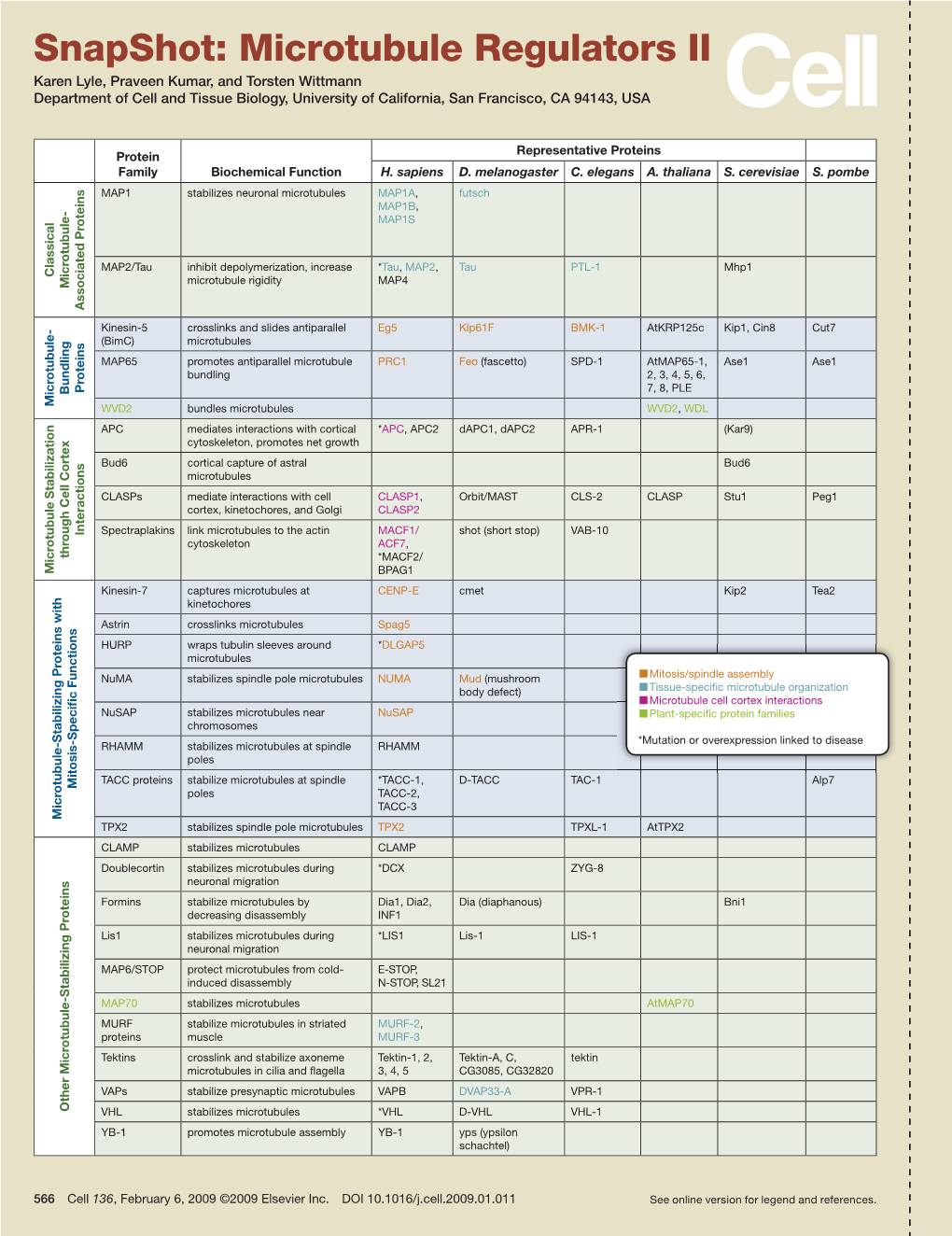
Snapshot: Microtubule Regulators II
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Cyclin D1/Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 Interacts with Filamin a and Affects the Migration and Invasion Potential of Breast Cancer Cells
Published OnlineFirst February 28, 2010; DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-1108 Tumor and Stem Cell Biology Cancer Research Cyclin D1/Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 Interacts with Filamin A and Affects the Migration and Invasion Potential of Breast Cancer Cells Zhijiu Zhong, Wen-Shuz Yeow, Chunhua Zou, Richard Wassell, Chenguang Wang, Richard G. Pestell, Judy N. Quong, and Andrew A. Quong Abstract Cyclin D1 belongs to a family of proteins that regulate progression through the G1-S phase of the cell cycle by binding to cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk)-4 to phosphorylate the retinoblastoma protein and release E2F transcription factors for progression through cell cycle. Several cancers, including breast, colon, and prostate, overexpress the cyclin D1 gene. However, the correlation of cyclin D1 overexpression with E2F target gene regulation or of cdk-dependent cyclin D1 activity with tumor development has not been identified. This suggests that the role of cyclin D1 in oncogenesis may be independent of its function as a cell cycle regulator. One such function is the role of cyclin D1 in cell adhesion and motility. Filamin A (FLNa), a member of the actin-binding filamin protein family, regulates signaling events involved in cell motility and invasion. FLNa has also been associated with a variety of cancers including lung cancer, prostate cancer, melanoma, human bladder cancer, and neuroblastoma. We hypothesized that elevated cyclin D1 facilitates motility in the invasive MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. We show that MDA-MB-231 motility is affected by disturbing cyclin D1 levels or cyclin D1-cdk4/6 kinase activity. -

