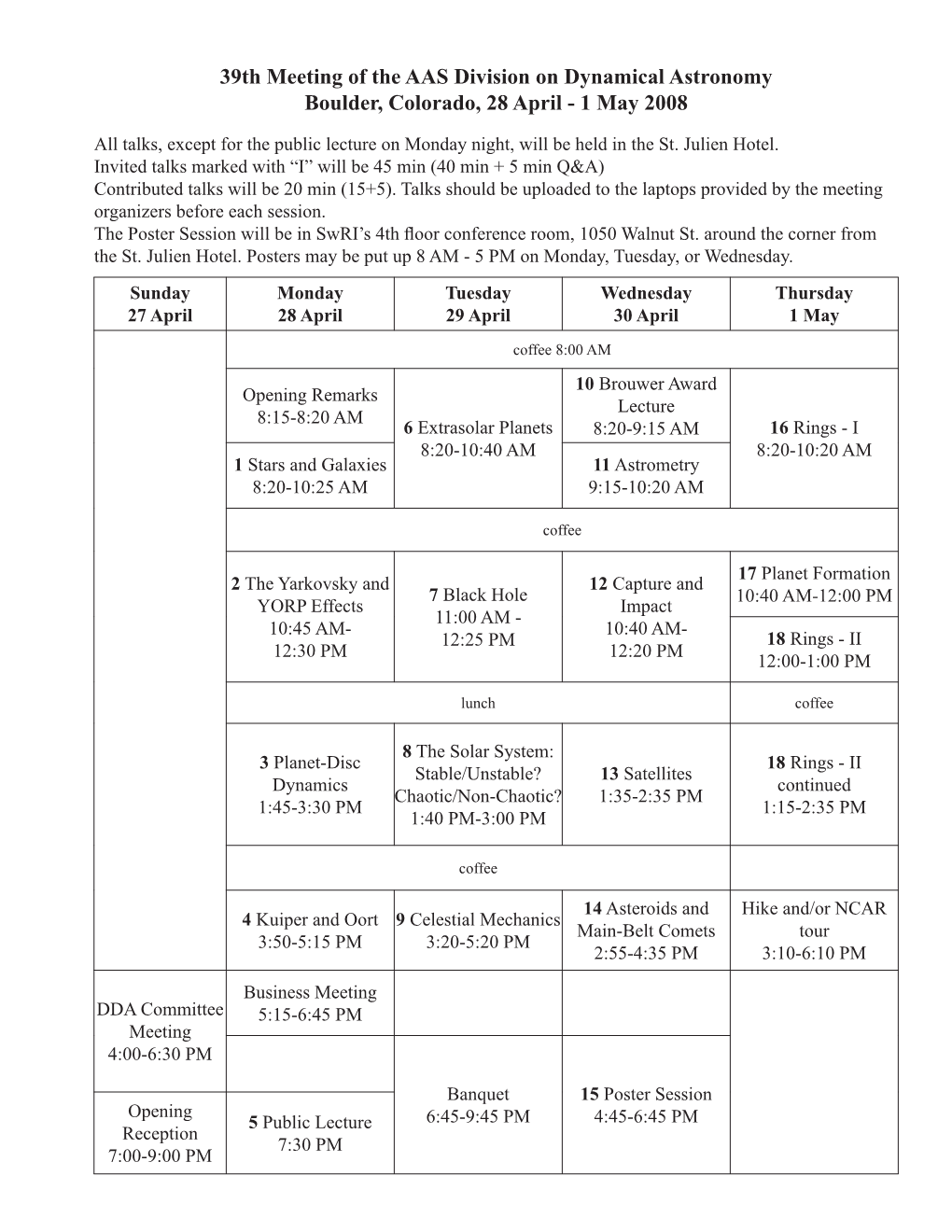
39Th Meeting of the AAS Division on Dynamical Astronomy Boulder, Colorado, 28 April - 1 May 2008
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Occultation Evidence for a Satellite of the Trojan Asteroid (911) Agamemnon Bradley Timerson1, John Brooks2, Steven Conard3, David W
Occultation Evidence for a Satellite of the Trojan Asteroid (911) Agamemnon Bradley Timerson1, John Brooks2, Steven Conard3, David W. Dunham4, David Herald5, Alin Tolea6, Franck Marchis7 1. International Occultation Timing Association (IOTA), 623 Bell Rd., Newark, NY, USA, [email protected] 2. IOTA, Stephens City, VA, USA, [email protected] 3. IOTA, Gamber, MD, USA, [email protected] 4. IOTA, KinetX, Inc., and Moscow Institute of Electronics and Mathematics of Higher School of Economics, per. Trekhsvyatitelskiy B., dom 3, 109028, Moscow, Russia, [email protected] 5. IOTA, Murrumbateman, NSW, Australia, [email protected] 6. IOTA, Forest Glen, MD, USA, [email protected] 7. Carl Sagan Center at the SETI Institute, 189 Bernardo Av, Mountain View CA 94043, USA, [email protected] Corresponding author Franck Marchis Carl Sagan Center at the SETI Institute 189 Bernardo Av Mountain View CA 94043 USA [email protected] 1 Keywords: Asteroids, Binary Asteroids, Trojan Asteroids, Occultation Abstract: On 2012 January 19, observers in the northeastern United States of America observed an occultation of 8.0-mag HIP 41337 star by the Jupiter-Trojan (911) Agamemnon, including one video recorded with a 36cm telescope that shows a deep brief secondary occultation that is likely due to a satellite, of about 5 km (most likely 3 to 10 km) across, at 278 km ±5 km (0.0931″) from the asteroid’s center as projected in the plane of the sky. A satellite this small and this close to the asteroid could not be resolved in the available VLT adaptive optics observations of Agamemnon recorded in 2003. -

