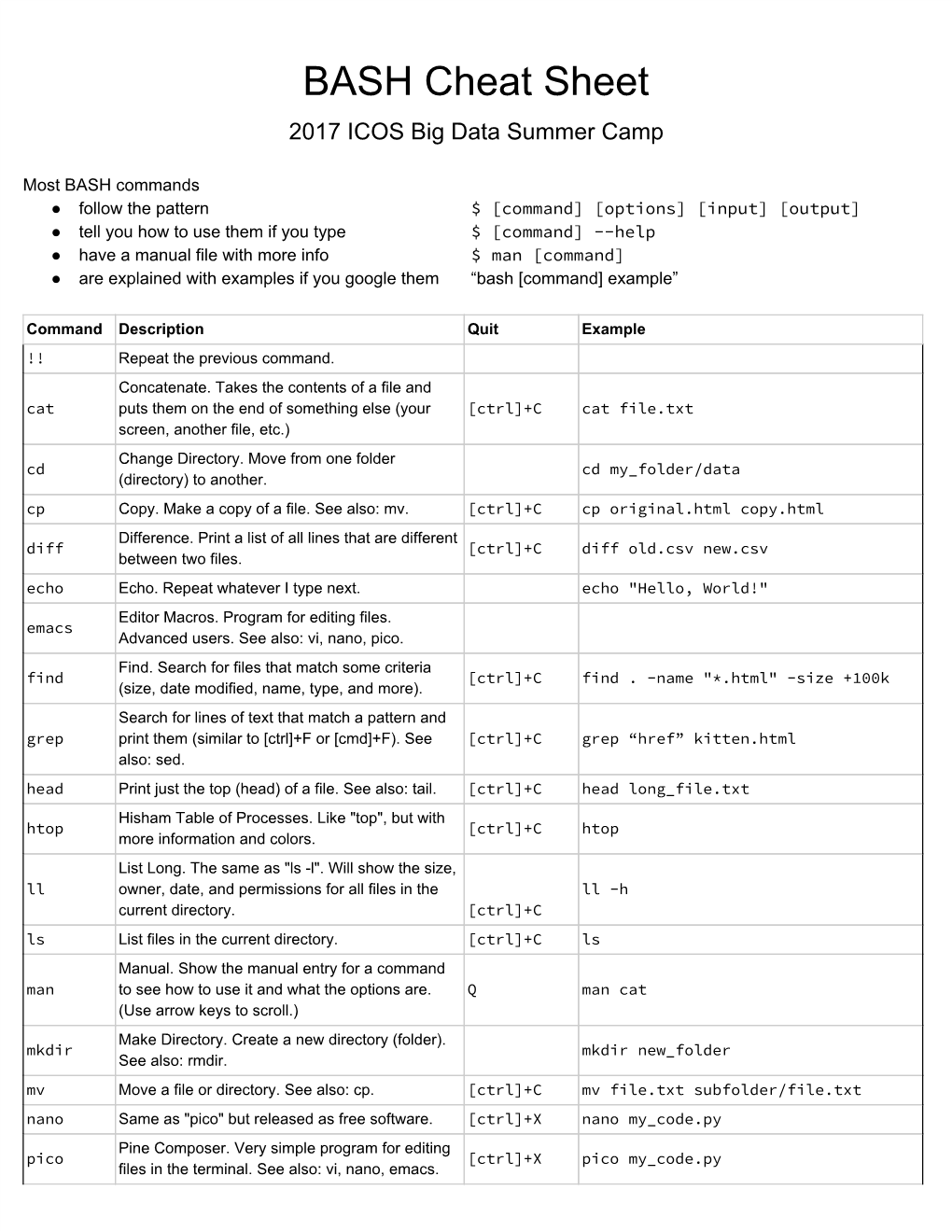
BASH Cheat Sheet 2017 ICOS Big Data Summer Camp
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Top 15 ERP Software Vendors – 2010
Top 15 ERP Software Vendors – 2010 Profiles of the Leading ERP Vendors Find the best ERP system for your company. For more information visit Business-Software.com/ERP. About ERP Software Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is not a new concept. It was introduced more than 40 years ago, when the first ERP system was created to improve inventory control and management at manufacturing firms. Throughout the 70’s and 80’s, as the number of companies deploying ERP increased, its scope expanded quite a bit to include various production and materials management functions, although it was designed primarily for use in manufacturing plants. In the 1990’s, vendors came to realize that other types of business could benefit from ERP, and that in order for a business to achieve true organizational efficiency, it needed to link all its internal business processes in a cohesive and coordinated way. As a result, ERP was transformed into a broad-reaching environment that encompassed all activities across the back office of a company. What is ERP? An ERP system combines methodologies with software and hardware components to integrate numerous critical back-office functions across a company. Made up of a series of “modules”, or applications that are seamlessly linked together through a common database, an ERP system enables various departments or operating units such as Accounting and Finance, Human Resources, Production, and Fulfillment and Distribution to coordinate activities, share information, and collaborate. Key Benefits for Your Company ERP systems are designed to enhance all aspects of key operations across a company’s entire back-office – from planning through execution, management, and control. -