Supplementary Figures
Mena regulates the LINC complex to control actin–nuclear lamina associations, trans-nuclear membrane signalling and cancer gene expression Frederic Li Mow Chee!, Bruno Beernaert!, Alexander Loftus!, Yatendra Kumar", Billie G. C. Griffith!, Jimi C. Wills!, Ann P. Wheeler#, J. Douglas Armstrong$, Maddy Parsons%, Irene M. Leigh,(, Charlotte M. Proby&, Alex von Kriegsheim!, Wendy A. Bickmore", Margaret C. Frame,* & Adam Byron,* Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2 Supplementary Figure 3 Supplementary Table 1 Supplementary Table 2 Supplementary Table 3 Supplementary Table 4 !Cancer Research UK Edinburgh Centre, Institute of Genetics and Cancer, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH< =XR, UK. "MRC Human Genetics Unit, Institute of Genetics and Cancer, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH< =XU, UK. #Advanced Imaging Resource, Institute of Genetics and Cancer, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EH< =XU, UK. $Simons Initiative for the Developing Brain, School of Informatics, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh EHH IYL, UK. %Randall Centre for Cell and Molecular Biophysics, King’s College London, London SEM MUL, UK. &Division of Molecular and Clinical Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Dundee, Dundee DD <HN, UK. 'Institute of Dentistry, Barts and the London School of Medicine and Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, London EM =AT, UK. *email: [email protected] or [email protected] 1 a cSCC IAC correlation b cSCC IAC pathways c Core adhesome network ENAH −log10(q) MACF1 CSRP1 Met1 Met4 0 5 10 + + CORO2A Integrin signalling + CFL1 pathway PRNP ILK + HSPB1 PALLD PPFIA1 TES RDX Cytoskeletal regulation + VASP + + ARPC2 by Rho GTPase PPP2CA + Met1 + LASP1 MYH9 + VIM TUBA4A Huntington ITGA3 + disease ITGB4 VCL CAV1 ACTB ROCK1 KTN1 FLNA+ CALR DNA FBLIM1 CORO1B RAC1 + replication +ACTN1 ITGA6 + Met4 ITGAV Parkinson ITGB1 disease Actin cytoskel. -

