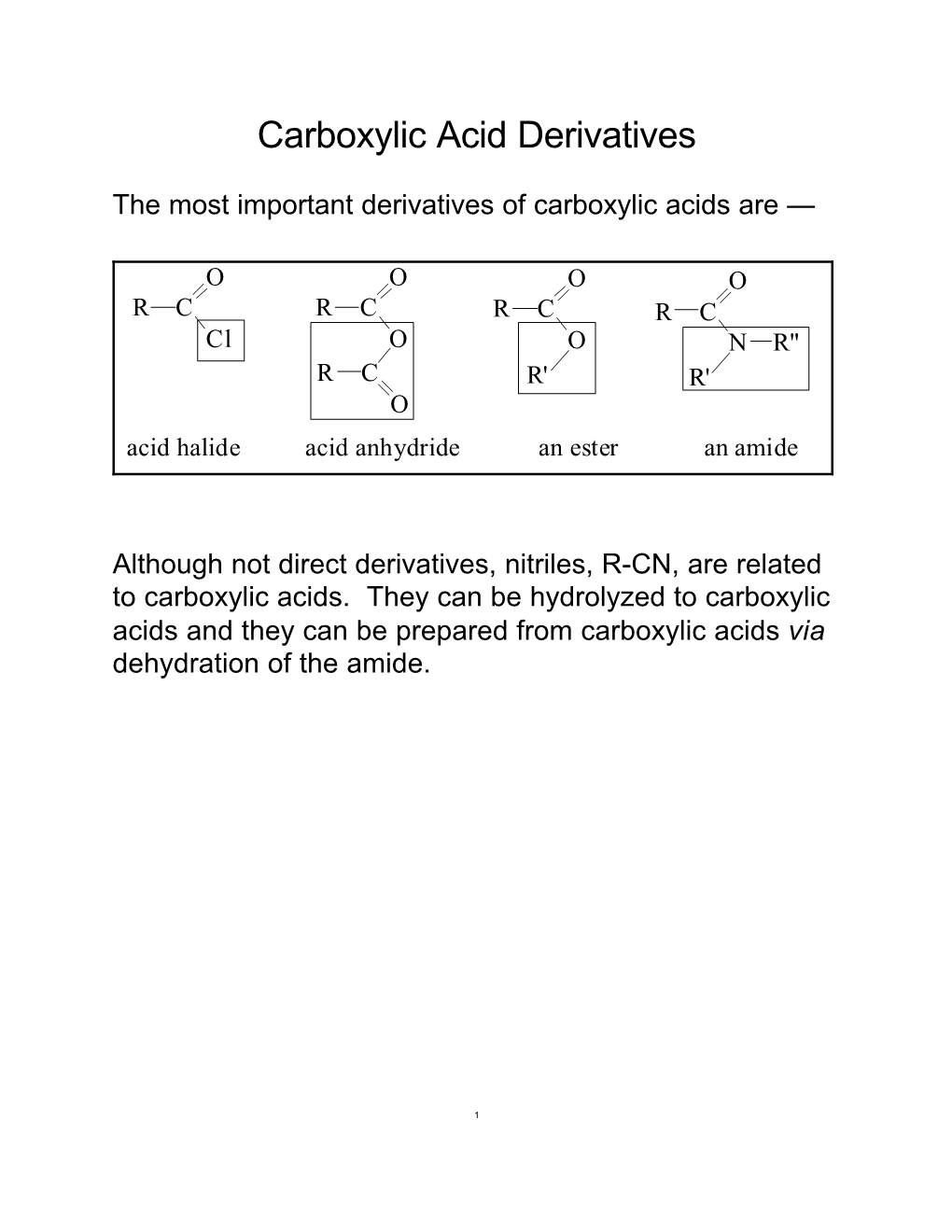
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Chapter 21 the Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems © 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 21 The Chemistry of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Solutions to In-Text Problems 21.1 (b) (d) (e) (h) 21.2 (a) butanenitrile (common: butyronitrile) (c) isopentyl 3-methylbutanoate (common: isoamyl isovalerate) The isoamyl group is the same as an isopentyl or 3-methylbutyl group: (d) N,N-dimethylbenzamide 21.3 The E and Z conformations of N-acetylproline: 21.5 As shown by the data above the problem, a carboxylic acid has a higher boiling point than an ester because it can both donate and accept hydrogen bonds within its liquid state; hydrogen bonding does not occur in the ester. Consequently, pentanoic acid (valeric acid) has a higher boiling point than methyl butanoate. Here are the actual data: INSTRUCTOR SUPPLEMENTAL SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS • CHAPTER 21 2 21.7 (a) The carbonyl absorption of the ester occurs at higher frequency, and only the carboxylic acid has the characteristic strong, broad O—H stretching absorption in 2400–3600 cm–1 region. (d) In N-methylpropanamide, the N-methyl group is a doublet at about d 3. N-Ethylacetamide has no doublet resonances. In N-methylpropanamide, the a-protons are a quartet near d 2.5. In N-ethylacetamide, the a- protons are a singlet at d 2. The NMR spectrum of N-methylpropanamide has no singlets. 21.9 (a) The first ester is more basic because its conjugate acid is stabilized not only by resonance interaction with the ester oxygen, but also by resonance interaction with the double bond; that is, the conjugate acid of the first ester has one more important resonance structure than the conjugate acid of the second. -

