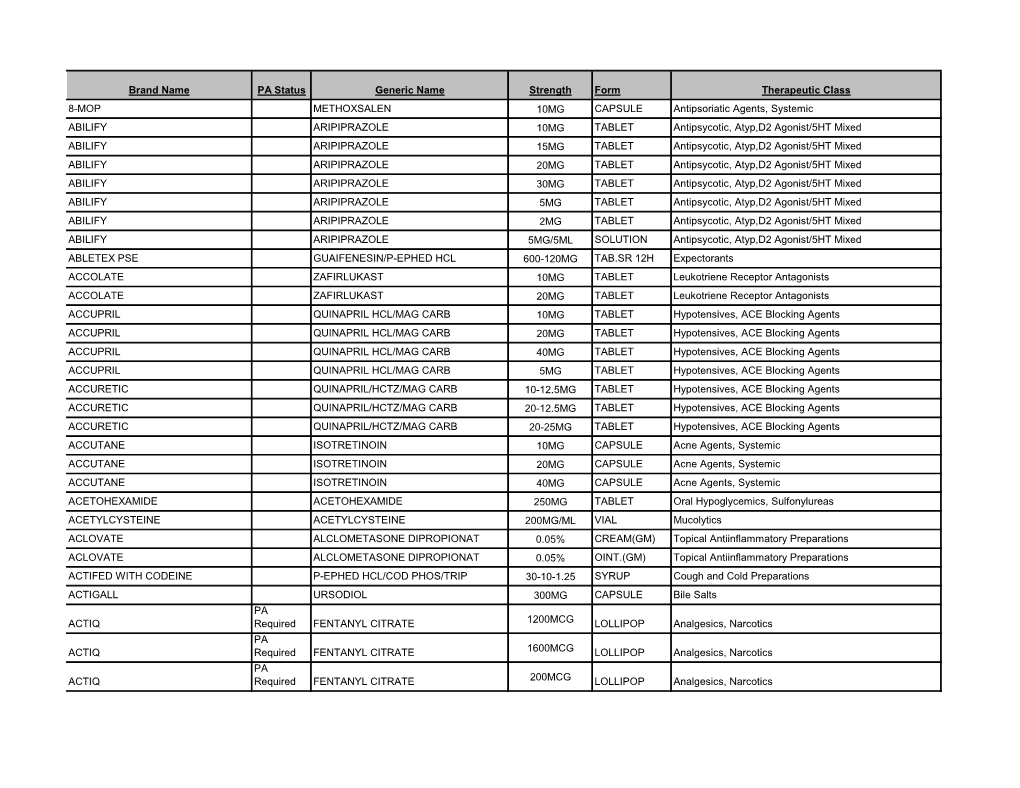
Brand Name PA Status Generic Name Strength Form Therapeutic Class 8
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317805 A1 Mckay Et Al
US 20080317805A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0317805 A1 McKay et al. (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 25, 2008 (54) LOCALLY ADMINISTRATED LOW DOSES Publication Classification OF CORTICOSTEROIDS (51) Int. Cl. A6II 3/566 (2006.01) (76) Inventors: William F. McKay, Memphis, TN A6II 3/56 (2006.01) (US); John Myers Zanella, A6IR 9/00 (2006.01) Cordova, TN (US); Christopher M. A6IP 25/04 (2006.01) Hobot, Tonka Bay, MN (US) (52) U.S. Cl. .......... 424/422:514/169; 514/179; 514/180 (57) ABSTRACT Correspondence Address: This invention provides for using a locally delivered low dose Medtronic Spinal and Biologics of a corticosteroid to treat pain caused by any inflammatory Attn: Noreen Johnson - IP Legal Department disease including sciatica, herniated disc, Stenosis, mylopa 2600 Sofamor Danek Drive thy, low back pain, facet pain, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid Memphis, TN38132 (US) arthritis, osteolysis, tendonitis, carpal tunnel syndrome, or tarsal tunnel syndrome. More specifically, a locally delivered low dose of a corticosteroid can be released into the epidural (21) Appl. No.: 11/765,040 space, perineural space, or the foramenal space at or near the site of a patient's pain by a drug pump or a biodegradable drug (22) Filed: Jun. 19, 2007 depot. E Day 7 8 Day 14 El Day 21 3OO 2OO OO OO Control Dexamethasone DexamethasOne Dexamethasone Fuocinolone Fluocinolone Fuocinolone 2.0 ng/hr 1Ong/hr 50 ng/hr 0.0032ng/hr 0.016 ng/hr 0.08 ng/hr Patent Application Publication Dec. 25, 2008 Sheet 1 of 2 US 2008/0317805 A1 900 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 80.0 - 7OO – 6OO - 5OO - E Day 7 EDay 14 40.0 - : El Day 21 2OO - OO = OO – Dexamethasone Dexamethasone Dexamethasone Fuocinolone Fluocinolone Fuocinolone 2.0 ng/hr 1Ong/hr 50 ng/hr O.OO32ng/hr O.016 ng/hr 0.08 nghr Patent Application Publication Dec. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0110428A1 De Juan Et Al
US 200601 10428A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2006/0110428A1 de Juan et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2006 (54) METHODS AND DEVICES FOR THE Publication Classification TREATMENT OF OCULAR CONDITIONS (51) Int. Cl. (76) Inventors: Eugene de Juan, LaCanada, CA (US); A6F 2/00 (2006.01) Signe E. Varner, Los Angeles, CA (52) U.S. Cl. .............................................................. 424/427 (US); Laurie R. Lawin, New Brighton, MN (US) (57) ABSTRACT Correspondence Address: Featured is a method for instilling one or more bioactive SCOTT PRIBNOW agents into ocular tissue within an eye of a patient for the Kagan Binder, PLLC treatment of an ocular condition, the method comprising Suite 200 concurrently using at least two of the following bioactive 221 Main Street North agent delivery methods (A)-(C): Stillwater, MN 55082 (US) (A) implanting a Sustained release delivery device com (21) Appl. No.: 11/175,850 prising one or more bioactive agents in a posterior region of the eye so that it delivers the one or more (22) Filed: Jul. 5, 2005 bioactive agents into the vitreous humor of the eye; (B) instilling (e.g., injecting or implanting) one or more Related U.S. Application Data bioactive agents Subretinally; and (60) Provisional application No. 60/585,236, filed on Jul. (C) instilling (e.g., injecting or delivering by ocular ion 2, 2004. Provisional application No. 60/669,701, filed tophoresis) one or more bioactive agents into the Vit on Apr. 8, 2005. reous humor of the eye. Patent Application Publication May 25, 2006 Sheet 1 of 22 US 2006/0110428A1 R 2 2 C.6 Fig. -

