Ukraine SITREP 6-10-2015
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
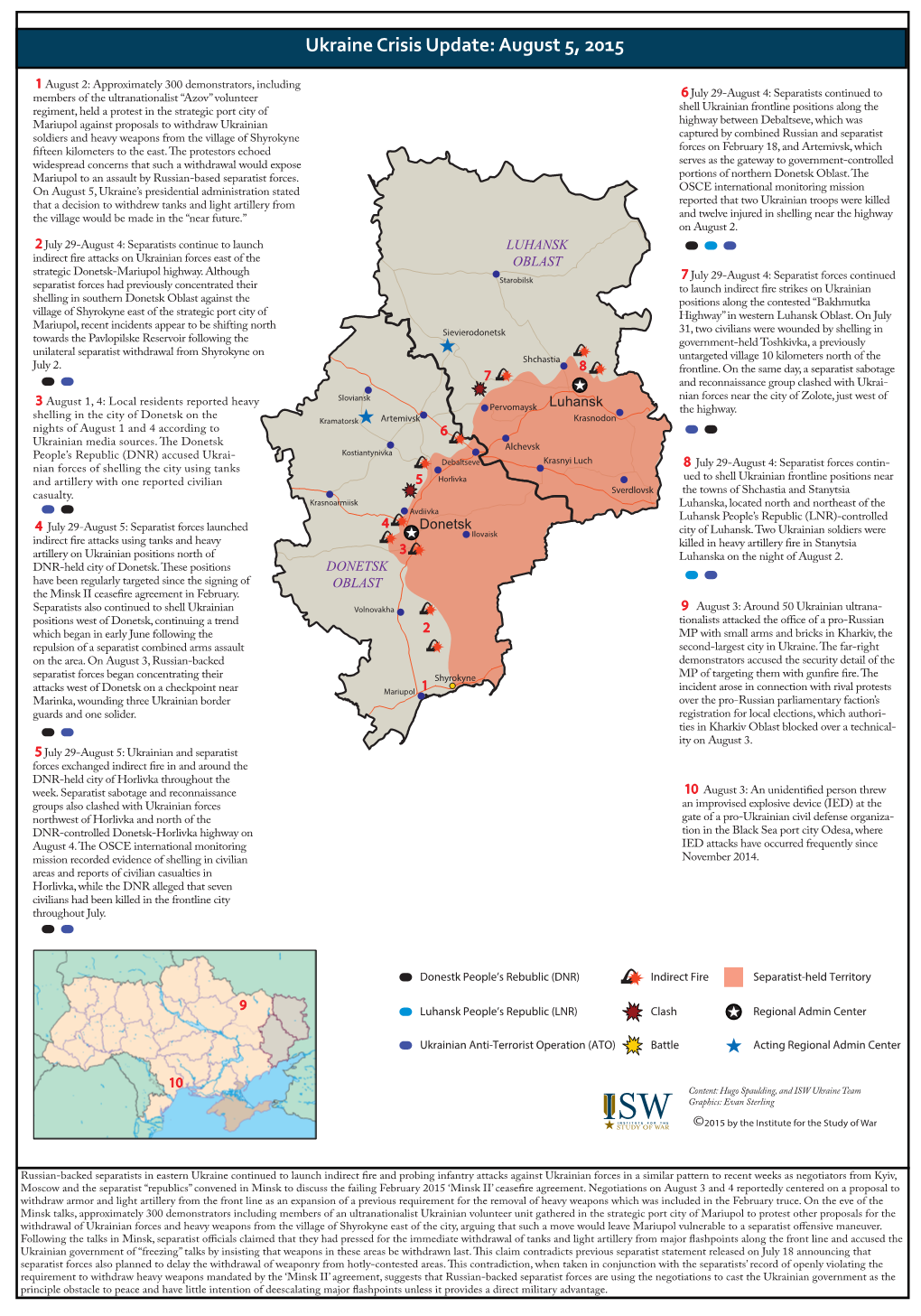
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Peacekeepers in the Donbas JFQ 91, 4Th Quarter 2017 12 India to Lead the Mission
Eastern Ukrainian woman, one of over 1 million internally displaced persons due to conflict, has just returned from her destroyed home holding all her possessions, on main street in Nikishino Village, March 1, 2015 (© UNHCR/Andrew McConnell) cal ploy; they have suggested calling Putin’s bluff. However, they also realize Peacekeepers the idea of a properly structured force with a clear mandate operating in support of an accepted peace agreement in the Donbas could offer a viable path to peace that is worth exploring.2 By Michael P. Wagner Putin envisions a limited deploy- ment of peacekeepers on the existing line of contact in Donbas to safeguard OSCE-SMM personnel.3 Such a plan ince the conflict in Ukraine September 5, 2017, when he proposed could be effective in ending the conflict began in 2014, over 10,000 introducing peacekeepers into Eastern and relieving immediate suffering, but it people have died in the fighting Ukraine to protect the Organiza- S could also lead to an open-ended United between Russian-backed separatists tion for Security and Co-operation in Nations (UN) commitment and make and Ukrainian forces in the Donbas Europe–Special Monitoring Mission long-term resolution more challenging. region of Eastern Ukraine. The Ukrai- to Ukraine (OSCE-SMM). Despite Most importantly, freezing the conflict nian government has repeatedly called halting progress since that time, restart- in its current state would solidify Russian for a peacekeeping mission to halt ing a peacekeeping mission remains an control of the separatist regions, enabling the bloodshed, so Russian President important opportunity.1 Many experts it to maintain pressure on Ukraine by Vladimir Putin surprised the world on remain wary and dismiss it as a politi- adjusting the intensity level as it de- sires. -

