Press Release
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Showcasing Innovative Greece
Showcasing Innovative Greece Edited by Christos Bezirtzoglou Foreword The first experimental activities to support innovation in relation to regional and social policy, effectively pi- oneering the development of the knowledge-based economy at regional level, were launched by the Commis- sion in 1993-94. Today, nearly one in three regional authorities across the EU-15 have formulated a Regional Innovation Strategy or a Regional Innovation Society Initiative, aimed at developing effective innovation sys- tems and spreading Information & Communication Technologies related know-how at regional level. A new system for European Regional Development Fund regional programmes of innovative actions was in- troduced in 2001 to underpin the Community priorities to increase regional competitiveness, technology and innovation by applying new forms of IT and promoting sustainable development. For first time, in 2002 the Region of Peloponnesus was actively involved into initiatives preparing the ground and paving the way for the promotion of innovation with the development of a Regional Innovation Strategy (RIPE programme). The strategic approach has been based on a widespread public debate that facilitates and promotes consensus and encourages a shared strategic view of the Region’s economy through the develop- ment of long term plans by businesses. The scheme has been fully endorsed and agreed upon by the relevant support agencies. In particularly, the project has provided an impulse for the region to tackle the issue of in- novation. In the case of the Information Society, for less information society mature prefectures of the region For prefectures with a lower level of awareness and maturity regarding the Information Society and what it entails, the RIPE programme promotion has proved crucial. -

The Role of Innovation in Regional Development in Greece
MASTER THESIS THE ROLE OF INNOVATION IN REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT IN GREECE POSING A GREEK CASE STUDY BETWEEN THE DEBATE OF PLACE- BASED VS SPATIAL BLIND POLICIES BY THEODOROS SOUKOS SUPERVISOR PHILIP MCCANN UNIVERSITY OF GRONINGEN FACULTY OF SPATIAL SCIENCES RESEARCH MASTER IN REGIONAL STUDIES: SPACES AND PLACES, ANALYSIS AND INTERVENTION MASTER THESIS THE ROLE OF INNOVATION IN REGIONAL DEVELOPMENT IN GREECE POSING A GREEK CASE STUDY BETWEEN THE DEBATE OF PLACE-BASED VS SPATIAL BLIND POLICIES BY THEODOROS SOUKOS ST. NUMBER: 2351366 SUPERVISOR PHILIP MCCANN GRONINGEN, AUGUST 2014 2 ABSTRACT The role of innovation in regional economic development attracts increasingly the interest of public policies. Especially among the regions of the EU, the innovation policy and its relation to the cohesion policy framework gather much of this interest. This master thesis examines the role of innovation policy in regional development of a particular case study region in Greece. In order to investigate this role, the master thesis draws a special attention into the debate between the spatial blind policy argument (World Bank) and the place-based policy argument (OECD) and their policy implications. The review of the theory and the policy debate provides the most important insights for guidance of this research. In the first stage of this research, the investigation of prominent documents and studies on innovation performance of Greece, Greek regions and the region of Attica in particular highlights some key policy areas for consideration. The second stage of this research is devoted to interviews with policy experts with respect to innovation. The results of the interviews were extracted through the framework analysis approach to qualitative research. -

RIS3 Regional Assessment: Central Greece
Smart Specialisation Strategies in Greece – expert team review for DG REGIO RIS3 Regional Assessment: Central Greece A report to the European Commission, Directorate General for Regional Policy, Unit I3 - Greece & Cyprus December 2012 (final version) Alasdair Reid, Nicos Komninos, Jorge-A. Sanchez-P., Panayiotis Tsanakas Table of Contents 1. Executive summary: Overall conclusions and recommendations 1 2. Regional Innovation Performance and potential 3 2.1 Regional profile and specialisation 3 2.2 The strengths and weaknesses of the regional innovation system 5 3. Stakeholder involvement and governance of research and innovation policies 6 3.1 Stakeholder involvement in strategy design and implementation 6 3.2 Multi-level governance and synergies between policies and funds 7 3.3 Vision for the Region 8 4. Towards a regional smart specialisation strategy 8 4.1 The regional research and innovation policy 8 4.2 Cluster and entrepreneurship policies 9 4.3 Digital economy and ICT policies 11 5. Monitoring and evaluation 13 Appendix A List of people attending regional workshop 14 Appendix B List of key documents and reference materials 14 Appendix C Key Actors in the regional innovation system 14 Appendix D Regional RTDI funding under the OP Competitiveness and Innovation 16 Appendix E Total Gross value added at basic prices – Central Greece 17 Appendix F Relative regional specialisation in 20 industries – Central Greece 18 Figures Figure 1 Summary benchmark of regional innovation performance ...............................3 Figure 2 : SWOT of -