Avoiding the Top 10 Software Security Design Flaws
AVOIDING THE TOP 10 SOFTWARE SECURITY DESIGN FLAWS Iván Arce, Kathleen Clark-Fisher, Neil Daswani, Jim DelGrosso, Danny Dhillon, Christoph Kern, Tadayoshi Kohno, Carl Landwehr, Gary McGraw, Brook Schoenfield, Margo Seltzer, Diomidis Spinellis, Izar Tarandach, and Jacob West CONTENTS Introduction ..................................................................................................................................................... 5 Mission Statement ..........................................................................................................................................6 Preamble ........................................................................................................................................................... 7 Earn or Give, but Never Assume, Trust ...................................................................................................9 Use an Authentication Mechanism that Cannot be Bypassed or Tampered With .................... 11 Authorize after You Authenticate ...........................................................................................................13 Strictly Separate Data and Control Instructions, and Never Process Control Instructions Received from Untrusted Sources ........................................................................................................... 14 Define an Approach that Ensures all Data are Explicitly Validated .............................................16 Use Cryptography Correctly .................................................................................................................... -

HECO-UNIX-Top Cladding Screw Into the Timber
HECO-UNIX -top Cladding Screw THE UNIQUE CLADDING SCREW WITH CONTRACTION EFFECT APPLICATION EXAMPLES Façade construction Secure and reliable façade fixing Louvred façades 1 2 3 The variable pitch of the HECO-UNIX full The smaller thread pitch means that the Gap free axial fixing of the timber board thread takes hold boards are clamped firmly together via the HECO-UNIX full thread PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS The HECO-UNIX-top Cladding Screw into the timber. The façade is secured axially via with contraction effect the thread, which increases the pull-out strength. HECO-UNIX-top full thread This results in fewer fastening points and an Timber façades are becoming increasingly popular ultimately more economical façade construction. Contraction effect thanks to the full in both new builds and renovations. This applica - Thanks to the full thread, the sole function of thread with variable thread pitch tion places high demands on fastenings. The the head is to fit the screw drive. As such, the Axial fixing of component façade must be securely fixed to the sub-structure HECO-UNIX-top façade screw has a small and the fixings should be invisible or attractive raised head, which allows simple, concealed Reduced spreading effect thanks to to look at. In addition, the structure must be installation preventing any water penetration the HECO-TOPIX ® tip permanently sound if it is constantly exposed to through the screw. The screws are made of the weather. The HECO-UNIX-top façade screw stainless steel A2, which safely eliminates the Raised countersunk head is the perfect solution to all of these requirements. -