Implementing GIS Projects Based on Emission Trading with Ukraine -Expected to Utilize Japan’S Advanced Energy Conservation Technologies-
http://www.nedo.go.jp/english /index.html June 22, 2012 Implementing GIS Projects Based On Emission Trading With Ukraine -Expected To Utilize Japan’s Advanced Energy Conservation Technologies- The New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) and the State Environmental Investment Agency of Ukraine (SEIA) have agreed to implement 4 projects including the Replacement of Police Cars With Hybrid Vehicle Project based on the Green Investment Scheme (GIS*1) concluded through the GIS agreement*2. With this agreement, the allocation of GIS financial resources Ukraine received from NEDO through emission trading has been finalized. 【Project Outline】 Project Title Project Outline By replacing existing police cars with highly fuel efficient hybrid vehicle, i) Police Cars Replacement the project aims to reduce fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas Project emissions. ii) Educational Facility By installing solar power generation device and solar power hot water “ARTEK” Energy device to educational facility “ARTEK”, the project aims to reduce Conservation Project energy and fossil fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. By dispersing existing one Horlivka City Heat Distribution Public iii) Horlivka City Heat Corporation boiler house to four, and by replacing outdated boilers with Distribution Improvement newest and high efficient boilers, the project aims to reduce fossil fuel Project consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. By improving heat insulation capacity of window frames and walls of 42 iv) Social Project facilities including schools, hospitals, etc in 4 oblasts in Ukraine, the (Improvement of Heat project aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Including the latest Insulation Capacity of Public agreement, social projects will be implemented at 340 places in 1 Facilities Project) autonomous republic, and 10 oblasts. -

