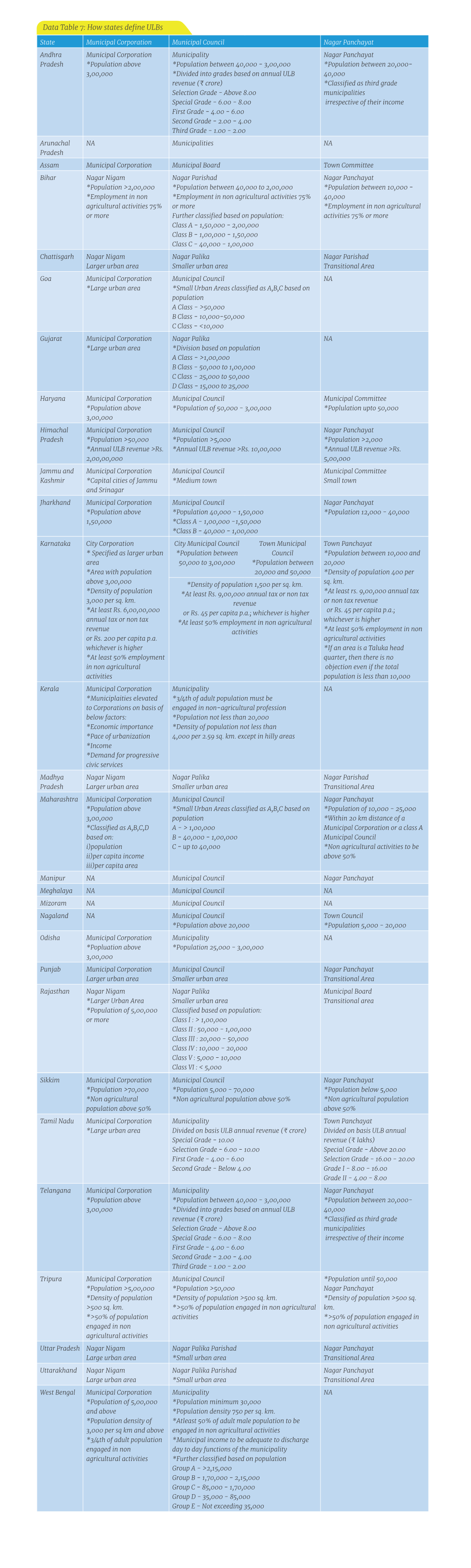
Data Table 7: How States Define Ulbs
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Office of Nagar Panchayat Ukhimath
OFFICE OF NAGAR PANCHAYAT UKHIMATH DETAIL PROJECT REPORT,OF RAJIV AWAS YOJNA,UKHIMATH DETAIL PROJECT REPORT OF RAJIV AWAS YOJNA FOR UKHIMATH RAY PROJECTS OF DISASTER AREA IN UTTARAKHAND PROPOSED APPROVED APPROVED APPROVED UKIMATH IN UTTARAKHAND STATE Route Map Project Location 1.Ukhimath is a pilgrimage site in Rudraprayag district, Uttarakhand, India.It is at an elevation of 1311 metres and at a distance of 41 km fromRudraprayag. During the winters, the idols from Kedarnath temple, and Madhyamaheshwar are brought to Ukhimath and worshipped there for six months. 2.Ukhimath can be used as center destination for visiting different places located nearby, i.e. Madhmaheshwar (Second kedar),Tungnath ji (Third kedar) and Deoria Tal(natural fresh water lake) and many other picturesque places. 3.One of the town severely affected by water induced disaster occurred in 2013. 4. Population as per census 2011 :3125 5.Total area: 2.78263 sq.km RAY INTERVENTION 1. INTERVENTION : In-Situ Housing 2. WARD SPECIFIC : 4 Ward Areas 3. WARD AREAS : Identified by UKHIMATH NAGAR PANCHAYAT 4.OWNERSHIP OF LAND : BENEFICIARY OWNED 5. SLUM FREE CITY PLAN OF ACTION : COMPLIED Project Overview Information about the project area: Ukhimath •Nagar Panchayat Ukhimath created in 2013 •Population as per census 2011 :3125 •Mode of earning in town: :Service/Business/Labour Ward Population and area detail s.no Ward no Wards name Population Area(sq. km) 1 1 Gandhinagar 785 0.49125 2 2 Udaipur 760 0.5132 3 3 Omkareshwar 790 1.18977 4 4 Bhatteshwar 780 0.58841 Total 3125 2.78263 -

Community Based Monitoring System for Access to Basic Minimum Services, Kerala
Community Based Monitoring System for Access to Basic Minimum Services, Kerala D Narayana Slim Haddad Smitha Aravind Katia Mohindra Paper to be presented at the PEP-CBMS conference in Dakar, June 16-20, 2004. Community Based Monitoring System for Access to Basic Minimum Services, Kerala 1. Introduction The paper presents a brief outline of the approach and results arrived so far of the CBMS in Kerala, India. The organization of the paper is as follows. It begins by presenting the attempt at democratic decentralization in India over the last ten years- the constitutional amendment, the structure of governance, and the mandate of the local governments. The problems faced by the local governments in fulfilling the mandate of data based planning and monitoring is explained followed by the presentation of the salient aspects of the project, Community Based Monitoring System for Access to Basic Minimum Services, Kerala. The attempt at building a database at the local level and the three track approach of the CBMS in Kerala is, then discussed in some detail. 2. The 73rd and 74th Amendments to the Constitution of India, which became law in April 1993, provided the foundation for a comparable democratic decentralization in the rural and urban areas respectively across the states of India. The Amendments made it mandatory for each state to constitute Local Self-Government Institutions (called Panchayats in rural areas) at the village, intermediate and district levels (except for states with less than two million population). The three-tier structure of governance in India following the formation of Panchayats and Municipalities is shown in Figure 1. -