Country Compendium
Country Compendium A companion to the English Style Guide July 2021 Translation © European Union, 2011, 2021. The reproduction and reuse of this document is authorised, provided the sources and authors are acknowledged and the original meaning or message of the texts are not distorted. The right holders and authors shall not be liable for any consequences stemming from the reuse. CONTENTS Introduction ...............................................................................1 Austria ......................................................................................3 Geography ................................................................................................................... 3 Judicial bodies ............................................................................................................ 4 Legal instruments ........................................................................................................ 5 Government bodies and administrative divisions ....................................................... 6 Law gazettes, official gazettes and official journals ................................................... 6 Belgium .....................................................................................9 Geography ................................................................................................................... 9 Judicial bodies .......................................................................................................... 10 Legal instruments ..................................................................................................... -

Notio Aigaio
The added value of regional programmes of innovative actions stems from the lessons that can be drawn from these innovative approaches, which allow for experimentation with new ideas and the demonstration of new hypotheses. This ranges from the possibilities of identification of good practice, to the exchange of knowledge and experience that can be trans- ferred to the Community Support Framework mainstream programmes. This publication takes a closer look both at the first and second genera- tion of the Greek regional programmes of innovative actions. Based on their implementation experiences, it illustrates their individual actions in addition to attempting to produce diverse classification typologies of these Greek "innovative actions". Europe is more than a bloc of nations. It is also a collection of regions. But regional wealth variations remain high and in most Member States it is the regions with the capital cities that have the highest per capita GDP. It is widely accepted that each region needs to brand her global (global and local) image according to its unique physical and intangible assets. Practical activities need to be designed, implemented and monitored on the spot. I hope that this book will help policy makers and other regional innova- Showcasing Innovative Greece Innovative Showcasing tion policy practitioners to make more informed choices towards this goal. Anna ANDRICOPOULOU Project Manager Net Force 2006 ISBN: 960-89350-0-8 Edited by Christos Bezirtzoglou by Christos Edited Co-financed by the ERDF Showcasing Innovative Greece EU Region of Peloponnesus Showcasing Innovative Greece Edited by Christos Bezirtzoglou Foreword The first experimental activities to support innovation in relation to regional and social policy, effectively pi- oneering the development of the knowledge-based economy at regional level, were launched by the Commis- sion in 1993-94. -

Transition to First Birth During the Great Recession: the Case of Greece Charalampos Dantis and Ester Lucia Rizzi*
Dantis and Rizzi Genus (2020) 76:1 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41118-019-0070-1 Genus ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Transition to first birth during the Great Recession: the case of Greece Charalampos Dantis and Ester Lucia Rizzi* * Correspondence: ester.rizzi@ uclouvain.be Abstract: In this study, we examine the effects of the economic uncertainty of Center for Demographic Research partners on the transition to first birth in Greece before and after the onset of the (DEMO), Université Catholique de recent economic crisis. After selecting a sample of childless couples, we applied a Louvain, Place Montesquieu, 1 / – L2.08.03, 1348 Louvain-la-Neuve, random effects model to EU-SILC data for the period 2005 2013. Few studies have Belgium focused on the association between economic uncertainty and fertility in Greece considering characteristics of both partners. Even fewer studies have examined panel data in the context of the recent crisis. Our findings show that Greek couples in which both partners are employed, have a high income, or are highly educated are in a more favourable position to have a first child. During the Greek Great Recession, corresponding in our study to the period 2010–2013, the odds of having a first child decreased to half the odds in the 2005–2009 period. The recession period also modified the effect of couples’ characteristics on first childbearing. During the economic crisis, male breadwinner couples were particularly penalized in their transition to have a first child. Surprisingly, couples with at least one temporary worker, usually the woman, were encouraged to have their first child. -

