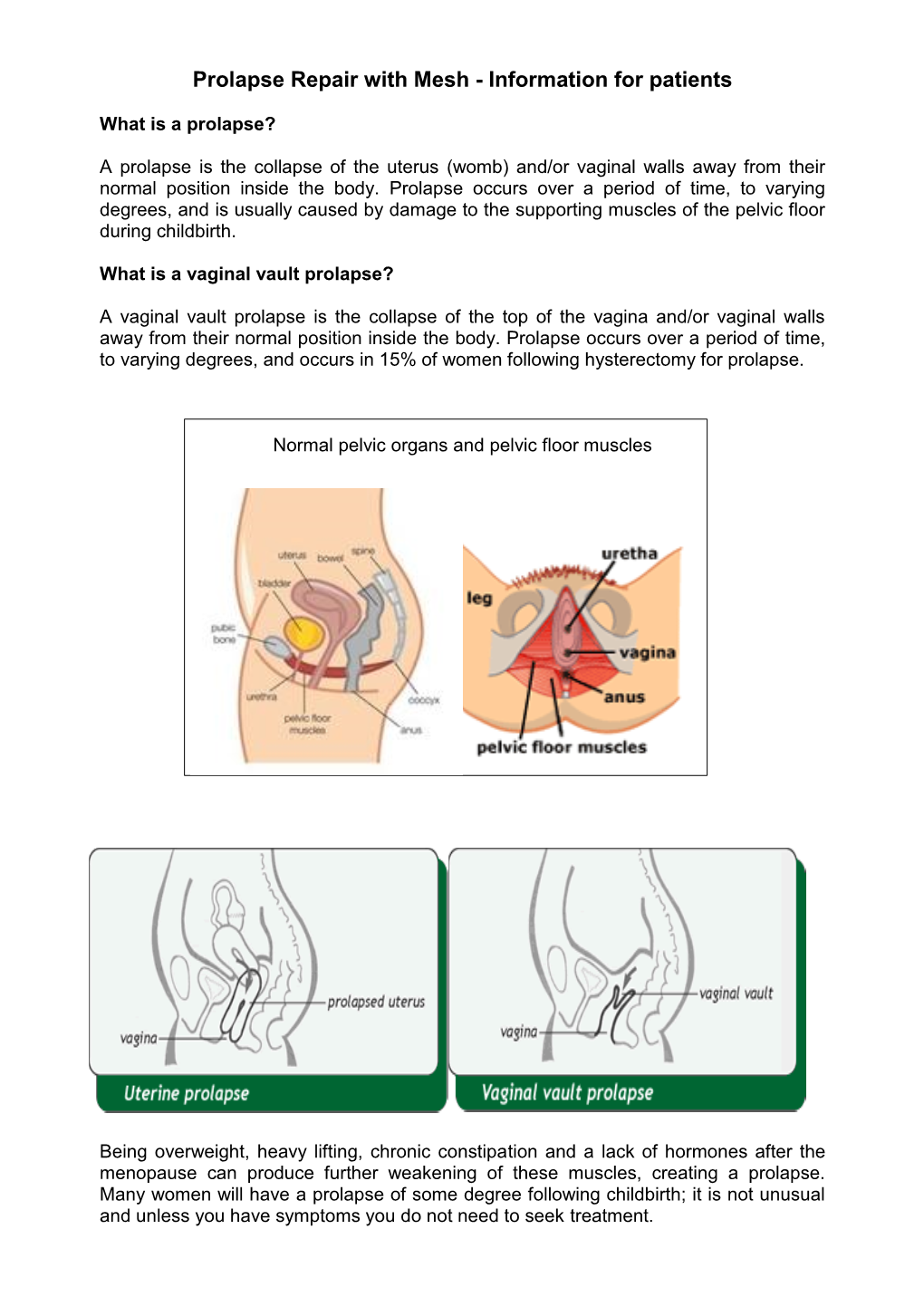
Prolapse and Sacrohysteropexy
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Laparoscopic Organopexy with Non-Mesh Genital (LONG)
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Laparoscopic Organopexy with Non-mesh Genital (LONG) Suspension: A Novel Uterine Received: 14 November 2017 Accepted: 19 February 2018 Preservation Procedure for the Published: xx xx xxxx Treatment of Apical Prolapse Cheng-Yu Long1,2,3, Chiu-Lin Wang2,3, Chin-Ru Ker1, Yung-Shun Juan4, Eing-Mei Tsai1,3 & Kun-Ling Lin 1,3 To assess whether our novel uterus-sparing procedure- laparoscopic organopexy with non-mesh genital(LONG) suspension is an efective, safe, and timesaving surgery for the treatment of apical prolapse. Forty consecutive women with main uterine prolapse stage II or greater defned by the POP quantifcation(POP-Q) staging system were referred for LONG procedures at our hospitals. Clinical evaluations before and 6 months after surgery included pelvic examination, urodynamic study, and a personal interview to evaluate urinary and sexual symptoms with overactive bladder symptom score(OABSS), the short forms of Urogenital Distress Inventory(UDI-6) and Incontinence Impact Questionnaire(IIQ-7), and the Female Sexual Function Index(FSFI). After follow-up time of 12 to 30 months, anatomical cure rate was 85%(34/40), and the success rates for apical, anterior, and posterior vaginal prolapse were 95%(38/40), 85%(34/40), and 97.5%(39/40), respectively. Six recurrences of anterior vaginal wall all sufered from signifcant cystocele (stage3; Ba>+1) preoperatively. The average operative time was 73.1 ± 30.8 minutes. One bladder injury occurred and was recognized during surgery. The dyspareunia domain and total FSFI scores of the twelve sexually-active premenopausal women improved postoperatively in a signifcant manner (P < 0.05). -