BSD UNIX Toolbox 1000+ Commands for Freebsd, Openbsd
76034ffirs.qxd:Toolbox 4/2/08 12:50 PM Page iii BSD UNIX® TOOLBOX 1000+ Commands for FreeBSD®, OpenBSD, and NetBSD®Power Users Christopher Negus François Caen 76034ffirs.qxd:Toolbox 4/2/08 12:50 PM Page ii 76034ffirs.qxd:Toolbox 4/2/08 12:50 PM Page i BSD UNIX® TOOLBOX 76034ffirs.qxd:Toolbox 4/2/08 12:50 PM Page ii 76034ffirs.qxd:Toolbox 4/2/08 12:50 PM Page iii BSD UNIX® TOOLBOX 1000+ Commands for FreeBSD®, OpenBSD, and NetBSD®Power Users Christopher Negus François Caen 76034ffirs.qxd:Toolbox 4/2/08 12:50 PM Page iv BSD UNIX® Toolbox: 1000+ Commands for FreeBSD®, OpenBSD, and NetBSD® Power Users Published by Wiley Publishing, Inc. 10475 Crosspoint Boulevard Indianapolis, IN 46256 www.wiley.com Copyright © 2008 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Indianapolis, Indiana Published simultaneously in Canada ISBN: 978-0-470-37603-4 Manufactured in the United States of America 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data is available from the publisher. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, scanning or otherwise, except as permitted under Sections 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act, without either the prior written permission of the Publisher, or authorization through payment of the appropriate per-copy fee to the Copyright Clearance Center, 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923, (978) 750-8400, fax (978) 646-8600. Requests to the Publisher for permis- sion should be addressed to the Legal Department, Wiley Publishing, Inc., 10475 Crosspoint Blvd., Indianapolis, IN 46256, (317) 572-3447, fax (317) 572-4355, or online at http://www.wiley.com/go/permissions. -

What Is UNIX? the Directory Structure Basic Commands Find
What is UNIX? UNIX is an operating system like Windows on our computers. By operating system, we mean the suite of programs which make the computer work. It is a stable, multi-user, multi-tasking system for servers, desktops and laptops. The Directory Structure All the files are grouped together in the directory structure. The file-system is arranged in a hierarchical structure, like an inverted tree. The top of the hierarchy is traditionally called root (written as a slash / ) Basic commands When you first login, your current working directory is your home directory. In UNIX (.) means the current directory and (..) means the parent of the current directory. find command The find command is used to locate files on a Unix or Linux system. find will search any set of directories you specify for files that match the supplied search criteria. The syntax looks like this: find where-to-look criteria what-to-do All arguments to find are optional, and there are defaults for all parts. where-to-look defaults to . (that is, the current working directory), criteria defaults to none (that is, select all files), and what-to-do (known as the find action) defaults to ‑print (that is, display the names of found files to standard output). Examples: find . –name *.txt (finds all the files ending with txt in current directory and subdirectories) find . -mtime 1 (find all the files modified exact 1 day) find . -mtime -1 (find all the files modified less than 1 day) find . -mtime +1 (find all the files modified more than 1 day) find . -

LS Series Pistons Professional Professional As the Leader in LS-1 Forged Pistons, Wiseco Pulled out All the Stops When Designing the LS Series
Pro Prof ProfessionalProfessional Professional P Professional Hi-PerformanceForged ROFESSIONAL Professional Automotive Professional Professional ProfessionalCHEVY Professional ProfessionalRacing Pistons Professional Professional ProfessionalEFI Late Models Professional Professio for Professional NEW ArmorGlide Coated Skirts LS Series Pistons Professional Professional As the leader in LS-1 forged pistons, Wiseco pulled out all the stops when designing the LS Series. These pistons are designed to accommodate the reluctor ring on stroker cranks without having to notch the pin bosses. Offset pins like O.E. and skirt shapes specifi cally designed for street applications make these the best available. They have been tested successfully in the highest horsepower applications. LS Series LS 5.3 • 3.622 Stroke Std. Tension Rings Kit Bore Comp. Stroke Rod 0 Deck at Std. Avg. Volume Compression ratio at: Pin Part # 1/16, 1/16, 3mm Valve Part # Ht. Deck Ht. Wt. 58cc 61cc (included) (included) Pocket K474M96 3.780 3785HF 1.300 3.622 6.098 9.209 9.240 FT -2.2 10.9 10.4 S643 LS1,2,6 K474M965 3.800 6.125 9.236 .927 x 2.250 3805HF LS 5.3 • 4.000 Stroke K473M96 3.780 3785HF 1.110 4.000 6.098 9.209 9.240 -7cc 11.2 10.8 S643 LS1,2,6 K473M965 3.800 6.125 9.236 .927 x 2.250 3805HF LS7 • OE Titanium Rod & Pin Dia. Kit Comp. Std. Avg. Compression ratio at: Pin Part # Std. Tension Rings Valve Bore Stroke Rod 0 Deck at Volume 1.2, 1.2, 3mm Part # Ht. Deck Ht. Wt. 72cc (included) (included) Pocket K0004X125 4.125 4127GFX 1.175 4.000 6.067 9.242 9.240 2.5 12.0 S761 LS7 K0004X130 4.130 .9252 x 2.250 4137GFX • 2618 Alloy: High strength. -

