Linux Command-Line Cheat Sheet
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Unix Command Line; Editors
Unix command line; editors Karl Broman Biostatistics & Medical Informatics, UW–Madison kbroman.org github.com/kbroman @kwbroman Course web: kbroman.org/AdvData My goal in this lecture is to convince you that (a) command-line-based tools are the things to focus on, (b) you need to choose a powerful, universal text editor (you’ll use it a lot), (c) you want to be comfortable and skilled with each. For your work to be reproducible, it needs to be code-based; don’t touch that mouse! Windows vs. Mac OSX vs. Linux Remote vs. Not 2 The Windows operating system is not very programmer-friendly. Mac OSX isn’t either, but under the hood, it’s just unix. Don’t touch the mouse! Open a terminal window and start typing. I do most of my work directly on my desktop or laptop. You might prefer to work remotely on a server, instead. But I can’t stand having any lag in looking at graphics. If you use Windows... Consider Git Bash (or Cygwin) or turn on the Windows subsystem for linux 3 Cygwin is an effort to get Unix command-line tools in Windows. Git Bash combines git (for version control) and bash (the unix shell); it’s simpler to deal with than Cygwin. Linux is now accessible in Windows 10, but you have to enable it. If you use a Mac... Consider Homebrew and iTerm2 Also the XCode command line tools 4 Homebrew is a packaging system; iTerm2 is a Terminal replacement. The XCode command line tools are a must for most unixy things on a Mac. -

Linux Tutorial Last Updated: September 29 2021 for Windows Users
VLAAMS SUPERCOMPUTER Innovative Computing CENTRUM for A Smarter Flanders Linux Tutorial Last updated: September 29 2021 For Windows Users Authors: Jasper Devreker (UGent), Ewan Higgs (UGent), Kenneth Hoste (UGent) Acknowledgement: VSCentrum.be Audience: This document is a hands-on guide for using the Linux command line in the context of the UGent HPC infrastructure. The command line (sometimes called ’shell’) can seems daunting at first, but with a little understanding can be very easy to use. Everything you do startsatthe prompt. Here you have the liberty to type in any commands you want. Soon, you will be able to move past the limited point and click interface and express interesting ideas to the computer using the shell. Gaining an understanding of the fundamentals of Linux will help accelerate your research using the HPC infrastructure. You will learn about commands, managing files, and some scripting basics. Notification: In$ commands this tutorial specific commands are separated from the accompanying text: These should be entered by the reader at a command line in a terminal on the UGent-HPC. They appear in all exercises preceded by a $ and printed in bold. You’ll find those actions ina grey frame. Button are menus, buttons or drop down boxes to be pressed or selected. “Directory” is the notation for directories (called “folders” in Windows terminology) or specific files. (e.g., “/user/home/gent/vsc400/vsc40000”) “Text” Is the notation for text to be entered. Tip: A “Tip” paragraph is used for remarks or tips. They can also be downloaded from the VSC website at https://www.vscentrum.be. -