The In¯Uence of Medication on Erectile Function
International Journal of Impotence Research (1997) 9, 17±26 ß 1997 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0955-9930/97 $12.00 The in¯uence of medication on erectile function W Meinhardt1, RF Kropman2, P Vermeij3, AAB Lycklama aÁ Nijeholt4 and J Zwartendijk4 1Department of Urology, Netherlands Cancer Institute/Antoni van Leeuwenhoek Hospital, Plesmanlaan 121, 1066 CX Amsterdam, The Netherlands; 2Department of Urology, Leyenburg Hospital, Leyweg 275, 2545 CH The Hague, The Netherlands; 3Pharmacy; and 4Department of Urology, Leiden University Hospital, P.O. Box 9600, 2300 RC Leiden, The Netherlands Keywords: impotence; side-effect; antipsychotic; antihypertensive; physiology; erectile function Introduction stopped their antihypertensive treatment over a ®ve year period, because of side-effects on sexual function.5 In the drug registration procedures sexual Several physiological mechanisms are involved in function is not a major issue. This means that erectile function. A negative in¯uence of prescrip- knowledge of the problem is mainly dependent on tion-drugs on these mechanisms will not always case reports and the lists from side effect registries.6±8 come to the attention of the clinician, whereas a Another way of looking at the problem is drug causing priapism will rarely escape the atten- combining available data on mechanisms of action tion. of drugs with the knowledge of the physiological When erectile function is in¯uenced in a negative mechanisms involved in erectile function. The way compensation may occur. For example, age- advantage of this approach is that remedies may related penile sensory disorders may be compen- evolve from it. sated for by extra stimulation.1 Diminished in¯ux of In this paper we will discuss the subject in the blood will lead to a slower onset of the erection, but following order: may be accepted. -

CANVAS Trial)
Effectiveness research with Real World Data to support FDA’s regulatory decision making 1. RCT Details This section provides a high-level overview of the RCT that the described real-world evidence study is trying to replicate as closely as possible given the remaining limitations inherent in the healthcare databases. 1.1 Title Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes (CANVAS trial) 1.2 Intended aim(s) To compare canagliflozin to placebo on cardiovascular (CV) events including CV death, heart attack, and stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), whose diabetes is not well controlled at the beginning of the study and who have a history of CV events or have a high risk for CV events. 1.3 Primary endpoint for replication and RCT finding Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events, Including CV Death, Nonfatal Myocardial Infarction (MI), and Nonfatal Stroke 1.4 Required power for primary endpoint and noninferiority margin (if applicable) With 688 cardiovascular safety events recorded across the trials, there would be at least 90% power, at an alpha level of 0.05, to exclude an upper margin of the 95% confidence interval for the hazard ratio of 1.3. 1.5 Primary trial estimate targeted for replication HR = 0.86 (95% CI 0.75–0.97) comparing canagliflozin to placebo (Neal et al., 2017) 2. Person responsible for implementation of replication in Aetion Ajinkya Pawar, Ph.D. implemented the study design in the Aetion Evidence Platform. S/he is not responsible for the validity of the design and analytic choices. All implementation steps are recorded and the implementation history is archived in the platform. -

