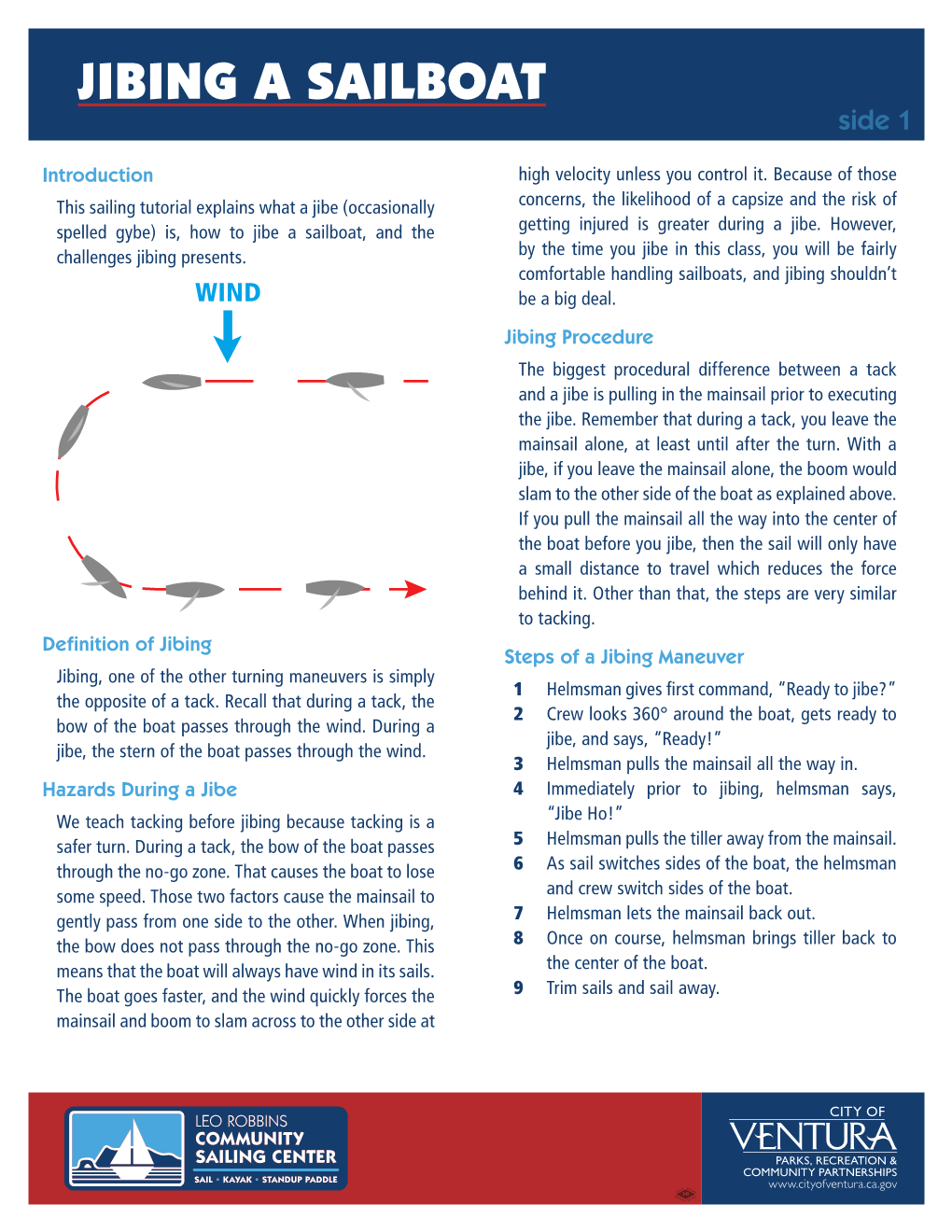
JIBING a SAILBOAT Side 1
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

