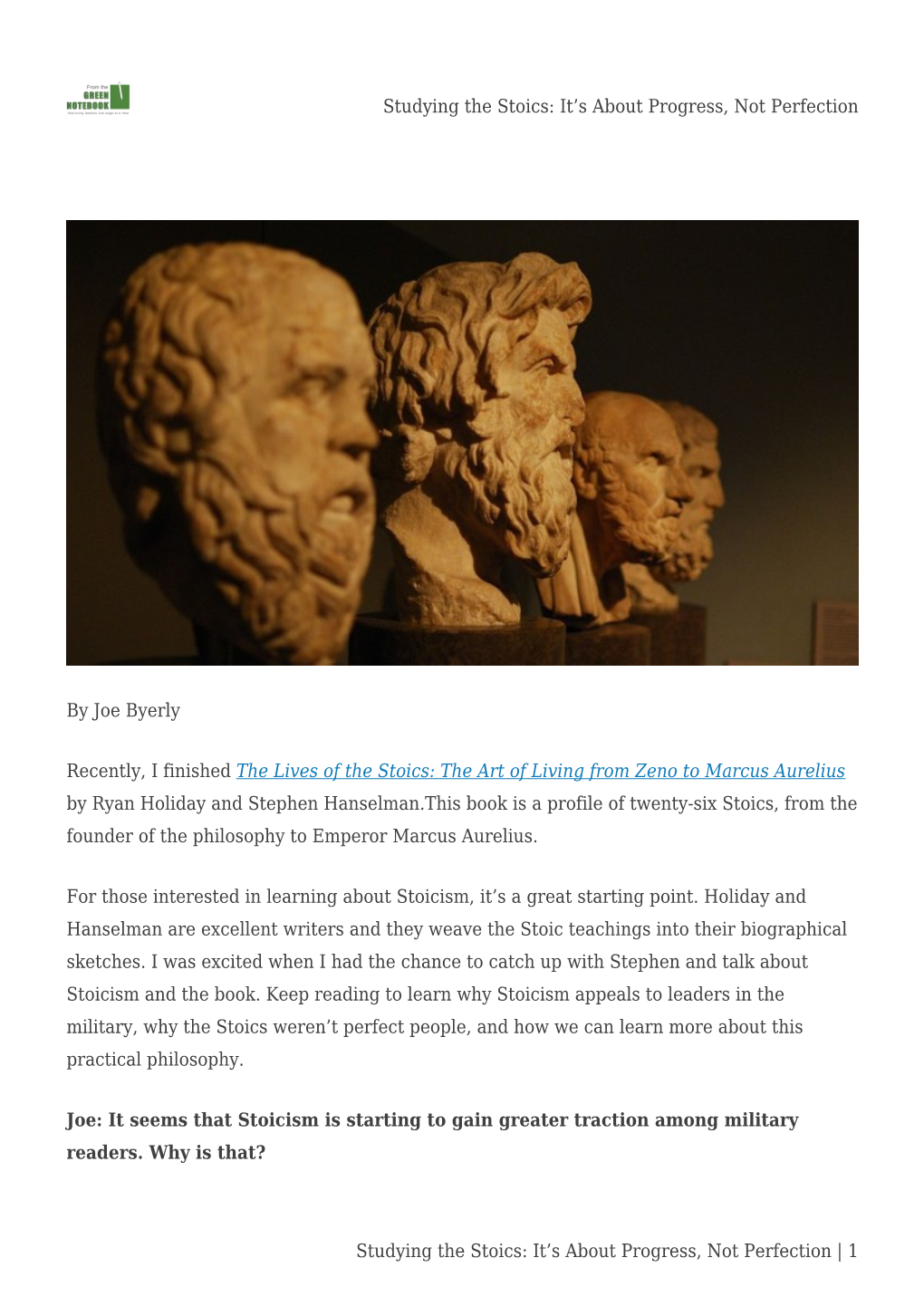
Studying the Stoics: It's About Progress, Not Perfection
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Stoic Enlightenments
Copyright © 2011 Margaret Felice Wald All rights reserved STOIC ENLIGHTENMENTS By MARGARET FELICE WALD A Dissertation submitted to the Graduate School-New Brunswick Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Graduate Program in English written under the direction of Michael McKeon and approved by ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ ________________________ New Brunswick, New Jersey October 2011 ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION Stoic Enlightenments By MARGARET FELICE WALD Dissertation Director: Michael McKeon Stoic ideals infused seventeenth- and eighteenth-century thought, not only in the figure of the ascetic sage who grins and bears all, but also in a myriad of other constructions, shaping the way the period imagined ethical, political, linguistic, epistemological, and social reform. My dissertation examines the literary manifestation of Stoicism’s legacy, in particular regarding the institution and danger of autonomy, the foundation and limitation of virtue, the nature of the passions, the difference between good and evil, and the referentiality of language. Alongside the standard satirical responses to the ancient creed’s rigor and rationalism, seventeenth- and eighteenth-century poetry, drama, and prose developed Stoic formulations that made the most demanding of philosophical ideals tenable within the framework of common experience. Instead of serving as hallmarks for hypocrisy, the literary stoics I investigate uphold a brand of stoicism fit for the post-regicidal, post- Protestant Reformation, post-scientific revolutionary world. My project reveals how writers used Stoicism to determine the viability of philosophical precept and establish ways of compensating for human fallibility. The ambivalent status of the Stoic sage, staged and restaged in countless texts, exemplified the period’s anxiety about measuring up to its ideals, its efforts to discover the plenitude of ii natural laws and to live by them. -