GNU M4, Version 1.4.7 a Powerful Macro Processor Edition 1.4.7, 23 September 2006
GNU M4, version 1.4.7 A powerful macro processor Edition 1.4.7, 23 September 2006 by Ren´eSeindal This manual is for GNU M4 (version 1.4.7, 23 September 2006), a package containing an implementation of the m4 macro language. Copyright c 1989, 1990, 1991, 1992, 1993, 1994, 2004, 2005, 2006 Free Software Foundation, Inc. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License.” i Table of Contents 1 Introduction and preliminaries ................ 3 1.1 Introduction to m4 ............................................. 3 1.2 Historical references ............................................ 3 1.3 Invoking m4 .................................................... 4 1.4 Problems and bugs ............................................. 8 1.5 Using this manual .............................................. 8 2 Lexical and syntactic conventions ............ 11 2.1 Macro names ................................................. 11 2.2 Quoting input to m4........................................... 11 2.3 Comments in m4 input ........................................ 11 2.4 Other kinds of input tokens ................................... 12 2.5 How m4 copies input to output ................................ 12 3 How to invoke macros........................ -

GNU M4, Version 1.4.19 a Powerful Macro Processor Edition 1.4.19, 28 May 2021
GNU M4, version 1.4.19 A powerful macro processor Edition 1.4.19, 28 May 2021 by Ren´eSeindal, Fran¸coisPinard, Gary V. Vaughan, and Eric Blake ([email protected]) This manual (28 May 2021) is for GNU M4 (version 1.4.19), a package containing an implementation of the m4 macro language. Copyright c 1989{1994, 2004{2014, 2016{2017, 2020{2021 Free Software Foundation, Inc. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.3 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is included in the section entitled \GNU Free Documentation License." i Table of Contents 1 Introduction and preliminaries ::::::::::::::::: 3 1.1 Introduction to m4 :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: 3 1.2 Historical references :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: 3 1.3 Problems and bugs ::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: 4 1.4 Using this manual :::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: 5 2 Invoking m4::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::: 7 2.1 Command line options for operation modes ::::::::::::::::::::: 7 2.2 Command line options for preprocessor features ::::::::::::::::: 8 2.3 Command line options for limits control ::::::::::::::::::::::: 10 2.4 Command line options for frozen state ::::::::::::::::::::::::: 11 2.5 Command line options for debugging :::::::::::::::::::::::::: 11 2.6 Specifying input files on the command line ::::::::::::::::::::: -

An Overview of the Scala Programming Language
An Overview of the Scala Programming Language Second Edition Martin Odersky, Philippe Altherr, Vincent Cremet, Iulian Dragos Gilles Dubochet, Burak Emir, Sean McDirmid, Stéphane Micheloud, Nikolay Mihaylov, Michel Schinz, Erik Stenman, Lex Spoon, Matthias Zenger École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland Technical Report LAMP-REPORT-2006-001 Abstract guage for component software needs to be scalable in the sense that the same concepts can describe small as well as Scala fuses object-oriented and functional programming in large parts. Therefore, we concentrate on mechanisms for a statically typed programming language. It is aimed at the abstraction, composition, and decomposition rather than construction of components and component systems. This adding a large set of primitives which might be useful for paper gives an overview of the Scala language for readers components at some level of scale, but not at other lev- who are familar with programming methods and program- els. Second, we postulate that scalable support for compo- ming language design. nents can be provided by a programming language which unies and generalizes object-oriented and functional pro- gramming. For statically typed languages, of which Scala 1 Introduction is an instance, these two paradigms were up to now largely separate. True component systems have been an elusive goal of the To validate our hypotheses, Scala needs to be applied software industry. Ideally, software should be assembled in the design of components and component systems. Only from libraries of pre-written components, just as hardware is serious application by a user community can tell whether the assembled from pre-fabricated chips. -

