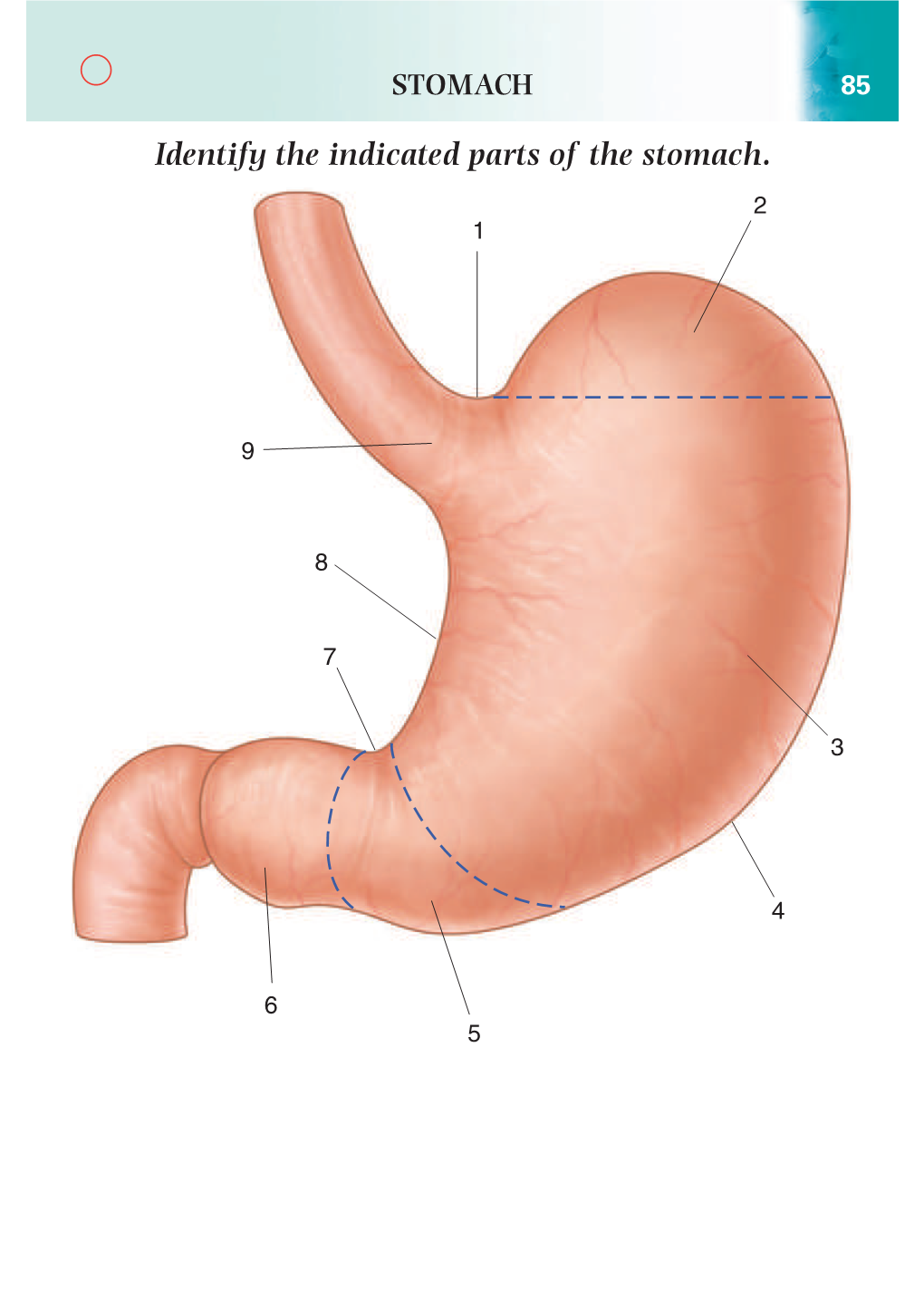
Identify the Indicated Parts of the Stomach. 2 1
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Jemds.Com Case Report
Jemds.com Case Report RIGHT SIDED SIGMOID COLON AND REDUNDANT DESCENDING COLON ON CONVENTIONAL AND CT IMAGING Mandeep Singh1, Madhan Kumar2, Daisy Gupta3 1Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Amritsar, Punjab, India. 2Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Amritsar, Punjab, India. 3Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Amritsar, Punjab, India. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Singh M, Kumar M, Gupta D. Right sided sigmoid colon and redundant descending colon on conventional and CT imaging. J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci. 2018;7(44):5617-5620, DOI: 10.14260/jemds/2018/1073 CASE PRESENTATION Investigations A 62-year-old male presented with history of severe On Plain X-Ray Abdomen constipation, abdominal distension, haemorrhoids and blood No abnormal air-fluid levels were seen. There were no in stool in surgical OPD of Guru Nanak Dev Hospital, abnormal radio-opaque shadows seen. Bilateral psoas Amritsar. The patient was referred for barium studies of shadows and soft tissue shadows were identified as normal. colon, which showed a loop of colon in pelvic region (at normal location of ileal loops) and redundant and long On Barium Enema descending colon extending across midline to reach hepatic After filling the rectum, the contrast was identified as filling flexure on right and continuing as sigmoid colon on right side. the sigmoid colon, which was present anomalously towards Transverse colon and ascending colon were normal in length the right side. Filling of barium outlined the extension of and position. On CECT abdomen of the patient, a long colon from sigmoid on right side with coiling in right iliac segment of descending colon was identified. -