Jan 19, 2009 Listing of Generic, Non
http://www.medword.com/uspa.html Jan 19, 2009 Listing of generic, non-prescription, prescription, and OTC (over-the-counter) p harmaceuticals A-200 Gel Concentrate A-200 Shampoo Concentrate A-25 A-Cillin A-Fil A-Hydrocort A-methaPred A-Phedrin A-Spas S/L A Plus A.C. & C. A.P.L. A.R.M. Allergy Relief A.R.M. Maximum Strength Caplets A/B Otic A/Fish Oil A/T/S abacavir abarelix-depot-F abarelix-depot-M Abbokinase Abbokinase Open-Cath Abelcet Abenol Abitrate Absorbine Athletes Foot Absorbine Jock Itch Absorbine Jr. Antifungal AC acarbose Accolate Accupep HPF Accupril Accuretic Accutane Accutane Roche acebutolol Acel-Imune Acellular DTP Aceon Acet-2 Acet-3 Acet Codeine 30 Acet Codeine 60 Aceta Aceta Elixir Aceta Tablets acetaminophen acetaminophen-butalbital acetaminophen-caffeine acetaminophen-chlorpheniramine acetaminophen-codeine acetaminophen-dextromethorphan acetaminophen-diphenhydramine acetaminophen-hydrocodone acetaminophen-oxycodone acetaminophen-phenyltoloxamine acetaminophen-propoxyphene acetaminophen-propoxyphene hydrochloride acetaminophen-propoxyphene napsylate acetaminophen-pseudoephedrine acetazolam acetazolamide Acetest acetic acid Acetocot acetohexamide acetophenazine Acetoxyl 10 Gel Acetoxyl 2.5 Gel Acetoxyl 20 Gel Acetoxyl 5 Gel acetylsalicylic acid Achromycin Achromycin V aciclovir Acid Control Acid Phos Fluor Rinse Acilac Aciphex acitretin Aclophen Aclovate Acne-10 Lotion Acne-5 Lotion Acne-Aid Aqua Gel Acne-Aid Gel Acne-Aid Vanishing Cream Acne Aid 10 Cream Acne Lotion 10 Acne Prone Skin Sunscreen Acne Wash Acno Acnomel -

Steroid Hormones Part Two
Steroid Hormones Part Two Medicinal Chemistry III / 4th stage/ 1st Semester Lecture 9 Dr.Narmin Hama Amin Androgens Endogenous Androgens Testosterone and its more potent reduction product 5α-DHT are produced in significantly greater amounts in males than in females, but females also produce low amounts of these “male” sex hormones. Endogenous compounds have two important activities: ➢ Androgenic activity (promoting male sex characteristics) ➢ Anabolic activity (muscle building). ➢ Biosynthesis Testosterone can be synthesized through pregnenolone, DHEA(dehydroepiandrosterone) , and androstenedione Metabolism of Androgens ▪ Testosterone is rapidly converted to 5α-DHT in many tissues by the action of 5α-reductase. Depending on the tissue, this is either to activate testosterone to the more potent androgen, DHT (e.g., in the prostate), or a step in the metabolic inactivation of this androgen. The primary route for metabolic inactivation of testosterone and DHT is oxidation to the 17-one. The 3-one group is also reduced to the 3α- (major) and 3α- ols (minor). ▪ Androsterone is the major urinary metabolite and was the first “androgenic” steroid isolated. These metabolites are excreted mainly as the corresponding glucuronides Metabolism of Androgens SARs Of Androgens Testosterone exerts its physiological activity after its conversion to Dihydrotestosterone. A steroidal skeleton is minimum structural requirement to have androgenic activity. 17β hydroxyl function to be essential for androgenic and anabolic activity. Reduction of the A ring e.g., DHT may increase potency. Introduction of 17α methyl group confers oral activity on testosterone. Testosterone not effective orally, because metabolic changes at 17-β oxygen, which is used to attach the receptor site. 17-α alkyl groups prevent these metabolic changes so that compounds are orally active. -

