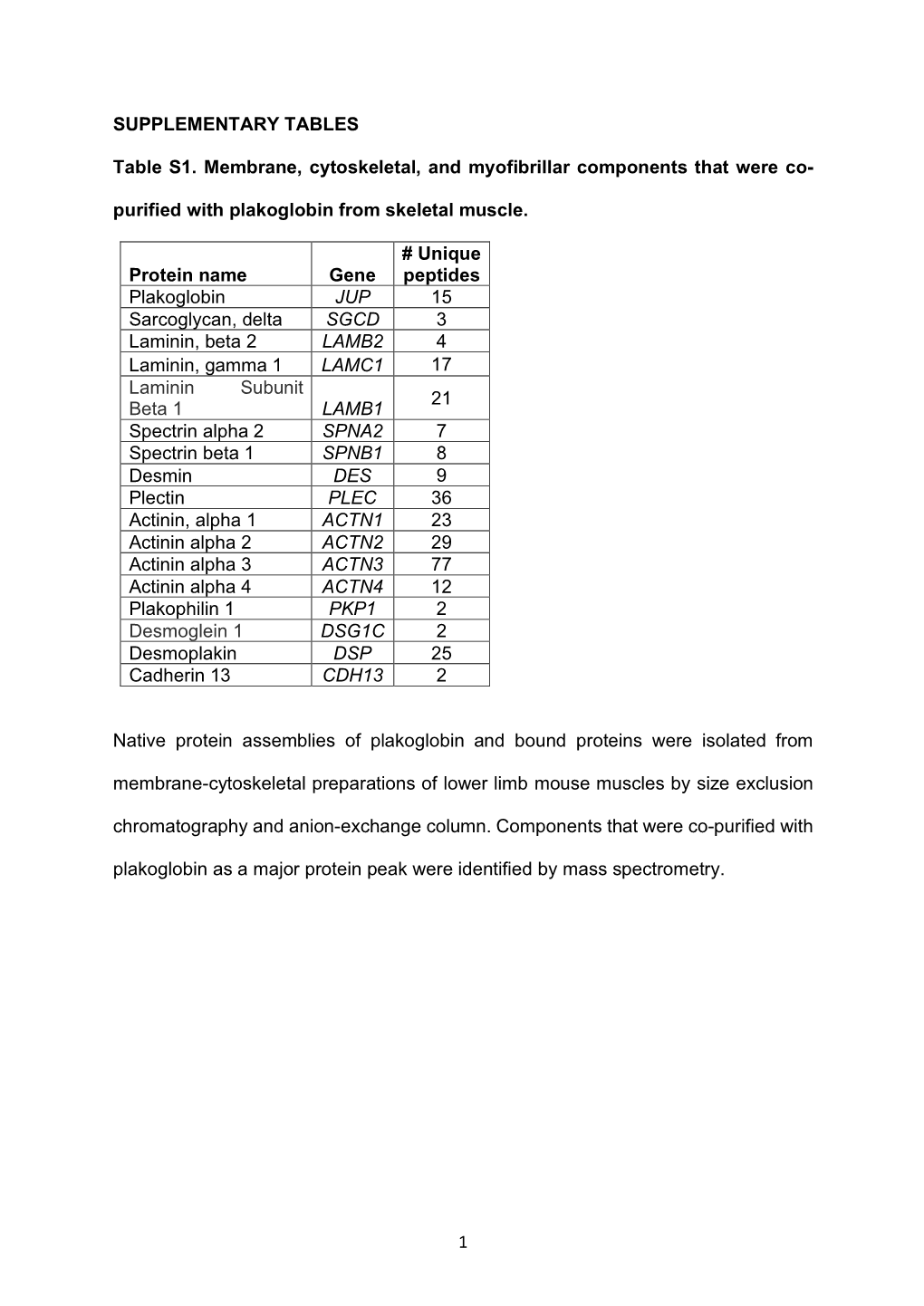
1 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Table S1. Membrane, Cytoskeletal, And
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

