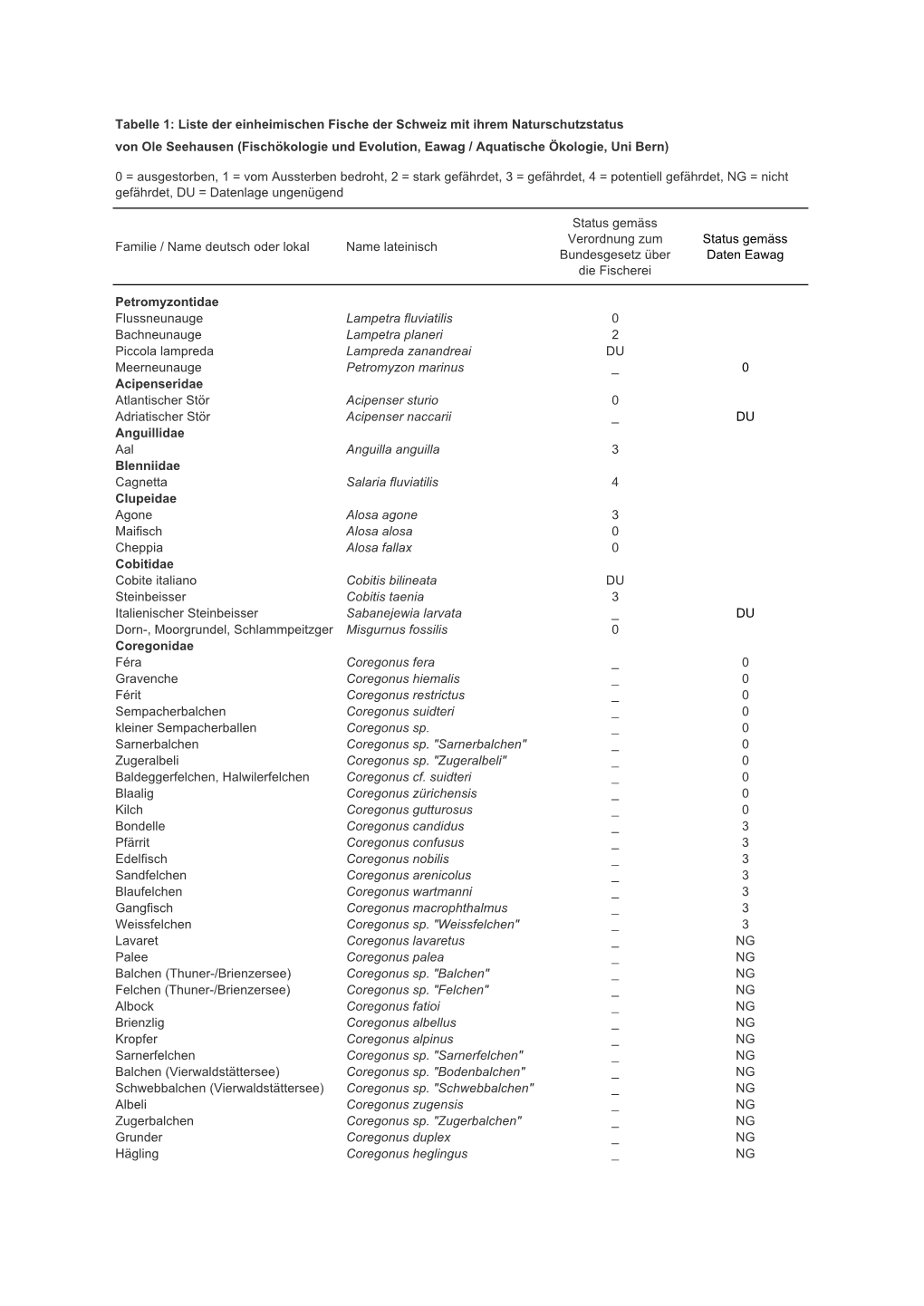
Artenliste Schweizer Fische
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

(Coregonus Lavaretus (L.)) Caused by Competitor Invasion
Speciation Reversal in European Whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus (L.)) Caused by Competitor Invasion Shripathi Bhat1*, Per-Arne Amundsen1, Rune Knudsen1, Karl Øystein Gjelland3, Svein-Erik Fevolden1, Louis Bernatchez2, Kim Præbel1 1 Department of Arctic and Marine Biology, University of Tromsø, Tromsø, Norway, 2 Institut de Biologie Inte´grative et des Syste`mes (IBIS), Universite´ Laval, Que´bec, Canada, 3 Norwegian Institute for Nature Research, Tromsø, Norway Abstract Invasion of exotic species has caused the loss of biodiversity and imparts evolutionary and ecological changes in the introduced systems. In northern Fennoscandia, European whitefish (Coregonus lavaretus (L.)) is a highly polymorphic species displaying adaptive radiations into partially reproductively isolated and thus genetically differentiated sympatric morphs utilizing the planktivorous and benthivorous food niche in many lakes. In 1993, Lake Skrukkebukta was invaded by vendace (Coregonus albula (L.)) which is a zooplanktivorous specialist. The vendace displaced the densely rakered whitefish from its preferred pelagic niche to the benthic habitat harbouring the large sparsely rakered whitefish. In this study, we investigate the potential influence of the vendace invasion on the breakdown of reproductive isolation between the two whitefish morphs. We inferred the genotypic and phenotypic differentiation between the two morphs collected at the arrival (1993) and 15 years after (2008) the vendace invasion using 16 microsatellite loci and gill raker numbers, the most distinctive adaptive phenotypic trait between them. The comparison of gill raker number distributions revealed two modes growing closer over 15 years following the invasion. Bayesian analyses of genotypes revealed that the two genetically distinct whitefish morphs that existed in 1993 had collapsed into a single population in 2008. -

First Record of a Coregonid Fish Species, Coregenus Albula (Linnaeus, 1758) (Salmoniformes: Salmonidae) in Aktaş Lake Shared Between Turkey and Georgia
J. Black Sea/Mediterranean Environment Vol. 25, No. 3: 325-332 (2019) SHORT COMMUNICATION First record of a coregonid fish species, Coregenus albula (Linnaeus, 1758) (Salmoniformes: Salmonidae) in Aktaş Lake shared between Turkey and Georgia Sedat V. Yerli Department of Biology, Hacettepe University, SAL, Beytepe, Ankara, TURKEY Corresponding author: [email protected] Abstract The genus Coregenus (Salmoniformes: Salmonidae) was recently considered not to be represented in Turkey. European cisco or vendace, Coregonus albula (Linnaeus, 1758) was reported for the first time for Turkey in this article with fifteen samples in Aktaş Lake, Ardahan. This species should be added to the checklist of Turkish fish fauna. Turkish name is proposed as “Akbalık” for this species. Keywords: Coregonus albula, first record, Aktaş Lake, Kartsakhi, alkaline lake, Georgia, Turkey Received: 30.10.2019, Accepted: 26.11.2019 Vendace or European cisco Coregonus albula (Linnaeus, 1758) is a native species for northern Europe. Berg (1948) reported the distribution of this species its morphological measurements