RIS3 Review Report Epirus
Smart Specialisation Strategies in Greece – expert team review for DG REGIO RIS3 Regional Assessment: Epirus A report to the European Commission, Directorate General for Regional Policy, Unit I3 - Greece & Cyprus December 2012 (final version) Alasdair Reid, Nicos Komninos, Jorge-A. Sanchez-P., Panayiotis Tsanakas Table of Contents 1. Executive summary: Overall conclusions and recommendations 1 2. Regional Innovation Performance and potential 3 2.1 Regional profile and specialisation 3 2.2 The strengths and weaknesses of the regional innovation system 6 3. Stakeholder involvement and governance of research and innovation policies 8 3.1 Stakeholder involvement in strategy design and implementation 8 3.2 Multi-level governance and synergies between policies and funds 10 3.3 Vision for the region 10 4. Towards a regional smart specialisation strategy 11 4.1 Regional research and innovation policies 11 4.2 Cluster and entrepreneurship policies 13 4.3 Digital economy and ICT policies 15 5. Monitoring and evaluation 16 Appendix A List of people attending the workshop 17 Appendix B List of key documents and reference materials 17 Appendix C Key actors in the regional innovation system 17 Appendix D Regional RTDI funding under the OP Competitiveness and Innovation 19 Appendix E Gross value added by sector in Epirus (% of total value added) 20 Figures Figure 1 Summary benchmark of regional innovation performance, Epirus .................. 3 Figure 2 Relative regional specialisation in 20 industries – Epirus ................................ 4 Figure 3: SWOT of regional innovation potential and specialisation .............................. 5 Figure 4 : Current and future regional R&I priorities ......................................................11 Smart Specialisation Strategies in Greece – expert team review for DG REGIO 1. -

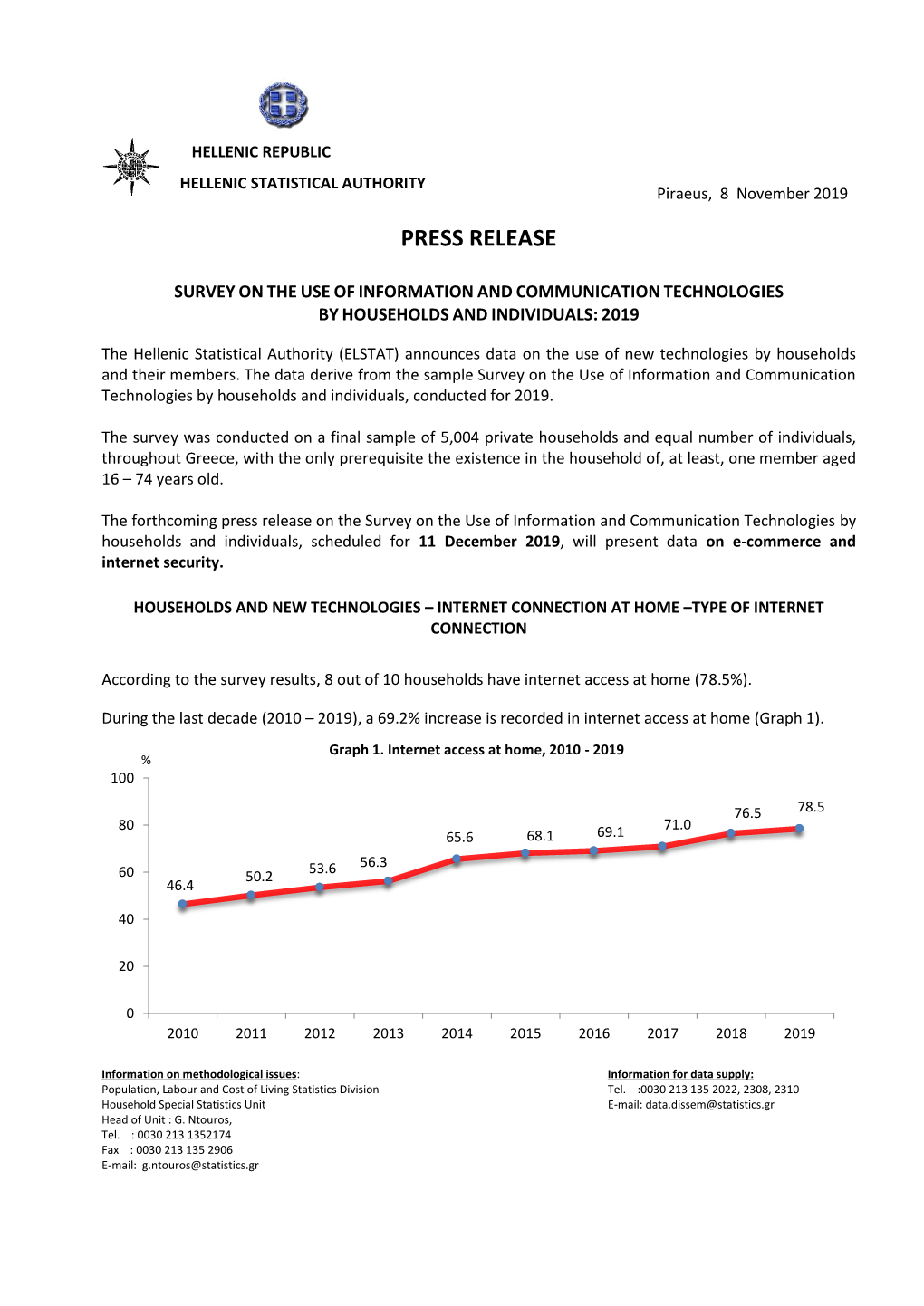
Press Release Survey on the Use of Information and Communication Technologies by Households and Individuals: 2016
HELLENIC REPUBLIC HELLENIC STATISTICAL AUTHORITY Piraeus, 14 December 2016 PRESS RELEASE SURVEY ON THE USE OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES BY HOUSEHOLDS AND INDIVIDUALS: 2016 E-COMMERCE – PRIVACY AND PROTECTION OF PERSONAL DATA The Hellenic Statistical Authority announces data on the use of information and communication technologies by households and their members and more specifically on e-commerce and privacy and protection of personal data of users. The data derive from the sample Survey on the Use of Information and Communication Technologies by households and individuals, conducted for 2016. The survey was conducted on 4,774 private households and equal number of household members, throughout Greece, with the only prerequisite the existence in the household of, at least, one member aged 16 – 74 years old. BACKGROUNG AND PURPOSE OF THE SURVEY The survey collects data on the access of households to selected information and communication technologies. More specifically, data are collected on internet access and ubiquitous internet access, transactions with public authorities via the internet (e-government), e-commerce, etc. The survey was first conducted in Greece in 2002 and it is fully harmonized with the corresponding surveys conducted by the other EU Member States. The survey data are collected via telephone by means of questions answered by one only member of the household that is randomly selected, with the only prerequisite that he/she is 16-74 years old. The questionnaire helps collecting data with regard to the household, in general, as well as individual information concerning the selected household member. E-COMMERCE 3 out of 10 persons (32.8%) aged 16-74 years old, having E-commerce, 2010-2016 ever accessed the internet, purchased or ordered goods or % 40 services over the internet for 33,8 32,8 29,5 private use, during the 1st 26,9 27,0 quarter of 2016. -