Crohn's Disease of the Colon
Gut, 1968, 9, 164-176 Gut: first published as 10.1136/gut.9.2.164 on 1 April 1968. Downloaded from Crohn's disease of the colon V. J. McGOVERN AND S. J. M. GOULSTON From the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney, Australia The fact that Crohn's disease may involve the colon never affected unless there had been surgical inter- either initially or in association with small bowel ference. There was no overt manifestation of mal- disease is now firmly established due largely to the absorption in any of these patients. evidence presented by Lockhart-Mummery and In 18 cases the colon alone was involved. Five had Morson (1960, 1964) and Marshak, Lindner, and universal involvement, five total involvement with Janowitz (1966). This entity is clearly distinct from sparing of the rectum, two involvement of the ulcerative colitis and other forms of colonic disease. descending colon only, two the transverse colon only, Our own experience with this disorder reveals many and in the other four there was variable involvement similarities with that published from the U.K. and of areas of large bowel (Fig. 2). the U.S.A. Thirty patients with Crohn's disease involving the large bowel were seen at the Royal CLINICAL FEATURES Prince Alfred Hospital during the last decade, the majority during the past five years. The criteria for The age incidence varied from 6 to 69 years when the inclusion were based on histological examination of patient was first seen, the majority being between the operative specimens in 28 and on clinical and radio- ages of 11 and 50. -

Vestibule Lingual Frenulum Tongue Hyoid Bone Trachea (A) Soft Palate
Mouth (oral cavity) Parotid gland Tongue Sublingual gland Salivary Submandibular glands gland Esophagus Pharynx Stomach Pancreas (Spleen) Liver Gallbladder Transverse colon Duodenum Descending colon Small Jejunum Ascending colon intestine Ileum Large Cecum intestine Sigmoid colon Rectum Appendix Anus Anal canal © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Nasopharynx Hard palate Soft palate Oral cavity Uvula Lips (labia) Palatine tonsil Vestibule Lingual tonsil Oropharynx Lingual frenulum Epiglottis Tongue Laryngopharynx Hyoid bone Esophagus Trachea (a) © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 2 Upper lip Gingivae Hard palate (gums) Soft palate Uvula Palatine tonsil Oropharynx Tongue (b) © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 3 Nasopharynx Hard palate Soft palate Oral cavity Uvula Lips (labia) Palatine tonsil Vestibule Lingual tonsil Oropharynx Lingual frenulum Epiglottis Tongue Laryngopharynx Hyoid bone Esophagus Trachea (a) © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 4 Visceral peritoneum Intrinsic nerve plexuses • Myenteric nerve plexus • Submucosal nerve plexus Submucosal glands Mucosa • Surface epithelium • Lamina propria • Muscle layer Submucosa Muscularis externa • Longitudinal muscle layer • Circular muscle layer Serosa (visceral peritoneum) Nerve Gland in Lumen Artery mucosa Mesentery Vein Duct oF gland Lymphoid tissue outside alimentary canal © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 5 Diaphragm Falciform ligament Lesser Liver omentum Spleen Pancreas Gallbladder Stomach Duodenum Visceral peritoneum Transverse colon Greater omentum Mesenteries Parietal peritoneum Small intestine Peritoneal cavity Uterus Large intestine Cecum Rectum Anus Urinary bladder (a) (b) © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 6 Cardia Fundus Esophagus Muscularis Serosa externa • Longitudinal layer • Circular layer • Oblique layer Body Lesser Rugae curvature of Pylorus mucosa Greater curvature Duodenum Pyloric Pyloric sphincter antrum (a) (valve) © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. 7 Fundus Body Rugae of mucosa Pyloric Pyloric (b) sphincter antrum © 2018 Pearson Education, Inc. -

