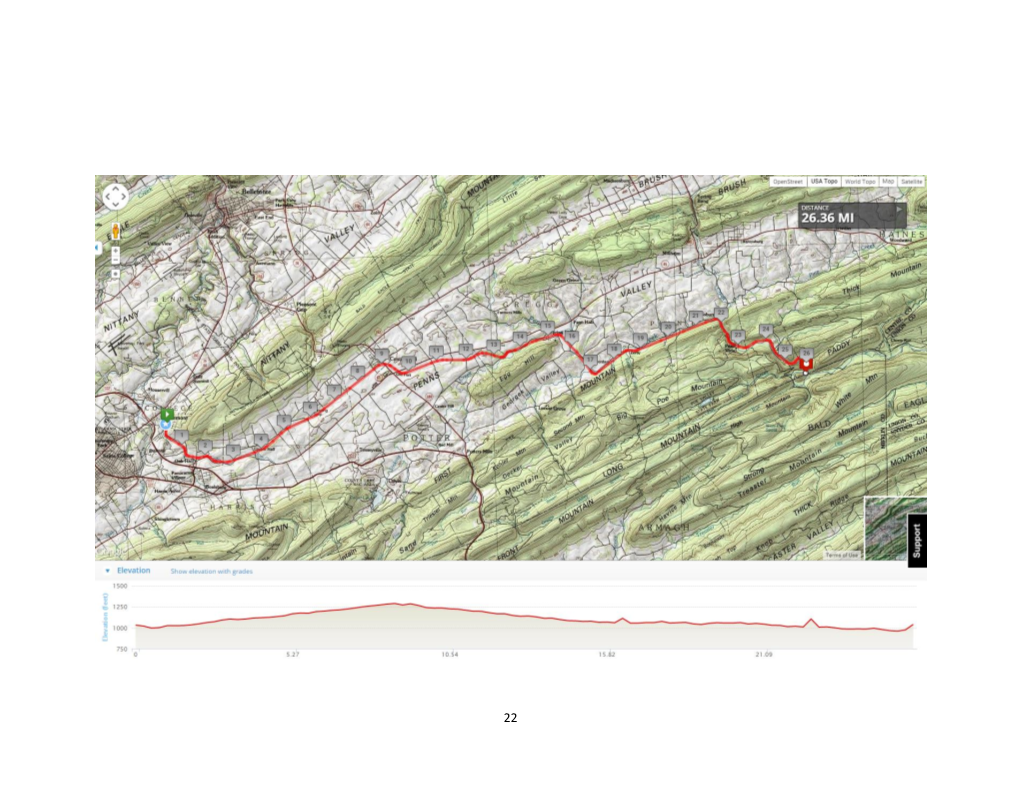
Penns Valley Rail Trail
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-
Kayaking • Fishing • Lodging Table of Contents
KAYAKING • FISHING • LODGING TABLE OF CONTENTS Fishing 4-13 Kayaking & Tubing 14-15 Rules & Regulations 16 Lodging 17-19 1 W. Market St. Lewistown, PA 17044 www.JRVVisitors.com 717-248-6713 [email protected] The Juniata River Valley Visitors Bureau thanks the following contributors to this directory. Without your knowledge and love of our waterways, this directory would not be possible. Joshua Hill Nick Lyter Brian Shumaker Penni Abram Paul Wagner Bob Wert Todd Jones Helen Orndorf Ryan Cherry Thankfully, The Juniata River Valley Visitors Bureau Jenny Landis, executive director Buffie Boyer, marketing assistant Janet Walker, distribution manager 2 PAFLYFISHING814 Welcome to the JUNIATA RIVER VALLEY Located in the heart of Central Pennsylvania, the Juniata River Valley, is named for the river that flows from Huntingdon County to Perry County where it meets the Susquehanna River. Spanning more than 100 miles, the Juniata River flows through a picturesque valley offering visitors a chance to explore the area’s wide fertile valleys, small towns, and the natural heritage of the region. The Juniata River watershed is comprised of more than 6,500 miles of streams, including many Class A fishing streams. The river and its tributaries are not the only defining characteristic of our landscape, but they are the center of our recreational activities. From traditional fishing to fly fishing, kayaking to camping, the area’s waterways are the ideal setting for your next fishing trip or family vacation. Come and “Discover Our Good Nature” any time of year! Find Us! The Juniata River Valley is located in Central Pennsylvania midway between State College and Harrisburg. -