Injectable Medication Hcpcs/Dofr Crosswalk
INJECTABLE MEDICATION HCPCS/DOFR CROSSWALK HCPCS DRUG NAME GENERIC NAME PRIMARY CATEGORY SECONDARY CATEGORY J0287 ABELCET Amphotericin B lipid complex THERAPEUTIC INJ HOME HEALTH/INFUSION** J0400 ABILIFY Aripiprazole, intramuscular, 0.25 mg THERAPEUTIC INJ J0401 ABILIFY MAINTENA Apriprazole 300mg, IM injection THERAPEUTIC INJ J9264 ABRAXANE paclitaxel protein-bound particles, 1 mg J1120 ACETAZOLAMIDE SODIUM Acetazolamide sodium injection THERAPEUTIC INJ J0132 ACETYLCYSTEINE INJ Acetylcysteine injection, 10 mg THERAPEUTIC INJ ACTEMRA 162mg/0.9ml Syringe (50242- J3262 SELF-INJECTABLE 0138-01) Tocilizumab, 1 mg ACTEMRA INJECTION (50242-0136-01, J3262 50242-0137-01) Tocilizumab 200mg, 400mg THERAPEUTIC INJ J0800 ACTHAR HP Corticotropin injection THERAPEUTIC INJ Hemophilus influenza b vaccine (Hib), PRP-T conjugate (4- 90648 ACTHIB dose schedule), for intramuscular use THERAPEUTIC INJ IMMUNIZATIONS J0795 ACTHREL Corticorelin ovine triflutal THERAPEUTIC INJ J9216 ACTIMMUNE Interferon gamma 1-b 3 miillion units SELF-INJECTABLE CHEMO ADJUNCT* J2997 ACTIVASE Alteplase recombinant, 1mg THERAPEUTIC INJ HOME HEALTH/INFUSION** J0133 ACYCLOVIR SODIUM Acyclovir, 5 mg THERAPEUTIC INJ HOME HEALTH/INFUSION** 90715 ADACEL Tdap vaccine, > 7 yrs, IM THERAPEUTIC INJ IMMUNIZATIONS J2504 ADAGEN Pegademase bovine, 25 IU THERAPEUTIC INJ HOME HEALTH/INFUSION** J9042 ADCETRIS Brentuximab vedotin Injection THERAPEUTIC INJ CHEMOTHERAPY J0153 ADENOCARD Adenosine 6 MG THERAPEUTIC INJ J0171 ADRENALIN Adrenalin (epinephrine) inject THERAPEUTIC INJ J9000 ADRIAMYCIN Doxorubicin -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0159073 A1 De Juan Et Al
US 20110159073A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2011/0159073 A1 de Juan et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 30, 2011 (54) METHODS AND DEVICES FOR THE Publication Classification TREATMENT OF OCULAR CONDITIONS (51) Int. Cl. (76) Inventors: Eugene de Juan, LaCanada, CA A6F 2/00 (2006.01) (US); Signe E. Varner, Los (52) U.S. Cl. ........................................................ 424/427 Angeles, CA (US); Laurie R. Lawin, New Brighton, MN (US) (57) ABSTRACT Featured is a method for instilling one or more bioactive (21) Appl. No.: 12/981,038 agents into ocular tissue within an eye of a patient for the treatment of an ocular condition, the method comprising con (22) Filed: Dec. 29, 2010 currently using at least two of the following bioactive agent delivery methods (A)-(C): (A) implanting a Sustained release Related U.S. Application Data delivery device comprising one or more bioactive agents in a (63) Continuation of application No. 1 1/175,850, filed on posterior region of the eye so that it delivers the one or more Jul. 5, 2005, now abandoned. bioactive agents into the vitreous humor of the eye; (B) instill ing (e.g., injecting or implanting) one or more bioactive (60) Provisional application No. 60/585,236, filed on Jul. 2, agents Subretinally; and (C) instilling (e.g., injecting or deliv 2004, provisional application No. 60/669,701, filed on ering by ocular iontophoresis) one or more bioactive agents Apr. 8, 2005. into the vitreous humor of the eye. Patent Application Publication Jun. 30, 2011 Sheet 1 of 22 US 2011/O159073 A1 Patent Application Publication Jun. -