1 Metabolic Dysfunction Is Restricted to the Sciatic Nerve in Experimental
Page 1 of 255 Diabetes Metabolic dysfunction is restricted to the sciatic nerve in experimental diabetic neuropathy Oliver J. Freeman1,2, Richard D. Unwin2,3, Andrew W. Dowsey2,3, Paul Begley2,3, Sumia Ali1, Katherine A. Hollywood2,3, Nitin Rustogi2,3, Rasmus S. Petersen1, Warwick B. Dunn2,3†, Garth J.S. Cooper2,3,4,5* & Natalie J. Gardiner1* 1 Faculty of Life Sciences, University of Manchester, UK 2 Centre for Advanced Discovery and Experimental Therapeutics (CADET), Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester Academic Health Sciences Centre, Manchester, UK 3 Centre for Endocrinology and Diabetes, Institute of Human Development, Faculty of Medical and Human Sciences, University of Manchester, UK 4 School of Biological Sciences, University of Auckland, New Zealand 5 Department of Pharmacology, Medical Sciences Division, University of Oxford, UK † Present address: School of Biosciences, University of Birmingham, UK *Joint corresponding authors: Natalie J. Gardiner and Garth J.S. Cooper Email: [email protected]; [email protected] Address: University of Manchester, AV Hill Building, Oxford Road, Manchester, M13 9PT, United Kingdom Telephone: +44 161 275 5768; +44 161 701 0240 Word count: 4,490 Number of tables: 1, Number of figures: 6 Running title: Metabolic dysfunction in diabetic neuropathy 1 Diabetes Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 15, 2015 Diabetes Page 2 of 255 Abstract High glucose levels in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) have been implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy (DN). However our understanding of the molecular mechanisms which cause the marked distal pathology is incomplete. Here we performed a comprehensive, system-wide analysis of the PNS of a rodent model of DN. -

Plakoglobin Is Required for Effective Intermediate Filament Anchorage to Desmosomes Devrim Acehan1, Christopher Petzold1, Iwona Gumper2, David D
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Plakoglobin Is Required for Effective Intermediate Filament Anchorage to Desmosomes Devrim Acehan1, Christopher Petzold1, Iwona Gumper2, David D. Sabatini2, Eliane J. Mu¨ller3, Pamela Cowin2,4 and David L. Stokes1,2,5 Desmosomes are adhesive junctions that provide mechanical coupling between cells. Plakoglobin (PG) is a major component of the intracellular plaque that serves to connect transmembrane elements to the cytoskeleton. We have used electron tomography and immunolabeling to investigate the consequences of PG knockout on the molecular architecture of the intracellular plaque in cultured keratinocytes. Although knockout keratinocytes form substantial numbers of desmosome-like junctions and have a relatively normal intercellular distribution of desmosomal cadherins, their cytoplasmic plaques are sparse and anchoring of intermediate filaments is defective. In the knockout, b-catenin appears to substitute for PG in the clustering of cadherins, but is unable to recruit normal levels of plakophilin-1 and desmoplakin to the plaque. By comparing tomograms of wild type and knockout desmosomes, we have assigned particular densities to desmoplakin and described their interaction with intermediate filaments. Desmoplakin molecules are more extended in wild type than knockout desmosomes, as if intermediate filament connections produced tension within the plaque. On the basis of our observations, we propose a particular assembly sequence, beginning with cadherin clustering within the plasma membrane, followed by recruitment of plakophilin and desmoplakin to the plaque, and ending with anchoring of intermediate filaments, which represents the key to adhesive strength. Journal of Investigative Dermatology (2008) 128, 2665–2675; doi:10.1038/jid.2008.141; published online 22 May 2008 INTRODUCTION dense plaque that is further from the membrane and that Desmosomes are large macromolecular complexes that mediates the binding of intermediate filaments. -