11 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND NITRILES Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES 2 CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES R C N nitrile R = CH3 acetonitrile 3 STRUCTURE AND BONDING 4 NOMENCLATURE—THE IUPAC SYSTEM heptanoic acid benzoic acid cyclopentane carboxylic acid 4,5-dimethyl 3-pentenoic 3-bromobenzoic p-toluic 1-methyl- hexanoic acid acid acid acid cyclopropanecarboxylic acid 5 NOMENCLATURE-COMMON NAMES προτοσ πιον 6 NOMENCLATURE-POLYIACIDS Oxalis acetosella Malon Succinum HOOC COOH COOH propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid 7 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES • Carboxylic acids exhibit dipole-dipole interactions because they have polar C—O and O—H bonds. • They also exhibit intermolecular hydrogen bonding. • In the gas phase and in apolar solvents, carboxylic acids often exist as dimers held together by two intermolecular hydrogen bonds. 8 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES 9 ACIDITY OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS The acetate anion has two C—O bonds of equal length (1.27 Å) and intermediate between the length of a C—O single bond (1.36 Å) and C=O (1.21 Å). 10 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS—STRONG ORGANIC BRØNSTED-LOWRY ACIDS 11 THE INDUCTIVE EFFECT IN ALIPHATIC CARBOXYLIC ACIDS 12 THE INDUCTIVE EFFECT IN ALIPHATIC CARBOXYLIC ACIDS 13 SUBSTITUTED BENZOIC ACIDS 14 SUBSTITUTED BENZOIC ACIDS 15 PREPARATION OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS [1] Oxidation of 1° alcohols [2] Oxidation of alkyl benzenes 16 PREPARATION OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS [3] From alkyl halides CN CN- i. NaOH + ii.H3O Br COOH i. CO2 Mg + ii. H3O MgBr R MgBr R OMgBr H O+ R OH 3 + Mg++ + Br- O C O O O 17 PREPARATION OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS [5] From alkyl halides. -