in the former USSR and adjacent countries. Froese and Pauly (2019) summarized the natural distribution of vendace as Baltic basin, several lakes of upper Volga drainage; some lakes of White Sea basin and North Sea basin east of Elbe drainage; anadromous in Gulf of Finland and marine in northernmost freshened part of Gulf of Bothnia between Finland and Sweden; in Lake Inari, northern Finland; lower Rhine (now extirpated). The vendace was introduced, intentionally in some countries in Europe and United States of America. Vendace was introduced in 1959, 1982-1987 in the Irtysh River Basin and in 1960-61 in Lake Balkhash in Kazakhstan (Mitrofanov and Petr 1999). -

Coregonus Lavaretus Complex 1.4 Alternative Species Scientific Name 1.5 Common Name (In National Language) Whitefish 2
European Community Directive on the Conservation of Natural Habitats and of Wild Fauna and Flora (92/43/EEC) Fourth Report by the United Kingdom under Article 17 on the implementation of the Directive from January 2013 to December 2018 Supporting documentation for the conservation status assessment for the species: S6353 ‐ WhitefishCoregonus ( lavaretus) SCOTLAND IMPORTANT NOTE ‐ PLEASE READ • The information in this document is a country‐level contribution to the UK Reporton the conservation status of this species, submitted to the European Commission aspart of the 2019 UK Reporting under Article 17 of the EU Habitats Directive. • The 2019 Article 17 UK Approach document provides details on how this supporting information was used to produce the UK Report. • The UK Report on the conservation status of this species is provided in a separate doc‐ ument. • The reporting fields and options used are aligned to those set out in the European Com‐ mission guidance. • Explanatory notes (where provided) by the country are included at the end. These pro‐ vide an audit trail of relevant supporting information. • Some of the reporting fields have been left blank because either: (i) there was insuffi‐ cient information to complete the field; (ii) completion of the field was not obligatory; (iii) the field was not relevant to this species (section 12 Natura 2000 coverage forAnnex II species) and/or (iv) the field was only relevant at UK‐level (sections 9 Future prospects and 10 Conclusions). • For technical reasons, the country‐level future trends for Range, Population and Habitat for the species are only available in a separate spreadsheet that contains all the country‐ level supporting information. -

Lake Superior Food Web MENT of C
ATMOSPH ND ER A I C C I A N D A M E I C N O I S L T A R N A T O I I O T N A N U E .S C .D R E E PA M RT OM Lake Superior Food Web MENT OF C Sea Lamprey Walleye Burbot Lake Trout Chinook Salmon Brook Trout Rainbow Trout Lake Whitefish Bloater Yellow Perch Lake herring Rainbow Smelt Deepwater Sculpin Kiyi Ruffe Lake Sturgeon Mayfly nymphs Opossum Shrimp Raptorial waterflea Mollusks Amphipods Invasive waterflea Chironomids Zebra/Quagga mussels Native waterflea Calanoids Cyclopoids Diatoms Green algae Blue-green algae Flagellates Rotifers Foodweb based on “Impact of exotic invertebrate invaders on food web structure and function in the Great Lakes: NOAA, Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory, 4840 S. State Road, Ann Arbor, MI A network analysis approach” by Mason, Krause, and Ulanowicz, 2002 - Modifications for Lake Superior, 2009. 