Least Bittern (Ixobrychus Exilis)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

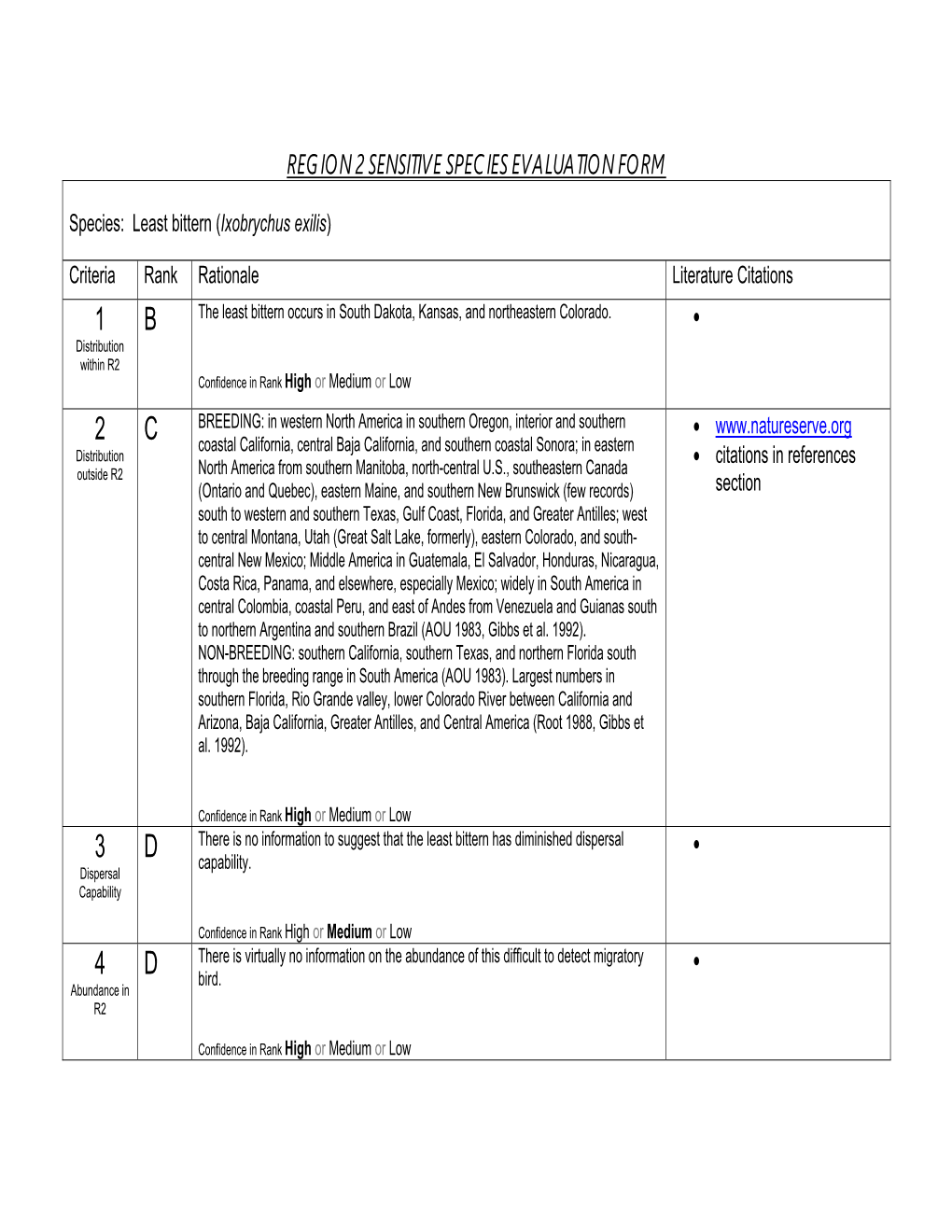
Bird List Column A: We Should Encounter (At Least a 90% Chance) Column B: May Encounter (About a 50%-90% Chance) Column C: Possible, but Unlikely (20% – 50% Chance)
THE PHILIPPINES Prospective Bird List Column A: we should encounter (at least a 90% chance) Column B: may encounter (about a 50%-90% chance) Column C: possible, but unlikely (20% – 50% chance) A B C Philippine Megapode (Tabon Scrubfowl) X Megapodius cumingii King Quail X Coturnix chinensis Red Junglefowl X Gallus gallus Palawan Peacock-Pheasant X Polyplectron emphanum Wandering Whistling Duck X Dendrocygna arcuata Eastern Spot-billed Duck X Anas zonorhyncha Philippine Duck X Anas luzonica Garganey X Anas querquedula Little Egret X Egretta garzetta Chinese Egret X Egretta eulophotes Eastern Reef Egret X Egretta sacra Grey Heron X Ardea cinerea Great-billed Heron X Ardea sumatrana Purple Heron X Ardea purpurea Great Egret X Ardea alba Intermediate Egret X Ardea intermedia Cattle Egret X Ardea ibis Javan Pond-Heron X Ardeola speciosa Striated Heron X Butorides striatus Yellow Bittern X Ixobrychus sinensis Von Schrenck's Bittern X Ixobrychus eurhythmus Cinnamon Bittern X Ixobrychus cinnamomeus Black Bittern X Ixobrychus flavicollis Black-crowned Night-Heron X Nycticorax nycticorax Western Osprey X Pandion haliaetus Oriental Honey-Buzzard X Pernis ptilorhynchus Barred Honey-Buzzard X Pernis celebensis Black-winged Kite X Elanus caeruleus Brahminy Kite X Haliastur indus White-bellied Sea-Eagle X Haliaeetus leucogaster Grey-headed Fish-Eagle X Ichthyophaga ichthyaetus ________________________________________________________________________________________________________ WINGS ● 1643 N. Alvernon Way Ste. 109 ● Tucson ● AZ ● 85712 ● www.wingsbirds.com -