Praise for Ryan Holiday and Trust Me, I'm Lying
PRAISE FOR RYAN HOLIDAY AND TRUST ME, I’M LYING “Holiday effectively maps the news media landscape. Media students and bloggers would do well to heed Holiday’s informative, timely, and provocative advice.” — Publishers Weekly “This book will make online media giants very, very uncomfortable.” —Drew Curtis, founder, Fark.com “Ryan Holiday’s brilliant exposé of the unreality of the Internet should be required reading for every thinker in America.” —Edward Jay Epstein, author of How America Lost Its Secrets: Edward Snowden, the Man and the Theft “Ryan Holiday is the Machiavelli of the Internet age. Dismiss his message at your own peril: He speaks truths about the dark side of internet media which no one else dares mention.” —Michael Ellsberg, author of The Education of Millionaires “[Like] Upton Sinclair on the blogosphere.” —Tyler Cowen, MarginalRevolution.com, author of Average Is Over Trust Me I’m Lying b-format.indd 1 29/11/2017 16:02 “Ryan Holiday is the internet’s sociopathic id.” — Dan Mitchell, SF Weekly “Ryan Holiday is a media genius who promotes, inflates, and hacks some of the biggest names and brands in the world.” —Chase Jarvis, founder and CEO, CreativeLive “Ryan has a truly unique perspective on the seedy underbelly of digital culture.” —Matt Mason, former director of marketing, BitTorrent “While the observation that the internet favors speed over accuracy is hardly new, Holiday lays out how easily it is to twist it toward any end. Trust Me, I’m Lying provides valuable food for thought regarding how we receive—and perceive— information.” — New York Post Trust Me I’m Lying b-format.indd 2 29/11/2017 16:02 TRUST ME, I’M LYING Ryan Holiday is a bestselling author and a leading media strategist. -