734-741-2235 - www.glerl.noaa.gov Lake Superior Food Web Sea Lamprey Macroinvertebrates Sea lamprey (Petromyzon marinus). An aggressive, non-native parasite that Chironomids/Oligochaetes. Larval insects and worms that live on the lake fastens onto its prey and rasps out a hole with its rough tongue. bottom. Feed on detritus. Species present are a good indicator of water quality. Piscivores (Fish Eaters) Amphipods (Diporeia). The most common species of amphipod found in fish diets that began declining in the late 1990’s. Chinook salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha). Pacific salmon species stocked as a trophy fish and to control alewife. Opossum shrimp (Mysis relicta). An omnivore that feeds on algae and small cladocerans. -

Coregonus Maraena) Ecological Risk Screening Summary
Maraena Whitefish (Coregonus maraena) Ecological Risk Screening Summary U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, April 2011 Revised, September 2014 and June 2017 Web Version, 09/14/2017 Image: E. Östman. Public domain. Available: http://eol.org/data_objects/26779416. (June 2017). 1 Native Range, and Status in the United States Native Range From Froese and Pauly (2017): “Europe: In the Baltic Sea: Swedish coast (including Bothnian Gulf, not in Gotland); in southern Baltic, extending from the Schlei to Gulf of Finland. Southeast North Sea Basin: Ems, Weser and Elbe drainages 1 and small rivers of Schleswig-Holstein and Denmark. Landlocked in several lakes in Poland, Sweden, and Russia.” Status in the United States From Neilson (2017): “Failed introduction.” “A shipment of 409 individuals from Lake Miedwie (formerly Madue Lake), Poland was stocked in Garnder Lake, Michigan in 1877 (Baird 1879; Todd 1983).” Means of Introductions in the United States From Neilson (2017): “Coregonus maraena, along with other species of Coregonus, was intentionally stocked as a food fish by the U.S. Fish Commission (Todd 1983). According to Baird (1879), 1,000 eggs of C. maraena were shipped from Poland to Michigan in 1877 and hatched in captivity at the State Hatching House in Detroit. A total of 409 of the young fish were stocked in Gardner Lake (Baird 1879; Todd 1983). Baird (1879) considered the stocking an experimental introduction of a European food fish.” Remarks From Neilson (2017): “There is much confusion regarding the identity of whitefish imported from Germany in the late 1800s by the U.S. Fish Commission, primarily due to the uncertain taxonomy and systematics of Coregonus (Kottelat and Freyhof 2007). -

Identification and Modelling of a Representative Vulnerable Fish Species for Pesticide Risk Assessment in Europe
Identification and Modelling of a Representative Vulnerable Fish Species for Pesticide Risk Assessment in Europe Von der Fakultät für Mathematik, Informatik und Naturwissenschaften der RWTH Aachen University zur Erlangung des akademischen Grades eines Doktors der Naturwissenschaften genehmigte Dissertation vorgelegt von Lara Ibrahim, M.Sc. aus Mazeraat Assaf, Libanon Berichter: Universitätsprofessor Dr. Andreas Schäffer Prof. Dr. Christoph Schäfers Tag der mündlichen Prüfung: 30. Juli 2015 Diese Dissertation ist auf den Internetseiten der Universitätsbibliothek online verfügbar Erklärung Ich versichere, dass ich diese Doktorarbeit