RIS3 Review Report Western Greece
Smart Specialisation Strategies in Greece – expert team review for DG REGIO RIS3 Regional Assessment: West- ern Greece A report to the European Commission, Directorate General for Regional Policy, Unit I3 - Greece & Cyprus December 2012 (final version) Alasdair Reid, Nicos Komninos, Jorge-A. Sanchez-P., Panayiotis Tsanakas Contents 1. Executive summary 1 2. Regional Innovation System - performance and potential 3 2.1 Regional innovation performance and specialisation profile 3 2.2 The strengths and weaknesses of the regional innovation system 6 3. Stakeholder involvement and governance of research and innovation policies 7 3.1 Stakeholder involvement in strategy design and implementation 7 3.2 Multi-level governance and synergies between policies and funding sources 9 3.3 Vision for the region 9 4. Towards a regional innovation and smart specialisation strategy 10 4.1 Regional research and innovation policy 10 4.2 Cluster and entrepreneurship policies 12 4.3 Digital economy and ICT policies 14 4.3.1 Broadband infrastructure and NGA networks 15 4.3.2 E-services 15 4.3.3 Ensuring investments in e-government 16 5. Monitoring and evaluation 19 Appendix A List of people interviewed 20 Appendix B Key documents and references 21 Appendix C Estimated Structural Fund allocation for RTDI per Greek region 22 Appendix D Regional RTDI funding under the OP Competitiveness and Innovation 23 Appendix E Total Gross value added at basic prices – Western Greece 24 Appendix F Relative regional specialisation in 20 industries – Western Greece 25 Figures Figure 1 Summary benchmark of regional innovation performance ............................... 4 Figure 2 : SWOT of regional innovation potential and specialisation ............................ -