Research Article Characterization of the Equine Skeletal Muscle
McGivney et al. BMC Genomics 2010, 11:398 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2164/11/398 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access CharacterizationResearch article of the equine skeletal muscle transcriptome identifies novel functional responses to exercise training Beatrice A McGivney1, Paul A McGettigan1, John A Browne1, Alexander CO Evans1,3, Rita G Fonseca2, Brendan J Loftus3, Amanda Lohan3, David E MacHugh1,3, Barbara A Murphy1, Lisa M Katz2 and Emmeline W Hill*1 Abstract Background: Digital gene expression profiling was used to characterize the assembly of genes expressed in equine skeletal muscle and to identify the subset of genes that were differentially expressed following a ten-month period of exercise training. The study cohort comprised seven Thoroughbred racehorses from a single training yard. Skeletal muscle biopsies were collected at rest from the gluteus medius at two time points: T1 - untrained, (9 ± 0.5 months old) and T2 - trained (20 ± 0.7 months old). Results: The most abundant mRNA transcripts in the muscle transcriptome were those involved in muscle contraction, aerobic respiration and mitochondrial function. A previously unreported over-representation of genes related to RNA processing, the stress response and proteolysis was observed. Following training 92 tags were differentially expressed of which 74 were annotated. Sixteen genes showed increased expression, including the mitochondrial genes ACADVL, MRPS21 and SLC25A29 encoded by the nuclear genome. Among the 58 genes with decreased expression, MSTN, a negative regulator of muscle growth, had the greatest decrease. Functional analysis of all expressed genes using FatiScan revealed an asymmetric distribution of 482 Gene Ontology (GO) groups and 18 KEGG pathways. -

Desmoplakin Assembly Dynamics in Four Dimensions
JCB: ARTICLE Desmoplakin assembly dynamics in four dimensions: multiple phases differentially regulated by intermediate filaments and actin Lisa M. Godsel,1 Sherry N. Hsieh,1 Evangeline V. Amargo,1 Amanda E. Bass,1 Lauren T. Pascoe-McGillicuddy,1,4 Arthur C. Huen,1 Meghan E. Thorne,1 Claire A. Gaudry,1 Jung K. Park,1 Kyunghee Myung,3 Robert D. Goldman,3,4 Teng-Leong Chew,3 and Kathleen J. Green1,2 1Department of Pathology, 2Department of Dermatology, 3Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, and 4The R.H. Lurie Cancer Center, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL 60611 he intermediate filament (IF)–binding protein des- sensitive translocation of cytoplasmic particles to matur- moplakin (DP) is essential for desmosome function ing borders, with kinetics ranging from 0.002 to 0.04 T and tissue integrity, but its role in junction assembly m/s. DP mutants that abrogate or enhance association Downloaded from is poorly understood. Using time-lapse imaging, we show with IFs exhibit delayed incorporation into junctions, al- that cell–cell contact triggers three temporally overlap- tering particle trajectory or increasing particle pause ping phases of DP-GFP dynamics: (1) the de novo ap- times, respectively. Our data are consistent with the idea pearance of punctate fluorescence at new contact zones that DP assembles into nascent junctions from both diffus- after as little as 3 min; (2) the coalescence of DP and the ible and particulate pools in a temporally overlapping jcb.rupress.org armadillo protein plakophilin 2 into discrete cytoplasmic series of events triggered by cell–cell contact and regu- particles after as little as 15 min; and (3) the cytochalasin- lated by actin and DP–IF interactions. -

List of Down-Regulated Transcripts
Supplementary Table 1: List of down-regulated transcripts (Fold Change>1.7 and p<0.05). List of the transcipts downregulated by Tpr-Met in P27 cachectic gastrocnemius muscles. Shown are the transcripts gene annotation: Mus Musculus Entrez Gene ID, official symbol from NCBI, average (AVG) Log2 Ratio derived from Illumina microarrays (3 replicates/condition), fold change and p-value computations, Log2 ratio over AVG Log2 controls and full definition of the genes. All genes modulated with a fold change > 1.7 and p-value<0.05 are included. AVG Entrez Gene Fold Symbol Log2 T-test Ctrl Ctrl Ctrl TM TM TM Definition ID Change Ratio - - - - 26908 Eif2s3y 3.598 12.1 0.000 0.146 0.248 0.102 3.712 3.571 -3.510 eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 3, structural gene Y-linked (Eif2s3y), mRNA. - - - 13628 Eef1a2 1.333 2.5 0.011 -0.444 0.261 0.183 1.503 0.950 -1.546 eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 2 (Eef1a2), mRNA. - - - 13628 Eef1a2 1.298 2.5 0.031 -0.383 0.275 0.108 1.632 0.605 -1.656 eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 alpha 2 (Eef1a2), mRNA. - - - 56222 Cited4 1.268 2.4 0.029 -0.466 0.035 0.431 1.109 0.889 -1.805 Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator, with Glu/Asp-rich carboxy-terminal domain, 4 (Cited4), mRNA. - - - 18810 Plec1 1.246 2.4 0.022 -0.440 0.327 0.113 1.303 0.779 -1.657 plectin 1 (Plec1), transcript variant 10, mRNA. - - - 20741 Spnb1 1.238 2.4 0.016 -0.384 0.314 0.071 1.129 0.902 -1.684 spectrin beta 1 (Spnb1), mRNA. -

