Fractured Wrist – After Surgery Information for Patients
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Wrist Fracture – Advice Following Removal of Your Cast
Wrist Fracture – advice following removal of your cast A plaster cast usually prevents a fracture from moving, but allows your fingers to move. The cast also reduces pain. What to expect It usually takes four to six weeks for new bone to form to heal your fracture. When the cast is removed most people find that their wrist is stiff, weak and uncomfortable to start with. It may also be prone to swelling and the skin dry or flaky, this is quite normal. It is normal to get some pain after your fracture. If you need painkillers you should take them as prescribed as this will allow you to do your exercises and use your wrist for light activities. You can ask a Pharmacist about over the counter painkillers. If your pain is severe, continuous or excessive you should contact your GP. The new bone gradually matures and becomes stronger over the next few months. It is likely to be tender and may hurt if you bang it. The muscles will be weak initially, but they should gradually build up as you start to use your hand and wrist. When can I start to use my hand and wrist? It is important to try and use your hand and wrist as normally as possible. Start with light activities like fastening buttons, washing your face, eating, turning the pages of books over etc. Build up as pain allows. Avoid lifting a kettle for 4 weeks If I have been given a Wrist splint You may have been given a wrist splint to wear. -

Wrist Fracture
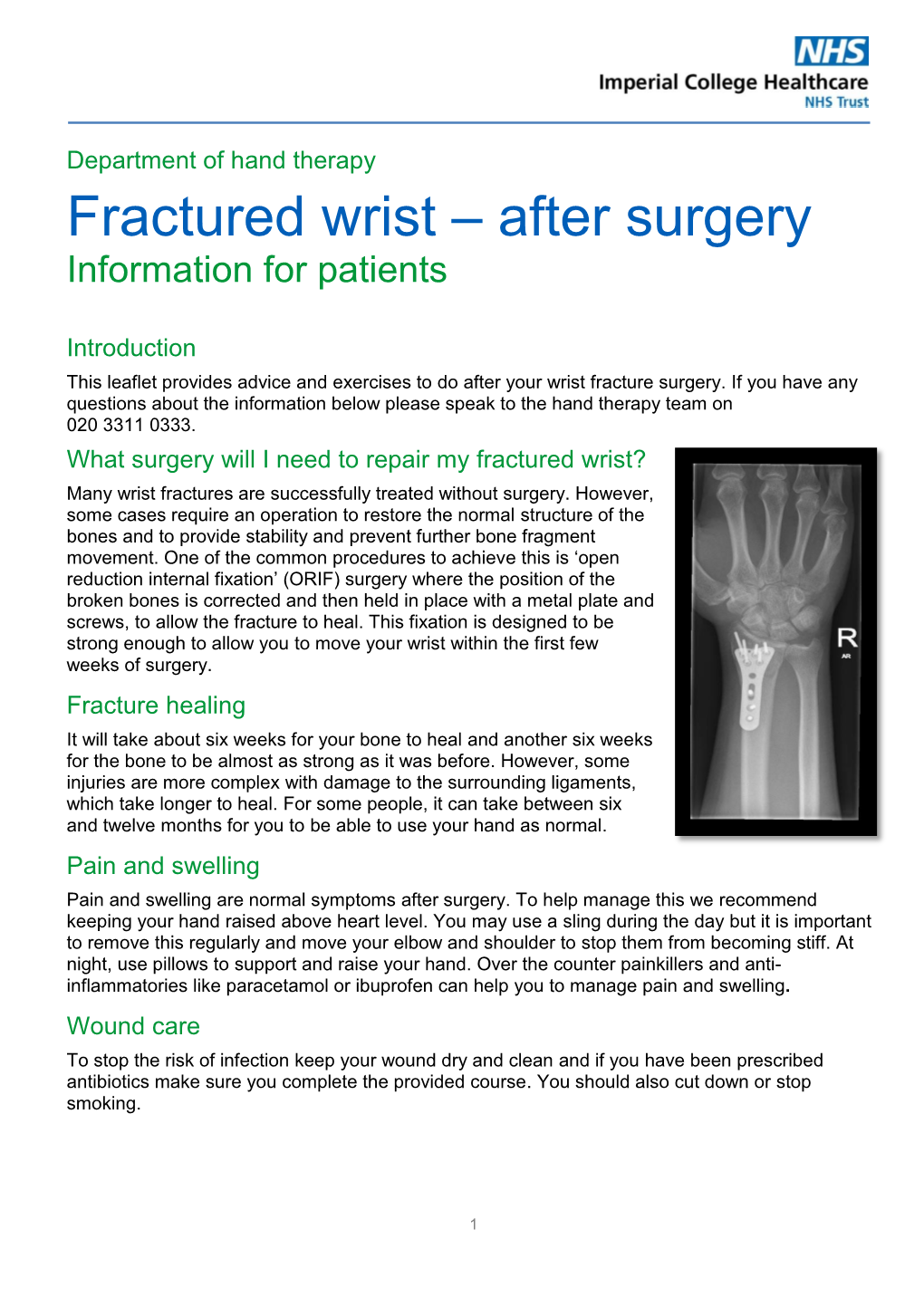
Hand Conditions: WRIST FRACTURE A wrist fracture is a break in one or more of the bones in the wrist. The wrist is made up of the two bones in the forearm called the radius and the ulna. It also includes eight carpal bones. The carpal bones lie between the end of the forearm bones and the bases of the fi ngers. The most commonly fractured carpal bone is called the scaphoid or navicular bone. This fact sheet will focus on fractures of the carpal bones of the wrist. Causes A wrist fracture is caused by trauma to the bones in the wrist. Trauma may be caused by: • Falling on an outstretched arm • Direct blow to the wrist • Severe twist of the wrist Risk Factors Factors that increase your chance of developing a wrist fracture include: • Participating in contact sports, such as football or soccer • Participating in activities such as in-line skating, skateboarding, or bike riding • Participating in any activity which could cause you to fall on your outstretched hand • Violence or high-velocity trauma, such as an automobile accident Symptoms If you have any of these symptoms, do not assume they are due to a wrist fracture. Symptoms of a wrist fracture include. • Pain • Swelling and tenderness around the wrist • Bruising around the wrist • Limited range of wrist or thumb motion • Visible deformity in the wrist For more information visit us online at www.ptandme.com Hand Conditions: WRIST FRACTURE Diagnosis Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, physical activity, and how the injury occurred. The injured area will be examined. -