selbständig und nur unter Verwendung der angegebenen Hilfsmittel angefertigt habe. Weiterhin versichere ich, die aus benutzten Quellen wörtlich oder inhaltlich entnommenen Stellen als solche kenntlich gemacht zu haben. Lara Ibrahim Aachen, am 18 März 2015 Zusammenfassung Die Zulassung von Pflanzenschutzmitteln in der Europäischen Gemeinschaft verlangt unter anderem eine Abschätzung des Risikos für Organismen in der Umwelt, die nicht Ziel der Anwendung sind. Unvertretbare Auswirkungen auf den Naturhalt sollen vermieden werden. Die ökologische Risikoanalyse stellt die dafür benötigten Informationen durch eine Abschätzung der Exposition der Organismen und der sich daraus ergebenden Effekte bereit. Die Effektabschätzung beruht dabei hauptsächlich auf standardisierten ökotoxikologischen Tests im Labor mit wenigen, oft nicht einheimischen Stellvertreterarten. In diesen Tests werden z. B. Effekte auf das Überleben, das Wachstum und/oder die Reproduktion von Fischen bei verschiedenen Konzentrationen der Testsubstanz gemessen und Endpunkte wie die LC50 (Lethal Concentrations for 50%) oder eine NOEC (No Observed Effect Concentration, z. B. für Wachstum oder Reproduktionsparameter) abgeleitet. Für Fische und Wirbeltiere im Allgemeinen beziehen sich die spezifischen Schutzziele auf das Überleben von Individuen und die Abundanz und Biomasse von Populationen. -

Rote Liste Der Fische (Pisces) Österreichs
Rote Liste der Fische (Pisces) Österreichs Georg Wolfram, Ernst Mikschi*‡ Zusammenfassung Die vorliegende Arbeit folgt den Richtlinien zur Fortschreibung der Roten Liste gefähr- deter Tiere Österreichs (Zulka et al. 2001, Umweltbundesamt-Monographien Band 15, Wien). Die aktuelle Checkliste der Fische Österreichs umfasst 84 Taxa. Im Vergleich zur letzten Roten Liste (Spindler et al. 1997, Umweltbundesamt-Monographien Band 87, Wien) wurden einige Taxa aufgrund aktueller nomenklatorischer und taxonomischer Entwicklungen, auf die gesondert eingegangen wird, neu aufgenommen. Zwei Taxa werden als weltweit ausgestorben (Kategorie EX; Extinct) beurteilt, fünf Taxa sind regional ausgestorben (Kategorie RE; Regionally Extinct). In der Gefährdungs- kategorie „Critically Endangered“ (CR, vom Aussterben bedroht) finden sich sechs Ar- ten, 18 in der Kategorie „Endangered“ (EN; stark gefährdet) und 15 in der Kategorie „Vulnerable“ (VU; gefährdet). Neun Arten stehen auf der Vorwarnliste (Kategorie NT; Near Threatened), 17 weitere Arten, also rund ein Fünftel der aufgenommenen Taxa, sind in Österreich der Kategorie „Least Concern“ (LC; nicht gefährdet) zugeordnet. Für drei Taxa mit äußerst unsicherer taxonomischer Situation reicht die Datenlage für eine Ein- stufung nicht aus (Kategorie DD; Data Deficient). Bei weiteren neun in die Checkliste aufgenommenen Arten handelt es sich um überregional verbreitete und reproduzierende Neozoen, die explizit nicht in die Beurteilung im Rahmen der Roten Liste einbezogen werden (Kategorie NE; Not Evaluated). Aufgrund geänderter Definitionen der Gefährdungskategorien ist die vorliegende Ar- beit mit der Roten Liste von Spindler et al. (1997, Umweltbundesamt-Monographien Band 87, Wien) nur bedingt vergleichbar. Die meisten Unterschiede der Gefährdungs- einstufung sind auf methodische Änderungen oder eine geänderte Datenlage zurückzu- führen. Abstract: Red List of Endangered Fishes (Pisces) in Austria The present paper follows the guidelines for updating the Red Lists of threatened animals of Austria (Zulka et al. -