Universidade Estadual De Campinas Instituto De Biologia
UNIVERSIDADE ESTADUAL DE CAMPINAS INSTITUTO DE BIOLOGIA VERÔNICA APARECIDA MONTEIRO SAIA CEREDA O PROTEOMA DO CORPO CALOSO DA ESQUIZOFRENIA THE PROTEOME OF THE CORPUS CALLOSUM IN SCHIZOPHRENIA CAMPINAS 2016 1 VERÔNICA APARECIDA MONTEIRO SAIA CEREDA O PROTEOMA DO CORPO CALOSO DA ESQUIZOFRENIA THE PROTEOME OF THE CORPUS CALLOSUM IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Dissertação apresentada ao Instituto de Biologia da Universidade Estadual de Campinas como parte dos requisitos exigidos para a obtenção do Título de Mestra em Biologia Funcional e Molecular na área de concentração de Bioquímica. Dissertation presented to the Institute of Biology of the University of Campinas in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master in Functional and Molecular Biology, in the area of Biochemistry. ESTE ARQUIVO DIGITAL CORRESPONDE À VERSÃO FINAL DA DISSERTAÇÃO DEFENDIDA PELA ALUNA VERÔNICA APARECIDA MONTEIRO SAIA CEREDA E ORIENTADA PELO DANIEL MARTINS-DE-SOUZA. Orientador: Daniel Martins-de-Souza CAMPINAS 2016 2 Agência(s) de fomento e nº(s) de processo(s): CNPq, 151787/2F2014-0 Ficha catalográfica Universidade Estadual de Campinas Biblioteca do Instituto de Biologia Mara Janaina de Oliveira - CRB 8/6972 Saia-Cereda, Verônica Aparecida Monteiro, 1988- Sa21p O proteoma do corpo caloso da esquizofrenia / Verônica Aparecida Monteiro Saia Cereda. – Campinas, SP : [s.n.], 2016. Orientador: Daniel Martins de Souza. Dissertação (mestrado) – Universidade Estadual de Campinas, Instituto de Biologia. 1. Esquizofrenia. 2. Espectrometria de massas. 3. Corpo caloso. -

Plakins, a Versatile Family of Cytolinkers: Roles in Skin Integrity and in Human Diseases Jamal-Eddine Bouameur1,2, Bertrand Favre1 and Luca Borradori1
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Elsevier - Publisher Connector REVIEW Plakins, a Versatile Family of Cytolinkers: Roles in Skin Integrity and in Human Diseases Jamal-Eddine Bouameur1,2, Bertrand Favre1 and Luca Borradori1 The plakin family consists of giant proteins involved in in (Roper et al., 2002; Jefferson et al., 2004; Sonnenberg and the cross-linking and organization of the cytoskeleton Liem, 2007; Boyer et al., 2010; Suozzi et al., 2012). and adhesion complexes. They further modulate sev- Mammalian plakins share a similar structural organization eral fundamental biological processes, such as cell and comprise seven members: bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 adhesion, migration, and polarization or signaling (BPAG1), desmoplakin, envoplakin, epiplakin, microtubule- pathways. Inherited and acquired defects of plakins actin cross-linking factor 1 (MACF1), periplakin, and plectin in humans and in animal models potentially lead to (Figure 1) (Choi et al., 2002; Jefferson et al., 2007; Choi and dramatic manifestations in the skin, striated muscles, Weis, 2011; Ortega et al., 2011). The existence of develop- and/or nervous system. These observations unequivo- mentally regulated and tissue-specific splice variants of some cally demonstrate the key role of plakins in the plakins further increases the diversity and versatility of these proteins (Table 1; Figure 1; Leung et al., 2001; Rezniczek et al., maintenance of tissue integrity. Here we review the 2003; Lin et al., 2005; Jefferson et al., 2006; Cabral et al., 2010). characteristics of the mammalian plakin members BPAG1 (bullous pemphigoid antigen 1), desmoplakin, PLAKINS IN THE EPIDERMIS plectin, envoplakin, epiplakin, MACF1 (microtubule- Epithelial BPAG1 (BPAG1e, also called BP230) constitutes the actin cross-linking factor 1), and periplakin, highlight- epithelium-specific isoform of BPAG1 and is localized in basal ing their role in skin homeostasis and diseases. -

How Microtubules Control Focal Adhesion Dynamics
JCB: Review Targeting and transport: How microtubules control focal adhesion dynamics Samantha Stehbens and Torsten Wittmann Department of Cell and Tissue Biology, University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA 94143 Directional cell migration requires force generation that of integrin-mediated, nascent adhesions near the cell’s leading relies on the coordinated remodeling of interactions with edge, which either rapidly turn over or connect to the actin cytoskeleton (Parsons et al., 2010). Actomyosin-mediated the extracellular matrix (ECM), which is mediated by pulling forces allow a subset of these nascent FAs to grow integrin-based focal adhesions (FAs). Normal FA turn- and mature, and provide forward traction forces. However, in over requires dynamic microtubules, and three members order for cells to productively move forward, FAs also have to of the diverse group of microtubule plus-end-tracking release and disassemble underneath the cell body and in the proteins are principally involved in mediating micro- rear of the cell. Spatial and temporal control of turnover of tubule interactions with FAs. Microtubules also alter these mature FAs is important, as they provide a counterbalance to forward traction forces, and regulated FA disassembly is the assembly state of FAs by modulating Rho GTPase required for forward translocation of the cell body. An important signaling, and recent evidence suggests that microtubule- question that we are only beginning to understand is how FA mediated clathrin-dependent and -independent endo turnover is spatially and temporally regulated to allow cells cytosis regulates FA dynamics. In addition, FA-associated to appropriately respond to extracellular signals, allowing for microtubules may provide a polarized microtubule track for coordinated and productive movement. -