New Jersey Windsurfing and Watersports Association Newsletter
1 New Jersey Windsurfing and Watersports Association Newsletter Vol. 10, Issue 1. Spring 2018 Corinne; mid downwind 360 in Bonaire: February, 2018 Photograph: Pawel Szulga Editing and Layout: Alasdair Gilfillan 5. More Winter sailing By Jimmy Rivera Contributors: Jeff Bauer, Will Flannery, Alasdair 5. More Winter sailing part 2. and Corinne Gilfillan, Ken and From Brad Miley and Chris Eileen Hoff, Tom Latham, Brad Cowan Miley, Brain Rauch, Jimmy Rivera 5. More Winter sailing part 3. Photographs/Videos: From Brian Rauch and Gary Gary and Sue Berezny, Chris and Sue Berezny Cowan, Will Flannery, Alasdair Gilfillan, Jibe City, Tom Latham, 6. Special Feature – Wind Foiling Karen Marriott, MW sails, Jimmy By Ken and Eileen Hoff Rivera, Pawel Szulga, Britt Viehman 7. Special Feature – Sargassum invades Caribbean Windsurf Resort: Windsurfers to Contents: the rescue By Alasdair and Corinne Gilfillan Page Article 10. Special Feature – Introducing MW sails 2. Letter from the President By Tom Latham 2. 2018 NJWWA Schedule of Events 10. Special Feature – The Will to Windsurf By Tom Flannery 3. 2108 ABK Camp Schedule 12. Interesting Web Links 3. Call for contributions for 2019 NJWWA Calendar 12. Disclaimer 4. Club News 12. Classifieds, Past and Future Issues Winter Iceboarding By Tom Latham 13. Sponsors 2 Letter from the President On another note, we are in desperate need of someone to volunteer to help us revamp the NJWWA website. Barb and I have attempted to do it ourselves but we lack the technological expertise to bring it to fruition. If you have the skills, we need your help!!! Thank you all for your continued support of the NJWWA and I hope to see you on the water soon! Jeff Bauer, President ([email protected]) 2018 NJWWA Schedule of Events st Sunday July 1 2018: NJWWA Windsurfing Fun Fest @ Bayview Park, Happy Spring fellow NJWWA’ers! LBI. -

Safety and Rescue
SAFETY AND RESCUE Ventilation and Fueling everyone on your boat knows the location of the fire the tide changes direction is known as “slack water.” extinguisher and its use. Operation of a fire extinguish- “High tide” is the highest level a tide reaches during Gasoline fumes are heavier than air and will er is rather simple. Just remember PASS. ascending waters, and “low tide” is the lowest level a settle to the lowest part of the boat’s interior hull, tide reaches during descending waters. the bilge. All motorboats, except open boats, must The tidal cycle is the high tide followed approxi- have at least two ventilator ducts with cowls (intake Running Aground mately 6 hours later by low tide (two highs and two and exhaust). Exhaust blowers are part of most boat Keep a sharp lookout when traveling on waters lows per day). The tidal range is the vertical distance ventilation systems. Permanently installed fuel that have shallow areas to avoid running aground. between high and low tides. The tidal range varies tanks must be vented. Navigational charts, buoys, and depth finders can from 1 to 11 feet in Pennsylvania on the Delaware Most boat explosions occur from improper fuel- assist in this task. If you run aground and the impact River. Boaters should consult tide tables for times of ing. Portable gas tanks should be filled on the dock does not appear to cause a leak, follow these steps to high and low tides. or pier, not on board. The vent on the tank should refloat the boat: be closed and the gas pumped carefully, maintain- • Do not put the boat in reverse. -

Sailing in Heavy Weather
SAILING IN HEAVY WEATHER John Jourdane As the wind increases you need to reduce sail area the keep the boat under control Why we need smaller sails as the wind builds Think of a weather vane Keep the helm balanced Pac Cup Rules – Heavy Air Sails 1. Mainsail – must be able to reduce luff length by 10% 2. Boat shall carry at least 2 of the following 3 sails: a. A trysail with sail numbers on both sides, which can be set independently of the boom, has an area less than 17.5% of E x P, and which is capable of being attached to the mast. Sails newer than 1/1/2014 must be constructed of highly visible material. b. A storm jib with an alternate means of attachment to the headstay, if the head foil fails, and highly visible material c. A heavy-weather jib of area not greater than 13.5% of the foretriangle squared. The North Pacific High As the wind increases Go to progressively smaller jibs Reef the mainsail Put more reefs in the main Put up the storm jib or storm staysail Deep-reefed main alone Storm trysail and storm jib or storm staysail Heave to with trysail and storm jib or storm staysail Storm trysail or storm staysail alone Reefed Main and Small Jib Storm Sails Should be purpose-built for your boat Need to be made from heavy material to withstand the beating a storm can produce Storm Jib Gale Sail Gale Sail Gale Sail Storm Staysail Storm Jib Stow the storm jib in it’s own bag in an easily accessible place. -