7 Planetary Rings Matthew S
7 Planetary Rings Matthew S. Tiscareno Center for Radiophysics and Space Research, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA 1Introduction..................................................... 311 1.1 Orbital Elements ..................................................... 312 1.2 Roche Limits, Roche Lobes, and Roche Critical Densities .................... 313 1.3 Optical Depth ....................................................... 316 2 Rings by Planetary System .......................................... 317 2.1 The Rings of Jupiter ................................................... 317 2.2 The Rings of Saturn ................................................... 319 2.3 The Rings of Uranus .................................................. 320 2.4 The Rings of Neptune ................................................. 323 2.5 Unconfirmed Ring Systems ............................................. 324 2.5.1 Mars ............................................................... 324 2.5.2 Pluto ............................................................... 325 2.5.3 Rhea and Other Moons ................................................ 325 2.5.4 Exoplanets ........................................................... 327 3RingsbyType.................................................... 328 3.1 Dense Broad Disks ................................................... 328 3.1.1 Spiral Waves ......................................................... 329 3.1.2 Gap Edges and Moonlet Wakes .......................................... 333 3.1.3 Radial Structure ..................................................... -

14790 (Stsci Edit Number: 0, Created: Friday, July 29, 2016 2:42:55 PM EST) - Overview
Proposal 14790 (STScI Edit Number: 0, Created: Friday, July 29, 2016 2:42:55 PM EST) - Overview 14790 - Investigating the binary nature of active asteroid 288P/300163 Cycle: 24, Proposal Category: GO (Availability Mode: SUPPORTED) INVESTIGATORS Name Institution E-Mail Dr. Jessica Agarwal (PI) (ESA Member) (Conta Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research [email protected] ct) Dr. David Jewitt (CoI) (AdminUSPI) (Contact) University of California - Los Angeles [email protected] Dr. Harold A. Weaver (CoI) (Contact) The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Labor [email protected] atory Max Mutchler (CoI) (Contact) Space Telescope Science Institute [email protected] Dr. Stephen M. Larson (CoI) University of Arizona [email protected] VISITS Visit Targets used in Visit Configurations used in Visit Orbits Used Last Orbit Planner Run OP Current with Visit? 01 (1) 288P WFC3/UVIS 1 29-Jul-2016 15:42:51.0 yes 02 (1) 288P WFC3/UVIS 1 29-Jul-2016 15:42:52.0 yes 03 (1) 288P WFC3/UVIS 1 29-Jul-2016 15:42:53.0 yes 04 (1) 288P WFC3/UVIS 1 29-Jul-2016 15:42:54.0 yes 05 (1) 288P WFC3/UVIS 1 29-Jul-2016 15:42:54.0 yes 5 Total Orbits Used ABSTRACT We propose to study the suspected binary nature of active asteroid 288P/300163. We aim to confirm or disprove the existence of a binary nucleus, and - if confirmed - to measure the mutual orbital period and orbit orientation of the compoents, and their sizes. We request 5 orbits of WFC3 1 Proposal 14790 (STScI Edit Number: 0, Created: Friday, July 29, 2016 2:42:55 PM EST) - Overview imaging, spaced at intervals of 8-12 days. -