Conserved Microtubule–Actin Interactions in Cell Movement and Morphogenesis
REVIEW Conserved microtubule–actin interactions in cell movement and morphogenesis Olga C. Rodriguez, Andrew W. Schaefer, Craig A. Mandato, Paul Forscher, William M. Bement and Clare M. Waterman-Storer Interactions between microtubules and actin are a basic phenomenon that underlies many fundamental processes in which dynamic cellular asymmetries need to be established and maintained. These are processes as diverse as cell motility, neuronal pathfinding, cellular wound healing, cell division and cortical flow. Microtubules and actin exhibit two mechanistic classes of interactions — regulatory and structural. These interactions comprise at least three conserved ‘mechanochemical activity modules’ that perform similar roles in these diverse cell functions. Over the past 35 years, great progress has been made towards under- crosstalk occurs in processes that require dynamic cellular asymme- standing the roles of the microtubule and actin cytoskeletal filament tries to be established or maintained to allow rapid intracellular reor- systems in mechanical cellular processes such as dynamic shape ganization or changes in shape or direction in response to stimuli. change, shape maintenance and intracellular organelle movement. Furthermore, the widespread occurrence of these interactions under- These functions are attributed to the ability of polarized cytoskeletal scores their importance for life, as they occur in diverse cell types polymers to assemble and disassemble rapidly, and to interact with including epithelia, neurons, fibroblasts, oocytes and early embryos, binding proteins and molecular motors that mediate their regulated and across species from yeast to humans. Thus, defining the mecha- movement and/or assembly into higher order structures, such as radial nisms by which actin and microtubules interact is key to understand- arrays or bundles. -

Absence of NEFL in Patient-Specific Neurons in Early-Onset Charcot-Marie-Tooth Neuropathy Markus T
ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Absence of NEFL in patient-specific neurons in early-onset Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy Markus T. Sainio, MSc, Emil Ylikallio, MD, PhD, Laura M¨aenp¨a¨a, MSc, Jenni Lahtela, PhD, Pirkko Mattila, PhD, Correspondence Mari Auranen, MD, PhD, Johanna Palmio, MD, PhD, and Henna Tyynismaa, PhD Dr. Tyynismaa [email protected] Neurol Genet 2018;4:e244. doi:10.1212/NXG.0000000000000244 Abstract Objective We used patient-specific neuronal cultures to characterize the molecular genetic mechanism of recessive nonsense mutations in neurofilament light (NEFL) underlying early-onset Charcot- Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease. Methods Motor neurons were differentiated from induced pluripotent stem cells of a patient with early- onset CMT carrying a novel homozygous nonsense mutation in NEFL. Quantitative PCR, protein analytics, immunocytochemistry, electron microscopy, and single-cell transcriptomics were used to investigate patient and control neurons. Results We show that the recessive nonsense mutation causes a nearly total loss of NEFL messenger RNA (mRNA), leading to the complete absence of NEFL protein in patient’s cultured neurons. Yet the cultured neurons were able to differentiate and form neuronal networks and neuro- filaments. Single-neuron gene expression fingerprinting pinpointed NEFL as the most down- regulated gene in the patient neurons and provided data of intermediate filament transcript abundancy and dynamics in cultured neurons. Blocking of nonsense-mediated decay partially rescued the loss of NEFL mRNA. Conclusions The strict neuronal specificity of neurofilament has hindered the mechanistic studies of re- cessive NEFL nonsense mutations. Here, we show that such mutation leads to the absence of NEFL, causing childhood-onset neuropathy through a loss-of-function mechanism. -