Porations and the Maharashtra Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats and Industrial Townships (Amendment and Continuance) Ordinance, 2016 (Mah
¨É½þÉ®úɹ]Åõ ¶ÉɺÉxÉ ®úÉVÉ{ÉjÉ +ºÉÉvÉÉ®úhÉ ¦ÉÉMÉ +É`ö ´É¹ÉÇ 2, +ÆEòú 59(2)] ¨ÉÆMɳý´ÉÉ®ú, +ÉìMɺ]õ 30, 2016/¦ÉÉpù 8, ¶ÉEäò 1938 [{ÉÞ¹`ä 10, ËEò¨ÉiÉ : ¯û{ɪÉä 27.00 +ºÉÉvÉÉ®úhÉ Gò¨ÉÉÆEòú 95 |ÉÉÊvÉEÞòiÉ |ÉEòɶÉxÉ ¨É½þÉ®úɹ]Åõ Ê´ÉvÉÉxɨÉÆb÷³ýÉSÉä +ÊvÉÊxÉªÉ¨É ´É ®úÉVªÉ{ÉɱÉÉÆxÉÒ |ÉJªÉÉÊ{ÉiÉ Eäò±Éä±Éä +vªÉÉnäù¶É ´É Eäò±Éä±Éä Ê´ÉÊxÉªÉ¨É +ÉÊhÉ Ê´ÉÊvÉ ´É xªÉÉªÉ Ê´É¦ÉÉMÉÉEòbÚ÷xÉ +ɱÉä±ÉÒ Ê´ÉvÉäªÉEäò (<ÆOÉVÉÒ +xÉÖ´ÉÉnù). In pursuance of clause (3) of article 348 of the Constitution of India, the following translation in English of the Maharashtra Municipal Corporations and the Maharashtra Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats and Industrial Townships (Amendment and Continuance) Ordinance, 2016 (Mah. Ord. XVI of 2016), is hereby published under the authority of the Governor. By order and in the name of the Governor of Maharashtra, P. H. MALI, Principal Secretary to Government, Law and Judiciary Department. [Translation in English of the Maharashtra Municipal Corporations and the Maharashtra Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats and Industrial Townships (Amendment and Continuance) Ordinance, 2016 (Mah. Ord. XVI of 2016), published under the authority of the Governor.] URBAN DEVELOPMENT DEPARTMENT Mantralaya, Madam Cama Marg, Hutatma Rajguru Chowk, Mumbai 400 032, dated the 30th August 2016. MAHARASHTRA ORDINANCE No. XVI OF 2016. AN ORDINANCE further to amend the Maharashtra Municipal Corporations Act and the Maharashtra Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats and Industrial Townships Act, 1965. WHEREAS the Governor of Maharashtra had promulgated the (Amendment) Bill, 2016 (L.A. -

Decentralisation and Municipalities
DECENTRALISATION AND MUNICIPALITIES The 73rd and 74th Constitution Amendment Acts are sister legislations passed by the Parliament in 1992. The 73rd Constitution Amendment Act provided directions for the creation of Panchayats in the rural areas and the 74th Constitution Amendment Act provided for the creation of Municipalities in urban areas. The two legislations laid a broad framework for the setting up of Panchayats and Municipalities by the states. The legislations also stipulated a time limit within which the state governments were to enact conforming legislations to enable setting up of Panchayats and Municipalities, that is by the 1st of July 1994. Prior to the enactment of these two legislations, the functioning of the local bodies was totally dependent on the whims and fancies of the state governments. The supersession of the local