Unix/Linux Command Reference
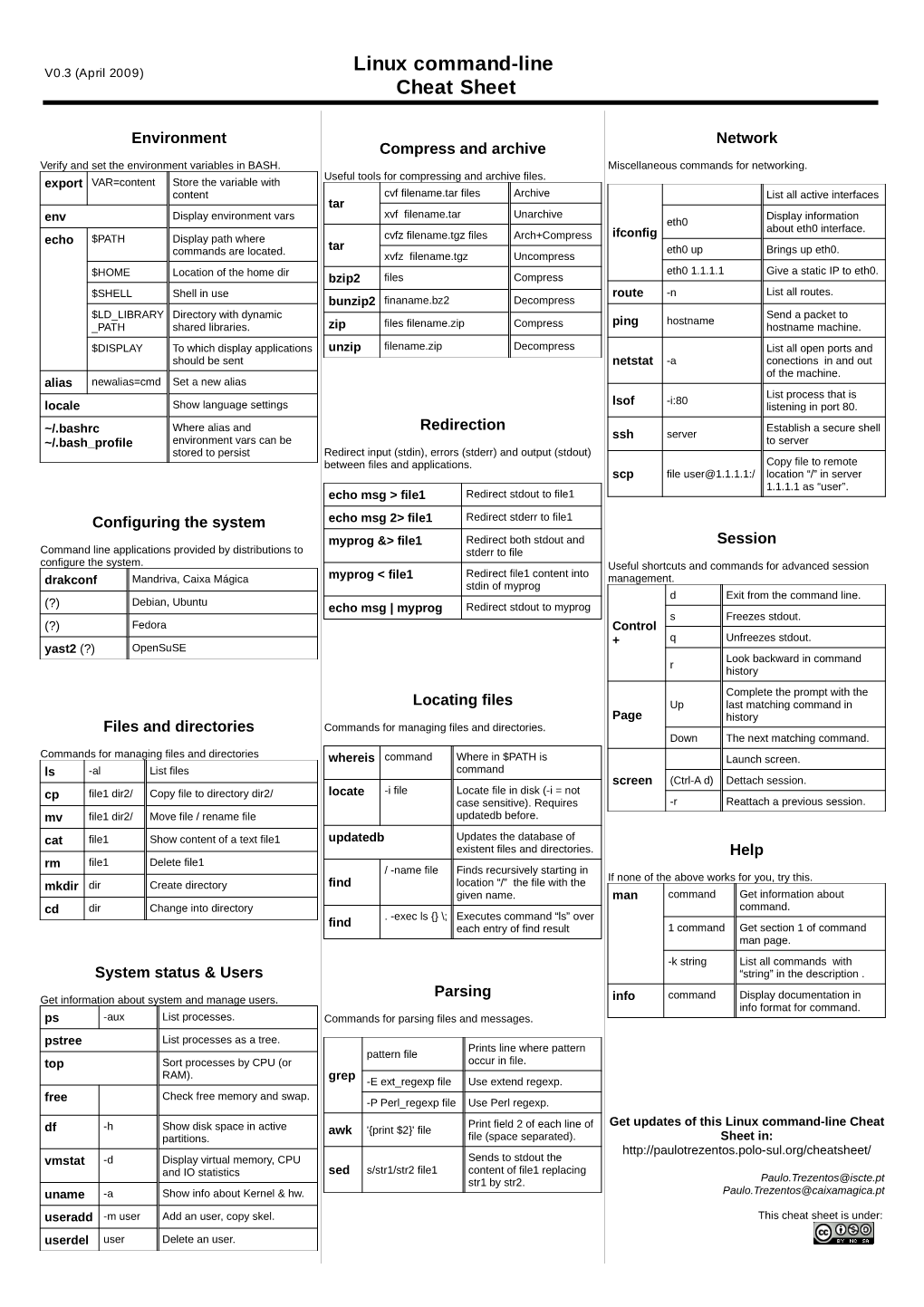
Unix/Linux Command Reference .com File Commands System Info ls – directory listing date – show the current date and time ls -al – formatted listing with hidden files cal – show this month's calendar cd dir - change directory to dir uptime – show current uptime cd – change to home w – display who is online pwd – show current directory whoami – who you are logged in as mkdir dir – create a directory dir finger user – display information about user rm file – delete file uname -a – show kernel information rm -r dir – delete directory dir cat /proc/cpuinfo – cpu information rm -f file – force remove file cat /proc/meminfo – memory information rm -rf dir – force remove directory dir * man command – show the manual for command cp file1 file2 – copy file1 to file2 df – show disk usage cp -r dir1 dir2 – copy dir1 to dir2; create dir2 if it du – show directory space usage doesn't exist free – show memory and swap usage mv file1 file2 – rename or move file1 to file2 whereis app – show possible locations of app if file2 is an existing directory, moves file1 into which app – show which app will be run by default directory file2 ln -s file link – create symbolic link link to file Compression touch file – create or update file tar cf file.tar files – create a tar named cat > file – places standard input into file file.tar containing files more file – output the contents of file tar xf file.tar – extract the files from file.tar head file – output the first 10 lines of file tar czf file.tar.gz files – create a tar with tail file – output the last 10 lines -