Effects of Activation of the LINE-1 Antisense Promoter on the Growth of Cultured Cells
www.nature.com/scientificreports OPEN Efects of activation of the LINE‑1 antisense promoter on the growth of cultured cells Tomoyuki Honda1*, Yuki Nishikawa1, Kensuke Nishimura1, Da Teng1, Keiko Takemoto2 & Keiji Ueda1 Long interspersed element 1 (LINE‑1, or L1) is a retrotransposon that constitutes ~ 17% of the human genome. Although ~ 6000 full‑length L1s spread throughout the human genome, their biological signifcance remains undetermined. The L1 5′ untranslated region has bidirectional promoter activity with a sense promoter driving L1 mRNA production and an antisense promoter (ASP) driving the production of L1‑gene chimeric RNAs. Here, we stimulated L1 ASP activity using CRISPR‑Cas9 technology to evaluate its biological impacts. Activation of the L1 ASP upregulated the expression of L1 ASP‑driven ORF0 and enhanced cell growth. Furthermore, the exogenous expression of ORF0 also enhanced cell growth. These results indicate that activation of L1 ASP activity fuels cell growth at least through ORF0 expression. To our knowledge, this is the frst report demonstrating the role of the L1 ASP in a biological context. Considering that L1 sequences are desilenced in various tumor cells, our results indicate that activation of the L1 ASP may be a cause of tumor growth; therefore, interfering with L1 ASP activity may be a potential strategy to suppress the growth. Te human genome contains many transposable element-derived sequences, such as endogenous retroviruses and long interspersed element 1 (LINE-1, or L1). L1 is one of the major classes of retrotransposons, and it constitutes ~ 17% of the human genome1. Full-length L1 consists of a 5′ untranslated region (UTR), two open reading frames (ORFs) that encode the proteins ORF1p and ORF2p, and a 3′ UTR with a polyadenylation signal. -

Integrating Single-Step GWAS and Bipartite Networks Reconstruction Provides Novel Insights Into Yearling Weight and Carcass Traits in Hanwoo Beef Cattle
animals Article Integrating Single-Step GWAS and Bipartite Networks Reconstruction Provides Novel Insights into Yearling Weight and Carcass Traits in Hanwoo Beef Cattle Masoumeh Naserkheil 1 , Abolfazl Bahrami 1 , Deukhwan Lee 2,* and Hossein Mehrban 3 1 Department of Animal Science, University College of Agriculture and Natural Resources, University of Tehran, Karaj 77871-31587, Iran; [email protected] (M.N.); [email protected] (A.B.) 2 Department of Animal Life and Environment Sciences, Hankyong National University, Jungang-ro 327, Anseong-si, Gyeonggi-do 17579, Korea 3 Department of Animal Science, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord 88186-34141, Iran; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +82-31-670-5091 Received: 25 August 2020; Accepted: 6 October 2020; Published: 9 October 2020 Simple Summary: Hanwoo is an indigenous cattle breed in Korea and popular for meat production owing to its rapid growth and high-quality meat. Its yearling weight and carcass traits (backfat thickness, carcass weight, eye muscle area, and marbling score) are economically important for the selection of young and proven bulls. In recent decades, the advent of high throughput genotyping technologies has made it possible to perform genome-wide association studies (GWAS) for the detection of genomic regions associated with traits of economic interest in different species. In this study, we conducted a weighted single-step genome-wide association study which combines all genotypes, phenotypes and pedigree data in one step (ssGBLUP). It allows for the use of all SNPs simultaneously along with all phenotypes from genotyped and ungenotyped animals. Our results revealed 33 relevant genomic regions related to the traits of interest. -

Primary Structure of Tektin Al
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 89, pp. 8567-8571, September 1992 Cell Biology Primary structure of tektin Al: Comparison with intermediate- filament proteins and a model for its association with tubulin (basal body/centriole/dlia/flageila/microtubule) J. M. NORRANDER*, L. A. AMOSt, AND R. W. LINCK* *Department of Cell Biology and Neuroanatomy, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455; and tLaboratory of Molecular Biology, Medical Research Center, Hills Road, Cambridge, CB2 2QH, United Kingdom Communicated by M. F. Perutz, May 19, 1992 (receivedfor review January 22, 1992) ABSTRACT Tektins are proteins that form rilamentous MATERIALS AND METHODS polymers in the walls of ciliary and flagellar microtubules and that have biochemical and immunological properties similar to S. purpuratus gametes were collected, handled, and cultured those of intermediate-filament proteins. We report here the at 16'C, as described (14). At desired times, aliquots of sequence of a cDNA for tektin Al, one of the main tektins from eggs/embryos were isolated and frozen in liquid N2. Total Strongylocentrotus purpuratus sea urchin embryos. By hybrid- RNA and poly(A)+ mRNA were isolated (15). A Agtll cDNA ization analysis, tektin A mRNA appears maximally at cilio- expression library, constructed from blastulae (gift of T. L. genesis. The predicted structure of tektin Al (Mr 52,955) is a Thomas, Texas A & M, College Station, TX), was screened series of a-helical rod segments separated by nonhelical link- with polyclonal antibodies (16) against S. purpuratus sperm ers. The two halves of the rod appear homologous and are flagellar tektin A (11). The largest clone isolated, tekA10-2, probably related by gene duplication. -