bodies was a very common occurrence. Further, the vital arms necessary for the efficient functioning of the local bodies such as the District Planning Committee, Metropolitan Planning Committee, Wards Committee, State Election Commission etc., are either missing or not in a functional state. Although the setting up of these institutions has been made mandatory by the Constitution, in most states they are still not in place. The reasons for their absence or ineffectivity have been discussed in this paper. The legislation apart from laying broad criteria for constitution, composition of Municipalities, elections/removal of Mayor or Chairpersons, qualification/disqualification of membership, setting up of State Election Commission etc., left it to the state governments to prescribe the actual norms. This was done while keeping in mind the federal nature of our political system and also since a minority government was tabling the Bill in the Parliament and was dependent on other regional parties for its passage. -

Town Wise Revised Action Plan for Polluted River Stretches in the State of Bihar Original Application No: 200/2014 (Matter : M.C
INDEX Town wise Revised Action Plan for polluted River Stretches in the State of Bihar Original application No: 200/2014 (Matter : M.C. Mehta Vs Union of India & Orgs) S.No. Particulars Page No 1 Synopsis 1-7 Maps showing ongoing /Proposed Sewerage Scheme in 2 8 Towns under Polluted Stretch & Tributaries Map showing Patna town division into zones for Sewerage 3 9 Schemes Compliance report in terms of progress in Quarter related to 4 10-15 STPs in the state of Bihar Report related to Polluted Stretches and Lying of sewage 5 network, collection and disposal of sewage, interception and 16-33 diversion of drains carrying sewage to STP. 6 Ganga River Tributary Towns 34-35 7 SWM Status & Action Plan for Ganga & its Tributaries 36-38 8 ODF Status & Action Plan of Ganga & its tributaries 39 9 Status of Plastic Waste Management 40 10 Annexures Status of Ongoing / Tendered / Tender to be floated of Schemes under Namami Gange Program i. and 41-48 Status of Screening with Sewerage Schemes : Annexure- i Solid Waste Management Status Report in Ganga Towns and ii. Status of different Components of SWM and allied Works at 49-52 Ghats: Annexure- ii Report of Plastic Carry Bags Since coming into effect of iii. Plastic Waste Management Byelaws till date: 53-56 Annexure- iii Toilet Status of Ganga Town ULBs and Status of ODF ULBs iv. Certified by QCI: 57-59 Annexure- iv 60-68 and 69 11 Status on Utilization of treated sewage (Column- 1) 12 Flood Plain regulation 69 (Column-2) 13 E Flow in river Ganga & tributaries 70 (Column-4) 14 Assessment of E Flow 70 (Column-5) 70 (Column- 3) 15 Adopting good irrigation practices to Conserve water and 71-76 16 Details of Inundated area along Ganga river with Maps 77-90 17 Rain water harvesting system in river Ganga & tributaries 91-96 18 Letter related to regulation of Ground water 97 Compliance report to the prohibit dumping of bio-medical 19 98-99 waste Securing compliance to ensuring that water quality at every 20 100 (Column- 5) point meets the standards. -