List of Persons and Entities Under EU Restrictive Measures Over the Territorial Integrity of Ukraine
dhdsh PRESS Council of the European Union EN List of persons and entities under EU restrictive measures over the territorial integrity of Ukraine List of Persons Name Identifying Reasons Date of listing information 1. Sergey Valeryevich DOB: 26.11.1972. Aksyonov was elected 'Prime Minister of Crimea' in the Crimean 17.3.2014 AKSYONOV, Verkhovna Rada on 27 February 2014 in the presence of pro-Russian POB: Beltsy (Bălţi), gunmen. His 'election' was decreed unconstitutional by the acting Sergei Valerievich now Republic of Ukrainian President Oleksandr Turchynov on 1 March 2014. He actively AKSENOV (Сергей Moldova lobbied for the 'referendum' of 16 March 2014 and was one of the co- Валерьевич signatories of the ’treaty on Crimea´s accession to the Russian AKCëHOB), Federation’ of 18 March 2014. On 9 April 2014 he was appointed acting Serhiy Valeriyovych ‘Head’ of the so-called ‘Republic of Crimea’ by President Putin. On 9 AKSYONOV (Сергiй October 2014, he was formally ‘elected’ 'Head' of the so-called 'Republic Валерiйович Аксьонов) of Crimea'. Aksyonov subsequently decreed that the offices of ‘Head’ and ‘Prime Minister’ be combined. Member of the Russia State Council. 1/83 dhdsh PRESS Council of the European Union EN Name Identifying Reasons Date of listing information 2. Rustam Ilmirovich DOB: 15.8.1976 As former Deputy Minister of Crimea, Temirgaliev played a relevant role 17.3.2014 TEMIRGALIEV in the decisions taken by the ‘Supreme Council’ concerning the POB: Ulan-Ude, ‘referendum’ of 16 March 2014 against the territorial integrity of Ukraine. (Рустам Ильмирович Buryat ASSR He lobbied actively for the integration of Crimea into the Russian Темиргалиев) (Russian SFSR) Federation. -

B COUNCIL REGULATION (EU) No 269/2014 of 17 March
02014R0269 — EN — 09.11.2016 — 011.001 — 1 This text is meant purely as a documentation tool and has no legal effect. The Union's institutions do not assume any liability for its contents. The authentic versions of the relevant acts, including their preambles, are those published in the Official Journal of the European Union and available in EUR-Lex. Those official texts are directly accessible through the links embedded in this document ►B COUNCIL REGULATION (EU) No 269/2014 of 17 March 2014 concerning restrictive measures in respect of actions undermining or threatening the territorial integrity, sovereignty and independence of Ukraine (OJ L 78, 17.3.2014, p. 6) Amended by: Official Journal No page date ►M1 Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 284/2014 of 21 March L 86 27 21.3.2014 2014 ►M2 Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 433/2014 of 28 April 2014 L 126 48 29.4.2014 ►M3 Council Regulation (EU) No 476/2014 of 12 May 2014 L 137 1 12.5.2014 ►M4 Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 477/2014 of 12 May 2014 L 137 3 12.5.2014 ►M5 Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 577/2014 of 28 May 2014 L 160 7 29.5.2014 ►M6 Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 753/2014 of 11 July 2014 L 205 7 12.7.2014 ►M7 Council Regulation (EU) No 783/2014 of 18 July 2014 L 214 2 19.7.2014 ►M8 Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 810/2014 of 25 July 2014 L 221 1 25.7.2014 ►M9 Council Regulation (EU) No 811/2014 of 25 July 2014 L 221 11 25.7.2014 ►M10 Council Implementing Regulation (EU) No 826/2014 of 30 July 2014 L 226 16 30.7.2014 ►M11 Council -