The Rings and Inner Moons of Uranus and Neptune: Recent Advances and Open Questions
Workshop on the Study of the Ice Giant Planets (2014) 2031.pdf THE RINGS AND INNER MOONS OF URANUS AND NEPTUNE: RECENT ADVANCES AND OPEN QUESTIONS. Mark R. Showalter1, 1SETI Institute (189 Bernardo Avenue, Mountain View, CA 94043, mshowal- [email protected]! ). The legacy of the Voyager mission still dominates patterns or “modes” seem to require ongoing perturba- our knowledge of the Uranus and Neptune ring-moon tions. It has long been hypothesized that numerous systems. That legacy includes the first clear images of small, unseen ring-moons are responsible, just as the nine narrow, dense Uranian rings and of the ring- Ophelia and Cordelia “shepherd” ring ε. However, arcs of Neptune. Voyager’s cameras also first revealed none of the missing moons were seen by Voyager, sug- eleven small, inner moons at Uranus and six at Nep- gesting that they must be quite small. Furthermore, the tune. The interplay between these rings and moons absence of moons in most of the gaps of Saturn’s rings, continues to raise fundamental dynamical questions; after a decade-long search by Cassini’s cameras, sug- each moon and each ring contributes a piece of the gests that confinement mechanisms other than shep- story of how these systems formed and evolved. herding might be viable. However, the details of these Nevertheless, Earth-based observations have pro- processes are unknown. vided and continue to provide invaluable new insights The outermost µ ring of Uranus shares its orbit into the behavior of these systems. Our most detailed with the tiny moon Mab. Keck and Hubble images knowledge of the rings’ geometry has come from spanning the visual and near-infrared reveal that this Earth-based stellar occultations; one fortuitous stellar ring is distinctly blue, unlike any other ring in the solar alignment revealed the moon Larissa well before Voy- system except one—Saturn’s E ring. -

Planetary Rings
CLBE001-ESS2E November 10, 2006 21:56 100-C 25-C 50-C 75-C C+M 50-C+M C+Y 50-C+Y M+Y 50-M+Y 100-M 25-M 50-M 75-M 100-Y 25-Y 50-Y 75-Y 100-K 25-K 25-19-19 50-K 50-40-40 75-K 75-64-64 Planetary Rings Carolyn C. Porco Space Science Institute Boulder, Colorado Douglas P. Hamilton University of Maryland College Park, Maryland CHAPTER 27 1. Introduction 5. Ring Origins 2. Sources of Information 6. Prospects for the Future 3. Overview of Ring Structure Bibliography 4. Ring Processes 1. Introduction houses, from coalescing under their own gravity into larger bodies. Rings are arranged around planets in strikingly dif- Planetary rings are those strikingly flat and circular ap- ferent ways despite the similar underlying physical pro- pendages embracing all the giant planets in the outer Solar cesses that govern them. Gravitational tugs from satellites System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Like their account for some of the structure of densely-packed mas- cousins, the spiral galaxies, they are formed of many bod- sive rings [see Solar System Dynamics: Regular and ies, independently orbiting in a central gravitational field. Chaotic Motion], while nongravitational effects, includ- Rings also share many characteristics with, and offer in- ing solar radiation pressure and electromagnetic forces, valuable insights into, flattened systems of gas and collid- dominate the dynamics of the fainter and more diffuse dusty ing debris that ultimately form solar systems. Ring systems rings. Spacecraft flybys of all of the giant planets and, more are accessible laboratories capable of providing clues about recently, orbiters at Jupiter and Saturn, have revolutionized processes important in these circumstellar disks, structures our understanding of planetary rings. -