Stoicism a School of Thought That Flourished in Greek and Roman
Stoicism A school of thought that flourished in Greek and Roman antiquity. It was one of the loftiest and most sublime philosophies in the record of Western civilization. In urging participation in the affairs of man, Stoics have always believed that the goal of all inquiry is to provide man with a mode of conduct characterized by tranquillity of mind and certainty of moral worth. Nature and scope of Stoicism For the early Stoic philosopher, as for all the post-Aristotelian schools, knowledge and its pursuit are no longer held to be ends in themselves. The Hellenistic Age was a time of transition, and the Stoic philosopher was perhaps its most influential spokesman. A new culture was in the making. The heritage of an earlier period, with Athens as its intellectual leader, was to continue, but to undergo many changes. If, as with Socrates, to know is to know oneself, rationality as the sole means by which something outside of the self might be achieved may be said to be the hallmark of Stoic belief. As a Hellenistic philosophy, Stoicism presented an ars vitae, a way of accommodation for people to whom the human condition no longer appeared as the mirror of a universal, calm, and ordered existence. Reason alone could reveal the constancy of cosmic order and the originative source of unyielding value; thus, reason became the true model for human existence. To the Stoic, virtue is an inherent feature of the world, no less inexorable in relation to man than are the laws of nature. The Stoics believed that perception is the basis of true knowledge. -

Early Pyrrhonism As a Sect of Buddhism? a Case Study in the Methodology of Comparative Philosophy
Comparative Philosophy Volume 9, No. 2 (2018): 1-40 Open Access / ISSN 2151-6014 / www.comparativephilosophy.org https://doi.org/10.31979/2151-6014(2018).090204 EARLY PYRRHONISM AS A SECT OF BUDDHISM? A CASE STUDY IN THE METHODOLOGY OF COMPARATIVE PHILOSOPHY MONTE RANSOME JOHNSON & BRETT SHULTS ABSTRACT: We offer a sceptical examination of a thesis recently advanced in a monograph published by Princeton University Press entitled Greek Buddha: Pyrrho’s Encounter with Early Buddhism in Central Asia. In this dense and probing work, Christopher I. Beckwith, a professor of Central Eurasian studies at Indiana University, Bloomington, argues that Pyrrho of Elis adopted a form of early Buddhism during his years in Bactria and Gandhāra, and that early Pyrrhonism must be understood as a sect of early Buddhism. In making his case Beckwith claims that virtually all scholars of Greek, Indian, and Chinese philosophy have been operating under flawed assumptions and with flawed methodologies, and so have failed to notice obvious and undeniable correspondences between the philosophical views of the Buddha and of Pyrrho. In this study we take Beckwith’s proposal and challenge seriously, and we examine his textual basis and techniques of translation, his methods of examining passages, his construal of problems and his reconstruction of arguments. We find that his presuppositions are contentious and doubtful, his own methods are extremely flawed, and that he draws unreasonable conclusions. Although the result of our study is almost entirely negative, we think it illustrates some important general points about the methodology of comparative philosophy. Keywords: adiaphora, anātman, anattā, ataraxia, Buddha, Buddhism, Democritus, Pāli, Pyrrho, Pyrrhonism, Scepticism, trilakṣaṇa 1. -

Ryan Holiday and Stephen Hanselman
The DAILY STOIC 366 Meditations on Wisdom, Perseverance, and the Art of Living RYAN HOLIDAY AND STEPHEN HANSELMAN PROFILE BOOKS First published in Great Britain in 2016 by PROFILE BOOKS LTD 3 Holford Yard Bevin Way London WC1X 9HD www.pro lebooks.com First published in the United States of America in 2016 by PORTFOLIO/PENGUIN An imprint of Penguin Random House LLC Copyright © Ryan Holiday and Stephen Hanselman, 2016 Translations by Stephen Hanselman 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Printed and bound in Great Britain by Clays, St Ives plc The moral right of the author has been asserted. All rights reserved. Without limiting the rights under copyright reserved above, no part of this publication may be reproduced, stored or introduced into a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form or by any means (electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise), without the prior written permission of both the copyright owner and the publisher of this book. A CIP catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library. ISBN 978 1 78125 765 4 eISBN 978 1 78283 317 8 “Of all people only those are at leisure who make time for philos- ophy, only they truly live. Not satis#ed to merely keep good watch over their own days, they annex every age to their own. All the harvest of the past is added to their store. Only an ingrate would fail to see that these great architects of venerable thoughts were born for us and have designed a way of life for us.” — S$%$&' CONTENTS INTRODUCTION * PART 1: THE DISCIPLINE OF PERCEPTION JANUARY: CLARITY + FEBRUARY: -