Donetsk and Luhansk Oblasts, 2019
Changes in Social Cohesion, Citizens’ Satisfaction and Visions of Reintegration Donetsk and Luhansk oblasts, 2019 Funded by the USAID, implemented by the Centre for Sustainable Peace and Democratic Development (SeeD), and in partnership with the UN Recovery and Peacebuilding Programme. PARTICIPATORY MULTIDISCIPLINARY Multi-stakeholder Inspired by numerous collaboration for disciplines continuous improvement TREND PREDICTIVE REVEALING Advanced analysis Longitudinal to test theories analysis to track of change societal changes ADAPTIVE Reflects local needs and phenomena AGENDA METHODOLOGY CHANGES IN CITIZENS’ SATISFACTION Human security Service delivery Support for reforms Trust in authorities REINTEGRATION OF THE NGCA Future visions Openness to dialogue HOW DO WE MEASURE CIVIC DUTY 5.3 DONETSK & LUHANSK PHENOMENA? OBLASTS DONETSK & LUHANSK 5.1 CONTACT LINE CIVIC DUTY • What happens to Ukraine in the future is not my problem • There is no point in voting in elections 10 9 8 • I believe that ordinary people like 7 6 me cannot change anything 5 4 3 • I believe politics is for politicians 2 1 RANGE SEA OF AZOV OF SCORES 0 SAMPLING STRATEGY 9,055 RESPONDENTS: 3,325 respondents from Luhansk and Donetsk oblasts 1,811 contact line 3,000 city booster from 15 cities 619 non-governmental controlled area 300 ATO veterans * For more information on the methodology, please visit: SEA OF AZOV https://scoreforpeace.org/en/use/methodology How secure do residents of Donetsk & Luhansk oblasts feel? HUMAN SECURITY (ALL) HUMAN SECURITY DONETSK & LUHANSK 4.7 -

VITALY TIMOFEEV (Kharkiv, Ukraine and Portland, ME, USA) REX A
VITALY TIMOFEEV (Kharkiv, Ukraine and Portland, ME, USA) REX A. WADE (Fairfax, VA, USA) KHARKIV IN THE POST-PERESTROIKA DAYS: SOME POLITICAL TENDENCIES "There is only one thing left - to punch someone's snout...! (Kharkiv post-Communist press ascribes this phrase to A. Zdorovyi, Deputy Head of Kharkiv regional administration.) . One of the most important,. yet most puz?.??tg, features of the post-Soviet era is the political life and configuration of the larger cities. As the cities of Russia, Ukraine and the other republics struggle with the new phenomenon of multi-party politics in a constantly shifting political arena, even identifying the major groupings and issues is a complex task. Political par- ties tend to be small, often transitory, and suffer from a generalized public distrust of political parties as such. Indeed, it can be enormously difficult even to be precise about what is political. Trivial things in some circum- stances become political, while at the same time key political figures some- times suggest that political life does not exist at all in their cities. Still, a better sense of the political landscape of the large cities of the post-Soviet world is important to understanding what is happening there and where the future might lead. We will try to contribute to understanding this important feature of the new order by looking at political tendencies in one major city, Kharkiv (Khar'kov).1 the sixth largest city of the former Soviet Union and the second largest of the Ukrainian Republic. Our essay focuses especially on the situation in the summer of 1993, with some observations 2 about earlier and later developments. -

Russia and Ukraine: Military-Strategic Options, and Possible Risks, for Moscow
Russia and Ukraine: Military-strategic options, and possible risks, for Moscow Johan Norberg & Fredrik Westerlund A further Russian military intervention in Ukraine would long-term strategic buffer zone against NATO without not only be damaging to the security of both Ukraine and taking significant military-strategic risks. Russia’s armed Europe. It could also entail significant military-strategic forces are nominally impressive in size, but are spread risks for Russia, reducing its military options in other thinly over the country’s enormous territory in peacetime, strategic directions such as Central Asia and the Caucasus. based on Russia’s current threat assessments. While Russian officials still claim they have a one- Russian strategic and doctrinal documents reveal a million-strong army, it may still face military-strategic world view that sees military threats and dangers from overstretch should the Kremlin decide to launch extended all directions. Apart from NATO expansion to Russia’s combat operations in Ukraine. What are the reasons for west, instability looms in the Caucasus and Central Asia this? What military options are available to secure Russia to the south. Furthermore, Russia’s force posture in the from perceived threats in its western strategic direction? Eastern Military District (MD) clearly shows that China What risks do operations beyond Crimea entail? A closer is a military concern, requiring preparations to augment look at the military-strategic issues is warranted, beginning Russian forces there. Although the armed forces are with the Russian threat assessment and peacetime military geographically dispersed, Russia can concentrate forces for posture, however other Russian rationales for intervention offensive operations to seize and hold territory but only in in Ukraine – such as political and economic considerations one strategic direction at a time. -