Mast Furling Installation Guide
NORTH SAILS MAST FURLING INSTALLATION GUIDE Congratulations on purchasing your new North Mast Furling Mainsail. This guide is intended to help better understand the key construction elements, usage and installation of your sail. If you have any questions after reading this document and before installing your sail, please contact your North Sails representative. It is best to have two people installing the sail which can be accomplished in less than one hour. Your boat needs facing directly into the wind and ideally the wind speed should be less than 8 knots. Step 1 Unpack your Sail Begin by removing your North Sails Purchasers Pack including your Quality Control and Warranty information. Reserve for future reference. Locate and identify the battens (if any) and reserve for installation later. Step 2 Attach the Mainsail Tack Begin by unrolling your mainsail on the side deck from luff to leech. Lift the mainsail tack area and attach to your tack fitting. Your new Mast Furling mainsail incorporates a North Sails exclusive Rope Tack. This feature is designed to provide a soft and easily furled corner attachment. The sail has less patching the normal corner, but has the Spectra/Dyneema rope splayed and sewn into the sail to proved strength. Please ensure the tack rope is connected to a smooth hook or shackle to ensure durability and that no chafing occurs. NOTE: If your mainsail has a Crab Claw Cutaway and two webbing attachment points – Please read the Stowaway Mast Furling Mainsail installation guide. Step 2 www.northsails.com Step 3 Attach the Mainsail Clew Lift the mainsail clew to the end of the boom and run the outhaul line through the clew block. -

J Lotuff Wianno Senior Tuning Guide.Pages
Wianno Senior Racing Guide I. Crew Page 2 II. Boat Setup Page 5 III. Sail Trim Page 9 IV. Quick Reference Page 14 Contact [email protected] with questions or comments. **pre-Doyle Mainsail (2013)** I. Crew: At the most basic, you cannot get around the racecourse without a crew. At the highest level of the sport where everyone has the best equipment, crew contribution is the deciding factor. Developing and maintaining an enthusiastic, competent, reliable, and compatible crew is therefore a key area of focus for the racer aspiring to excellent results. Prior to the Class Championship you should have your crew set up, with assigned positions and job responsibilities – well trained in tacking, jibing, roundings and starts. The following may help you set up your program to attract good crew. First, good sailors want to do well. So do everything you can to make sure that you understand how to make the boat go fast and do everything you can to ensure that your boat is in good racing condition (more on these two issues later). If you are a helmsman make sure that your driving skills are developed to your best abilities. Assemble sailors who are better than you or find an enthusiastic non-sailor to train and encourage. Arrange practice time either pre/post-race or on a non-racing day. The right type of crew personality will want to improve performance and the best way to do this is to spend time together in the boat. If your crew does not wish to make the effort to spend time in the boat, cast a wider net. -

Boom Vang Rigging
Congratulations! You purchased the best known and best built pocket cruising vessels available. We invite you to spend a few moments with the following pages to become better acquainted with your new West Wight Potter. If at any point we can assist you, please call 800 433 4080 Fair Winds International Marine Standing Rigging The mast is a 2” aluminum extrusion with a slot on the aft side to which the sail’s boltrope or mainsail slides (options item) enter when hoisting the main sail. Attached to the mast will be two side stays, called Shrouds, and a Forestay. These three stainless cables represent the standing rigging of the West Wight Potter 15. The attachment points for the shroud adjusters are on the side of the deck. Looking at the boat you will find ¼” U-Bolts mounted through the deck on either side of the boat and the adjuster goes over these U-Bolts. Once the shroud adjuster slides in, the clevis pin inserts through the adjuster and is held in place with a lock ring. When both side stays are in place we move onto the mast raising. Mast Raising First, remove the mast pin holding the mast base in the bow pulpit. Second, move the mast back towards the mast step on the cabin top of the boat and pin the mast base into the aft section of the mast step (the mast step is bolted onto the cabin top of the boat). The mast crutch on the transom of the boat will support the aft end of the mast. -