CPT / HCPCS Code Drug Description Approximate Cost Share
The information listed here is for our most prevalent plan. The amount you pay for a covered drug will depend on your plan’s coverage. Please refer to your Medical Plan GTB for more information. To find out the cost of your drugs, please contact HMSA Customer Service at 1-800-776-4672. If you receive services from a nonparticipating provider, you are responsible for a copayment plus any difference between the actual charge and the eligible charge. Legend $0 = no cost share $ = $100 and under $$ = over $100 to $250 $$$ = over $250 to $500 $$$$ = over $500 to $1000 $$$$$ = over $1000 1 = Please call HMSA Customer Service 1-800-776-4672 for cost share information. 2 = The cost share for this drug is dependent upon the diagnosis. Please call HMSA Customer Service at 1-800-772-4672 for more information. 3 = Cost share information for these drugs is dependent upon the dose prescribed. Please call HMSA Customer Service at 1- 800-772-4672 for more information. CPT / HCPCS approximate Code Drug Description cost share J0129 Abatacept Injection $$$$ J0130 Abciximab Injection 3 J0131 Acetaminophen Injection $ J0132 Acetylcysteine Injection $ J0133 Acyclovir Injection $ J0135 Adalimumab Injection $$$$ J0153 Adenosine Inj 1Mg $ J0171 Adrenalin Epinephrine Inject $ J0178 Aflibercept Injection $$$ J0180 Agalsidase Beta Injection 3 J0200 Alatrofloxacin Mesylate 3 J0205 Alglucerase Injection 3 J0207 Amifostine 3 J0210 Methyldopate Hcl Injection 3 J0215 Alefacept 3 J0220 Alglucosidase Alfa Injection 3 J0221 Lumizyme Injection 3 J0256 Alpha 1 Proteinase Inhibitor -

Canine Pemphigus Vulgaris Treated with Gold Salt Therapy
CASE REPORT Canine Pemphigus Vulgaris Treated with Gold Salt Therapy G.P. OLYNYK AND B.J. GUTHRIE Edgemont Veterinary Clinic, #12, 34 Edgedale Drive North West, Calgary, Alberta T3A 2R4 Summary treated with antibiotics, prednisone, euthanasia, gold salt therapy, or A nine year old spayed female Collie vitamins and metronidazole with no further antibiotic-corticosteroid treat- was diagnosed as having pemphigus lasting or dramatic improvement. The ments with the owner. vulgaris. Response to corticosteroid dog had previously been diagnosed as On May 13, 1982 we initiated auro- and antibiotic therapies was unsatis- having hip dysplasia and secondary thioglucose3 therapy as outlined pre- factory. Aurothioglucose therapy was arthritis. viously (1). Two intramuscular injec- used later as the sole treatment. The tions of 5.0 and 10.0 mg were given as dog achieved a complete remission Clinical Findings and Treatment tests of tolerance on May 13 and 20 lasting at least ten months. At first presentation, the physical respectively. The therapeutic series examination was unremarkable with involved six weekly intramuscular Resumme' the exception of skin lesions. The injections at 1.0 mg/kg. These injec- Traitement du pemphigus vulgaire refractory nature and the location and tions were given May 27, June 3, 10, canin avec de l'aurothioglucose nature of the lesions suggested a diag- 17, 24 and 30. No other therapy was Les auteurs ont diagnostique la nosis of pemphigus vulgaris. used. A physical examination, weigh- pemphigus vulgaire, chez une chienne A biopsy was obtained; the resulting in and discussion with the owner Collie castree et agee de neuf ans. -