Microtubule-Associated Protein Tau (Molecular Pathology/Neurodegenerative Disease/Neurofibriliary Tangles) M
Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 85, pp. 4051-4055, June 1988 Medical Sciences Cloning and sequencing of the cDNA encoding a core protein of the paired helical filament of Alzheimer disease: Identification as the microtubule-associated protein tau (molecular pathology/neurodegenerative disease/neurofibriliary tangles) M. GOEDERT*, C. M. WISCHIK*t, R. A. CROWTHER*, J. E. WALKER*, AND A. KLUG* *Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QH, United Kingdom; and tDepartment of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge Clinical School, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2QQ, United Kingdom Contributed by A. Klug, March 1, 1988 ABSTRACT Screening of cDNA libraries prepared from (21). This task is made all the more difficult because there is the frontal cortex ofan zheimer disease patient and from fetal no functional or physiological assay for the protein(s) of the human brain has led to isolation of the cDNA for a core protein PHF. The only identification so far possible is the morphol- of the paired helical fiament of Alzheimer disease. The partial ogy of the PHFs at the electron microscope level, and here amino acid sequence of this core protein was used to design we would accept only experiments on isolated individual synthetic oligonucleotide probes. The cDNA encodes a protein of filaments, not on neurofibrillary tangles (in which other 352 amino acids that contains a characteristic amino acid repeat material might be occluded). One thus needs a label or marker in its carboxyl-terminal half. This protein is highly homologous for the PHF itself, which can at the same time be used to to the sequence ofthe mouse microtubule-assoiated protein tau follow the steps of the biochemical purification. -

Neurofilaments: Neurobiological Foundations for Biomarker Applications
Neurofilaments: neurobiological foundations for biomarker applications Arie R. Gafson1, Nicolas R. Barthelmy2*, Pascale Bomont3*, Roxana O. Carare4*, Heather D. Durham5*, Jean-Pierre Julien6,7*, Jens Kuhle8*, David Leppert8*, Ralph A. Nixon9,10,11,12*, Roy Weller4*, Henrik Zetterberg13,14,15,16*, Paul M. Matthews1,17 1 Department of Brain Sciences, Imperial College, London, UK 2 Department of Neurology, Washington University School of Medicine, St Louis, MO, USA 3 a ATIP-Avenir team, INM, INSERM , Montpellier university , Montpellier , France. 4 Clinical Neurosciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Southampton, Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, United Kingdom 5 Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Montreal, Québec, Canada 6 Department of Psychiatry and Neuroscience, Laval University, Quebec, Canada. 7 CERVO Brain Research Center, 2601 Chemin de la Canardière, Québec, QC, G1J 2G3, Canada 8 Neurologic Clinic and Policlinic, Departments of Medicine, Biomedicine and Clinical Research, University Hospital Basel, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland. 9 Center for Dementia Research, Nathan Kline Institute, Orangeburg, NY, 10962, USA. 10Departments of Psychiatry, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, 10016, 11 Neuroscience Institute, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, 10016, USA. 12Department of Cell Biology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, 10016, USA 13 University College London Queen Square Institute of Neurology, London, UK 14 UK Dementia Research Institute at University College London 15 Department of Psychiatry and Neurochemistry, Institute of Neuroscience and Physiology, the Sahlgrenska Academy at the University of Gothenburg, Mölndal, Sweden 16 Clinical Neurochemistry Laboratory, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Mölndal, Sweden 17 UK Dementia Research Institute at Imperial College, London * Co-authors ordered alphabetically Address for correspondence: Prof.