Chapter 14 – Female Reproductive Organs
Chapter 14 – Female reproductive organs The fee allowance for a hysteroscopy procedure includes an amount for dilation and curettage (D&C) and the insertion of a Mirena coil so we will not reimburse additional fees charged for these procedures. Similarly, where a therapeutic hysteroscopy is carried out, we will not pay any additional fees charged for a diagnostic hysteroscopy. The fee allowance for a hysterectomy procedure for ovarian malignancy includes an amount for the removal of the omentum and so this should not be charged as an additional procedure. A cystoscopy should not be charged as an additional procedure alongside any suspension/uro-gynaecological procedure. The insertion of a suprapubic catheter is considered part and parcel of procedures such as a suprapubic sling or the retropubic suspension of the bladder neck and so we will not pay any additional fees charged for this procedure. The fee allowance for a colposcopy procedure includes an amount for a punch biopsy. The fee allowance for a therapeutic laparoscopy includes an amount for a diagnostic laparoscopy. The code for the insertion of a prosthesis into the ureter is intended for use by urologists inserting a stent and not for circumstances where the ureter is being identified during hysterectomy. However, we recognise this does involve some additional work and consider a small uplift in the fee to be reasonable. Many pathological processes result in the formation of adhesions so ‘adhesiolysis’ is considered to be a normal part and parcel of these procedures. Therefore, we do not have a specific code for the division of adhesions. -

To Repair Uterine Prolapse
IP 372/2 [IPGXXX] NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE INTERVENTIONAL PROCEDURES PROGRAMME Interventional procedure overview of uterine suspension using mesh (including sacrohysteropexy) to repair uterine prolapse Uterine prolapse happens when the womb (uterus) slips down from its usual position into the vagina. Uterine suspension using mesh involves attaching 1 end of the mesh to the lower part of the uterus or cervix. The other end is attached to a bone at the base of the spine or to a ligament in the pelvis. The procedure can be done through open abdominal surgery or laparoscopy (keyhole surgery). The aim is to support the womb. Introduction The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) has prepared this interventional procedure (IP) overview to help members of the interventional procedures advisory committee (IPAC) make recommendations about the safety and efficacy of an interventional procedure. It is based on a rapid review of the medical literature and specialist opinion. It should not be regarded as a definitive assessment of the procedure. Date prepared This IP overview was prepared in January 2016. Procedure name Uterine suspension using mesh (including sacrohysteropexy) to repair uterine prolapse. Specialist societies Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG) British Society of Urogynaecology (BSUG) British Association of Urological Surgeons (BAUS). IP overview: Uterine suspension using mesh (including sacrohysteropexy) to repair uterine prolapse. Page 1 of 75 IP 372/2 [IPGXXX] Description Indications and current treatment Uterine prolapse is when the uterus descends from its usual position, into and sometimes through, the vagina. It can affect quality of life by causing symptoms of pressure and discomfort, and by its effects on urinary, bowel and sexual function. -