Platonic and Stoic Passions in Philo of Alexandria Loren Kerns George Fox University, [email protected]
Digital Commons @ George Fox University George Fox Evangelical Seminary 2013 Platonic and Stoic Passions in Philo of Alexandria Loren Kerns George Fox University, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.georgefox.edu/gfes Part of the Christianity Commons, and the Church History Commons Recommended Citation Kerns, Loren, "Platonic and Stoic Passions in Philo of Alexandria" (2013). George Fox Evangelical Seminary. Paper 6. http://digitalcommons.georgefox.edu/gfes/6 This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by Digital Commons @ George Fox University. It has been accepted for inclusion in George Fox Evangelical Seminary by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons @ George Fox University. Kings College London Platonic and Stoic Passions in Philo of Alexandria A Dissertation submitted to The School of Arts and Humanities In Candidacy for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy Department of Theology and Religious Studies By Loren Kerns London, United Kingdom July 2013 Copyright by Loren Kerns, 2013 All rights reserved. Abstract Philo of Alexandria forged his theory of the soul and its passions while expositing the meaning of Torah. Though writing as a Jewish teacher and disciple of Moses, his biblical reflections display a strong orientation toward Middle-Platonic philosophy. On the topic of the soul and its passions, however, Philo also exhibits significant Stoic influence. The introduction notes Philo’s apparent incompatible use of both the complex Platonic and the monistic Stoic psychological models. After assessing the degree to which Philo understood 'passion' to be a type of Stoic impulse or opinion (chapter one), chapter two demonstrates that Philo consistently drew upon the Stoics’ depiction of all passions as irrational, excessive, and unnatural. -

Moore, K. 2009 'Persaeus of Citium: a Lapsed Stoic?' Rosetta 7: 1-21. Http
Moore, K. 2009 ‘Persaeus of Citium: A Lapsed Stoic?’ Rosetta 7: 1-21. http://rosetta.bham.ac.uk/issue7/persaeus-citium/ http://rosetta.bham.ac.uk/issue7/persaeus-citium/ Persaeus of Citium: A Lapsed Stoic? Kenneth Moore Abstract: This article examines the historical evidence on the life of Persaeus of Citium, a Stoic philosopher and immediate student of Zeno, the founder of Stoicism. It also considers the anecdotal accounts of Persaeus’ actions with regard to Stoic philosophy as it was understood to apply during his lifetime. Persaeus was one of an elite group of scholars present at the court of Antigonus II Gonatus, King of Macedon and appears to have had a direct involvement in the political affairs of Macedonia. His activities, as recounted in the surviving sources, seem to run contrary to established Stoic customs, in particular the preference for praxis over theoria.1 However, there is also some indication that he may have been vilified by his scholarly and political enemies. This article provides a brief glimpse into the life and times of Persaeus as well as the turbulent fourth/third centuries in Greece. Introduction: Persaeus (ca. 306-243 BCE), of Citium, son of Demetrius, was a Stoic philosopher. He was also a student and close acquaintance of Zeno of Citium (ca. 334-262 BCE), the founder of Stoicism. It is difficult to obtain a clear picture of his life and philosophy since none of his own works survive and most of the sources that deal with him come from late antiquity and provide relatively little, albeit potentially quite significant, information. -