Hydrolysis of Amides: a Kinetic Study of Substituent Effects on the Acidic and Basic Hydrolysis of Aliphatic Amides
University of Wollongong Research Online University of Wollongong Thesis Collection 1954-2016 University of Wollongong Thesis Collections 1969 Hydrolysis of amides: a kinetic study of substituent effects on the acidic and basic hydrolysis of aliphatic amides Grahame Leslie Jackson Wollongong University College Follow this and additional works at: https://ro.uow.edu.au/theses University of Wollongong Copyright Warning You may print or download ONE copy of this document for the purpose of your own research or study. The University does not authorise you to copy, communicate or otherwise make available electronically to any other person any copyright material contained on this site. You are reminded of the following: This work is copyright. Apart from any use permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, no part of this work may be reproduced by any process, nor may any other exclusive right be exercised, without the permission of the author. Copyright owners are entitled to take legal action against persons who infringe their copyright. A reproduction of material that is protected by copyright may be a copyright infringement. A court may impose penalties and award damages in relation to offences and infringements relating to copyright material. Higher penalties may apply, and higher damages may be awarded, for offences and infringements involving the conversion of material into digital or electronic form. Unless otherwise indicated, the views expressed in this thesis are those of the author and do not necessarily represent the views of the University of Wollongong. Recommended Citation Jackson, Grahame Leslie, Hydrolysis of amides: a kinetic study of substituent effects on the acidic and basic hydrolysis of aliphatic amides, Doctor of Philosophy thesis, Department of Chemistry, University of Wollongong, 1969. -

Estimation of Hydrolysis Rate Constants of Carboxylic Acid Ester and Phosphate Ester Compounds in Aqueous Systems from Molecular Structure by SPARC
Estimation of Hydrolysis Rate Constants of Carboxylic Acid Ester and Phosphate Ester Compounds in Aqueous Systems from Molecular Structure by SPARC R E S E A R C H A N D D E V E L O P M E N T EPA/600/R-06/105 September 2006 Estimation of Hydrolysis Rate Constants of Carboxylic Acid Ester and Phosphate Ester Compounds in Aqueous Systems from Molecular Structure by SPARC By S. H. Hilal Ecosystems Research Division National Exposure Research Laboratory Athens, Georgia U.S. Environmental Protection Agency Office of Research and Development Washington, DC 20460 NOTICE The information in this document has been funded by the United States Environmental Protection Agency. It has been subjected to the Agency's peer and administrative review, and has been approved for publication. Mention of trade names of commercial products does not constitute endorsement or recommendation for use. ii ABSTRACT SPARC (SPARC Performs Automated Reasoning in Chemistry) chemical reactivity models were extended to calculate hydrolysis rate constants for carboxylic acid ester and phosphate ester compounds in aqueous non- aqueous and systems strictly from molecular structure. The energy differences between the initial state and the transition state for a molecule of interest are factored into internal and external mechanistic perturbation components. The internal perturbations quantify the interactions of the appended perturber (P) with the reaction center (C). These internal perturbations are factored into SPARC’s mechanistic components of electrostatic and resonance effects. External perturbations quantify the solute-solvent interactions (solvation energy) and are factored into H-bonding, field stabilization and steric effects. These models have been tested using 1471 reliable measured base, acid and general base-catalyzed carboxylic acid ester hydrolysis rate constants in water and in mixed solvent systems at different temperatures. -

Drain Cleaner
Create account Log in Article Talk Read Edit VieMw ohriestorySearch Wiki Loves Earth in focus during May 2015 Discover nature, make it visible, take photos, help Wikipedia! Main page Contents Featured content Drain cleaner Current events From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Random article Donate to Wikipedia This article needs additional citations for Wikipedia store verification. Please help improve this article by Interaction adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced Help material may be challenged and removed. (July About Wikipedia Community portal 2014) Recent changes A drain cleaner is a chemical based consumer product that unblocks sewer Contact page pipes or helps to prevent the occurrence of clogged drains. The term may also Tools refer to the individual who uses performs the activity with chemical drain What links here cleaners or devices known as plumber's snake. Drain cleaners can be classified Related changes Upload file in two categories: chemical, or device. Special pages If a single sink, toilet, or tub or shower drain is clogged the first choice is Permanent link normally a drain cleaner that can remove soft obstructions such as hair and Page information grease clogs that can accumulate close to interior drain openings. Chemical Wikidata item drain cleaners, plungers, handheld drain augers, air burst drain cleaners, Cite this page and home remedy drain cleaners are intended for this purpose. Print/export If more than one plumbing fixture is clogged the first choice is normally a Create a book drain cleaner that can remove soft or hard obstructions along the entire Download as PDF length of the drain, from the drain opening through the main sewer drain to Printable version the lateral piping outside the building. -