40 Individuals 1 Viktor YANUKOVYCH(YANUKOVICH
(Attachment) 40 individuals 1 Viktor YANUKOVYCH(YANUKOVICH) Former President of Ukraine Date of birth:July 9, 1950 Place of birth:Yenakievo (Ukraine) 2 Sergey(Sergei) AKSYONOV(AKSENOV) “Acting Head of the Republic of Crimea” Date of birth:November 26, 1972 Place of birth:Balti (Republic of Moldova) 3 Vladimir KONSTANTINOV “Speaker of the State Council of the Republic of Crimea” Date of birth:November 19, 1956 Place of birth:Vladimirovca (Republic of Moldova) 4 Rustam TEMIRGALIEV Former “Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Republic of Crimea” Date of birth:August 15, 1976 Place of birth:Ulan-Ude (Russian Federation) 5 Denis (Denys) BEREZOVSKIY(BEREZOVSKY/BEREZOVSKII) Deputy Commander of the Black Sea Fleet of the Russian Navy Date of birth:July 15, 1974 Place of birth:Kharkiv (Ukraine) 6 Aleksei(Alexey) CHALIY(CHALYY) Former “Governor of the City of Sevastopol” Date of birth:June 13, 1961 7 Petr(Pyotr) ZIMA Former Head of the Security Service of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea Date of birth:March 29, 1965 8 Yuriy (Yurii) ZHEREBTSOV “Counsellor of the Speaker of the State Council of the Republic of Crimea” Date of birth:November 19, 1969 9 Sergey(Sergei) TSEKOV Member of the Federation Council of the Russian Federation (from “the Republic of Crimea”) Date of birth:September 28, 1953 10 Mikhail MALYSHEV “Chairman of the Electoral Commission of the Republic of Crimea” Date of birth:October 10, 1955 11 Valery(Valeriy/Valerii) MEDVEDEV “Chairman of the Electoral Commission of the City of Sevastopol” Date of birth:August 21, -

Donbas, Ukraine: Organizations and Activities
Geneva Centre for Security Sector Governance Civil Society in Donbas, Ukraine: Organizations and Activities Volodymyr Lukichov Tymofiy Nikitiuk Liudmyla Kravchenko Luhansk oblast DONBAS DONBAS Stanytsia Donetsk Luhanska Zolote oblast Mayorske Luhansk Donetsk Maryinka Novotroitske RUSSIA Hnutove Mariupol Sea of Azov About DCAF DCAF - Geneva Centre for Security Sector Governance is dedicated to improving the se- curity of people and the States they live in within a framework of democratic governance, the rule of law, and respect for human rights. DCAF contributes to making peace and de- velopment more sustainable by assisting partner states and international actors supporting them to improve the governance of their security sector through inclusive and participatory reforms. It creates innovative knowledge products, promotes norms and good practices, provides legal and policy advice and supports capacity building of both state- and non-state security sector stakeholders. Active in over 70 countries, DCAF is internationally recognized as one of the world’s leading centres of excellence for security sector governance (SSG) and security sector reform (SSR). DCAF is guided by the principles of neutrality, impartiality, local ownership, inclusive participation, and gender equality. www.dcaf.ch. Publisher DCAF - Geneva Centre for Security Sector Governance P.O.Box 1360 CH-1211 Geneva 1 Switzerland [email protected] +41 (0) 22 730 9400 Authors: Volodymyr Lukichov, Tymofiy Nikitiuk, Liudmyla Kravchenko Copy-editor: dr Grazvydas Jasutis, Richard Steyne -