System Analysis and Tuning Guide System Analysis and Tuning Guide SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 System Analysis and Tuning Guide System Analysis and Tuning Guide SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 An administrator's guide for problem detection, resolution and optimization. Find how to inspect and optimize your system by means of monitoring tools and how to eciently manage resources. Also contains an overview of common problems and solutions and of additional help and documentation resources. Publication Date: September 24, 2021 SUSE LLC 1800 South Novell Place Provo, UT 84606 USA https://documentation.suse.com Copyright © 2006– 2021 SUSE LLC and contributors. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or (at your option) version 1.3; with the Invariant Section being this copyright notice and license. A copy of the license version 1.2 is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”. For SUSE trademarks, see https://www.suse.com/company/legal/ . All other third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Trademark symbols (®, ™ etc.) denote trademarks of SUSE and its aliates. Asterisks (*) denote third-party trademarks. All information found in this book has been compiled with utmost attention to detail. However, this does not guarantee complete accuracy. Neither SUSE LLC, its aliates, the authors nor the translators shall be held liable for possible errors or the consequences thereof. Contents About This Guide xii 1 Available Documentation xiii -

Philadelphia Water Department Guide for Urban
CITY OF PHILADELPHIA Philadelphia Water Department Guide for Urban Gardens & Farms: Getting Water Access 2019 2.2 - October v. The Philadelphia Water Department (PWD) is pleased to present this guide in support of Philadelphia’s robust urban gardening and farming community. Urban gardens and farms provide many wonderful benefits to residents by: • Preserving open and green space • Fostering natural beauty • Providing a sense of community • Reducing stormwater runoff by soaking up rain • Making healthy foods accessible Our goal is to ensure that urban gardens and farms have access to the water they need to flourish. This guide provides a number of options to obtain water, either year-round or seasonally. PWD recommends urban gardens and farms establish a permanent water service when growers have the capacity and permission to do so. A permanent water service better protects the city’s drinking water supply and is a more reliable and practical source of water. Interested gardens and farms should work with the Pennsylvania Horticultural Society (PHS) or the Neighborhood Gardens Trust (NGT) when setting up a permanent water service as participants in PWD’s Urban Garden Program. 2. New Water Sources Gardeners in Philadelphia have four options New water lines that go directly to a garden vary in cost, for accessing water for plants: depending on factors such as location. The cost of installing a 1. Private, existing water sources new water line begins at $3,000, but can sometimes cost more 2. New, dedicated water lines than $10,000, depending upon the distance between the water 3. Rain collection main and the garden. -

Introduction to Unix Part I: the Essentials
Introduction to Unix Part I: The Essentials Frederick J Tan Bioinformatics Research Faculty Carnegie Institution of Washington, Department of Embryology 9 April 2013 Unix, Linux, Ubuntu, Oh My! 2 A Three Hour Tour Part I: The Essentials client-server model, command-line interface, navigation, viewing files, searching, finding help Part II: Special Topics account settings, multi-tasking, programming, installing programs, file systems, system administration 3 The Awesome Power of the Client-Server Model 4 A Tale of Two Interfaces Command Line Graphical Terminal.app, Unix shell Finder.app, Galaxy breadth, cutting-edge discovery, visualization 5 Running Programs Using the Command-Line Interface command-line graphical type in the name of the to run a program program and hit <ENTER> double click on an icon (e.g. bowtie2) type in options after the program, to modify how a click on check boxes, before hitting <ENTER> program operates select from pull-down menus (e.g. bowtie2 --very-sensitive) 6 The Anatomy of a Shell Prompt workshop@ubuntu:~$ The text in between the colon (:) The $ symbol indicates The symbol and the dollar sign ($) indicates that the server is ready to indicates where what what directory you are in. perform a command. you type in will appear. /home/workshop$ $ ssh [email protected] 7 Task 1: Connect to your server and start top with -i option Start VirtualBox Start Ubuntu Secure SHell $ ssh [email protected] <ENTER> <SPACE> Shell Prompt /home/workshop$ <TAB> Start top -i $ top -i <CTRL> <UP> <DOWN> 8 Task 2: Figure