Targeting Emotion in Early Stoicism
Binghamton University The Open Repository @ Binghamton (The ORB) The Society for Ancient Greek Philosophy Newsletter 12-28-2002 Targeting Emotion in Early Stoicism Scott M. Rubarth Rollins College, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://orb.binghamton.edu/sagp Part of the Ancient History, Greek and Roman through Late Antiquity Commons, Ancient Philosophy Commons, and the History of Philosophy Commons Recommended Citation Rubarth, Scott M., "Targeting Emotion in Early Stoicism" (2002). The Society for Ancient Greek Philosophy Newsletter. 353. https://orb.binghamton.edu/sagp/353 This Article is brought to you for free and open access by The Open Repository @ Binghamton (The ORB). It has been accepted for inclusion in The Society for Ancient Greek Philosophy Newsletter by an authorized administrator of The Open Repository @ Binghamton (The ORB). For more information, please contact [email protected]. Targeting Emotion in Early Stoicism Scott M. Rubarth, Rollins College Presented to the Society for Ancient Greek Philosophy at the 2002 meeting with the Eastern Division of the American Philosophical Association, in Philadelphia The Stoic sage is a cold, heartless being who would not grieve over the loss of a beloved companion or child. Unmoved, unemotional, uncaring, the sage is an ethical and emotional monstrosity hiding behind the pretension of the so-called virtues of detachment and austerity. That, at least, is how many who study Stoic ethics perceive the sage in regard to his/her emotional life. 1 In this paper I will argue that this conception of the Stoic theory of emotion and passion is misleading; emotions, in fact, are central to Stoic ethics and apatheia should not be confused with the contemporary idea of apathy or emotional flatness. -

2280-2; Most Can Also Be Found Grouped by Topic in Motto (1970)
1 Not as a Deserter, But as a Spy: Seneca’s Reception of Epicureanism Within the history of Epicurus’ reception at Rome the figure of Seneca the Younger occupies a position of particular interest. Though not himself an Epicurean, Seneca is deeply engaged with Epicurean thought and Epicurean texts; in fact, he refers to Epicurus or to his doctrines and members of his community more than eighty times, in eight of his works, including over forty direct quotations from Epicurean writings.1 Yet his reactions are initially hard to fathom. At times painstakingly accurate, he is also capable of what seems like willful misrepresentation of Epicurus’ views; often antagonistic, he is also on occasion strikingly appreciative of what Epicurus has to offer. On some points he does not hesitate to express as his own view ideas which he knows to be Epicurean in origin. More than that, he will sometimes modify and develop those ideas in ways that make him a fascinating and yet puzzling case of Epicurean influence outside the Garden. The complexity of Seneca’s response at one time made him the case in point for that older view of Roman philosophy that spoke of “eclecticism.” Indeed the very notion of eclecticism as formulated by Eduard Zeller and Karl Praechter was devised in part as a way of accounting for Seneca’s extraordinary attitude toward the rival school.2 Even Pierluigi Donini, who in 1988 effectively demolished the wider picture of philosophy under the Roman empire as predominantly eclectic, finds Seneca to be “a completely isolated and peculiar instance.”3 More recently, numerous careful studies of the particulars of Seneca’s thought have established across the board that Seneca is indeed what he claims to be, a committed though not subservient adherent of Stoicism in all its essentials.4 For that reason it is all the 1 A full list of references is provided in Ferguson (1990), 2280-2; most can also be found grouped by topic in Motto (1970) . -

The Obstacle Is the Way Rating Focus Take-Aways
The Obstacle Is the Way The Timeless Art of Turning Trials into Triumph Ryan Holiday © 2014 From THE OBSTACLE IS THE WAY by Ryan Holiday. Summarized by arrangement with Portfolio, an imprint of Penguin Publishing Group, a division of Penguin Random House LLC 224 pages [@]Book: getab.li/23482 Rating Take-Aways 9 Applicability • Stoicism – an operating manual for life – is a pragmatic philosophy that helps people overcome their difficulties. 9 Innovation 9 Style • This venerable philosophy inspired George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, Adam 9 Smith and Frederick the Great, as well as many contemporary leaders. • Stoicism rests on three primary disciplines: “perception, action and the will.” • Perception is the way you see the world. Viewing it realistically or with a bias can help Focus or hinder you. Leadership & Management • The right action is always directed, deliberate, bold and persistent. Strategy The world can break your body, but thanks to willpower, it can never break your spirit Sales & Marketing • and mind. You – not some external entity – control your will. Finance Human Resources • Obstacles that stand in the way of progress can actually promote progress. IT, Production & Logistics • People improve by facing and meeting challenges head-on. Career & Self-Development Small Business • The obstacles you overcome provide benefits you could not otherwise realize. Economics & Politics Industries • How you think about and react to obstacles while maintaining your composure defines you. Global Business Concepts & Trends To purchase personal subscriptions or corporate solutions, visit our website at www.getAbstract.com, send an email to [email protected], or call us at our US office (1-305-936-2626) or at our Swiss office (+41-41-367-5151). -