Ixobrychus Exilis (Gmelin) Leastleast Bitternbittern, Page 1
Ixobrychus exilis (Gmelin) Leastleast Bitternbittern, Page 1 State Distribution Best Survey Period Copyright The Otter Side Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Status: State threatened state.” Wood (1951) identified the species as a summer resident and common in southern tiers of counties and Global and state rank: G5/S2 Cheboygan County, but rare and local in the Upper Peninsula. Least bittern was later described by Payne Family: Ardeidae – Herons, Egrets, and Bitterns (1983) as an uncommon transient and summer resident, with nesting confirmed in 27 counties. Michigan Total range: Five subspecies of least bittern are found Breeding Bird Atlas (Atlas) surveys conducted in the throughout much of North, Central, and South America 1980s confirmed breeding in 20 survey blocks in 17 (Gibbs et al. 1992). In North America, this species is counties (Adams 1991). All of these observations primarily restricted to the eastern U.S., ranging from occurred in the Lower Peninsula, with the number of the Great Plains states eastward to the Atlantic Coast blocks and counties with confirmed breeding nearly split and north to the Great Lakes region and the New between the northern (9 blocks in 8 counties) and England states (Evers 1994). Western populations are southern (11 blocks in 9 counties) Lower Peninsula concentrated in low-lying areas of the Central Valley (Adams 1991). Researchers confirmed nesting at and Modoc Plateau of California, the Klamath and several sites on Saginaw Bay and observed possible Malheur basins of Oregon, and along the Colorado breeding in Munuscong Bay wetlands (Chippewa River in southwest Arizona and southeast California County) during avian studies conducted in the mid- (Gibbs et al. -

Compendium of Avian Ecology
Compendium of Avian Ecology ZOL 360 Brian M. Napoletano All images taken from the USGS Patuxent Wildlife Research Center. http://www.mbr-pwrc.usgs.gov/id/framlst/infocenter.html Taxonomic information based on the A.O.U. Check List of North American Birds, 7th Edition, 1998. Ecological Information obtained from multiple sources, including The Sibley Guide to Birds, Stokes Field Guide to Birds. Nest and other images scanned from the ZOL 360 Coursepack. Neither the images nor the information herein be copied or reproduced for commercial purposes without the prior consent of the original copyright holders. Full Species Names Common Loon Wood Duck Gaviiformes Anseriformes Gaviidae Anatidae Gavia immer Anatinae Anatini Horned Grebe Aix sponsa Podicipediformes Mallard Podicipedidae Anseriformes Podiceps auritus Anatidae Double-crested Cormorant Anatinae Pelecaniformes Anatini Phalacrocoracidae Anas platyrhynchos Phalacrocorax auritus Blue-Winged Teal Anseriformes Tundra Swan Anatidae Anseriformes Anatinae Anserinae Anatini Cygnini Anas discors Cygnus columbianus Canvasback Anseriformes Snow Goose Anatidae Anseriformes Anatinae Anserinae Aythyini Anserini Aythya valisineria Chen caerulescens Common Goldeneye Canada Goose Anseriformes Anseriformes Anatidae Anserinae Anatinae Anserini Aythyini Branta canadensis Bucephala clangula Red-Breasted Merganser Caspian Tern Anseriformes Charadriiformes Anatidae Scolopaci Anatinae Laridae Aythyini Sterninae Mergus serrator Sterna caspia Hooded Merganser Anseriformes Black Tern Anatidae Charadriiformes Anatinae -