AHNELT H. 2008. Bestimmungsschlüssel Für Die In
Ahnelt H. 2008 Bestimmungsschlüssel 1 BESTIMMUNGSSCHLÜSSEL FÜR DIE IN ÖSTERREICH VORKOMMENDEN FISCHE HARALD AHNELT Department für Theoretische Biologie, Fakultät für Lebenswissenschaften, Universität Wien, Althanstrasse 14, 1090 Wien [email protected] Online: 10 September 2008 Zitiervorschlag: Ahnelt H. 2008 Bestimmungsschlüssel für die in Österreich vorkommenden Fische. http://homepage.univie.ac.at/harald.ahnelt/Harald_Ahnelts_Homepage/Publications.html [Download-Datum] Bestimmungsschlüssel heimischer Fische Dieser Bestimmungsschlüssel ist für die Fischarten Österreichs ausgelegt. Merkmale und Merkmalskombinationen können daher bei Anwendung auf Fische anderer Länder zu nicht korrekten Ergebnissen führen. Identification key for Austrian freshwater fishes This identification key should only be used for fishes from Austrian freshwaters. This key will possibly not work for fishes from other European countries. Nobody is perfect – schon gar nicht ein Bestimmungsschlüssel. Ein Bestimmungsschlüssel baut auf charakteristischen Merkmalen auf, er vereinfacht und kann keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit erheben. Auch dieser Bestimmungsschlüssel ist nur ein Versuch ein komplexes System in einen übersichtliche Form zu bringen. Die Natur sieht aber oft anders aus. Die Bandbreite an Merkmalen ist bei vielen Arten groß. Manche Populationen sind an unterschiedliche Umweltbedingungen angepasst und bilden unterscheidbare ökologische Formen. Andere Populationen sind isoliert und einige davon sind systematisch noch ungenügend erforscht. Möglicherweise taucht ja in Österreich noch die eine oder andere neue Art auf. Sollte es einmal nicht passen, oder wenn sich ein Fehler eingeschlichen hat, ersuche ich um Information - [email protected] oder unter obiger Adresse. Verbesserungsvorschläge und Ergänzungen sind willkommen. Ahnelt H. 2008 Bestimmungsschlüssel 2 Einleitung 1858 erschien das Buch „Die Süßwasserfische der Österreichischen Monarchie mit Rücksicht auf die angrenzenden Länder“, verfasst von den Österreichern Johann Jakob Heckel und Rudolf Kner. -

Genome Composition Plasticity in Marine Organisms
Genome Composition Plasticity in Marine Organisms A Thesis submitted to University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy for the degree of DOCTOR OF PHYLOSOPHY in “Applied Biology” XXVIII cycle by Andrea Tarallo March, 2016 1 University of Naples “Federico II”, Naples, Italy Research Doctorate in Applied Biology XXVIII cycle The research activities described in this Thesis were performed at the Department of Biology and Evolution of Marine Organisms, Stazione Zoologica Anton Dohrn, Naples, Italy and at the Fishery Research Laboratory, Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan from April 2013 to March 2016. Supervisor Dr. Giuseppe D’Onofrio Tutor Doctoral Coordinator Prof. Claudio Agnisola Prof. Ezio Ricca Candidate Andrea Tarallo Examination pannel Prof. Maria Moreno, Università del Sannio Prof. Roberto De Philippis, Università di Firenze Prof. Mariorosario Masullo, Università degli Studi Parthenope 2 LIST OF PUBLICATIONS 1. On the genome base composition of teleosts: the effect of environment