Seneca-Letters.Pdf
CLARENDON LATER ANCIENT PHILOSOPHERS Series editors: Jonathan Barnes, Universite´ de Paris IV—Sorbonne and A. A. Long, University of California, Berkeley SENECA SELECTED PHILOSOPHICAL LETTERS Seneca’s Letters to Lucilius are a rich source of information about ancient Stoicism, an influential work for early modern philosophers, and a fascinating philosophical document in their own right. This selection of the letters aims to include those which are of greatest philosophical interest, especially those which highlight the debates between Stoics and Platonists or Aristotelians in the first century AD, and the issue, still important today, of how technical philosophical enquiry is related to the various purposes for which philosophy is practised. In addition to examining the philosophical content of each letter, Brad Inwood’s commentary discusses the literary and historical background of the letters and to their relationship with other prose works by Seneca. Seneca is the earliest Stoic author for whom we have access to a large number of complete works, and these works were highly influential in later centuries. He was also a politically influential advisor to the Roman emperor Nero and a celebrated author of prose and verse. His philosophical acuity and independence of mind make his works exciting and challenging for the modern reader. Brad Inwood is Professor of Classics and Philosophy at the University of Toronto. PUBLISHEDINTHESERIES Alcinous: The Handbook of Platonism John Dillon Epictetus: Discourses, Book Robert Dobbin Galen: On the Therapeutic Method, Books I and II R. J. Hankinson Porphyry: Introduction Jonathan Barnes Seneca: Selected Philosophical Letters Brad Inwood Sextus Empiricus: Against the Ethicists Richard Bett Sextus Empiricus: Against the Grammarians David Blank SENECA SELECTED PHILOSOPHICAL LETTERS Translated with an Introduction and Commentary by BRAD INWOOD 1 1 Great Clarendon Street, Oxford Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. -

Download Conspiracy Peter Thiel Hulk Hogan Gawker and the Anatomy of Intrigue Pdf Book by Ryan Holiday
Download Conspiracy Peter Thiel Hulk Hogan Gawker and the Anatomy of Intrigue pdf book by Ryan Holiday You're readind a review Conspiracy Peter Thiel Hulk Hogan Gawker and the Anatomy of Intrigue book. To get able to download Conspiracy Peter Thiel Hulk Hogan Gawker and the Anatomy of Intrigue you need to fill in the form and provide your personal information. Book available on iOS, Android, PC & Mac. Gather your favorite books in your digital library. * *Please Note: We cannot guarantee the availability of this ebook on an database site. Ebook File Details: Original title: Conspiracy: Peter Thiel, Hulk Hogan, Gawker, and the Anatomy of Intrigue 336 pages Publisher: Portfolio (February 27, 2018) Language: English ISBN-10: 9780735217645 ISBN-13: 978-0735217645 ASIN: 0735217645 Product Dimensions:6.4 x 1.1 x 9.2 inches File Format: PDF File Size: 18132 kB Description: A stunning story about how power works in the modern age--the book the New York Times called one helluva page-turner and The Sunday Times of London celebrated as riveting...an astonishing modern media conspiracy that is a fantastic read. Pick up the book everyone is talking about.In 2007, a short blogpost on Valleywag, the Silicon Valley-vertical... Review: One of my favorite authors, John McPhee, wrote a book about single tennis match called Levels of the Game. A book about a single tennis game does not sound like there can be much to it, but the story of the match is really the story of two men, how they were raised, what lead them to that space and time and playing style, and what that match meant as..