The First Recorded Cory's Bittern (Ixobrychus "Neoxenus") from South America
April 1985] ShortCommunications 413 American passerine birds in the nesting cycle. central coastalCalifornia. Unpublished M.S. the- Ornithol. Monogr. 9: 1-76. sis,Berkeley, California, Univ. California. WILLIAMS,P. L. 1982. A comparisonof colonial and non-colonial nesting by Northern Orioles in Received27 April 1984,accepted 16 November1984. The First RecordedCory's Bittern (lxobrychus "neoxenus")from South America DANTE MARTINS TEIXEIRA• AND HERCULANO M. F. ALVARENGA2 •MuseuNacional, Rio de Janeiro(R J), CEP 20942, Brazil,and 2RuaColdmbia 99, Taubat[ (SP), CEP 12100, Brazil Describedby Cory (1886), Ixobrychus"neoxenus" is ochraceous,and all previously described I. "neoxe- considereda variant morph of the Least Bittern (Ixo- nus" have been adults. brychuse. exilis),characterized by contrasting dark Bent (1926) considered I. "neoxenus"to be an ex- chestnutunderparts and blackishupperparts. About ample of melanismand erythrism, and a comparison 30 specimensare known, mostlyfrom southernFlor- of our specimen with typically colored I. exiliseryth- ida and Ontario, but there are also records from Mas- romelasseems to point to hyperpigmentation.Indeed, sachusetts,New York, Ohio, Illinois, Michigan, and a superproductionof eumelanins and phaeomelanins Wisconsin (Bent 1926, Hancock and Elliot 1978). Thus, perhapscould explain the deep blackishtinges of the it was quite a surprisefor us to obtain a specimenof upperparts and the rufous chestnut color of the the SouthAmerican Ixobrychus exilis erythromelas in foreneck,breast, etc. observedin this unusualplum- this rather uncommonplumage. Apparently, this is age (Vevers 1964). the first time this morph has been reportedoutside As mentioned above, I. "neoxenus" is considered a North America. rare morph, and our observations in southeastern The bird was collectedon 13 May 1967 in the rice Brazil seem to reinforce this supposition.Although fields of the Paraibado Sul drainage,county of Tau- I. -

Status and Conservation of American and Least Bitterns in South Carolina William Post Charleston Museum, 360 Meeting Street, Charleston, SC 29403
Status and Conservation of American and Least Bitterns in South Carolina William Post Charleston Museum, 360 Meeting Street, Charleston, SC 29403 Introduction Two species of solitary marsh-nesting Ardeidae, the American Bittern (Botaurus lentiginosus) and the Least Bittern (Ixobrychus exilis), nest in North America. Both have been classified in parts of their respective ranges as threatened, endangered, or of special concern. Their population declines are related to destruction of freshwater wetlands. Due to the secretive behavior of these birds and the relatively inaccessible habitats that they occupy, little is known about their biology in southeastern North America. In this paper I review what is known of the two species in South Carolina and adjacent areas. American Bittern Autumn and winter. Unlike other herons occurring in the Southeast, most individuals of this species are solitary and cryptic all year. This behavior makes it difficult to locate more than one or two individuals in a day’s field work. Because the American Bittern occurs in the summer as either a breeder or vagrant, it is difficult to establish the dates of its arrival in the autumn or of its departure in the spring. Single birds reported on the edge of Hell-Hole Swamp, Charleston County, on 11 August 1921 (E. A. Hyer) and at Bear Island, Colleton County, on 10 July 1991 (J. E. Cely) were possibly vagrants (McNair and Post 1993). Tomkins (1958) states that although the American Bittern was “more common than one would suspect” during winter at the Savannah River Wildlife Refuge (Jasper County), E. O. Mellinger, the refuge manager, had no information that the species occurred in summer. -