Hydrolysis of Amides Hydrolysis of Amides
Chem 234 Organic Chemistry II Professor Duncan J. Wardrop HO H H H N Cl NH S HN N N H OH O Cl Cl CO2H H N Cl H HO O O O N O O H H O CH3 O O NH H O MeO N O O O HO OMe O O OMe HO OMe N3 O CH H H2NSO2 3 N Br Br N H O N N CF3 Spring 2004 University of Illinois at Chicago 20.6 Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Anhydrides Reactions of Anhydrides O O RCOCR' O RCOR' O RCNR'2 O RCO– Reactions of Anhydrides Carboxylic acid anhydrides react with alcohols to give esters: O O O O R'OH R' R O R R O R OH normally, symmetrical anhydrides are used (both R groups the same) reaction can be carried out in presence of pyridine (a base) or it can be catalyzed by acids Reactions of Anhydrides Carboxylic acid anhydrides react with alcohols to give esters: O O O O RCOCR + R'OH RCOR' + RCOH H O R C OR' via: OCR O Reactions of Anhydrides- Examples O O CH3 OH CH3 O H2SO4 O CH3 CH CH CH 3 3 3 CH3 O (60%) Reactions of Anhydrides with Amines Acid anhydrides react with ammonia and amines to give amides: O O O O – RCOCR + 2R'2NH RCNR'2 + RCO H O + R'2NH2 R C NR' via: 2 OCR O Reactions of Anhydrides with Amines- Example O O NH2 CH3 NH CH3 O CH3 O CH3 CH3 CH3 CH3 (98%) Reactions of Anhydrides with Water Acid anhydrides react with water to give carboxylic acids (carboxylate ion in base): O O O RCOCR + H2O 2RCOH O O O – – RCOCR + 2HO 2RCO + H2O Reactions of Anhydrides with Water Acid anhydrides react with water to give carboxylic acids (carboxylate ion in base): O O O RCOCR + H2O 2RCOH H O R C OH OCR O Reactions of Anhydrides with Water - Example O O COH O + H2O COH O O 20.7 Sources -

Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Are Described As Compounds That Can Be Converted to Carboxylic Acids Via Simple Acidic Or Basic Hydrolysis
Carboxylic acid Derivatives Carboxylic acid derivatives are described as compounds that can be converted to carboxylic acids via simple acidic or basic hydrolysis. The most important acid derivatives are esters, amides and nitriles, although acid halides and anhydrides are also derivatives (really activated forms of a carboxylic acid). Esters of Carboxylic Acids These are derivatives of carboxylic acids where the hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group. We have already seen that esters are produced via the reaction of an alcohol with a carboxylic acid. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape).docx Page 1 Nomenclature The names of esters are derived from the names of the compounds that are used to create them. The first word of the name comes from the alkyl group of the alcohol, and the second part comes from the carboxylate group of the acid used. E.g. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape).docx Page 2 A cyclic ester is called a lactone. IUPAC names of lactones are derived by adding the term lactone at the end of the name of the parent hydroxycarboxylic acid it came from. E.g. Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape).docx Page 3 Amides of Carboxylic Acids An amide is a composite of a carboxylic acid and an amine (or ammonia). Heating the salt formed when an amine and carboxylic acid react together, drives off the water produced, and an amide is formed. Amides are much less basic than their parent amines since the lone pair of electrons on Nitrogen are delocalized onto the carbonyl oxygen. In fact in strong acid, it is the oxygen that gets protonated first! Ch21 Carboxylic acid Derivatives(landscape).docx Page 4 This conjugation means the N should be sp2 hybridized, and indeed the amide nitrogen has a planar arrangement of bonds with bond angles close to 120°. -