Study Guide Medical Terminology by Thea Liza Batan About the Author
Study Guide Medical Terminology By Thea Liza Batan About the Author Thea Liza Batan earned a Master of Science in Nursing Administration in 2007 from Xavier University in Cincinnati, Ohio. She has worked as a staff nurse, nurse instructor, and level department head. She currently works as a simulation coordinator and a free- lance writer specializing in nursing and healthcare. All terms mentioned in this text that are known to be trademarks or service marks have been appropriately capitalized. Use of a term in this text shouldn’t be regarded as affecting the validity of any trademark or service mark. Copyright © 2017 by Penn Foster, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of the material protected by this copyright may be reproduced or utilized in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or by any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the copyright owner. Requests for permission to make copies of any part of the work should be mailed to Copyright Permissions, Penn Foster, 925 Oak Street, Scranton, Pennsylvania 18515. Printed in the United States of America CONTENTS INSTRUCTIONS 1 READING ASSIGNMENTS 3 LESSON 1: THE FUNDAMENTALS OF MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY 5 LESSON 2: DIAGNOSIS, INTERVENTION, AND HUMAN BODY TERMS 28 LESSON 3: MUSCULOSKELETAL, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM TERMS 44 LESSON 4: DIGESTIVE, URINARY, AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM TERMS 69 LESSON 5: INTEGUMENTARY, NERVOUS, AND ENDOCRINE S YSTEM TERMS 96 SELF-CHECK ANSWERS 134 © PENN FOSTER, INC. 2017 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY PAGE III Contents INSTRUCTIONS INTRODUCTION Welcome to your course on medical terminology. You’re taking this course because you’re most likely interested in pursuing a health and science career, which entails proficiencyincommunicatingwithhealthcareprofessionalssuchasphysicians,nurses, or dentists. -