March 21–25, 2016
FORTY-SEVENTH LUNAR AND PLANETARY SCIENCE CONFERENCE PROGRAM OF TECHNICAL SESSIONS MARCH 21–25, 2016 The Woodlands Waterway Marriott Hotel and Convention Center The Woodlands, Texas INSTITUTIONAL SUPPORT Universities Space Research Association Lunar and Planetary Institute National Aeronautics and Space Administration CONFERENCE CO-CHAIRS Stephen Mackwell, Lunar and Planetary Institute Eileen Stansbery, NASA Johnson Space Center PROGRAM COMMITTEE CHAIRS David Draper, NASA Johnson Space Center Walter Kiefer, Lunar and Planetary Institute PROGRAM COMMITTEE P. Doug Archer, NASA Johnson Space Center Nicolas LeCorvec, Lunar and Planetary Institute Katherine Bermingham, University of Maryland Yo Matsubara, Smithsonian Institute Janice Bishop, SETI and NASA Ames Research Center Francis McCubbin, NASA Johnson Space Center Jeremy Boyce, University of California, Los Angeles Andrew Needham, Carnegie Institution of Washington Lisa Danielson, NASA Johnson Space Center Lan-Anh Nguyen, NASA Johnson Space Center Deepak Dhingra, University of Idaho Paul Niles, NASA Johnson Space Center Stephen Elardo, Carnegie Institution of Washington Dorothy Oehler, NASA Johnson Space Center Marc Fries, NASA Johnson Space Center D. Alex Patthoff, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Cyrena Goodrich, Lunar and Planetary Institute Elizabeth Rampe, Aerodyne Industries, Jacobs JETS at John Gruener, NASA Johnson Space Center NASA Johnson Space Center Justin Hagerty, U.S. Geological Survey Carol Raymond, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Lindsay Hays, Jet Propulsion Laboratory Paul Schenk, -

Binary and Multiple Systems of Asteroids
Binary and Multiple Systems Andrew Cheng1, Andrew Rivkin2, Patrick Michel3, Carey Lisse4, Kevin Walsh5, Keith Noll6, Darin Ragozzine7, Clark Chapman8, William Merline9, Lance Benner10, Daniel Scheeres11 1JHU/APL [[email protected]] 2JHU/APL [[email protected]] 3University of Nice-Sophia Antipolis/CNRS/Observatoire de la Côte d'Azur [[email protected]] 4JHU/APL [[email protected]] 5University of Nice-Sophia Antipolis/CNRS/Observatoire de la Côte d'Azur [[email protected]] 6STScI [[email protected]] 7Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics [[email protected]] 8SwRI [[email protected]] 9SwRI [[email protected]] 10JPL [[email protected]] 11Univ Colorado [[email protected]] Abstract A sizable fraction of small bodies, including roughly 15% of NEOs, is found in binary or multiple systems. Understanding the formation processes of such systems is critical to understanding the collisional and dynamical evolution of small body systems, including even dwarf planets. Binary and multiple systems provide a means of determining critical physical properties (masses, densities, and rotations) with greater ease and higher precision than is available for single objects. Binaries and multiples provide a natural laboratory for dynamical and collisional investigations and may exhibit unique geologic processes such as mass transfer or even accretion disks. Missions to many classes of planetary bodies – asteroids, Trojans, TNOs, dwarf planets – can offer enhanced science return if they target binary or multiple systems. Introduction Asteroid lightcurves were often interpreted through the 1970s and 1980s as showing evidence for satellites, and occultations of stars by asteroids also provided tantalizing if inconclusive hints that asteroid satellites may exist. -