140503 IPF Signatures Supplement Withfigs Thorax
Supplementary material for Heterogeneous gene expression signatures correspond to distinct lung pathologies and biomarkers of disease severity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Daryle J. DePianto1*, Sanjay Chandriani1⌘*, Alexander R. Abbas1, Guiquan Jia1, Elsa N. N’Diaye1, Patrick Caplazi1, Steven E. Kauder1, Sabyasachi Biswas1, Satyajit K. Karnik1#, Connie Ha1, Zora Modrusan1, Michael A. Matthay2, Jasleen Kukreja3, Harold R. Collard2, Jackson G. Egen1, Paul J. Wolters2§, and Joseph R. Arron1§ 1Genentech Research and Early Development, South San Francisco, CA 2Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, CA 3Department of Surgery, University of California, San Francisco, CA ⌘Current address: Novartis Institutes for Biomedical Research, Emeryville, CA. #Current address: Gilead Sciences, Foster City, CA. *DJD and SC contributed equally to this manuscript §PJW and JRA co-directed this project Address correspondence to Paul J. Wolters, MD University of California, San Francisco Department of Medicine Box 0111 San Francisco, CA 94143-0111 [email protected] or Joseph R. Arron, MD, PhD Genentech, Inc. MS 231C 1 DNA Way South San Francisco, CA 94080 [email protected] 1 METHODS Human lung tissue samples Tissues were obtained at UCSF from clinical samples from IPF patients at the time of biopsy or lung transplantation. All patients were seen at UCSF and the diagnosis of IPF was established through multidisciplinary review of clinical, radiological, and pathological data according to criteria established by the consensus classification of the American Thoracic Society (ATS) and European Respiratory Society (ERS), Japanese Respiratory Society (JRS), and the Latin American Thoracic Association (ALAT) (ref. 5 in main text). Non-diseased normal lung tissues were procured from lungs not used by the Northern California Transplant Donor Network. -

Alpha;-Actinin-4 Promotes Metastasis in Gastric Cancer
Laboratory Investigation (2017) 97, 1084–1094 © 2017 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0023-6837/17 α-Actinin-4 promotes metastasis in gastric cancer Xin Liu and Kent-Man Chu Metastasis increases the mortality rate of gastric cancer, which is the third leading cause of cancer-associated deaths worldwide. This study aims to identify the genes promoting metastasis of gastric cancer (GC). A human cell motility PCR array was used to analyze a pair of tumor and non-tumor tissue samples from a patient with stage IV GC (T3N3M1). Expression of the dysregulated genes was then evaluated in GC tissue samples (n = 10) and cell lines (n =6) via qPCR. Expression of α-actinin-4 (ACTN4) was validated in a larger sample size (n = 47) by qPCR, western blot and immunohistochemistry. Knockdown of ACTN4 with specific siRNAs was performed in GC cells, and adhesion assays, transwell invasion assays and migration assays were used to evaluate the function of these cells. Expression of potential targets of ACTN4 were then evaluated by qPCR. Thirty upregulated genes (greater than twofold) were revealed by the PCR array. We focused on ACTN4 because it was upregulated in 6 out of 10 pairs of tissue samples and 5 out of 6 GC cell lines. Further study indicated that ACTN4 was upregulated in 22/32 pairs of tissue samples at stage III & IV (P = 0.0069). Knockdown of ACTN4 in GC cells showed no significant effect on cell proliferation, but significantly increased cell-matrix adhesion, as well as reduced migration and invasion of AGS, MKN7 and NCI-N87 cells. -