On the Rat Gastric Motility
The Japanese Journal of Physiology 16, pp.497-508, 1966 ON THE RAT GASTRIC MOTILITY Takesi HUKUHARA AND Toshiaki NEYA Department of Physiology, Okayama University Medical School, Okayama From the results obtained in the experiments carried out on the automa- ticity of the motility of dogs small intestine, HUKUHARA, NAKAYAMA and FU- KUDA8) concluded that the origin of the intestinal motility was of neurogenic nature, that is, rhythmic contractions of the small intestine were maintained by acetylcholine which was spontaneously released from the intramural ganglion cells, including not only their cell bodies, but also their axons. This hypothesis is naturally expected to be applied to the gastric motility. Taking these facts and hypothesis into consideration, a series of experiments has been performed on the gastric motility. The experimental results here reported are concerned with the problems: the localization and specificity of the pacemaker, the difference of behavior of different regions of the stomach and the mechanism underlying these phenomena. As for the gastric peristalsis, the results obtained by investigators until 1924 were summarized by MCCREA et al.14) Since then there could be found only a few literatures4,6,10,11) related with the problems concerned. METHODS In order to observe the movement of the rat stomach in vivo, the well-fed animals weighing from 80 to 200 g were anesthetized with the intraperitoneal administration of 50 mg/kg pentobarbital sodium (Nembutal, ABBOT). It was characteristic that the movement of the rat stomach was not impaired despite administering such a large dose of the drug as described above. The animal was then set in supine position to the frames installed in the internal space of the double-walled trough, the lumen of the wall being irrigated with water appropriately warmed to keep the temperature of the space at about 37•Ž. -

Sporadic (Nonhereditary) Colorectal Cancer: Introduction
Sporadic (Nonhereditary) Colorectal Cancer: Introduction Colorectal cancer affects about 5% of the population, with up to 150,000 new cases per year in the United States alone. Cancer of the large intestine accounts for 21% of all cancers in the US, ranking second only to lung cancer in mortality in both males and females. It is, however, one of the most potentially curable of gastrointestinal cancers. Colorectal cancer is detected through screening procedures or when the patient presents with symptoms. Screening is vital to prevention and should be a part of routine care for adults over the age of 50 who are at average risk. High-risk individuals (those with previous colon cancer , family history of colon cancer , inflammatory bowel disease, or history of colorectal polyps) require careful follow-up. There is great variability in the worldwide incidence and mortality rates. Industrialized nations appear to have the greatest risk while most developing nations have lower rates. Unfortunately, this incidence is on the increase. North America, Western Europe, Australia and New Zealand have high rates for colorectal neoplasms (Figure 2). Figure 1. Location of the colon in the body. Figure 2. Geographic distribution of sporadic colon cancer . Symptoms Colorectal cancer does not usually produce symptoms early in the disease process. Symptoms are dependent upon the site of the primary tumor. Cancers of the proximal colon tend to grow larger than those of the left colon and rectum before they produce symptoms. Abnormal vasculature and trauma from the fecal stream may result in bleeding as the tumor expands in the intestinal lumen. -