Abstracts of the 50Th DDA Meeting (Boulder, CO)
Abstracts of the 50th DDA Meeting (Boulder, CO) American Astronomical Society June, 2019 100 — Dynamics on Asteroids break-up event around a Lagrange point. 100.01 — Simulations of a Synthetic Eurybates 100.02 — High-Fidelity Testing of Binary Asteroid Collisional Family Formation with Applications to 1999 KW4 Timothy Holt1; David Nesvorny2; Jonathan Horner1; Alex B. Davis1; Daniel Scheeres1 Rachel King1; Brad Carter1; Leigh Brookshaw1 1 Aerospace Engineering Sciences, University of Colorado Boulder 1 Centre for Astrophysics, University of Southern Queensland (Boulder, Colorado, United States) (Longmont, Colorado, United States) 2 Southwest Research Institute (Boulder, Connecticut, United The commonly accepted formation process for asym- States) metric binary asteroids is the spin up and eventual fission of rubble pile asteroids as proposed by Walsh, Of the six recognized collisional families in the Jo- Richardson and Michel (Walsh et al., Nature 2008) vian Trojan swarms, the Eurybates family is the and Scheeres (Scheeres, Icarus 2007). In this theory largest, with over 200 recognized members. Located a rubble pile asteroid is spun up by YORP until it around the Jovian L4 Lagrange point, librations of reaches a critical spin rate and experiences a mass the members make this family an interesting study shedding event forming a close, low-eccentricity in orbital dynamics. The Jovian Trojans are thought satellite. Further work by Jacobson and Scheeres to have been captured during an early period of in- used a planar, two-ellipsoid model to analyze the stability in the Solar system. The parent body of the evolutionary pathways of such a formation event family, 3548 Eurybates is one of the targets for the from the moment the bodies initially fission (Jacob- LUCY spacecraft, and our work will provide a dy- son and Scheeres, Icarus 2011). -

Color Study of Asteroid Families Within the MOVIS Catalog David Morate1,2, Javier Licandro1,2, Marcel Popescu1,2,3, and Julia De León1,2
A&A 617, A72 (2018) Astronomy https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/201832780 & © ESO 2018 Astrophysics Color study of asteroid families within the MOVIS catalog David Morate1,2, Javier Licandro1,2, Marcel Popescu1,2,3, and Julia de León1,2 1 Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), C/Vía Láctea s/n, 38205 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain e-mail: [email protected] 2 Departamento de Astrofísica, Universidad de La Laguna, 38205 La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain 3 Astronomical Institute of the Romanian Academy, 5 Cu¸titulde Argint, 040557 Bucharest, Romania Received 6 February 2018 / Accepted 13 March 2018 ABSTRACT The aim of this work is to study the compositional diversity of asteroid families based on their near-infrared colors, using the data within the MOVIS catalog. As of 2017, this catalog presents data for 53 436 asteroids observed in at least two near-infrared filters (Y, J, H, or Ks). Among these asteroids, we find information for 6299 belonging to collisional families with both Y J and J Ks colors defined. The work presented here complements the data from SDSS and NEOWISE, and allows a detailed description− of− the overall composition of asteroid families. We derived a near-infrared parameter, the ML∗, that allows us to distinguish between four generic compositions: two different primitive groups (P1 and P2), a rocky population, and basaltic asteroids. We conducted statistical tests comparing the families in the MOVIS catalog with the theoretical distributions derived from our ML∗ in order to classify them according to the above-mentioned groups. We also studied the background populations in order to check how similar they are to their associated families. -