Powerview Command Reference
PowerView Command Reference TRACE32 Online Help TRACE32 Directory TRACE32 Index TRACE32 Documents ...................................................................................................................... PowerView User Interface ............................................................................................................ PowerView Command Reference .............................................................................................1 History ...................................................................................................................................... 12 ABORT ...................................................................................................................................... 13 ABORT Abort driver program 13 AREA ........................................................................................................................................ 14 AREA Message windows 14 AREA.CLEAR Clear area 15 AREA.CLOSE Close output file 15 AREA.Create Create or modify message area 16 AREA.Delete Delete message area 17 AREA.List Display a detailed list off all message areas 18 AREA.OPEN Open output file 20 AREA.PIPE Redirect area to stdout 21 AREA.RESet Reset areas 21 AREA.SAVE Save AREA window contents to file 21 AREA.Select Select area 22 AREA.STDERR Redirect area to stderr 23 AREA.STDOUT Redirect area to stdout 23 AREA.view Display message area in AREA window 24 AutoSTOre .............................................................................................................................. -

Checkpointing Under Linux with Berkeley Lab Checkpoint/Restart
N1GE6 Checkpointing and Berkeley Lab Checkpoint/Restart Liang PENG Lip Kian NG N1GE6 Checkpointing and Berkeley Lab Checkpoint/Restart Liang PENG Lip Kian NG APSTC-TB-2004-005 Abstract: N1GE6, formerly known as Sun Grid Engine, is widely used in HPTC environment for efficient utilization of compute resources. As applications in such environment are generally compute intensive, fault tolerance is required to minimize the impact of hardware failure. N1GE6 has several fault tolerance features and in this report, the focus will be on the checkpointing support and the integration of Berkeley Lab Checkpoint/Restart will be used as an example. Keywords: checkpoint, Grid Engine, blcr Email Address: [email protected] [email protected] Revision History Version Date Comments 1.1 Jul 14, 2004 1.2 Dec 28, 2004 Feedback from Reuti (reuti__at__staff.uni-marburg.de) • Transparent interface is user-level (Table 1). • Update to state diagram (Illustration 2). N1GE6 Checkpointing and Berkeley Lab Checkpoint/Restart Liang PENG Lip Kian NG Asia Pacific Science and Technology Center Sun Microsystems Pte Ltd, Singapore Introduction Checkpointing is the process of writing out the state information of a running application to physical storage periodically. With this feature, an application will be able to restart from the last checkpointed state instead of from the beginning which would have been computationally expensive in HPTC environment. In general, checkpointing tools can be classified into 2 different classes: • Kernel-level – Such tools are built into the kernel of the operating system. During a checkpoint, the entire process space (which tends to be huge) is written to physical storage. -

Lab Intro to Console Commands
New Lab Intro to KDE Terminal Konsole After completing this lab activity the student will be able to; Access the KDE Terminal Konsole and enter basic commands. Enter commands using a typical command line interface (CLI). Explain the use of the following commands, ls, ls –al, dir, mkdir, whoami, Explain the directory structure of a typical user. This lab activity will introduce you to one of the many command line interfaces available in Linux/UNIX operating systems and a few of the most basic commands. The command line interface you will be using for this lab activity is the console called the Konsole and is also referred to as Terminal. Note: As you notice, in the KDE system many features are written with the capital letter “K” in place of the first letter or the utility to reflect the fact it was modified for the KDE system. The original UNIX system did not use a graphical user interface GUI but rather was a command line interface (CLI) similar to the command prompt in Windows operating systems. The command line interface is referred to as a shell. Even today the command line interface (the shell) is used to issue commands on a Linux server to minimize system resources. For example, there is no need to start the GUI on the server to add a new user to an existing system. Starting the GUI will reduce the system performance because it requires RAM to run the GUI. A GUI will affect the overall performance of the server when it is supporting many users (clients). -