The Waterbirds and Coastal Seabirds of Timor-Leste: New Site Records Clarifying Residence Status, Distribution and Taxonomy
FORKTAIL 27 (2011): 63–72 The waterbirds and coastal seabirds of Timor-Leste: new site records clarifying residence status, distribution and taxonomy COLIN R. TRAINOR The status of waterbirds and coastal seabirds in Timor-Leste is refined based on surveys during 2005–2010. A total of 2,036 records of 82 waterbird and coastal seabirds were collected during 272 visits to 57 Timor-Leste sites, and in addition a small number of significant records from Indonesian West Timor, many by colleagues, are included. More than 200 new species by Timor-Leste site records were collected. Key results were the addition of three waterbirds to the Timor Island list (Red-legged Crake Rallina fasciata, vagrant Masked Lapwing Vanellus miles and recent colonist and Near Threatened Javan Plover Charadrius javanicus) and the first records in Timor-Leste for three irregular visitors: Australian White Ibis Threskiornis molucca, Ruff Philomachus pugnax and Near Threatened Eurasian Curlew Numenius arquata. Records of two subspecies of Gull-billed Tern Gelochelidon nilotica, including the first confirmed records outside Australia of G. n. macrotarsa, were also of note. INTRODUCTION number of field projects in Timor-Leste, including an Important Bird Areas programme and a doctoral study (Trainor et al. 2007a, Timor Island lies at the interface of continental South-East Asia and Trainor 2010). The residence status and nomenclature for some Australia and consequently its resident waterbird and coastal seabird species listed in a fieldguide (Trainor et al. 2007b) and recent review avifauna is biogeographically mixed. Some of the most notable (Trainor et al. 2008) are clarified. Three new island records are findings of a Timor-Leste field survey during 2002–2004 were the documented and substantial new ecological data on distribution discovery of resident breeding populations of the essentially Australian and habitat use are included. -

ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation: SECRETIVE MARSHBIRDS of URBAN WETLANDS in the WASHINGTON, DC METROPOLITAN AREA Patrice Nielson
ABSTRACT Title of Dissertation: SECRETIVE MARSHBIRDS OF URBAN WETLANDS IN THE WASHINGTON, DC METROPOLITAN AREA Patrice Nielson, Doctor of Philosophy 2016 Dissertation directed by: Dr. William Bowerman and Dr. Andrew Baldwin Environmental Science and Technology Secretive marshbirds are in decline across their range and are species of greatest conservation need in state Wildlife Action Plans. However, their secretive nature means there is relatively sparse information available on their ecology. There is demand for this information in the Washington, DC area for updating conservation plans and guiding wetland restoration. Rapid Wetland Assessment Methods are often used to monitor success of restoration but it is unknown how well they indicate marshbird habitat. Using the Standardized North American Marshbird Monitoring Protocol, I surveyed 51 points in 25 marshes in the DC area in 2013 – 2015. I also collected data on marsh area, buffer width, vegetation/water interspersion, vegetation characteristics, flooding, and invertebrates. At each bird survey point I assessed wetland quality using the Floristic Quality Assessment Index (FQAI) and California Rapid Wetland Assessment (CRAM) methods. I used Program Presence to model detection and occupancy probabilities of secretive marshbirds as a function of habitat variables. I found king rails (Rallus elegans) at five survey sites and least bittern (Ixobrychus exilis) at thirteen survey sites. Secretive marshbirds were using both restored and natural marshes, marshes with and without invasive plant species, and marshes with a variety of dominant vegetation species. King rail occupancy was positively correlated with plant diversity and invertebrate abundance and weakly negatively correlated with persistent vegetation. Least bittern occupancy was strongly negatively correlated woody vegetation and invertebrate abundance and weakly positively correlated with persistent vegetation. -

Acariformes: Prostigmata) M
Ixobrychiphilus, a new genus of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) M. Skoracki„ M. Zmudzinski„ P. Solarczyk, To cite this version: M. Skoracki„ M. Zmudzinski„ P. Solarczyk,. Ixobrychiphilus, a new genus of the family Syringophili- dae (Acariformes: Prostigmata). Acarologia, Acarologia, 2017, 57 (2), pp.269-273. 10.1051/acarolo- gia/20164155. hal-01493944 HAL Id: hal-01493944 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01493944 Submitted on 22 Mar 2017 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Acarologia 57(2): 269–273 (2017) DOI: 10.1051/acarologia/20164155 Ixobrychiphilus, a new genus of the family Syringophilidae (Acariformes: Prostigmata) Maciej SKORACKI1, Mateusz ZMUDZINSKI1 and Piotr SOLARCZYK2 (Received 21 April 2016; accepted 08 September 2016; published online 05 January 2017; edited by Philippe AUGER) 1 Department of Animal Morphology, Faculty of Biology, Adam Mickiewicz University, Umultowska 89, 61-614 Poznan, Poland. [email protected], [email protected] 2 Department of Biology and Medical Parasitology, Medical Faculty I, Poznan University of Medical Sciences, 10 Fredry Street, 61-701 Poznan, Poland. [email protected] ABSTRACT — A new monotypic genus of parasitic mites is proposed for Ixobrychiphilus wallacei n. -