Anti-ACTN2 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone FQ3630Z (DCABH-9438) This Product Is for Research Use Only and Is Not Intended for Diagnostic Use
Anti-ACTN2 monoclonal antibody, clone FQ3630Z (DCABH-9438) This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. PRODUCT INFORMATION Product Overview Rabbit monoclonal to Sarcomeric Alpha Actinin Antigen Description F-actin cross-linking protein which is thought to anchor actin to a variety of intracellular structures. This is a bundling protein. Immunogen A synthetic peptide (the amino acid sequence is considered to be commercially sensitive) corresponding to residues on the N-terminus of human Sarcomeric Alpha Actinin Isotype IgG Source/Host Rabbit Species Reactivity Mouse, Rat, Human Clone FQ3630Z Purity Tissue culture supernatant Conjugate Unconjugated Applications WB, IP, IHC-P Positive Control Human skeletal muscle, rat heart and human heart lysates and human muscle tissue. Format Liquid Size 100 μl Buffer pH: 7.40; Preservative: 0.01% Sodium azide; Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.05% BSA Preservative 0.01% Sodium Azide Storage Store at -20°C. Stable for 12 months at -20°C GENE INFORMATION Gene Name ACTN2 actinin, alpha 2 [ Homo sapiens ] Official Symbol ACTN2 45-1 Ramsey Road, Shirley, NY 11967, USA Email: [email protected] Tel: 1-631-624-4882 Fax: 1-631-938-8221 1 © Creative Diagnostics All Rights Reserved Synonyms ACTN2; actinin, alpha 2; alpha-actinin-2; F-actin cross-linking protein; alpha-actinin skeletal muscle; CMD1AA; Entrez Gene ID 88 Protein Refseq NP_001094 UniProt ID P35609 Chromosome Location 1q42-q43 Pathway Activation of NMDA receptor upon glutamate binding and postsynaptic events, -

Proteomic Expression Profile in Human Temporomandibular Joint
diagnostics Article Proteomic Expression Profile in Human Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction Andrea Duarte Doetzer 1,*, Roberto Hirochi Herai 1 , Marília Afonso Rabelo Buzalaf 2 and Paula Cristina Trevilatto 1 1 Graduate Program in Health Sciences, School of Medicine, Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Paraná (PUCPR), Curitiba 80215-901, Brazil; [email protected] (R.H.H.); [email protected] (P.C.T.) 2 Department of Biological Sciences, Bauru School of Dentistry, University of São Paulo, Bauru 17012-901, Brazil; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +55-41-991-864-747 Abstract: Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD) is a multifactorial condition that impairs human’s health and quality of life. Its etiology is still a challenge due to its complex development and the great number of different conditions it comprises. One of the most common forms of TMD is anterior disc displacement without reduction (DDWoR) and other TMDs with distinct origins are condylar hyperplasia (CH) and mandibular dislocation (MD). Thus, the aim of this study is to identify the protein expression profile of synovial fluid and the temporomandibular joint disc of patients diagnosed with DDWoR, CH and MD. Synovial fluid and a fraction of the temporomandibular joint disc were collected from nine patients diagnosed with DDWoR (n = 3), CH (n = 4) and MD (n = 2). Samples were subjected to label-free nLC-MS/MS for proteomic data extraction, and then bioinformatics analysis were conducted for protein identification and functional annotation. The three Citation: Doetzer, A.D.; Herai, R.H.; TMD conditions showed different protein expression profiles, and novel proteins were identified Buzalaf, M.A.R.; Trevilatto, P.C. -
![Alpha Actinin (ACTN1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: OTI7A4] Product Data](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/2048/alpha-actinin-actn1-mouse-monoclonal-antibody-clone-id-oti7a4-product-data-1032048.webp)
Alpha Actinin (ACTN1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: OTI7A4] Product Data
OriGene Technologies, Inc. 9620 Medical Center Drive, Ste 200 Rockville, MD 20850, US Phone: +1-888-267-4436 [email protected] EU: [email protected] CN: [email protected] Product datasheet for TA500072 alpha Actinin (ACTN1) Mouse Monoclonal Antibody [Clone ID: OTI7A4] Product data: Product Type: Primary Antibodies Clone Name: OTI7A4 Applications: IF, IHC, WB Recommend Dilution: WB 1:2000, IHC 1:50, IF 1:100 Reactivity: Human Host: Mouse Isotype: IgG2a Clonality: Monoclonal Immunogen: Human recombinant protein fragment corresponding to amino acids 650-893 of human alpha-actinin (NP_001093) produced in E.coli. Formulation: PBS (pH 7.3) containing 1% BSA, 50% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide. Concentration: 1 mg/ml Purification: Purified from mouse ascites fluids or tissue culture supernatant by affinity chromatography (protein A/G) Predicted Protein Size: 102.9 kDa Gene Name: actinin alpha 1 Database Link: NP_001093 Entrez Gene 87 Human Background: Alpha actinins belong to the spectrin gene superfamily which represents a diverse group of cytoskeletal proteins, including the alpha and beta spectrins and dystrophins. Alpha actinin is an actin-binding protein with multiple roles in different cell types. In nonmuscle cells, the cytoskeletal isoform is found along microfilament bundles and adherens-type junctions, where it is involved in binding actin to the membrane. In contrast, skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle isoforms are localized to the Z-disc and analogous dense bodies, where they help anchor the myofibrillar actin filaments. Synonyms: BDPLT15 Protein Families: Druggable Genome, ES Cell Differentiation/IPS This product is to be used for laboratory only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. -

Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Expression of Mir-133A
Supplemental Figure legends Figure S1. Expression of miR-133a and miR-1 in adult mice. (A) Expression of miR-133a in heart samples of miR-133a-1-KO and miR-133a-2-KO adult mice as detected by real-time PCR. Expression level of miR-133a in mutant hearts were normalized to GAPDH and compared to WT hearts. N=3 for each genotype group. (B) Northern blot analysis of heart and skeletal muscle RNA from adult mice. Ten micrograms of RNA from skeletal muscle and heart tissues were used in the Northern blots. 32P-labeled Start-Fire probes for miR-133a and miR-1 were used. Genotypes of mice are labeled on top. U6 probe was used as a loading control. GP, gastrocnemius- plantaris. (C) Expression of Mib1 mRNA and protein in dKO mice at P1. mRNA level of Mib1 as detected by real-time PCR in dKO hearts were normalized to GAPDH and compared to WT hearts. Error bars indicate SEM. Western blot analysis was performed on hearts from P1 wild type and dKO mutant mice. α -tubulin was detected as a loading control. Figure S2. Abnormal cardiomyocyte proliferation in miR-133a dKO hearts. Representative images of proliferating cardiomyocytes in WT and dKO hearts at P1. High magnification of immunohistochemistry on heart sections at P1 using phospho- histone H3 (PH3, red) and -actinin (green) was shown. Bar = 20 m. Figure S3. Expression of miR-133a in wild-type and beta-MHC-miR-133a transgenic hearts at E13.5 as detected by real-time PCR. Figure S4. Expression of miR-133a target genes in hearts of WT and dKO mutant mice at P1. -

Genetic Cardiomyopathies: the Lesson Learned from Hipscs
Journal of Clinical Medicine Review Genetic Cardiomyopathies: The Lesson Learned from hiPSCs Ilaria My 1,2 and Elisa Di Pasquale 2,3,* 1 Department of Biomedical Sciences, Humanitas University, Pieve Emanuele, 20090 Milan, Italy; [email protected] 2 Humanitas Clinical and Research Center—IRCCS, Rozzano, 20089 Milan, Italy 3 Institute of Genetic and Biomedical Research (IRGB)—UOS of Milan, National Research Council (CNR), 20138 Milan, Italy * Correspondence: [email protected] Abstract: Genetic cardiomyopathies represent a wide spectrum of inherited diseases and constitute an important cause of morbidity and mortality among young people, which can manifest with heart failure, arrhythmias, and/or sudden cardiac death. Multiple underlying genetic variants and molecular pathways have been discovered in recent years; however, assessing the pathogenicity of new variants often needs in-depth characterization in order to ascertain a causal role in the disease. The application of human induced pluripotent stem cells has greatly helped to advance our knowledge in this field and enabled to obtain numerous in vitro patient-specific cellular models useful to study the underlying molecular mechanisms and test new therapeutic strategies. A milestone in the research of genetically determined heart disease was the introduction of genomic technologies that provided unparalleled opportunities to explore the genetic architecture of cardiomyopathies, thanks to the generation of isogenic pairs. The aim of this review is to provide an overview of the main research that helped elucidate the pathophysiology of the most common genetic cardiomyopathies: hypertrophic, dilated, arrhythmogenic, and left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathies. A special focus is provided on the application of gene-editing techniques in understanding key disease characteristics and on the therapeutic approaches that have been tested.