A Brief Introduction to Unix-2019-AMS
A Brief Introduction to Linux/Unix – AMS 2019 Pete Pokrandt UW-Madison AOS Systems Administrator [email protected] Twitter @PTH1 Brief Intro to Linux/Unix o Brief History of Unix o Basics of a Unix session o The Unix File System o Working with Files and Directories o Your Environment o Common Commands Brief Intro to Unix (contd) o Compilers, Email, Text processing o Image Processing o The vi editor History of Unix o Created in 1969 by Kenneth Thompson and Dennis Ritchie at AT&T o Revised in-house until first public release 1977 o 1977 – UC-Berkeley – Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) o 1983 – Sun Workstations produced a Unix Workstation o AT&T unix -> System V History of Unix o Today – two main variants, but blended o System V (Sun Solaris, SGI, Dec OSF1, AIX, linux) o BSD (Old SunOS, linux, Mac OSX/MacOS) History of Unix o It’s been around for a long time o It was written by computer programmers for computer programmers o Case sensitive, mostly lowercase abbreviations Basics of a Unix Login Session o The Shell – the command line interface, where you enter commands, etc n Some common shells Bourne Shell (sh) C Shell (csh) TC Shell (tcsh) Korn Shell (ksh) Bourne Again Shell (bash) [OSX terminal] Basics of a Unix Login Session o Features provided by the shell n Create an environment that meets your needs n Write shell scripts (batch files) n Define command aliases n Manipulate command history n Automatically complete the command line (tab) n Edit the command line (arrow keys in tcsh) Basics of a Unix Login Session o Logging in to a unix -

SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 System Analysis and Tuning Guide System Analysis and Tuning Guide SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 System Analysis and Tuning Guide System Analysis and Tuning Guide SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 SP4 Publication Date: September 24, 2021 SUSE LLC 1800 South Novell Place Provo, UT 84606 USA https://documentation.suse.com Copyright © 2006– 2021 SUSE LLC and contributors. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or (at your option) version 1.3; with the Invariant Section being this copyright notice and license. A copy of the license version 1.2 is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”. For SUSE trademarks, see http://www.suse.com/company/legal/ . All other third party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. A trademark symbol (®, ™ etc.) denotes a SUSE or Novell trademark; an asterisk (*) denotes a third party trademark. All information found in this book has been compiled with utmost attention to detail. However, this does not guarantee complete accuracy. Neither SUSE LLC, its aliates, the authors nor the translators shall be held liable for possible errors or the consequences thereof. Contents About This Guide xi 1 Available Documentation xii 2 Feedback xiv 3 Documentation Conventions xv I BASICS 1 1 General Notes on System Tuning 2 1.1 Be Sure What Problem to Solve 2 1.2 Rule Out Common Problems 3 1.3 Finding the Bottleneck 3 1.4 Step-by-step Tuning 4 II SYSTEM MONITORING 5 2 System Monitoring Utilities 6 2.1 Multi-Purpose Tools 6 vmstat 7 -

Introduction to UNIX Summary of Some Useful Commands
Introduction to UNIX "...the number of UNIX installations has grown to 10, with more expected..." - Dennis Ritchie and Ken Thompson, June 1972 (Bell Lab.) Universities, research institutes, government bodies and computer companies all began using the powerful UNIX system to develop many of the technologies which today are part of a UNIX system. Guide to UNIX on the beginners level: http://www.ee.surrey.ac.uk/Teaching/Unix/ Summary of some useful commands: Some basic UNIX commands cd directory_name change to the directory directory_name cd .. change to the directory above the current directory cd ~ change to the home directory cp file_1 file_2 copy the file file_1 to the file file_2 ln –s source linkname link the file with the name source to the file linkname ls directory_name show the content of the directory directory_name ls –l directory_name show in detail the content of the directory directory_name ls –a directory_name show all files including hidden files of the directory directory_name mkdir directory_name create the new directory directory_name less file_name show the content of the file file_name tail file_name show the last part of a file file_name head file_name show the top part of a file file_name (x)emacs file_name edit the file file_name using the editor xemacs mv file_1 to file_2 change the filename file_1 to file_2 rm –i file_name remove the file file_name (the system asks for confirmation) rm –ri directory_name remove all files recursive in the directory directory_name rmdir directory_name remove the directory directory_name -