1 Rotation Periods of Binary Asteroids with Large Separations
Rotation Periods of Binary Asteroids with Large Separations – Confronting the Escaping Ejecta Binaries Model with Observations a,b,* b a D. Polishook , N. Brosch , D. Prialnik a Department of Geophysics and Planetary Sciences, Tel-Aviv University, Israel. b The Wise Observatory and the School of Physics and Astronomy, Tel-Aviv University, Israel. * Corresponding author: David Polishook, [email protected] Abstract Durda et al. (2004), using numerical models, suggested that binary asteroids with large separation, called Escaping Ejecta Binaries (EEBs), can be created by fragments ejected from a disruptive impact event. It is thought that six binary asteroids recently discovered might be EEBs because of the high separation between their components (~100 > a/Rp > ~20). However, the rotation periods of four out of the six objects measured by our group and others and presented here show that these suspected EEBs have fast rotation rates of 2.5 to 4 hours. Because of the small size of the components of these binary asteroids, linked with this fast spinning, we conclude that the rotational-fission mechanism, which is a result of the thermal YORP effect, is the most likely formation scenario. Moreover, scaling the YORP effect for these objects shows that its timescale is shorter than the estimated ages of the three relevant Hirayama families hosting these binary asteroids. Therefore, only the largest (D~19 km) suspected asteroid, (317) Roxane , could be, in fact, the only known EEB. In addition, our results confirm the triple nature of (3749) Balam by measuring mutual events on its lightcurve that match the orbital period of a nearby satellite in addition to its distant companion. -

Binary Asteroids and the Formation of Doublet Craters
ICARUS 124, 372±391 (1996) ARTICLE NO. 0215 Binary Asteroids and the Formation of Doublet Craters WILLIAM F. BOTTKE,JR. Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Mail Code 170-25, Pasadena, California 91125 E-mail: [email protected] AND H. JAY MELOSH Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona 85721 Received April 29, 1996; revised August 14, 1996 found we could duplicate the observed fraction of doublet cra- At least 10% (3 out of 28) of the largest known impact craters ters found on Earth, Venus, and Mars. Our results suggest on Earth and a similar fraction of all impact structures on that any search for asteroid satellites should place emphasis Venus are doublets (i.e., have a companion crater nearby), on km-sized Earth-crossing asteroids with short-rotation formed by the nearly simultaneous impact of objects of compa- periods. 1996 Academic Press, Inc. rable size. Mars also has doublet craters, though the fraction found there is smaller (2%). These craters are too large and too far separated to have been formed by the tidal disruption 1. INTRODUCTION of an asteroid prior to impact, or from asteroid fragments dispersed by aerodynamic forces during entry. We propose that Two commonly held paradigms about asteroids and some fast rotating rubble-pile asteroids (e.g., 4769 Castalia), comets are that (a) they are composed of non-fragmented after experiencing a close approach with a planet, undergo tidal chunks of rock or rock/ice mixtures, and (b) they are soli- breakup and split into multiple co-orbiting fragments. -

Asteroid Family Identification 613
Bendjoya and Zappalà: Asteroid Family Identification 613 Asteroid Family Identification Ph. Bendjoya University of Nice V. Zappalà Astronomical Observatory of Torino Asteroid families have long been known to exist, although only recently has the availability of new reliable statistical techniques made it possible to identify a number of very “robust” groupings. These results have laid the foundation for modern physical studies of families, thought to be the direct result of energetic collisional events. A short summary of the current state of affairs in the field of family identification is given, including a list of the most reliable families currently known. Some likely future developments are also discussed. 1. INTRODUCTION calibrate new identification methods. According to the origi- nal papers published in the literature, Brouwer (1951) used The term “asteroid families” is historically linked to the a fairly subjective criterion to subdivide the Flora family name of the Japanese researcher Kiyotsugu Hirayama, who delineated by Hirayama. Arnold (1969) assumed that the was the first to use the concept of orbital proper elements to asteroids are dispersed in the proper-element space in a identify groupings of asteroids characterized by nearly iden- Poisson distribution. Lindblad and Southworth (1971) cali- tical orbits (Hirayama, 1918, 1928, 1933). In interpreting brated their method in such a way as to find good agree- these results, Hirayama made the hypothesis that such a ment with Brouwer’s results. Carusi and Massaro (1978) proximity could not be due to chance and proposed a com- adjusted their method in order to again find the classical mon origin for the members of these groupings.