Draft 2021 LRTP
DRAFT SEDA‐COG Metropolitan Planning Organization (MPO) LONG RANGE TRANSPORTATION PLAN The Draft Long Range Transportation Plan includes regional overview information and the MPO region’s long range vision for prioritizing transportation investments. This copy of the draft plan is available as part of a 30‐day comment period beginning on May 24, 2021, and ending on June 22, 2021. The public comment period provides the public an opportunity to provide feedback on all facets of the Long Range Transportation Plan before its adoption. The plan can be reviewed online at: http://www.seda‐cog.org/departments/transportation/long‐range‐plan. Written and electronic comments may be submitted via email, SEDA‐COG web portal, fax, or Postal Service by 4:00 p.m. on Tuesday, June 22, 2021. Email comments may be submitted to lrtp@seda‐cog.org or through the web portal at http://www.seda‐cog.org/departments/transportation/transportation‐comments Comments may be faxed to 570‐524‐9190 Please address all written comments to: Mr. Don Kiel SEDA‐COG MPO 201 Furnace Road Lewisburg, PA 17837 If you would like to provide comments or discuss the draft plan in person, a Virtual Public Meeting will be held during the public comment period as follows: Date: June 3, 2021 Time: 7:00 p.m. to 8:00 p.m. Location: The content of this Notice is available in alternative formats and other languages upon request by contacting the SEDA‐COG MPO at 570‐524‐4491, or by written correspondence directed to the MPO at 201 Furnace Road, Lewisburg, PA 17837, or by email at jsaylor@seda‐cog.org. -

Brook Trout Outcome Management Strategy
Brook Trout Outcome Management Strategy Introduction Brook Trout symbolize healthy waters because they rely on clean, cold stream habitat and are sensitive to rising stream temperatures, thereby serving as an aquatic version of a “canary in a coal mine”. Brook Trout are also highly prized by recreational anglers and have been designated as the state fish in many eastern states. They are an essential part of the headwater stream ecosystem, an important part of the upper watershed’s natural heritage and a valuable recreational resource. Land trusts in West Virginia, New York and Virginia have found that the possibility of restoring Brook Trout to local streams can act as a motivator for private landowners to take conservation actions, whether it is installing a fence that will exclude livestock from a waterway or putting their land under a conservation easement. The decline of Brook Trout serves as a warning about the health of local waterways and the lands draining to them. More than a century of declining Brook Trout populations has led to lost economic revenue and recreational fishing opportunities in the Bay’s headwaters. Chesapeake Bay Management Strategy: Brook Trout March 16, 2015 - DRAFT I. Goal, Outcome and Baseline This management strategy identifies approaches for achieving the following goal and outcome: Vital Habitats Goal: Restore, enhance and protect a network of land and water habitats to support fish and wildlife, and to afford other public benefits, including water quality, recreational uses and scenic value across the watershed. Brook Trout Outcome: Restore and sustain naturally reproducing Brook Trout populations in Chesapeake Bay headwater streams, with an eight percent increase in occupied habitat by 2025. -

RV Sites in the United States Location Map 110-Mile Park Map 35 Mile
RV sites in the United States This GPS POI file is available here: https://poidirectory.com/poifiles/united_states/accommodation/RV_MH-US.html Location Map 110-Mile Park Map 35 Mile Camp Map 370 Lakeside Park Map 5 Star RV Map 566 Piney Creek Horse Camp Map 7 Oaks RV Park Map 8th and Bridge RV Map A AAA RV Map A and A Mesa Verde RV Map A H Hogue Map A H Stephens Historic Park Map A J Jolly County Park Map A Mountain Top RV Map A-Bar-A RV/CG Map A. W. Jack Morgan County Par Map A.W. Marion State Park Map Abbeville RV Park Map Abbott Map Abbott Creek (Abbott Butte) Map Abilene State Park Map Abita Springs RV Resort (Oce Map Abram Rutt City Park Map Acadia National Parks Map Acadiana Park Map Ace RV Park Map Ackerman Map Ackley Creek Co Park Map Ackley Lake State Park Map Acorn East Map Acorn Valley Map Acorn West Map Ada Lake Map Adam County Fairgrounds Map Adams City CG Map Adams County Regional Park Map Adams Fork Map Page 1 Location Map Adams Grove Map Adelaide Map Adirondack Gateway Campgroun Map Admiralty RV and Resort Map Adolph Thomae Jr. County Par Map Adrian City CG Map Aerie Crag Map Aeroplane Mesa Map Afton Canyon Map Afton Landing Map Agate Beach Map Agnew Meadows Map Agricenter RV Park Map Agua Caliente County Park Map Agua Piedra Map Aguirre Spring Map Ahart Map Ahtanum State Forest Map Aiken State Park Map Aikens Creek West Map Ainsworth State Park Map Airplane Flat Map Airport Flat Map Airport Lake Park Map Airport Park Map Aitkin Co Campground Map Ajax Country Livin' I-49 RV Map Ajo Arena Map Ajo Community Golf Course Map -