College Holiday : May 24
Sp21 CIS -18A-41Z: Introduction to Linux/Unix Midterm ONE: Apr 28, Midterm TWO: May 26 , Finals: Jun 21 CENSUS DATE: Apr 19 College Holiday : May 24 Assignment Due dates : Apr 12,19,26, May 3,10,17,25,31, Jun 7,14 No Makeups for any of the above. If you miss, you lose points. Plan accordingly. (Zoom, synchronous M/W, 6PM - 7 PM - Window ) (See http://www.deanza.edu/calendar/finalexams.html) Instructor communicates with student ONLY. • Zoom lectures attendance is not mandatory. Sessions will be recorded and shared in Canvas. • Students need to take midterms and finals -in-the-alloted-time-date. If student does not show up for midterm/finals then 0 points. • FINALS will be on Jun 21, via CANVAS. All times PDT. • If you have questions on assignment grade, email me and we will discuss and resolve it. Any feedback about your work is going to be via email M/W 6 thru 750PM • Do not use Shell programming/Sed/Awk/Perl/Python/Posix expressions for this class in your assignments. Stick to Syllabus. Refer to CANVAS for assignments ! College academic Calendar:Spring 2021 http://deanza.fhda.edu/calendar/springdates.html Instructor Information • Name: Lalitha Krishnamurthy • Email: krishnamurthylalitha at fhda dot edu • Email only in canvas please. • Online Lab Hours: Wednesdays 845pm - 10pm (via Canvas) • Office Hours: Available via synchronous zoom: Mondays 830-930pm PDT. • Lecture timings for CIS18A : M/W 6 PM - 750 PM - Online/Zoom via CANVAS Students, please read the following and plan accordingly • All communication with instructor is via Canvas for assignments and quizzes. -

System Analysis and Tuning Guide System Analysis and Tuning Guide SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 System Analysis and Tuning Guide System Analysis and Tuning Guide SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1 An administrator's guide for problem detection, resolution and optimization. Find how to inspect and optimize your system by means of monitoring tools and how to eciently manage resources. Also contains an overview of common problems and solutions and of additional help and documentation resources. Publication Date: September 24, 2021 SUSE LLC 1800 South Novell Place Provo, UT 84606 USA https://documentation.suse.com Copyright © 2006– 2021 SUSE LLC and contributors. All rights reserved. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or (at your option) version 1.3; with the Invariant Section being this copyright notice and license. A copy of the license version 1.2 is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”. For SUSE trademarks, see https://www.suse.com/company/legal/ . All other third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Trademark symbols (®, ™ etc.) denote trademarks of SUSE and its aliates. Asterisks (*) denote third-party trademarks. All information found in this book has been compiled with utmost attention to detail. However, this does not guarantee complete accuracy. Neither SUSE LLC, its aliates, the authors nor the translators shall be held liable for possible errors or the consequences thereof. Contents About This Guide xii 1 Available Documentation xiii -

Introduction to Unix Part I: the Essentials
Introduction to Unix Part I: The Essentials Frederick J Tan Bioinformatics Research Faculty Carnegie Institution of Washington, Department of Embryology 9 April 2013 Unix, Linux, Ubuntu, Oh My! 2 A Three Hour Tour Part I: The Essentials client-server model, command-line interface, navigation, viewing files, searching, finding help Part II: Special Topics account settings, multi-tasking, programming, installing programs, file systems, system administration 3 The Awesome Power of the Client-Server Model 4 A Tale of Two Interfaces Command Line Graphical Terminal.app, Unix shell Finder.app, Galaxy breadth, cutting-edge discovery, visualization 5 Running Programs Using the Command-Line Interface command-line graphical type in the name of the to run a program program and hit <ENTER> double click on an icon (e.g. bowtie2) type in options after the program, to modify how a click on check boxes, before hitting <ENTER> program operates select from pull-down menus (e.g. bowtie2 --very-sensitive) 6 The Anatomy of a Shell Prompt workshop@ubuntu:~$ The text in between the colon (:) The $ symbol indicates The symbol and the dollar sign ($) indicates that the server is ready to indicates where what what directory you are in. perform a command. you type in will appear. /home/workshop$ $ ssh [email protected] 7 Task 1: Connect to your server and start top with -i option Start VirtualBox Start Ubuntu Secure SHell $ ssh [email protected] <ENTER> <SPACE> Shell Prompt /home/workshop$ <TAB> Start top -i $ top -i <CTRL> <UP> <DOWN> 8 Task 2: Figure