The Maharashtra Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats and Industrial Townships Act, 1965
GOVERNMENT OF MAHARASHTRA LAW AND JUDICIARY DEPARTMENT (MAHARASHTRA ACT No. XL OF 1965) THE MAHARASHTRA MUNICIPAL COUNCILS, NAGAR PANCHAYATS AND INDUSTRIAL TOWNSHIPS ACT, 1965. (As modified upto 11th May 2016) PRINTED IN INDIA BY THE MANAGER, GOVERNMENT CENTRAL PRESS, MUMBAI AND PUBLISHED BY THE DIRECTOR, GOVERNMENT PRINTING, STATIONERY AND PUBLICATIONS, MAHARASHTRA STATE, MUMBAI 400 004 2016 [Price : Rs. 206.00] (i) THE MAHARASHTRA MUNICIPAL COUNCILS, NAGAR PANCHAYATS AND INDUSTRIAL TOWNSHIPS ACT, 1965 ————— CONTENTS PREAMBLE. SECTIONS. PAGES CHAPTER I. PRELIMINARY. 1. Short title, extent and commencement. 8 2. Definitions. 8 CHAPTER II. MUNICIPAL COUNCILS. (1) Municipal areas and their classification. 3. Specification of areas as smaller urban areas. 17 4. Classification of smaller urban areas. 18 5. Effect of reclassification of a municipal area. 18 6. Alteration of the limits of a municipal area. 19 (2) Municipal Authorities and Establishment of Councils. 7. Municipal authorities charged with execution of the Act. 19 8. Establishment and Incorporation of Councils. 19 9. Composition of Councils. 19 9A. Persons contesting election for reserved seat to submit Caste Certificate and Validity . 21 Certificate. (3) Elections and publication of names of elected and nominated Councillors. 10. Division of municipal area into wards and reservation of wards for Women, Scheduled . 22 Castes and Scheduled Tribes. 10A. State Election Commissioner. 24 10AA. Power of State Election Commissioner to issue directions to prevent impersonation. 24 11. Preparation of list of voters. 24 11A. [Deleted] . 24 11B. [Deleted] 12. Right to vote. 24 13. Manner of voting. 25 14. Other restrictions on voting. 25 15. Qualification for becoming Councillor. 25 16. -

Population of Class Wise Towns in Bihar
POPULATION OF CLASS WISE TOWNS IN BIHAR S. No. Towns Population S. No. Towns Population Class I Towns 17 Supaul (Nagar Parishad) 54085 1 Bettiah (Nagar Parishad) 116670 18 Araria (Nagar Parishad) 60861 2 Motihari (Nagar Parishad) 100683 19 Kishanganj (Nagar Parishad) 85590 3 Muzaffarpur (Nagar Nigam) 305525 20 Beehat (Nagar Parishad) 64579 4 Hajipur (Nagar Parishad) 119412 21 Barauni (Nagar Parishad) 58628 5 Patna (Nagar Nigam) 1432209 22 Benipur (Nagar Parishad) 62203 6 Danapur Nizamat (Nagar Parishad) 131176 Total 1557267 7 Bihar Sharif (Nagar Nigam) 232071 Class III Towns 8 Arrah (Nagar Nigam) 203380 1 Narkatiaganj (Nagar Parishad) 40830 9 Sasaram (Nagar Parishad) 131172 2 Ramnagar (Nagar Panchayat) 38554 10 Dehri DalmiyaNagar (Nagar Parishad) 119057 3 Chanpatia (Nagar Panchayat) 22038 11 Gaya (Nagar Nigam) 389192 4 Raxaul (Nagar Parishad) 41610 12 Bhagalpur (Nagar Nigam) 340767 5 Sugauli (Nagar Panchayat) 31432 13 Darbhanga (Nagar Nigam) 267348 6 Dhaka (Nagar Panchayat) 32632 14 Munger (Nagar Nigam) 188050 7 Areraj (Nagar Panchayat) 20356 15 Chapra (Nagar Parishad) 