Kochel Et Al., 2009
Geomorphology 110 (2009) 80–95 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Geomorphology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/geomorph Catastrophic middle Pleistocene jökulhlaups in the upper Susquehanna River: Distinctive landforms from breakout floods in the central Appalachians R. Craig Kochel a,⁎, Richard P. Nickelsen a, L. Scott Eaton b a Department of Geology, Bucknell University, Lewisburg, PA 17837, USA b Department of Geology & Environmental Science, James Madison University, Harrisonburg, VA 22807, USA article info abstract Article history: Widespread till and moraines record excursions of middle-Pleistocene ice that flowed up-slope into several Received 14 November 2008 watersheds of the Valley and Ridge Province along the West Branch of the Susquehanna River. A unique Received in revised form 23 March 2009 landform assemblage was created by ice-damming and jökulhlaups emanating from high gradient mountain Accepted 24 March 2009 watersheds. This combination of topography formed by multiple eastward-plunging anticlinal ridges, and the Available online 6 April 2009 upvalley advance of glaciers resulted in an ideal geomorphic condition for the formation of temporary ice- dammed lakes. Extensive low gradient (1°–2° slope) gravel surfaces dominate the mountain front Keywords: geomorphology in this region and defy simple explanation. The geomorphic circumstances that occurred Jökulhlaup Ice-damming in tributaries to the West Branch Susquehanna River during middle Pleistocene glaciation are extremely rare Susquehanna River and may be unique in the world. Failure of ice dams released sediment-rich water from lakes, entraining Middle Pleistocene cobbles and boulders, and depositing them in elongated debris fans extending up to 9 km downstream from Valley and Ridge their mountain-front breakout points. -

Investment Grade Audit Report
Investment Grade Audit Report A Guaranteed Energy Savings Project Serving: The PA Department of Conservation & Natural Resources (DCNR) – State Parks & Forests Central Region, PA Project No. GESA 2018-2 Contract No. GESA 2018-2.1 Commonwealth of Pennsylvania Department of General Services Harrisburg, PA March 20, 2020 Submitted by: Company Name: McClure Company Company Address: 4101 North Sixth Street, Harrisburg, PA 17110 Contact Person: Jon Zeller, Account Executive (484) 560-8437 (phone) (717) 236-5239 (fax) [email protected] GESA Program – Investment Grade Audit Report DCNR – State Parks & Forests Central Region, PA March 20, 2020 Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ...........................................................................................................1 2. PROJECT FINANCIALS.............................................................................................................3 3. SCOPE OF WORK .....................................................................................................................27 4. MEASUREMENT & VERIFICATION ....................................................................................56 5. COMMISSIONING, PREVENTIVE MAINTENANCE & TRAINING ...............................70 6. APPENDICES..............................................................................................................................74 A. LIGHTING LINE-BY-LINE DATA B. ENERGY SAVING CALCULATIONS C. EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATION / CUT-SHEETS TOC GESA Program – Investment Grade Audit Report DCNR -

Public Votes Loyalsock As PA River of the Year Perkiomen TU Leads
Winter 2018 Publication of the Pa. Council of Trout Unlimited www.patrout.org Perkiomen TU Students to leads restoration research brookies project on on Route 6 trek By Charlie Charlesworth namesake creek PATU President By Thomas W. Smith Perkiomen Valley TU President In summer 2018, six college students from our PATU 5 Rivers clubs will spend a The Perkiomen Valley Chapter of month trekking across Pennsylvania’s U.S. Trout Unlimited partnered with Sundance Route 6. Their purpose will be to explore, Creek Consulting, the Montgomery do research, collect data and still have time County Conservation District, Penn State do a little bit of fishing in the northern tier’s Master Watershed Stewards and Upper famed brook trout breeding grounds. Perkiomen High School for a stream They will be supported by the PA Fish restoration project on Perkiomen Creek, and Boat Commission, three colleges in- Contributed Photo which was carried out over five days in Volunteers work on a stream restora- cluding Mansfield, Keystone and hopefully See CREEK, page 7 tion project along Perkiomen Creek. See TREK, page 2 Public votes Loyalsock as PA River of the Year By Pennsylvania DCNR Home to legions of paddlers, anglers, and other outdoors enthusiasts in north central Pennsylvania, Loyalsock Creek has been voted the 2018 Pennsylvania River of the Year. The public was invited to vote online, choosing from among five waterways nominated across the state. Results were pariveroftheyear.org Photo See RIVER, page 2 Loyalsock Creek was voted 2018 Pennsylvania River of the Year. IN THIS ISSUE Keystone Coldwater Conference ..........................3 How to become a stream advocate.......................6 Headwaters .............................................................4 Minutes ....................................................................8 Treasurer’s Notes ...................................................5 Chapter Reports .................................................. -