Esophagus and Stomach
anatomy Mohammad Almuhtaseb Majdoleen Hamed Bayan Zaben Esophagus The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra. .In general, the esophagus starts at the lower border of cricoid cartilage and ends at the cardia of the stomach. The esophagus conducts food from the pharynx into the stomach. Wavelike contractions of the muscular coat, called peristalsis, propel the food onward. It passes through the diaphragm by an opening called ESOPHAGEAL HIATUS (orifice) at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach. In the neck, the esophagus lies in front of the vertebral column; laterally, it is related to the lobes of the thyroid gland; and anteriorly, it is in contact with the trachea and the recurrent laryngeal nerve. In the thorax, it passes downward and to the left through the superior and then the posterior mediastinum. At the level of the sternal angle, the aortic arch pushes the esophagus over to the midline. The relations of the thoracic part of the esophagus: 1-Anteriorly: The trachea and the left recurrent laryngeal nerve; the left principal bronchus, which constricts it (that’s mean any foreign body enters the esophagus will lodge in one of the 4 sites→At the beginning, left main bronchus, arch of the aorta, piercing of diaphragm) ; and the pericardium, which separates the esophagus from the left atrium. 2-Posteriorly: The bodies of the thoracic vertebrae; the thoracic duct; the azygos veins; the right posterior intercostal arteries; and, at its lower end, the descending thoracic aorta. -

COLON RESECTION (For TUMOR)
GASTROINTESTINAL PATHOLOGY GROSSING GUIDELINES Specimen Type: COLON RESECTION (for TUMOR) Procedure: 1. Measure length and range of diameter or circumference. 2. Describe external surface, noting color, granularity, adhesions, fistula, discontinuous tumor deposits, areas of retraction/puckering, induration, stricture, or perforation. 3. Measure the width of attached mesentery if present. Note any enlarged lymph nodes and thrombosed vessels or other vascular abnormalities. 4. Open the bowel longitudinally along the antimesenteric border, or opposite the tumor if tumor is located on the antimesenteric border, i.e. try to avoid cutting through the tumor. 5. Measure any areas of luminal narrowing or dilation (location, length, diameter or circumference, wall thickness), noting relation to tumor. 6. Describe tumor, noting size, shape, color, consistency, appearance of cut surface, % of circumference of the bowel wall involved by the tumor, depth of invasion through bowel wall, and distance from margins of resection (radial/circumferential margin, mesenteric margin, closest proximal or distal margin). a. If resection includes mesorectum, gross evaluation of the intactness of mesorectum must be included. For rectum, the location of the tumor must also be oriented: anterior, posterior, right lateral, left lateral. b. If a rectal tumor is close to distal margin, the distance of tumor to the distal margin should be measured when specimen is stretched. This is usually done during intraoperative gross consultation when specimen is fresh. c. If the tumor is in a retroperitoneal portion of the bowel (e.g. rectum), radial/retroperitoneal margin must be inked and one or more sections must be obtained (a shave margin, if tumor is far from the radial margin; and perpendicular sections showing the relationship of the tumor to the inked radial margin, if tumor is close to the radial margin). -