1 Introduction
State Service of Geodesy, Cartography and Cadastre State Scientific Production Enterprise “Kartographia” TOPONYMIC GUIDELINES For map and other editors For international use Ukraine Kyiv “Kartographia” 2011 TOPONYMIC GUIDELINES FOR MAP AND OTHER EDITORS, FOR INTERNATIONAL USE UKRAINE State Service of Geodesy, Cartography and Cadastre State Scientific Production Enterprise “Kartographia” ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Prepared by Nina Syvak, Valerii Ponomarenko, Olha Khodzinska, Iryna Lakeichuk Scientific Consultant Iryna Rudenko Reviewed by Nataliia Kizilowa Translated by Olha Khodzinska Editor Lesia Veklych ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ © Kartographia, 2011 ISBN 978-966-475-839-7 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Introduction ................................................................ 5 2 The Ukrainian Language............................................ 5 2.1 General Remarks.............................................. 5 2.2 The Ukrainian Alphabet and Romanization of the Ukrainian Alphabet ............................... 6 2.3 Pronunciation of Ukrainian Geographical Names............................................................... 9 2.4 Stress .............................................................. 11 3 Spelling Rules for the Ukrainian Geographical Names....................................................................... 11 4 Spelling of Generic Terms ....................................... 13 5 Place Names in Minority Languages -

Winterization Recommendations 2019-2020 Key Figures
Winterization Recommendations 2019-2020 Key figures In need In need coverage (total) (priority) (existing programmes) HHs in private Donetsk obl. 3,150 committed houses and + 37,126 HHs 5,500 apartments Luhansk obl. 2,350 gap GCA Indiv. in CCs committed and Social All Ukraine 7,700 Ind 7,700 Institutions 7,700 gap 5,531* gap 6,000 committed Donetsk obl. 33,500 HHs 14,603 HHs in private 8,603 gap houses and 2,500 committed apartments Luhansk obl. 20,700 HHs 9,000 NGCA 6,500 gap 11,347 committed Indiv. in non- Donetsk obl. 30,900 ind NA specialized CCs 19,553 gap and Social NA committed Luhansk obl. 19,100 ind NA Institutions NA gap 23,182* gap * Note: # of individuals in CCs and social institutions were divided by Cluster coefficient of 2.42 in order to get the final number in HHs Contents 1. Winterization context and objectives .............................................................................................. 2 2. Key recommendations ..................................................................................................................... 2 3. Winterization beneficiary prioritization ........................................................................................... 4 4. Heating ............................................................................................................................................. 6 (a) GCA ........................................................................................................................................... 6 (b) NGCA ....................................................................................................................................... -

Russian War Against Ukraine
KREMLIN’S BLACK BOOK Russian War Against Ukraine Ukrainian losses and costs as a result of the Russian temporary occupation of Crimea and its military aggression in the Donetsk and Luhansk regions OCTOBER 2015 Russian War Against Ukraine Blood and deaths on Putin’s hands The Russian Federation led by President Vladimir Putin has waged a war against Ukraine since February 2014. Russia’s temporary occupation of Crimea, its further aggression in the Donetsk & Luhansk regions, direct support of international terrorists on the territory of Ukraine, as well as black- mail and economic pressure have led to tremendous casualties, economic and infrastructure damages in Ukraine. Russian war against Ukraine is ongoing. Consistent fighting makes it difficult to name accurate numbers of those killed and wounded. They will be revealed inevitably just as the international condemnation of Vladimir Putin’s policy. Each victim will not be forgotten. Putin’s regime must be stopped. CONTENTS І. Our Losses. General information ІІ. Macroeconomic Data ІІІ. Industrial Losses І. OUR LOSSES Dead. Wounded. Victims According to the reports published by international organizations more than 7people have been883 killed as a result of Russian aggression by August 15, 2015 More than 17 610 were wounded ACCURATE NUMBERS COULD BE MUCH HIGHER Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs) 1 529 848 Ukrainians, including 193 027 children, were registered as IDPs as of October 2015. They fled from the temporarily occupied territories that suffered from the Russian troops and Russian-backed terrorist groups. The Government has financed monthly social payments for the total amount of more than UAH 2,5 bln1.