Summary of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Suspended-Sediment Loads and Trends Measured at the Chesapeake Bay Nontidal Network Stations for Water Years 2009–2018
Summary of Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Suspended-Sediment Loads and Trends Measured at the Chesapeake Bay Nontidal Network Stations for Water Years 2009–2018 Prepared by Douglas L. Moyer and Joel D. Blomquist, U.S. Geological Survey, March 2, 2020 The Chesapeake Bay nontidal network (NTN) currently consists of 123 stations throughout the Chesapeake Bay watershed. Stations are located near U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) stream-flow gages to permit estimates of nutrient and sediment loadings and trends in the amount of loadings delivered downstream. Routine samples are collected monthly, and 8 additional storm-event samples are also collected to obtain a total of 20 samples per year, representing a range of discharge and loading conditions (Chesapeake Bay Program, 2020). The Chesapeake Bay partnership uses results from this monitoring network to focus restoration strategies and track progress in restoring the Chesapeake Bay. Methods Changes in nitrogen, phosphorus, and suspended-sediment loads in rivers across the Chesapeake Bay watershed have been calculated using monitoring data from 123 NTN stations (Moyer and Langland, 2020). Constituent loads are calculated with at least 5 years of monitoring data, and trends are reported after at least 10 years of data collection. Additional information for each monitoring station is available through the USGS website “Water-Quality Loads and Trends at Nontidal Monitoring Stations in the Chesapeake Bay Watershed” (https://cbrim.er.usgs.gov/). This website provides State, Federal, and local partners as well as the general public ready access to a wide range of data for nutrient and sediment conditions across the Chesapeake Bay watershed. In this summary, results are reported for the 10-year period from 2009 through 2018. -

PINE CREEK WATERSHED TMDL Schuylkill County
PINE CREEK WATERSHED TMDL Schuylkill County For Acid Mine Drainage Affected Segments Prepared by: Pennsylvania Department of Environmental Protection November 10, 2008 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction................................................................................................................................. 3 Directions to the Pine Creek Watershed..................................................................................... 3 Watershed History ...................................................................................................................... 4 Segments addressed in this TMDL............................................................................................. 4 Clean Water Act Requirements .................................................................................................. 5 Section 303(d) Listing Process ................................................................................................... 6 Basic Steps for Determining a TMDL........................................................................................ 6 AMD Methodology..................................................................................................................... 7 TMDL Endpoints........................................................................................................................ 9 TMDL Elements (WLA, LA, MOS) .......................................................................................... 9 Allocation Summary................................................................................................................ -