179190 8 Sheohar (Nagar Panchayat) 21262 16 Siwan (Nagar Parishad) 109919 9 Bairgania (Nagar Panchayat) 34836 17 Saharsa (Nagar Parishad) 125167 10 Motipur (Nagar Panchayat) 21957 18 Purnia (Nagar Nigam) 171687 11 Kanti (Nagar Panchayat) 20871 19 Katihar (Nagar Nigam) 190873 12 Mahnar Bazar (Nagar Panchayat) 37370 Total 4853548 13 Lalganj (Nagar Panchayat) 29873 Class II Towns 14 Barh (Nagar Parishad) 48442 1 Begusarai (Nagar Nigam) 93741 15 Masaurhi (Nagar Parishad) 45248 -

The U.P. Panchayat Raj Act, 1947
THE U.P. PANCHAYAT RAJ ACT, 1947 (U.P. Act No. XXVI of 1947) [As amended by U.P. Act No. 9 of 1994, 12 of 1994, 21 of 1995, 29 of 1995, 21 of 1998, 27 of 1999, 33 of 1999, 22 of 2001, 24 of 2001, 12 of 2004 and Act No. 44 of 2007 also Amended by Uttaranchal Amendment Act No. 7, 8 of 2002 Act No. 30 of 2005 and Act No. 5 of 2007 2008 2 The U.P. Panchayat Raj Act, 1947 Contents Preamble Section Page CHAPTER I Preliminary 1. Short title, extent and commencement 9 2. Definitions 9 CHAPTER II Establishment and Constitution of Gram Sabhas 3. Gram Sabha 12 4. [Deleted ] 12 5. Membership of Gram Sabha 12 CHAPTER II-A Disqualification of members of Gram Panchayat and Electoral Rolls etc. 5-A Disqualification of membership 13 5-B Qualification for holding office of Pradhan 14 6. Cessation of membership 14 6-A Decision on question as to disqualifications 14 7. [deleted ] 15 8. Effect of change in population or inclusion of the area 15 of a [Gram Panchayat] in Municipalities etc. 9. Electoral roll for each territorial constituency 15 9-A Right to vote etc. 18 10. Removal of difficulty in the establishment of [Gram 19 Sabha] and in the working of a Gram Panchayat CHAPTER III The Gram Sabha : Its Meetings and Functions 11. Meeting and functions of the Gram Sabha 19 CHAPTER III-A Gram Panchayats 11-A Pradhan and Up-Pradhan of Gram Panchayat 20 11-B Election of Pradhan 21 11-C Election of Up-Pradhan and his term 22 11-D Prohibition of holding certain offices simultaneously 23 11-E Further bar on holding two offices simultaneously 23 11-F Declaration of Panchayat area 24 3 Section Page 12. -

The Maharashtra Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats and Industrial Townships (Amendment) Act, 2020 Act 7 of 2020 Amendment Appe
The Maharashtra Municipal Councils, Nagar Panchayats and Industrial Townships (Amendment) Act, 2020 Act 7 of 2020 Amendment appended: 12 of 2020, 33 of 2020 DISCLAIMER: This document is being furnished to you for your information by PRS Legislative Research (PRS). The contents of this document have been obtained from sources PRS believes to be reliable. These contents have not been independently verified, and PRS makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy, completeness or correctness. In some cases the Principal Act and/or Amendment Act may not be available. Principal Acts may or may not include subsequent amendments. For authoritative text, please contact the relevant state department concerned or refer to the latest government publication or the gazette notification. Any person using