Case Report High Fever As an Initial Symptom of Primary Gastric Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor in an Adult Woman
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(5):1468-1473 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000684 Case Report High fever as an initial symptom of primary gastric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in an adult woman Jiang-Feng Qiu, Yi-Jiu Shi, Lei Fang, Hui-Fang Wang, Mou-Cheng Zhang Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Ningbo First Hospital, Ningbo, 315010, China Received March 29, 2014; Accepted May 9, 2014; Epub May 15, 2014; Published May 30, 2014 Abstract: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, also known as inflammatory pseudotumor, plasma cell granuloma or inflammatory myofibroblastoma, is characterized histopathologically by myofibroblastic spindle cells with inflamma- tory cell infiltrates composed of plasma cells, lymphocytes and eosinophils. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor is typically seen in children or young adults and is most commonly localized to the lungs, but it can occur anywhere in the body. To date, however, only a few cases involving the stomach have been reported. Herein, we present a case of gastric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor in an adult woman with an initial symptom of high fever. Keywords: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, stomach, inflammatory pseudotumor, high fever, surgery Introduction tenderness. Routine blood tests revealed mi- crocytic hypochromic anemia with a hemoglo- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor (IMT) is an bin level of 10.8 g/dl and a hematocrit of 34.3%. uncommon mesenchymal neoplasm occurring Repeated blood cultures came up negative for mainly in children and young adults. IMT was the presence of bacteria or fungus. Radio- first described in the lung, but has since been logically, chest X-rays were normal, but con- observed in a wide variety of extrapulmonary trast-enhanced abdominal computed tomogra- sites such as the liver, urinary bladder, mesen- phy (CT) showed a 3.0 × 3.0 cm low-density tery, retroperitoneum, omentum and central mass located on the lesser curvature of the nervous system [1]. -

Colon and Rectum
AJC12 7/14/06 1:24 PM Page 107 12 Colon and Rectum (Sarcomas, lymphomas, and carcinoid tumors of the large intestine or appendix are not included.) C18.0 Cecum C18.5 Splenic flexure of C18.9 Colon, NOS C18.1 Appendix colon C19.9 Rectosigmoid C18.2 Ascending colon C18.6 Descending colon junction C18.3 Hepatic flexure of C18.7 Sigmoid colon C20.9 Rectum, NOS colon C18.8 Overlapping lesion of C18.4 Transverse colon colon SUMMARY OF CHANGES •A revised description of the anatomy of the colon and rectum better delineates the data concerning the boundaries between colon, rectum, and anal canal. Ade- nocarcinomas of the vermiform appendix are classified according to the TNM staging system but should be recorded separately, whereas cancers that occur in the anal canal are staged according to the classification used for the anus. •Smooth extramural nodules of any size in the pericolic or perirectal fat are con- sidered lymph node metastases and will be counted in the N staging. In contrast, irregularly contoured nodules in the peritumoral fat are considered vascular invasion and will be coded as transmural extension in the T category and further denoted as either a V1 (microscopic vascular invasion) if only microscopically visible or a V2 (macroscopic vascular invasion) if grossly visible. • Stage Group II is subdivided into IIA and IIB on the basis of whether the primary tumor is T3 or T4 respectively. • Stage Group III is subdivided into IIIA (T1-2N1M0), IIIB (T3-4N1M0), or IIIC (any TN2M0). INTRODUCTION The TNM classification for carcinomas of the colon and rectum provides more detail than other staging systems. -

How Can Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Help Me Make a Diagnosis in Dogs and Cats? Part 1
26 SURGERY VP SEPTEMBER 2017 How can upper gastrointestinal endoscopy help me make a diagnosis in dogs and cats? Part 1 DISEASE OF THE UPPER of all dogs and cats using a gastroscope Rugal folds can be used to guide GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT with an insertion tube diameter of you through the stomach as they run is common in small animal practice up to 10mm. The critical factor is the length of the stomach and not and flexible endoscopy can provide the ability to pass the gastroscope transversely. So, if you want to reach a powerful diagnostic tool in the through the pylorus and intubate the the pylorus, in general follow the rugal investigation of such cases. duodenum. folds. The problem facing the clinician is Most endoscopists will freely admit The angular incisure marks the the range in size of patients which may that this is the most difficult procedure entrance to the antral canal, appearing require endoscopic investigation; from to carry out, even with the best as a sharp fold on the lesser curvature. small cats and dogs to giant breeds equipment available. The procedure It is also where carcinoma of the such as the Great Dane. This variation can, though, be made much more canine stomach is most often detected. in size creates difficult if a To ensure that the important real challenges large diameter landmarks you are looking for are JAMES W. SIMPSON Figure 2. Normal anatomy of the in being able insertion tube always in the same place as you enter feline and canine stomach. to physically provides some tips on is used. -