Hālāwai Papa Alakaʻi Kūmau Keʻena Kuleana Hoʻokipa O Hawaiʻi Hālāwai Kino a Kikohoʻe In-Person and Virtual Regular
HĀLĀWAI PAPA ALAKAʻI KŪMAU KEʻENA KULEANA HOʻOKIPA O HAWAIʻI HĀLĀWAI KINO A KIKOHOʻE IN-PERSON AND VIRTUAL REGULAR BOARD MEETING HAWAI‘I TOURISM AUTHORITY Pōʻahā, 24 Iune 2021, 9:30 a.m. Thursday, June 24, 2021 at 9:30 a.m. Kikowaena Hālāwai O Hawaiʻi Hawaiʻi Convention Center Papahele ʻEhā | Lumi Nui C Fourth Floor | Ballroom C 1801 Alaākea Kalākaua 1801 Kalākaua Avenue Honolulu, Hawaiʻi 96815 Honolulu, Hawaiʻi 96815 ʻO ka hoʻopakele i ke ola o ka lehulehu ka makakoho The safety of the public is of the utmost nui. E maliu ana ke keʻena i ke kuhikuhina a nā loea no importance. Pursuant to expert guidance, HTA will ke kū kōwā, ka uhi maka, me nā koina pili olakino ʻē be following strict physical distancing, facial aʻe. Koi ʻia ke komo i ka uhi maka a me ke kū kōwā ma coverings, and other health-related requirements. nā keʻena a ma nā hālāwai. Face coverings and physical distancing are required in HTA offices and meetings. Koi ʻia ka hōʻoia i kou olakino maikaʻi ma mua o ke Entrance to the Hawaiʻi Convention Center requires komo i ke Kikowaena Hālāwai O Hawaiʻi ma ka ʻīpuka o a health screening at the center parking garage waena o ka hale hoʻokū kaʻa. E pāpā ʻia ke komo ʻana o entrance. Persons with a temperature of over ke kanaka nona ka piwa ma luna aʻe o ka 100.4°F. Inā 100.4°F will be denied entry. If you are not feeling ʻōmaʻimaʻi ʻoe, e ʻoluʻolu, e ʻimi i ke kauka nāna e well, we urge you to contact a healthcare provider. -

December 2007 Crew Journal of the Barque James Craig
December 2007 Crew journal of the barque James Craig Full & By December 2007 Full & By The crew journal of the barque James Craig http://www.australianheritagefleet.com.au/JCraig/JCraig.html Compiled by Peter Davey [email protected] Production and photos by John Spiers All crew and others associated with the James Craig are very welcome to submit material. The opinions expressed in this journal may not necessarily be the viewpoint of the Sydney Maritime Museum, the Sydney Heritage Fleet or the crew of the James Craig or its officers. 2 December 2007 Full & By APEC parade of sail - Windeward Bound, New Endeavour, James Craig, Endeavour replica, One and All Full & By December 2007 December 2007 Full & By Full & By December 2007 December 2007 Full & By Full & By December 2007 7 Radio procedures on James Craig adio procedures being used onboard discomfort. Effective communication Rare from professional to appalling relies on message being concise and clear. - mostly on the appalling side. The radio Consider carefully what is to be said before intercoms are not mobile phones. beginning to transmit. Other operators may The ship, and the ship’s company are be waiting to use the network. judged by our appearance and our radio procedures. Remember you may have Some standard words and phases. to justify your transmission to a marine Affirm - Yes, or correct, or that is cor- court of inquiry. All radio transmissions rect. or I agree on VHF Port working frequencies are Negative - No, or this is incorrect or monitored and tape recorded by the Port Permission not granted. -

Sail Trimming Guide for the Beneteau 37 September 2008
INTERNATIONAL DESIGN AND TECHNICAL OFFICE Sail Trimming Guide for the Beneteau 37 September 2008 © Neil Pryde Sails International 1681 Barnum Avenue Stratford, CONN 06614 Phone: 203-375-2626 • Fax: 203-375-2627 Email: [email protected] Web: www.neilprydesails.com All material herein Copyright 2007-2008 Neil Pryde Sails International All Rights Reserved HEADSAIL OVERVIEW: The Beneteau 37 built in the USA and supplied with Neil Pryde Sails is equipped with a 105% non-overlapping headsail that is 337sf / 31.3m2 in area and is fitted to a Profurl C320 furling unit. The following features are built into this headsail: • The genoa sheets in front of the spreaders and shrouds for optimal sheeting angle and upwind performance • The size is optimized to sheet correctly to the factory track when fully deployed and when reefed. • Reef ‘buffer’ patches are fitted at both head and tack, which are designed to distribute the loads on the sail when reefed. • Reefing marks located on the starboard side of the tack buffer patch provide a visual mark for setting up pre-determined reefing locations. These are located 508mm/1’-8” and 1040mm / 3’-5” aft of the tack. • A telltale ‘window’ at the leading edge of the sail located about 14% of the luff length above the tack of the sail and is designed to allow the helmsperson to easily see the wind flowing around the leading edge of the sail when sailing upwind and close-hauled. The tell-tales are red and green, so that one can quickly identify the leeward and weather telltales. -