Wild Trout Waters (Natural Reproduction) - September 2021
Pennsylvania Wild Trout Waters (Natural Reproduction) - September 2021 Length County of Mouth Water Trib To Wild Trout Limits Lower Limit Lat Lower Limit Lon (miles) Adams Birch Run Long Pine Run Reservoir Headwaters to Mouth 39.950279 -77.444443 3.82 Adams Hayes Run East Branch Antietam Creek Headwaters to Mouth 39.815808 -77.458243 2.18 Adams Hosack Run Conococheague Creek Headwaters to Mouth 39.914780 -77.467522 2.90 Adams Knob Run Birch Run Headwaters to Mouth 39.950970 -77.444183 1.82 Adams Latimore Creek Bermudian Creek Headwaters to Mouth 40.003613 -77.061386 7.00 Adams Little Marsh Creek Marsh Creek Headwaters dnst to T-315 39.842220 -77.372780 3.80 Adams Long Pine Run Conococheague Creek Headwaters to Long Pine Run Reservoir 39.942501 -77.455559 2.13 Adams Marsh Creek Out of State Headwaters dnst to SR0030 39.853802 -77.288300 11.12 Adams McDowells Run Carbaugh Run Headwaters to Mouth 39.876610 -77.448990 1.03 Adams Opossum Creek Conewago Creek Headwaters to Mouth 39.931667 -77.185555 12.10 Adams Stillhouse Run Conococheague Creek Headwaters to Mouth 39.915470 -77.467575 1.28 Adams Toms Creek Out of State Headwaters to Miney Branch 39.736532 -77.369041 8.95 Adams UNT to Little Marsh Creek (RM 4.86) Little Marsh Creek Headwaters to Orchard Road 39.876125 -77.384117 1.31 Allegheny Allegheny River Ohio River Headwater dnst to conf Reed Run 41.751389 -78.107498 21.80 Allegheny Kilbuck Run Ohio River Headwaters to UNT at RM 1.25 40.516388 -80.131668 5.17 Allegheny Little Sewickley Creek Ohio River Headwaters to Mouth 40.554253 -80.206802 -

Cbfposter Final New
. r Otsego r e C Lake v r i n e R The Chesapeake Bay Watershed v o i a t R l r l Cooperstown r i a c e h NEW YORK i d r l v e i a W v e i s n R R t U Cortland O o g n A watershed is all of the land whose water and a a n g o e m h h C rainfall will eventually drain into a particular river, g C u o o h i o T C c a t lake, bay, or other body of water. o n n r i R st ive e eo Rive r i v r a R nn a h e Binghampton u The Chesapeake Bay watershed is 64,000 square q s Elmira u miles and has 11,600 miles of tidal shoreline, S including tidal wetlands and islands. The watershed T Montrose i o g a encompasses parts of six states: Delaware, ine Creek P Wellsboro reek R a C i r and Maryland, New York, Pennsylvania, Virginia, and v e Tow k West Virginia, as well as Washington D.C. e e r C g Scranton Approximately 17 million people live in the n Laporte m o eek c r anch Su y C Br s L watershed; about 10 million people live along its ing q hon u r a e ve h i m R e a Rive a Wilkes Barre n t Williamsport r nn n s n a shores or near them. -

Where-To-Go Fifth Edition Buckskin Lodge #412 Order of the Arrow, WWW Theodore Roosevelt Council Boy Scouts of America 2002
Where-to-Go Fifth Edition Buckskin Lodge #412 Order of the Arrow, WWW Theodore Roosevelt Council Boy Scouts of America 2002 0 The "Where to Go" is published by the Where-to-Go Committee of the Buckskin Lodge #412 Order of the Arrow, WWW, of the Theodore Roosevelt Council, #386, Boy Scouts of America. FIFTH EDITION September, 1991 Updated (2nd printing) September, 1993 Third printing December, 1998 Fourth printing July, 2002 Published under the 2001-2002 administration: Michael Gherlone, Lodge Chief John Gherlone, Lodge Adviser Marc Ryan, Lodge Staff Adviser Edward A. McLaughlin III, Scout Executive Where-to-Go Committee Adviser Stephen V. Sassi Chairman Thomas Liddy Original Word Processing Andrew Jennings Michael Nold Original Research Jeffrey Karz Stephen Sassi Text written by Stephen Sassi 1 This guide is dedicated to the Scouts and volunteers of the Theodore Roosevelt Council Boy Scouts of America And the people it is intended to serve. Two roads diverged in a wood, and I - I took the one less traveled by, And that made all the difference...... - R.Frost 2 To: All Scoutmasters From: Stephen V. Sassi Buckskin Lodge Where to Go Adviser Date: 27 June 2002 Re: Where to Go Updates Enclosed in this program packet are updates to the Order of Arrow Where to Go book. Only specific portions of the book were updated and the remainder is unchanged. The list of updated pages appears below. Simply remove the old pages from the book and discard them, replacing the old pages with the new pages provided. First two pages Table of Contents - pages 1,2 Chapter 3 - pages 12,14 Chapter 4 - pages 15-19,25,26 Chapter 5 - All except page 35 (pages 27-34,36) Chapter 6 - pages 37-39, 41,42 Chapter 8 - pages 44-47 Chapter 9 - pages 51,52,54 Chapter 10 - pages 58,59,60 Chapter 11 - pages 62,63 Appendix - pages 64,65,66 We hope that this book will provide you with many new places to hike and camp.