and lifestyle A Tarallo, C Angelini, R Sanges, M Yagi, C Agnisola, G D’Onofrio BMC Genomics 17 (173) 2016 2. Length and GC Content Variability of Introns among Teleostean Genomes in the Light of the Metabolic Rate Hypothesis A Chaurasia, A Tarallo, L Bernà, M Yagi, C Agnisola, G D’Onofrio PloS one 9 (8), e103889 2014 3. The shifting and the transition mode of vertebrate genome evolution in the light of the metabolic rate hypothesis: a review L Bernà, A Chaurasia, A Tarallo, C Agnisola, G D'Onofrio Advances in Zoology Research 5, 65-93 2013 4. An evolutionary acquired functional domain confers neuronal fate specification properties to the Dbx1 transcription factor S Karaz, M Courgeon, H Lepetit, E Bruno, R Pannone, A Tarallo, F Thouzé, P Kerner, M Vervoort, F Causeret, A Pierani and G D’Onofrio EvoDevo, Submitted 5. -

Alaska Arctic Marine Fish Ecology Catalog
Prepared in cooperation with Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, Environmental Studies Program (OCS Study, BOEM 2016-048) Alaska Arctic Marine Fish Ecology Catalog Scientific Investigations Report 2016–5038 U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Cover: Photographs of various fish studied for this report. Background photograph shows Arctic icebergs and ice floes. Photograph from iStock™, dated March 23, 2011. Alaska Arctic Marine Fish Ecology Catalog By Lyman K. Thorsteinson and Milton S. Love, editors Prepared in cooperation with Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, Environmental Studies Program (OCS Study, BOEM 2016-048) Scientific Investigations Report 2016–5038 U.S. Department of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey U.S. Department of the Interior SALLY JEWELL, Secretary U.S. Geological Survey Suzette M. Kimball, Director U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, Virginia: 2016 For more information on the USGS—the Federal source for science about the Earth, its natural and living resources, natural hazards, and the environment—visit http://www.usgs.gov or call 1–888–ASK–USGS. For an overview of USGS information products, including maps, imagery, and publications, visit http://store.usgs.gov. Disclaimer: This Scientific Investigations Report has been technically reviewed and approved for publication by the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management. The information is provided on the condition that neither the U.S. Geological Survey nor the U.S. Government may be held liable for any damages resulting from the authorized or unauthorized use of this information. The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the opinions or policies of the U.S. -

Development of Larval Fish Rearing Techniques and Nutrient Requirements for the Green Mandarin, Synchiropus Splendidus: a Popular Marine Ornamental Fish
ResearchOnline@JCU This file is part of the following reference: Shao, Luchang (2016) Development of larval fish rearing techniques and nutrient requirements for the green mandarin, Synchiropus splendidus: a popular marine ornamental fish. PhD thesis, James Cook University. Access to this file is available from: http://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/47308/ The author has certified to JCU that they have made a reasonable effort to gain permission and acknowledge the owner of any third party copyright material