The Weather Helm Issue (Rev 20 02 2020)
Corbin 39 – the weather helm issue (rev 20 02 2020) Synopsis The subject of weather helm comes up repeatedly when discussing the Corbin 39 and not all of the folklore is justified. This note attempts to summarise the issue and to relate it to sufficient evidence, and to qualitative theory, that we can be reasonably certain of the situation. Remember - It is possible to overpower a yacht and induce weather helm, what we are trying to do is identify excessive weather helm. The key take-away is that the excessive weather helm was a genuine issue, which affected all the mk1 cutters irrespective of whether they were equipped with the taller double-spreader mast or the shorter single-spreader mast, provided that the mast was set in the intended aft mast position. Perhaps this was worse in the mk1 tallmast vs the mk1 shortmast, but we are not at all certain of that. All the mk1’s that had the forestay relocated onto a 3-foot long bowsprit were later able to alleviate this to an extent. The mk 1’s that have reduced the area of their main by shortening the mainsail boom & foot (or used in-mast furling) have reportedly completely eliminated this weather helm. All other versions including the mk1 ketches and all the mk2 cutters & ketches appear to be completely unaffected. This is the first openly published version of this analysis. Previous drafts were incomplete and drew erroneous conclusions in some areas due to an absence of reliable data. That has now been overcome as further evidence has come forwards, and so there are material differences between this version and previous drafts. -

JIB REEFING & FURLING Unit 0
MKIV OCEAN - JIB REEFING & FURLING Unit 0 Installation Manual – Intended for specialized personnel or expert users 5389 03/21 Preassembly Safety Precautions/Parts Description 2 Sizing Check 3 Parts 4 Rigging Parts Check/Tools 5 Dimensions/Sailmaker's Instructions 6 Toggle Deductions/Stay Into Foil Options 7 Top Foil Length 8 Short Top Foil 9 Confirm Foil Length 10 Assembly Foils/Connectors 11–14 Halyard Swivel and Drum Assembly 15 Rod Rigging 16 Turnbuckle/Toggle 17 Final/Feeder 18–19 Commissioning Turnbuckle 20 Lead Line to Cockpit 21 Halyard Wrap/Prevent Halyard Wrap 22 Pendant/Halyard Restrainer/ Halyard Tension 23 Operation Spinnaker Halyards/Headstay and Backstay Tension 24 Raise Sails 25 Furl/Reef 25–26 Secure Sail 26 Maintenance Clean/Inspect 27 Replace Line 27 Storage/Remove Furler 27 Troubleshooting/Warranty 28 Parts Lists 29-30 Contact Harken 32 Please read these instructions carefully before installing, servicing, or operating the equipment. This manual may be modified without notice. See: www.harken.com/en/support/manuals/ for updated versions. PLEASE SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS Safety Precautions/Parts Description Introduction This manual gives technical information on installation and service. This information is destined exclusively for specialized personnel or expert users. Installation, disassembling, and reassembling by personnel who are not experts may cause serious damage to property or injury to users and those in the vicinity of the product. If you do not understand an instruction contact Harken. The user must have appropriate training in order to use this product. Harken accepts no responsibility for damage or harm caused by not observing the safety requirements and instructions in this manual. -

SAFETY PRACTICES a BASIC GUIDE Adopted January 2002 Amended October 2014
INTERSCHOLASTIC SAILING ASSOCIATION SAFETY PRACTICES A BASIC GUIDE Adopted January 2002 Amended October 2014 Special thanks to our sister organization, the Intercollegiate Sailing Association of North America, for allowing us to use this Safety Guide, modeled after their own. TABLE OF CONTENTS General Safety Practices ..................................................... 1 Personal Equipment ............................................................ 2 Personal Training ................................................................ 4 Capsizes ............................................................................... 4 Safety Boats ........................................................................ 5 Safety Boat Crew Training ................................................... 6 Head Injury Awareness ....................................................... 9 References .......................................................................... 9 Foreword: Interscholastic (high school) sailing requires competitors to be safety conscious. It is our obligation to maintain the positive safety record that Interscholastic Sailing Association has enjoyed over the past 85 years. This is a BASIC GUIDE for Member Schools and District Associations to follow in regard to SAFETY PRACTICES during regattas, and instructional and recreational sailing. George H. Griswold As amended by Bill Campbell for ISSA 1. GENERAL SAFETY PRACTICES You sail because you enjoy it. In order to enhance and guarantee your enjoyment, there are a number of general