this material should take their own professional and legal advice before acting on any information contained in this document. PRS or any persons connected with it do not accept any liability arising from the use of this document. PRS or any persons connected with it shall not be in any way responsible for any loss, damage, or distress to any person on account of any action taken or not taken on the basis of this document. ¨É½þÉ®úɹ]Åõ ¶ÉɺÉxÉ ®úÉVÉ{ÉjÉ +ºÉÉvÉÉ®úhÉ ¦ÉÉMÉ +É`,ö ¨ÉÉSÉÇ 12, 2020/¡òɱMÉÖxÉ 22, ¶ÉEäò 1941 1 RNI No. MAHENG/2009/35528 ¨É½þÉ®úɹ]Åõ ¶ÉɺÉxÉ ®úÉVÉ{ÉjÉ +ºÉÉvÉÉ®úhÉ ¦ÉÉMÉ +É`ö ´É¹ÉÇ 6, +ÆEò 14(3)] MÉÖ°ü´ÉÉ®úú, ¨ÉÉSÉÇ 12, 2020/¡òɱMÉÖxÉ 22, ¶ÉEäò 1941 [{ÉÞ¹`äö 2, ËEò¨ÉiÉ : ¯û{ɪÉä 27.00 +ºÉÉvÉÉ®úhÉ Gò¨ÉÉÆEò 28 |ÉÉÊvÉEÞòiÉ |ÉEòɶÉxÉ ¨É½þÉ®úɹ]Åõ Ê´ÉvÉÉxɨÉÆb÷³ýÉSÉä +ÊvÉÊxÉªÉ¨É ´É ®úÉVªÉ{ÉɱÉÉÆxÉÒ |ÉJªÉÉÊ{ÉiÉ Eäò±Éä±Éä +vªÉÉnäù¶É ´É Eäò±Éä±Éä Ê´ÉÊxÉªÉ¨É +ÉÊhÉ Ê´ÉÊvÉ ´É xªÉÉªÉ Ê´É¦ÉÉMÉÉEòbÚ÷xÉ +ɱÉä±ÉÒ Ê´ÉvÉäªÉEäò (<ÆOÉVÉÒ +xÉÖ´ÉÉnù). -

Local Bodies
CHAPTER 42 LOCAL BODIES Local bodies are institutions of the local self governance, which look after the administration of an area or small community such as villages, towns, or cities. The Local bodies in India are broadly classified into two categories. The local bodies constituted for local planning, development and administration in the rural areas are referred as Rural Local Bodies (Panchayats) and the local bodies, which are constituted for local planning, development and administration in the urban areas are referred as Urban Local Bodies (Municipalities). However, provisions contained in Parts IX (Eleventh Schedule) and IX-A (Twelfth Schedule) of the Constitution providing for Panchayats and Municipalities respectively, exempt certain areas from the applicability of these Parts. The Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India deals with administration and control of scheduled areas and scheduled tribes in these areas. Similarly, Sixth Schedule made the provisions as to the administration of Tribal Areas in the States of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram. However, Nagalnd, Hills of Manipur are neither covered by provisions contained in Part IX and Part IXA nor covered in the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution and autonomy of the local governance of these areas is administered by their State’s Laws. Mizoram is entirely not covered under Part IX and Part IXA, however, some areas are covered under Sixth Schedule and the autonomy of these areas is established by State’s law. Some autonomous bodies in Assam have been established under State’s Laws for local governance. As per the Constitution (Eighty Third Amendment) Act 2000, the Article 243D relating to the reservation of seats in panchayats, is not applicable in Arunachal Pradesh. -

PANCHAYATI RAJ & MUNICIPALITIES – State List