Abdominal Sacrohysteropexy Versus Vaginal Hysterectomy for Pelvic Organ Prolapse in Young Women
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Bhalerao AV et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Apr;9(4):1434-1441 www.ijrcog.org pISSN 2320-1770 | eISSN 2320-1789 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20201201 Original Research Article Abdominal sacrohysteropexy versus vaginal hysterectomy for pelvic organ prolapse in young women Anuja V. Bhalerao, Vaidehi A. Duddalwar* Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, N. K. P. Salve Institute of Medical Sciences, Nagpur, Maharashtra, India Received: 11 February 2020 Accepted: 03 March 2020 *Correspondence: Dr. Vaidehi A. Duddalwar, E-mail: [email protected] Copyright: © the author(s), publisher and licensee Medip Academy. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Background: Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is the descent of the pelvic organs beyond their anatomical confines. The definitive treatment of symptomatic prolapse is surgery but its management in young is unique due to various considerations. Aim of this study was to evaluate anatomical and functional outcome after abdominal sacrohysteropexy and vaginal hysterectomy for pelvic organ prolapse in young women. Methods: A total 27 women less than 35 years of age with pelvic organ prolapse underwent either abdominal sacrohysteropexy or vaginal hysterectomy with repair. In all women, pre-op and post-op POP-Q was done for evaluation of anatomical defect and a validated questionnaire was given for subjective outcome. Results: Anatomical outcome was significant in both groups as per POP-Q grading but the symptomatic outcome was better for sacrohysteropexy with regard to surgical time, bleeding, ovarian conservation, urinary symptoms, sexual function. -

Sacrohysteropexy for Uterine Prolapse (Womb Prolapse)
Sacrohysteropexy for Uterine Prolapse (Womb Prolapse) Patient Information Leaflet About this leaflet You should use the information provided in this leaflet as a guide. The way each gynaecologist does this procedure may vary slightly as will care in the hospital after your procedure and the advice given to you when you get home. You should ask your gynaecologist about any concerns that you may have. You should take your time to read this leaflet. A page is provided at the end of the leaflet for you to write down any questions you may have. It is your right to know about your planned operation or procedure, why it has been recommended, what the alternatives are and what the risks and benefits are. These should be covered in this leaflet. You may also want to ask about your gynaecologist’s experience and results of treating your condition. Benefits and risks There are not many studies about the success and the risks of most of the procedures carried out to treat prolapse and incontinence, so it is often difficult to state them clearly. In this leaflet, we may refer to risks as common, rare and so on, or we may give an approximate level of risk. You can find more information about risk in a leaflet ‘Understanding how risk is discussed in healthcare’ published by the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. https://www.rcog.org.uk/globalassets/documents/patients/patient-information-leaflets/pi- understanding-risk.pdf The following table is taken from that leaflet British Society of Urogynaecology (BSUG) database To understand the success and risks of surgery for prolapse and incontinence the British Society of Urogynaecology has set up a national database. -

Sacrohysteropexy for Uterine Prolapse
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS Sacrohysteropexy for uterine prolapse We advise you to take your time to read If you have had a hysterectomy then the this leaflet. If you have any questions term ‘vault' is used to describe the area please write them down on the sheet where your womb would have been provided (towards the back) and we can attached to the top of the vagina. discuss them with you at our next meeting. It is your right to know about the Figure 1: A diagram, sideways on, operations being proposed, why they are showing the normal anatomy (dotted line) being proposed, what alternatives there and a prolapsing vaginal apex(continuous are and what the risks are. These should line). be covered in this leaflet. This leaflet describes what an apical vaginal prolapse is, what alternatives are available within our Trust, the risks involved in surgery and what operation we can offer. What is prolapse of the uterus/vaginal apex? A prolapse is where the vaginal tissue is weak and bulges downwards into the vagina itself. It is often accompanied by a posterior vaginal wall prolapse, either a high In severe cases it can even protrude posterior vaginal wall prolapse called an outside the vagina. Apical vaginal enterocele, or a low posterior vaginal Wall prolapse is a prolapse arising from the prolapse called a rectocele, or sometimes top of the vagina. The apex is the both. deepest part of the vagina (top of it/ roof) where the uterus (womb) usually is The pelvic floor muscles are a series of located. -