"Europe 2020" and the Greek Regions
A Service of Leibniz-Informationszentrum econstor Wirtschaft Leibniz Information Centre Make Your Publications Visible. zbw for Economics Saratsis, Yiannis; Kotios, Angelos Conference Paper Europe 2020 Strategy, Cohesion Policy and Greek Regions: Are we "smart" enough? 51st Congress of the European Regional Science Association: "New Challenges for European Regions and Urban Areas in a Globalised World", 30 August - 3 September 2011, Barcelona, Spain Provided in Cooperation with: European Regional Science Association (ERSA) Suggested Citation: Saratsis, Yiannis; Kotios, Angelos (2011) : Europe 2020 Strategy, Cohesion Policy and Greek Regions: Are we "smart" enough?, 51st Congress of the European Regional Science Association: "New Challenges for European Regions and Urban Areas in a Globalised World", 30 August - 3 September 2011, Barcelona, Spain, European Regional Science Association (ERSA), Louvain-la-Neuve This Version is available at: http://hdl.handle.net/10419/120131 Standard-Nutzungsbedingungen: Terms of use: Die Dokumente auf EconStor dürfen zu eigenen wissenschaftlichen Documents in EconStor may be saved and copied for your Zwecken und zum Privatgebrauch gespeichert und kopiert werden. personal and scholarly purposes. Sie dürfen die Dokumente nicht für öffentliche oder kommerzielle You are not to copy documents for public or commercial Zwecke vervielfältigen, öffentlich ausstellen, öffentlich zugänglich purposes, to exhibit the documents publicly, to make them machen, vertreiben oder anderweitig nutzen. publicly available on the internet, or to distribute or otherwise use the documents in public. Sofern die Verfasser die Dokumente unter Open-Content-Lizenzen (insbesondere CC-Lizenzen) zur Verfügung gestellt haben sollten, If the documents have been made available under an Open gelten abweichend von diesen Nutzungsbedingungen die in der dort Content Licence (especially Creative Commons Licences), you genannten Lizenz gewährten Nutzungsrechte. -

RIS3 Review Report Ionian Islands
Smart Specialisation Strategies in Greece – expert team review for DG REGIO RIS3 Regional Assessment: Ioanian Islands A report to the European Commission, Directorate General for Regional Policy, Unit I3 - Greece & Cyprus December 2012 (final version) Alasdair Reid, Nicos Komninos, Jorge-A. Sanchez-P., Panayiotis Tsanakas Table of Contents 1. Executive summary: Overall conclusions and recommendations 1 2. Regional Innovation Performance and potential 3 2.1 Regional profile and specialisation 3 2.2 The strengths and weaknesses of the regional innovation system 6 3. Stakeholder involvement and governance of research and innovation policies 6 4. Towards a regional smart specialisation strategy 8 4.1 Regional research and innovation policies 8 4.2 Cluster policies 10 4.3 Digital economy and ICT policies 12 5. Monitoring and evaluation 13 Appendix A Key documents and reference materials 14 Appendix B Key actors in the regional innovation system 14 Appendix C Regional RTDI funding under the OP Competitiveness and Innovation 15 Appendix D Total Gross value added at basic prices – Ionian Islands 16 Appendix E Relative regional specialisation in 20 industries in the Ionian Islands 17 Figures Figure 1 Summary benchmark of regional innovation performance ............................... 3 Figure 2: SWOT of regional innovation potential and specialisation .............................. 5 Figure 3: 3I regional programme of innovative actions - main actions ........................... 7 Figure 4: Virtual tour of the historic centre of Corfu ........................................................ 7 Figure 5 Priorities and funding of OP Ionian Islands 2007-2013 ....................................8 Figure 6: Current regional priorities for research and innovation ...................................8 Figure 7: Mature and Emerging Clusters in the Ionian Islands ..................................... 10 Figure 8: Technologies and clusters supporting tourism in the Balearic Islands .........11 Smart Specialisation Strategies in Greece – expert team review for DG REGIO 1. -

Diagnostic Report on Undeclared Work in Greece
Diagnostic report on undeclared work in Greece DIAGNOSTIC REPORT ON UNDECLARED WORK IN GREECE INTERNATIONAL LABOUR ORGANIZATION Copyright © International Labour Organization 2016 First published 2016 Publications of the International Labour Office enjoy copyright under Protocol 2 of the Universal Copyright Convention. Nevertheless, short excerpts from them may be reproduced without authorization, on condition that the source is indicated. For rights of reproduction or translation, application should be made to ILO Publications (Rights and Licensing), International Labour Office, CH-1211 Geneva 22, Switzerland, or by email: [email protected]. The International Labour Office welcomes such applications. Libraries, institutions and other users registered with a reproduction rights organization may make copies in accordance with the licences issued to them for this purpose. Visit www.ifrro.org to find the reproduction rights organization in your country. ILO Cataloguing in Publication Data Diagnostic report on undeclared work in Greece / International Labour Office, Employment Department, Informal Economy Unit. - Geneva: ILO, 2016. ISBN: 9789221313236; 9789221313243 (web pdf) International Labour Office. Employment Department. Clandestine employment / hidden economy / labour relations / employment policy / Greece 13.01.3 The designations employed in ILO publications, which are in conformity with United Nations practice, and the presentation of material therein do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the International Labour Office concerning the legal status of any country, area or territory or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers. The responsibility for opinions expressed in signed articles, studies and other contributions rests solely with their authors, and publication does not constitute an endorsement by the International Labour Office of the opinions expressed in them.