List of Birds in Palo Verde National Park, Costa Rica
http://www.nicoyapeninsula.com/paloverde/paloverdebirdlist.html Page 1 of 8 List of Birds in Palo Verde National Park, Costa Rica SPECIES English Spanish TINAMIFORMES TINAMIDAE Crypturellus cinnamomeus Thicket Tinamou Tinamú Canelo PODICIPEDIFORMES PODICIPEDIDAE Tachybaptus dominicus Least Grebe Zambullidor Enano Podilymbus podiceps Pied-billed Grebe Zambullidor Piquipinto PELECANIFORMES PHALACROCORACIDAE Phalacrocorax brasilianus Neotropic Cormorant Cormorán Neotropical ANHINGIDAE Anhinga anhinga Anhinga Pato Aguja FREGATIDAE Fregata magnificens Magnificent Frigatebird Rabihorcado Magno CICONIIFORMES ARDEIDAE Botaurus pinnatus Pinnated Bittern Avetoro Neotropical Ixobrychus exilis Least Bittern Avetorillo Pantanero Tigrisoma mexicanum Bare-throated Tiger-Heron Garza-Tigre Cuellinuda Ardea herodias Great Blue Heron Garzón Azulado Ardea alba Great Egret Garceta Grande Egretta thula Snowy Egret Garceta Nivosa Egretta caerulea Little Blue Heron Garceta Azul Egretta tricolor Tricolored Heron Garceta Tricolor Bubulcus ibis Cattle Egret Garcilla Bueyera Butorides virescens Green Heron Garcilla Verde Nycticorax nycticorax Black-crowned Night-Heron Martinete Coroninegro Nyctanassa violacea Yellow-crowned Night-Heron Martinete Cabecipinto Cochlearius cochlearius Boat-billed Heron Pico-Cuchara THRESKIORNITHIDAE Threskiornithinae Eudocimus albus White Ibis Ibis Blanco Plegadis falcinellus Glossy Ibis Ibis Morito Plataleinae Platalea ajaja Roseate Spoonbill Espátula Rosada CICONIIDAE Jabiru mycteria Jabiru Jabirú Mycteria americana Wood Stork Cigueñon -

Least Bittern Ixobrychus Exilis
Appendix A: Birds Least Bittern Ixobrychus exilis Federal Listing N/A State Listing SC Global Rank G5 State Rank S1 Regional Status Very High Photo by Pamela Hunt Justification (Reason for Concern in NH) Secretive marsh birds like the Least Bittern have generally been considered conservation priorities because of known losses of wetland habitats, combined with often poor data on species’ distribution, abundance, and trend. In the case of the Least Bittern, there are only a handful of potential breeding sites in New Hampshire, and some of these (plus a couple of historic sites) are in the more developed southeastern part of the state. Range‐wide, Least Bittern populations appear stable (Sauer et al. 2014), although data are limited, and Breeding Bird Atlases in the Northeast did not document significant range retractions in most areas. Distribution Breeds locally across the eastern United States, primarily in the Mississippi Valley and along the Atlantic and Gulf coastal plains. The species is highly dispersed and local in the West, and patchily distributed in Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean, and extends well south into South America (Poole et al. 2009). Northern populations withdraw to the southern U.S., Caribbean, and Central America in winter. Least Bitterns have been recorded during the breeding season (conservatively June‐July) at eight New Hampshire locations since 1990, as follows: •Tuttle Swamp, Newmarket (1999) •Stubb’s Pond, Newington (1999‐2001) •Jewell Brook wetlands, Stratham (2006) •Surrey Lane marsh, Durham (2006‐2014) •Lake Wantastiquet marshes, Hinsdale (2007‐2013) •North River Road, Epping (2009) •Thompson Wildlife Sanctuary, Sandwich (2009) •World End Pond, Salem (2014) Of these, three are considered sites where the species is considered a probable or confirmed breeder. -