Performing Vaginal Apical Suspension
NQF #C 2038 Performing vaginal apical suspension (uterosacral, iliococygeus, sacrospinous or sacral colpopexy) at the time of hysterectomy to address uterovaginal prolapse, Date Submitted: Jul 16, 2012 NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM Stage 1 Concept Submission and Evaluation Worksheet 1.0 This form contains the information submitted by measure developers/stewards, organized according to NQF’s concept evaluation criteria and process. The evaluation criteria, evaluation guidance documents, and a blank online submission form are available on the submitting standards web page. NQF #: C 2038 NQF Project: GI and GU Project Date Submitted: Jul 16, 2012 CONCEPT SPECIFICATIONS De.1 Concept Title: Performing vaginal apical suspension (uterosacral, iliococygeus, sacrospinous or sacral colpopexy) at the time of hysterectomy to address uterovaginal prolapse Co.1.1 Concept Steward: American Urogynecologic Society De.2 Brief Description of Concept: Percentage of female patients undergoing hysterectomy for the indication of uterovaginal prolapse in which a concomitant vaginal apical suspension (i.e.uterosacral, iliococygeus, sacrospinous or sacral colpopexy)is performed. 2a1.1 Numerator Statement: The number of female patients who have a concomitant vaginal apical suspension (i.e.uterosacral, iliococygeus, sacrospinous or sacral colpopexy) at the time of hysterectomy for uterovaginal prolapse. 2a1.4 Denominator Statement: Hysterectomy, performed for the indication of uterovaginal prolapse 2a1.8 Denominator Exclusions: • Patients with a gynecologic or other pelvic -

Textbook of Urogynaecology
Textbook of Urogynaecology Editors: Stephen Jeffery Peter de Jong Developed by the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology University of Cape Town Edited by Stephen Jeffery and Peter de Jong Creative Commons Attributive Licence 2010 This publication is part of the CREATIVE COMMONS You are free: to Share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work to Remix – to adapt the work Under the following conditions: Attribution. You must attribute the work in the manner specified by the author or licensor (but not in any way that suggests that they endorse you or your use of the work) Non-commercial. You may not use this work for commercial purposes. Share Alike. If you alter, transform, or build upon this work, you may distribute the resulting work but only under the same or similar license to this one. • For any reuse or distribution, you must make clear to others the license terms of this work. One way to do this is with a link to the license web page: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.5/za/ • Any of the above conditions can be waived if you get permission from the copyright holder. • Nothing in this license impairs or restricts the authors’ moral rights. • Nothing in this license impairs or restricts the rights of authors whose work is referenced in this document • Cited works used in this document must be cited following usual academic conventions • Citation of this work must follow normal academic conventions http://za.creativecommons.org Contents List of contributors 1 Foreword 2 The Urogynaecological History 3 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms and Urinary incontinence: Definitions and overview. -

Joint Report on Terminology for Surgical Procedures to Treat Pelvic
AUGS-IUGA JOINT PUBLICATION Joint Report on Terminology for Surgical Procedures to Treat Pelvic Organ Prolapse Developed by the Joint Writing Group of the American Urogynecologic Society and the International Urogynecological Association. Individual contributors are noted in the acknowledgment section. 03/02/2020 on BhDMf5ePHKav1zEoum1tQfN4a+kJLhEZgbsIHo4XMi0hCywCX1AWnYQp/IlQrHD3JfJeJsayAVVC6IBQr6djgLHr3m8XRMZF6k61FXizrL9aj3Mm1iL7ZA== by https://journals.lww.com/jpelvicsurgery from Downloaded meaningful data about specific procedures, standardized and Downloaded Abstract: Surgeries for pelvic organ prolapse (POP) are common, but widely accepted terminology must be adopted. Each term for a standardization of surgical terms is needed to improve the quality of in- given procedure must indicate to researchers, clinicians, and from vestigation and clinical care around these procedures. The American learners a specific and reliable minimal set of steps. The aim of https://journals.lww.com/jpelvicsurgery Urogynecologic Society and the International Urogynecologic Associ- this document is to propose a standardized terminology to de- ation convened a joint writing group consisting of 5 designees from scribe common surgeries for POP. each society to standardize terminology around common surgical terms in POP repair including the following: sacrocolpopexy (including sacral colpoperineopexy), sacrocervicopexy, uterosacral ligament suspension, sacrospinous ligament fixation, iliococcygeus fixation, uterine preserva- tion prolapse procedures or hysteropexy -