Cumulative Cross Index to Iarc Monographs
PERSONAL HABITS AND INDOOR COMBUSTIONS volume 100 e A review of humAn cArcinogens This publication represents the views and expert opinions of an IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, which met in Lyon, 29 September-6 October 2009 LYON, FRANCE - 2012 iArc monogrAphs on the evAluAtion of cArcinogenic risks to humAns CUMULATIVE CROSS INDEX TO IARC MONOGRAPHS The volume, page and year of publication are given. References to corrigenda are given in parentheses. A A-α-C .............................................................40, 245 (1986); Suppl. 7, 56 (1987) Acenaphthene ........................................................................92, 35 (2010) Acepyrene ............................................................................92, 35 (2010) Acetaldehyde ........................36, 101 (1985) (corr. 42, 263); Suppl. 7, 77 (1987); 71, 319 (1999) Acetaldehyde associated with the consumption of alcoholic beverages ..............100E, 377 (2012) Acetaldehyde formylmethylhydrazone (see Gyromitrin) Acetamide .................................... 7, 197 (1974); Suppl. 7, 56, 389 (1987); 71, 1211 (1999) Acetaminophen (see Paracetamol) Aciclovir ..............................................................................76, 47 (2000) Acid mists (see Sulfuric acid and other strong inorganic acids, occupational exposures to mists and vapours from) Acridine orange ...................................................16, 145 (1978); Suppl. 7, 56 (1987) Acriflavinium chloride ..............................................13, -

Channeling to Treatment and Associated Changes in Disease Activity Over 12 Months in Patients with RA Treated with Abatacept
553 Scientific Content On-demand Channeling to Treatment and Associated Changes in Disease Activity Over 12 Months in Patients To receive a copy of this poster With RA Treated With Abatacept Versus Other DMARDs in Real-World Community Practice Settings OR Text RWE to Scan QR code via a 1 2 1 1 1 1 3 1 +1-609-917-7119 barcode reader application L Ferri, JR Curtis, E Alemao, J Bryson, K Lozenski, S Balachandar, V Rajagopalan, Y Bao By requesting this content, you agree to receive a one-time communication using automated technology. Messaging & data rates may apply. Links are valid for 30 days after the congress presentation date. 1 2 3 Copies of this poster obtained through Quick Response (QR) code Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ, USA; University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, USA; Mu Sigma, Bangalore, India or text message are for personal use only and may not be reproduced without permission from ACR and the authors of this poster. Mean changes from baseline to Year 1 in CDAI scores were assessed using Introduction Figure 1. Study Design Table 2. Changes in CDAI Over 12 Months in Patients With RA*,† multivariate linear regressions adjusting for baseline covariates, including age, Abatacept, a selective T-cell co-stimulatory modulator, has shown efficacy sex, smoking status, BMI, Charlson Comorbidity Index, CDAI score and number Change from Difference in Window for measuring Baseline, Year 1, 1 n baseline, change, p value similar to TNF inhibitors (TNFi) for RA management in clinical trial settings. Baseline period follow-up disease LSM (95% CI)‡ LSM (95% CI)‡ of prior treatments (b/tsDMARDs, TNFi and cDMARDs).