Acid Hydrolysis
Dr. Sanyucta Kumari Assistant Professor (Chemistry) MLT College, Saharsa Acid hydrolysis In organic chemistry, acid hydrolysis is a hydrolysis process in which a protic acid is used to catalyze the cleavage of a chemical bond via a nucleophilic substitution reaction, with the addition of the elements of water (H2O). For example, in the conversion of cellulose or starch to glucose. For the case of esters and amides, it can be defined as an acid catalyzed nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. The term is also applied to certain nucleophilic addition reactions, such as in the acid catalyzed hydrolysis of nitriles to amides. Acid hydrolysis does not usually refer to the acid catalyzed addition of the elements of water to double or triple bonds by electrophilic addition as may originate from a hydration reaction. Acid hydrolysis is used to prepare other chemicals, such as: • Monosaccharide • Hydrochloric acid • Sulfuric acid • Trifluoroacetic acid • Formic acid • Nitric acid Acid hydrolysis can be utilized in the pretreatment of cellulosic material, so as to cut the interchain linkages in hemicelluose and cellulose. Alkaline hydrolysis Alkaline hydrolysis, in organic chemistry, usually refers to types of nucleophilic substitution reactions in which the attacking nucleophile is a hydroxide ion. Example In the alkaline hydrolysis of esters and amides the hydroxide ion nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon in a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. This mechanism is supported by isotope labeling experiments. For example, when ethyl propionate with an oxygen-18 labeled ethoxy group is treated with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), the oxygen-18 is completely absent from the sodium propionate product and is found exclusively in the ethanol formed. -

Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline and Acidic Conditions
molecules Article Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline and Acidic Conditions Zhangxia Wang and Haibo Ma * Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Vehicle Emissions Control, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210023, China; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +86-25-89685680 Abstract: Searching for functional polyesters with stability and degradability is important due to their potential applications in biomedical supplies, biomass fuel, and environmental protection. Recently, a cyclobutane-fused lactone (CBL) polymer was experimentally found to have superior stability and controllable degradability through hydrolysis reactions after activation by mechanical force. In order to provide a theoretical basis for developing new functional degradable polyesters, in this work, we performed a detailed quantum chemical study of the alkaline and acidic hydrolysis of CBL using dispersion-corrected density functional theory (DFT-D3) and mixed implicit/explicit solvent models. Various possible hydrolysis mechanisms were found: BAC2 and BAL2 in the alkaline condition and AAC2, AAL2, and AAL1 in the acidic condition. Our calculations indicated that CBL favors the BAC2 and AAC2 mechanisms in alkaline and acidic conditions, respectively. In addition, we found that incorporating explicit water solvent molecules is highly necessary because of their strong hydrogen-bonding with reactant/intermediate/product molecules. Keywords: hydrolysis mechanisms; cyclobutane-fused lactone; DFT; solvation model Citation: Wang, Z.; Ma, H. 1. Introduction Mechanisms of a Cyclobutane-Fused Recently, a cyclobutane-fused lactone (CBL) polymer was proposed and demonstrated Lactone Hydrolysis in Alkaline and to have superior stability and controllable degradability [1]. Cyclobutane shows a perfect Acidic Conditions. Molecules 2021, 26, stability to keep the polymer’s backbone when the ester groups are hydrolyzed under 3519. -

Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
CHAPTER 20 CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ACYL SUBSTITUTION his chapter differs from preceding ones in that it deals with several related classes Tof compounds rather than just one. Included are O X 1. Acyl chlorides, RCCl O O X X 2. Carboxylic acid anhydrides, RCOCR O X 3. Esters of carboxylic acids, RCORЈ O O O X X X Ј Ј 4. Carboxamides, RCNH2 ,,RCNHR and RCNR2 These classes of compounds are classified as carboxylic acid derivatives. All may be converted to carboxylic acids by hydrolysis. O O X X RCX ϩϩH2O RCOH HX Carboxylic acid Water Carboxylic Conjugate acid derivative acid of leaving group 774 Back Forward Main Menu TOC Study Guide TOC Student OLC MHHE Website 20.1 Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 775 The hydrolysis of a carboxylic acid derivative is but one example of a nucleophilic acyl substitution. Nucleophilic acyl substitutions connect the various classes of car- boxylic acid derivatives, with a reaction of one class often serving as preparation of another. These reactions provide the basis for a large number of functional group trans- formations both in synthetic organic chemistry and in biological chemistry. Also included in this chapter is a discussion of the chemistry of nitriles, compounds of the type RCPN. Nitriles may be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids or to amides and, so, are indirectly related to the other functional groups presented here. 20.1 NOMENCLATURE OF CARBOXYLIC ACID DERIVATIVES With the exception of nitriles (RCPN), all carboxylic acid derivatives consist of an acyl O X group (RC±) attached to an electronegative atom. Acyl groups are named by replacing the -ic acid ending of the corresponding carboxylic acid by -yl. -