included in this document. If you believe that this is not the case, please contact [email protected] and quote http://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/47308/ Development of larval fish rearing techniques and nutrient requirement for the green mandarin, Synchiropus splendidus: a popular marine ornamental fish Thesis submitted by Luchang Shao (MSc) in September 2016 For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy In the College of Marine and Environmental Science James Cook University Declaration on Ethics The research presented and reported in this thesis was conducted within the guidelines for research ethics outlined in the National Statement on Ethics Conduct in Research Involving Human (1999), the Joint NHMRC/AVCC Statement and Guidelines on Research Practice (1997), the James Cook University Policy on Experimentation Ethics Standard Practices and Guidelines (2001), and the James Cook University Statement and Guidelines on Research Practice (2001). The proposed research methodology received clearance from the James Cook University Experimentation Ethics Review Committee. Approval numbers: A1851; Principal investigator: Luchang Shao; Finish date: September 30, 2015 i Statement of contribution of others Financial support for this study was provided by Graduate Research School of James Cook University, JCU Postgraduate Research Scholarship. -

Age, Growth, and Size of Lake Superior Pygmy Whitefish (Prosopium Coulterii) Author(S): Taylor R
Age, Growth, and Size of Lake Superior Pygmy Whitefish (Prosopium coulterii) Author(s): Taylor R. Stewart and Derek H. OgleOwen T. Gorman and Mark R. Vinson Source: The American Midland Naturalist, 175(1):24-36. Published By: University of Notre Dame DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1674/amid-175-01-24-36.1 URL: http://www.bioone.org/doi/full/10.1674/amid-175-01-24-36.1 BioOne (www.bioone.org) is a nonprofit, online aggregation of core research in the biological, ecological, and environmental sciences. BioOne provides a sustainable online platform for over 170 journals and books published by nonprofit societies, associations, museums, institutions, and presses. Your use of this PDF, the BioOne Web site, and all posted and associated content indicates your acceptance of BioOne’s Terms of Use, available at www.bioone.org/page/terms_of_use. Usage of BioOne content is strictly limited to personal, educational, and non-commercial use. Commercial inquiries or rights and permissions requests should be directed to the individual publisher as copyright holder. BioOne sees sustainable scholarly publishing as an inherently collaborative enterprise connecting authors, nonprofit publishers, academic institutions, research libraries, and research funders in the common goal of maximizing access to critical research. Am. Midl. Nat. (2016) 175:24–36 Age, Growth, and Size of Lake Superior Pygmy Whitefish (Prosopium coulterii) 1 TAYLOR R. STEWART AND DEREK H. OGLE Department of Natural Resources, Northland College, Ashland, Wisconsin 54806 AND OWEN T. GORMAN AND MARK R. VINSON U. S. Geological Survey, Great Lakes Science Center, Lake Superior Biological Station, Ashland, Wisconsin 54806 ABSTRACT.—Pygmy Whitefish (Prosopium coulterii) are a small, glacial relict species with a disjunct distribution in North America and Siberia.