LOCAL GOVERNMENT: PANCHAYATI RAJ & MUNICIPALITIES – State List • PANCHAYATI RAJ – RURAL SELF GOVT • EVOLUTION – 1957, GOI: BALWANT RAI MEHTA COMMITTEE – to examine & suggest - Community Development Programme[1952] & National Extension Service [1953] – BALWANT RAI MEHTA COMMITTEE recommended: democratic decentralization 3-tire Panchayat system [organically linked] planning& developmental activities district collector – chair of zilla parishad adequate resources CCE-PDPU http://www.pdpu.ac.in/ VenkataKrishnan Source: Laxmikanth • 1959- Rajasthan – 1st to implement • Study team & committees (1960 - 1976): 13 • 1976- Committee on Community Development & Panchayat Raj – Daya Choubey 1977- GOI: ASHOK MEHTA COMMITTEE Recommendation 2-tier zilla parishad executive body official participation of political parties compulsory powers of taxation regular social audit elections within 6 months voluntary agencies reservation for SCs & STs constitutional recognition CCE-PDPU http://www.pdpu.ac.in/ VenkataKrishnan Source: Laxmikanth • 1985 – Planning Commission : GVK Rao, conclusion: Bureaucratization of development administration Recommendation Zilla Parishad to be pivot of democratic decentralization decentralized district planning post of District Development Commissioner Note: 1984, Hanumantha Rao – stressed the role of Dt. Collector CCE-PDPU http://www.pdpu.ac.in/ VenkataKrishnan Source: Laxmikanth 1986, GoI: L M Singhvi for Revitalisation of Panchayats Recommendation Constitutional recognition Free and fair elections Establishment of Nyaya -

(AMDA) in India 1 | Page List of Municipal Councils and Municipalitie
Association of Municipalities and Development Authorities (AMDA) in India List of Municipal Councils and Municipalities in India S. No State Contact person, Address, Phone Website Name of Municipal Name of Municipality/Town and Email Id Council/Boards /Municipal Committees 1 Andhra Commissioner & Director of https://cdma.ap.gov.i 1. Adoni (M) 1. Addanki Pradesh Municipal Administration n/ulb-lists-0 2. Bhimavaram (M) 2. Allagadda Padmini Enclave, 5th lane, 4/7, 3. Chilakaluripet (M) 3. Amalapuram Mahatma Gandhi Inner Ring Rd, 4. Dharmavaram (M) 4. Amudalavalasa Annapura Nagar, Guntur, Andhra 5. Gudivada (M) 5. Atmakurknl Pradesh 522034 6. Guntakal (M) 6. Atmakurnlr Phone: 0866-2456708 7. Hindupur (M) 7. Bapatla Email: [email protected] 8. Madanapalle (M) 8. Bobbili 9. Nandyal (M) 9. Budwel 10. Narasaraopet (M) 10. Cheemakurthy 11. Proddatur (M) 11. Chirala 12. Tadepalligudem (M) 12. Dhone 13. Tadpatri (M) 13. Giddalur 14. Tenali (M) 14. Gollaprolu 15. Vizianagaram (M) 15. Gooty 16. Gudur-Kurnool 17. Gudur-SPR NELLORE 18. Ichapuram 19. Jaggaiahpet 20. Jammalamadugu 21. Jangareddygudem 22. Kavali 23. Kadiri 24. Kalyanadurgam 25. Kandukur 26. Kanigiri 27. Kovvur 28. Macherla 29. Madakasira 30. Mandapet 31. Mangalagiri 1 | P a g e Association of Municipalities and Development Authorities (AMDA) in India S. No State Contact person, Address, Phone Website Name of Municipal Name of Municipality/Town and Email Id Council/Boards /Municipal Committees 32. Markapur 33. Mummidivaram 34. Mydukur 35. Nagari 36. Naidupet 37. Nandigama 38. Nandikotkur 39. Narasapur 40. Narsipatnam 41. Nellimarla 42. Nidadavole 43. Nuzividu 44. Palakol 45. Palakonda 46. Palamaner 47. Palasakasibugga 48.