Carbon Bond Formation and Synthesis
OCR Chemistry A H432 Synthesis Carbon – Carbon bond formation and Synthesis Synthesis involves designing a series of reactions that will transform a raw material that is readily available e.g. from crude oil, or in nature, into a target molecule that is expected to have a particular use – most typically medical. Reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds are therefore of key importance as they allow the carbon skeleton of the molecule to be modified progressively. Lengthening a carbon chain, or adding a branch This can be done by a nucleophilic substitution in which a halogen –X is replaced with a nitrile group –CN. Raw material: Haloalkane with –X where the new carbon is to be added Reagent: Sodium or potassium cyanide, NaCN or KCN Conditions: Ethanol solvent e.g. CH3CH2CH2Cl + KCN ! CH3CH2CH2CN + KCl 1-chloropropane butanenitrile The mechanism is exactly as we have seen before in nucleophilic substitutions: H H H H H H δ+ δ- H C C C Cl H C C C C N Cl H H H H H H .. C N Extending the chain using a carbonyl group We have already seen that aldehydes and ketones can also react with HCN by nucleophilic addition to form hydroxynitriles, extending the chain by adding a –CN group and simultaneously adding an –OH group. Raw material: Aldehyde/Ketone Reagents: Sodium cyanide + sulphuric acid (generates HCN in-situ) e.g. CH3CH2CHO + HCN ! CH3CH2CH(OH)CN propanal 2-hydroxybutanenitrile The mechanism is: δ- δ+ O δ+ H H H H H H H H H H H δ+ δ- .. H C C C O H C C C O H C C C OH OH H H H H C N H H C N . -

Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution
Reactions of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution . Interconversion of acid derivatives occur by nucleophilic acyl substitution. Nucleophile adds to the carbonyl forming a tetrahedral intermediate. Elimination of the leaving group regenerates the carbonyl. Nucleophilic acyl substitutions are also called acyl transfer reactions because they transfer the acyl group to the attacking nucleophile. Mechanism of Acyl Substitution This is an addition–elimination mechanism. Reactivity of Acid Derivatives Interconversion of Derivatives . More reactive derivatives can be converted to less reactive derivatives. Acid Chloride to Anhydride . The carboxylic acid attacks the acyl chloride, forming the tetrahedral intermediate. Chloride ion leaves, restoring the carbonyl. Deprotonation produces the anhydride. Acid Chloride to Ester . The alcohol attacks the acyl chloride, forming the tetrahedral intermediate. Chloride ion leaves, restoring the carbonyl. Deprotonation produces the ester. Acid Chloride to Amide . Ammonia yields a 1 amide. A 1 amine yields a 2 amide. A 2 amine yields a 3 amide. Anhydride to Ester . Alcohol attacks one of the carbonyl groups of the anhydride, forming the tetrahedral intermediate. The other acid unit is eliminated as the leaving group. Anhydride to Amide . Ammonia yields a 1 amide; a 1 amine yields a 2 amide; and a 2 amine yields a 3 amide. Ester to Amide: Ammonolysis . Nucleophile must be NH3 or 1 amine. Prolonged heating is required. Leaving Groups in Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution - . A strong base, such as methoxide ( OCH3), is not usually a leaving group, except in an exothermic step. Energy Diagram . In the nucleophilic acyl substitution, the elimination of the alkoxide is highly exothermic, converting the tetrahedral intermediate into a stable molecule.