Abstracts 1-20 ORAL POSTERS
SUPPLEMENT TO The Gray Journal APRIL 2016 ■ Volume 214, Number 4 Founded 1869 YMOB_16_214n4S_COVER.indd 801 3/7/16 1:15 PM CYAN MAGENTA YELLOW BLACK PANTONE 877 C YMOB_16_214n4S_00C1.pgs 03.07.2016 12:17 SUPPLEMENT TO APRIL 2016 - Volume 214, Number 4 ORAL PRESENTATIONS S455 Abstracts 1-20 ORAL POSTERS S467 Abstracts 1-26 NON-ORAL POSTERS S481 Abstracts 27-80 VIDEO PRESENTATIONS S509 Abstracts 1-10 VIDEOFESTS S512 Abstracts 11-25 VIDEO CAFES S516 Abstracts 26-39 Cover: Wildroze/E+/Getty Images Published by Elsevier Inc., 360 Park Avenue South, New York, NY 10010-1710. Supplement to APRIL 2016 American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology 1A BLACK YELLOW MAGENTA CYAN 01-80011531_P0001.pgs 03.07.2016 12:10 SOCIETY OF GYNECOLOGIC SURGEONS Founed in 1974 sgsonline.org Dear Colleagues, Friends and Guests, Welcome to sunny California! As President of the Society of Gynecologic Surgeons, it is my honor to welcome you to the 42nd Annual Scientific Meeting in Palm Springs, California April 10th-13th, 2016. Eric Sokol and the SGS Program Committee have put together what is going to be an informative, exciting and may be even a little controversial program for the scientific meeting and postgraduate courses this year. One primary component of the SGS mission is to promote excellence in gynecologic surgery. Innovation, when properly applied, is one of the key factors in furthering surgical excellence and, in that spirit, the theme of our meeting this year is “Innovative ways to improve surgical care, research, and education in gynecologic surgery.” The Keynote and TeLinde Lecturers will expound upon this topic looking at different sides of the coin, addressing how to promote what works and how to make surgery work more effectively. -

Sacrocolpopexy for Post Hysterectomy Vault Prolapse
19 Sacrocolpopexy for Post Hysterectomy Vault Prolapse Serge P. Marinkovic, Lisa M. Gillin and Christina M. Marinkovic Department of Surgery/Division of Urology, Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery Specialist St Joseph Hospital, Fort Wayne, Indiana, USA 1. Introduction Pelvic organ prolapse is most likely the result of one or more clinical entities that gradually assist in weakening the pelvic floor [Connell KA, 2011]. Direct childbirth trauma to the levator ani and surrounding pelvic floor tissue will decrease strength over the course of recurrent childbirth and time. These injuries compromise support of the pelvic floor and may deviate its apical S3 horizontal orientation, while constant collagen and elastin remodelling may lead to further pelvic floor demise and upstage pelvic organ prolapse [Connell KA, 2011]. Over two hundred thousand women undergo the repair of pelvic organ prolapse in the United States every year. In fact, the cost for diagnosis and treatment exceeds two billion dollars annually [Subak LL, 2001]. A Kaiser Permanente retrospective, observational study surveyed 149,554 female patients over the age of twenty and estimated that the lifetime risk of undergoing a single surgery for pelvic organ prolapse or urinary incontinence by age eighty was eleven percent [Olsen 1997]. Fig. 1. Stage 4 Complete Procidentia. The cervix is the dimple in the middle of the photograph. Patient underwent a total hysterectomy and a double mesh, anterior and posterior polypropylene mesh [Scali Method, 1974] sacrocolpopexy. www.intechopen.com 294 Hysterectomy The need for recurrent pelvic organ prolapse surgery [within four years of prolapse surgery] has been estimated to be twenty-nine percent. -

Sufu Winter 2020 Newsletter
SUFU WINTER 2020 NEWSLETTER PRESIDENT’S MESSAGE By: Sandip Vasavada, MD Dear SUFU members, speakers from many parts of the world. Dr. David Ginsberg and Dr. Stu Reynolds and the clinical committee have created I hope every one of you is doing well and a fantastic program that promises to still be as educational and staying healthy in this difficult time. I must say, thought provoking as ever. Both parts to the program will have this is not quite what I envisioned my SUFU several keynote speakers from around the world as well as Presidency would be like, but like so many of several “rooms” of virtual posters and podiums to enlighten us you, I have had to adapt to changes. One of the on the latest in FPMRS research and innovations. The clinical biggest paradigm shifts has been to replace portion of the program will be held on Friday, February 26 and our usual in-person annual meeting with a Saturday, February 27 from about 10:00 a.m. EST to 5:30 p.m. virtual option for this winter. Heather and the EST. Our meetings could not be held without the strong support WJ Weiser team did a great job in negotiating from so many of our industry partners. They will also be having with the hotel in Nashville and secured the commitment for several breakout symposia throughout the meeting that will be SUFU to be there now in 2023. Our 2022 meeting is slated to both engaging and interactive. be in San Diego. As always, please do not hesitate to reach out to us with any I know like many of you, I will miss the camaraderie and in- suggestions or to get more involved in SUFU.