SPLANCHNOLOGY Part I. Digestive System (Пищеварительная Система)
КАЗАНСКИЙ ФЕДЕРАЛЬНЫЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ ИНСТИТУТ ФУНДАМЕНТАЛЬНОЙ МЕДИЦИНЫ И БИОЛОГИИ Кафедра морфологии и общей патологии А.А. Гумерова, С.Р. Абдулхаков, А.П. Киясов, Д.И. Андреева SPLANCHNOLOGY Part I. Digestive system (Пищеварительная система) Учебно-методическое пособие на английском языке Казань – 2015 УДК 611.71 ББК 28.706 Принято на заседании кафедры морфологии и общей патологии Протокол № 9 от 18 апреля 2015 года Рецензенты: кандидат медицинских наук, доцент каф. топографической анатомии и оперативной хирургии КГМУ С.А. Обыдённов; кандидат медицинских наук, доцент каф. топографической анатомии и оперативной хирургии КГМУ Ф.Г. Биккинеев Гумерова А.А., Абдулхаков С.Р., Киясов А.П., Андреева Д.И. SPLANCHNOLOGY. Part I. Digestive system / А.А. Гумерова, С.Р. Абдулхаков, А.П. Киясов, Д.И. Андреева. – Казань: Казан. ун-т, 2015. – 53 с. Учебно-методическое пособие адресовано студентам первого курса медицинских специальностей, проходящим обучение на английском языке, для самостоятельного изучения нормальной анатомии человека. Пособие посвящено Спланхнологии (науке о внутренних органах). В данной первой части пособия рассматривается анатомическое строение и функции системы в целом и отдельных органов, таких как полость рта, пищевод, желудок, тонкий и толстый кишечник, железы пищеварительной системы, а также расположение органов в брюшной полости и их взаимоотношения с брюшиной. Учебно-методическое пособие содержит в себе необходимые термины и объём информации, достаточный для сдачи модуля по данному разделу. © Гумерова А.А., Абдулхаков С.Р., Киясов А.П., Андреева Д.И., 2015 © Казанский университет, 2015 2 THE ALIMENTARY SYSTEM (systema alimentarium/digestorium) The alimentary system is a complex of organs with the function of mechanical and chemical treatment of food, absorption of the treated nutrients, and excretion of undigested remnants. -

Variant Arterial Supply of the Descending Colon by the Coeliac Trunk: a Case Report
medicina Case Report Variant Arterial Supply of the Descending Colon by the Coeliac Trunk: A Case Report Sandra Petzold 1,†, Silke Diana Storsberg 2,†, Karin Fischer 1 and Sven Schumann 3,* 1 Institute of Anatomy, Medical Faculty, Otto-von-Guericke-University Magdeburg, 39120 Magdeburg, Germany; [email protected] (S.P.); karin.fi[email protected] (K.F.) 2 Institute for Anatomy and Clinical Morphology, School of Medicine, Faculty of Health, Witten/Herdecke University, 58448 Witten, Germany; [email protected] 3 University Medical Center, Institute for Microscopic Anatomy and Neurobiology, Johannes Gutenberg-University, 55131 Mainz, Germany * Correspondence: [email protected] † Contributed equally. Abstract: Background and Objectives: Knowledge of arterial variations of the intestines is of great importance in visceral surgery and interventional radiology. Materials and Methods: An unusual variation in the blood supply of the descending colon was observed in a Caucasian female body donor. Results: In this case, the left colic artery that regularly derives from the inferior mesenteric artery supplying the descending colon was instead a branch of the common hepatic artery. Conclusions: Here, we describe the very rare case of an aberrant left colic artery arising from the common hepatic artery in a dissection study. Keywords: left colic artery; aberrant left colic artery; common hepatic artery; arterial variations; mesenteric arteries; large intestines Citation: Petzold, S.; Storsberg, S.D.; Fischer, K.; Schumann, S. Variant 1. Introduction Arterial Supply of the Descending Accurate knowledge of large intestine vascular anatomy is of fundamental impor- Colon by the Coeliac Trunk: A Case tance, particularly in visceral surgery and interventional radiology.