Checklist of Birds of Pulau Ubin.Xls.Xlsx
CHECKLIST OF BIRDS OF PULAU UBIN Compiled and updated on 12 Sep 2014 by Robert Teo, National Parks Board Common Name ScientIfic Name 1 King Quail, Blue-breasted Quail Coturnix chinensis 2 Red Junglefowl Gallus gallus 3 Barred Buttonquail Turnix suscitator 4 Sunda Pygmy Woodpecker, Sunda Woodpecker Dendrocopus moluccensis 5 Rufous Woodpecker Celeus brachyurus 6 Banded Woodpecker Picus miniaceus 7 Laced Woodpecker Picus vittatus 8 Common Flameback, Common Goldenback Dinopium javanense 9 Coppersmith Barbet Megalaima haemacephala 10 Oriental Pied Hornbill Anthracoceros albirostris 11 Oriental Dollarbird, Dollarbird Eurystomus orientalis 12 Common Kingfisher Alcedo atthis 13 Blue-eared Kingfisher Alcedo meninting 14 Black-backed Kingfisher, Oriental Dwarf Kingfisher Ceyx erithacus 15 Stork-billed Kingfisher Halcyon capensis 16 Ruddy Kingfisher Halcyon coromanda 17 White-throated Kingfisher Halcyon smyrnensis 18 Black-capped Kingfisher Halcyon pileata 19 Collared Kingfisher Todirhamphus chloris 20 Blue-throated Bee-eater Merops viridis 21 Blue-tailed Bee-eater Merops philippinus 22 Chestnut-winged Cuckoo Clamator coromandus 23 Hodgson's Hawk Cuckoo Hierococcyx niscicolor 24 Indian Cuckoo Cuculus micropterus 25 Banded Bay Cuckoo Cacomantis sonneratii 26 Plaintive Cuckoo Cacomantis merulinus 27 Rusty-breasted Cuckoo Cacomantis sepulcralis 28 Little Bronze Cuckoo Chrysococcyx minutillus 29 Asian Drongo Cuckoo, Drongo Cuckoo Surniculus lugubris 30 Asian Koel Eudynarnys scolopacea 31 Chestnut-bellied Malkoha Phaenicophaeus sumatranus 32 Greater -

European Union Action Plans for Eight Priority Bird Species
Bittern (Botaurus stellaris) European Union Action Plans for 8 Priority Birds Species – Bittern European Union Action Plan for Bittern (Botaurus stellaris) Compiled by: Peter Newbery (RSPB, UK) Norbert Schäffer (RSPB/BirdLife International, UK) Ken Smith (RSPB, UK) with contributions from: Tom den Boer (Vogelbescherming Nederland, The Netherlands) Przemyslaw Chylarecki (Polish Academy of Sciences, Poland) Andreas von Lindeiner (Landesbund für Vogelschutz in Bayern, Germany) Jean-Laurent Lucchesi (Station Biologique de la Tour du Valat, France) Erwin Nemeth (BirdLife Österreich-Gesellschaft für Vogelkunde, Austria) Luca Puglisi (Dip. Scienze del Comportamento Animale e dell'Uomo, Italy) Additional information was provided by: Lars Broberg (Sweden) Alison Duncan (Ligue pour la Protection des Oiseaux, France) Birgit Gödert-Jacoby (Lëtzebuerger Natur - a Vulleschutzliga, Luxembourg) Deborah Harrison (RSPB, UK) Borja Heredia (Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Spain) Pertti Koskimies (Helsinki Zoological Museum, Finland) Richard Lansdown (Ardeola Environmental Services, Sweden) Jesper Madsen (Danmarks Miljøundersøgelser, Denmark) Francisco Moreira (Liga para a Protecçao da Natureza, Protugal) Costas Papaconstantinou (Hellenic Ornithological Society, Greece) Laurence Rose (RSPB, UK) Zoltan Waliczky (BirdLife International, UK) Marcus Walsh (BirdLife Suomi-Finland, Finland) Johanna Winkelman (Vogelbescherming Nederland, The Netherlands) Milestones in production of action plan Workshop: 16-18 April 1996 (Hilpoltstein, Bavaria) First draft: May 1996 Second draft: August 1996 Final draft: September 1999 Reviews This action plan will be monitored annually by the compilers and reviewed every five years (first review due 2001). Geographical scope This plan is intended for implementation by conservation organisations and others within the whole of the EU, although it is recognised that the Bittern does not currently breed in all member states.