PE1897 Wrist and Hand Stretches
Patient and Family Education Wrist and Hand Stretches How can I help my child do the stretches? Use these exercises to help stretch the You play an important role in your child’s therapy. Older children may need wrist and hand. reminders to do their stretches every day. You may need to help position your younger child for the stretches. Or you may need to help stretch your child’s hand or arm. Be sure to pay attention to your child’s alignment and posture to make sure each stretch is performed correctly. How often should my child do the stretches? These stretches should be done twice a day, or as instructed by your therapist: ______________________________________________________________ Stretches Wrist extension Hold arm out in front Use opposite hand to bend wrist up with fingers straight Option to straighten elbow for increased stretch Hold for 30 seconds or _______ Repeat 2 times or ___________ VHI Wrist extension Sit with elbows on table Place palms together Slowly lower wrists to table Hold for 30 seconds or ______ Repeat 2 times or __________ VHI Wrist flexion Hold arm out in front Use opposite hand to bend wrist down Option to straighten elbow for increased stretch Option to curl fingers for increased stretch Hold for 30 seconds or ______ VHI Repeat 2 times or __________ 1 of 2 Wrist and Hand Stretches Wrist radial/ulnar deviation To Learn More Hold arm at side of body with palm • Occupational/Physical facing forward Therapy 206-987-2113 Use opposite hand to straighten wrist toward the thumb side Do not allow the wrist to flex forward to extend backward Free Interpreter Hold for 30 seconds or ______ Services Repeat 2 times or __________ • In the hospital, ask BioEx Systems Inc.* your child’s nurse. -

Hand, Elbow, Wrist Pain
Physical and Sports Therapy Hand, Elbow, Wrist Pain The hand is a wondrously complex structure of tiny bones, muscles, ligaments, and tendons which work together to perform tasks. The wrist and elbow are stabilizing joints that support the steady use of the hand and provide attachment points for the muscles that control the hand and wrist. All three of these areas are prone to injury from overuse or trauma. Their complexity requires the skills of an expert for proper rehabilitation from injury. Some Hand, Wrist, and Elbow Issues Include: Tennis/Golfer’s Elbow: Tendonitis, or inflammation of the tendons, at the muscular attachments near the elbow. Symptoms typically include tenderness on the sides of the elbow, which increase with use of the wrist and hand, such as shaking hands or picking up a gallon of milk. Tendonitis responds well to therapy, using eccentric exercise, stretching, and various manual therapy techniques. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Compression of the Median Nerve at the hand/base of your wrist. Symptoms include pain, numbness, and tingling of the first three fingers. The condition is well-known for waking people at night. Research supports the use of therapy, particularly in the early phase, for alleviation of the compression through stretching and activity modification. Research indicates that the longer symptoms are present before initiating treatment, the worse the outcome for therapy and surgical intervention due to underlying physiological changes of the nerve. What can Physical or Occupational therapy do for Hand, Wrist, or Elbow pain? Hand, wrist, and elbow injuries are commonly caused by trauma, such as a fall or overuse. -

Standing Shoulder Flexion with Resistance
Prepared by Samantha Bohy Michigan STEP 1 STEP 2 Standing Shoulder Flexion with Resistance REPS: 15 | SETS: 2 | WEEKLY: 5x | Setup Begin in a standing upright position holding one end of a resistance band anchored under your foot with your thumb pointing forward. Movement Lift your arm straight forward to shoulder height, then slowly lower it back down and repeat. STEP 1 STEP 2 Single Arm Shoulder Extension with Resistance REPS: 15 | SETS: 2 | WEEKLY: 5x | Setup Begin standing tall, holding the end of a band that is anchored in front of you. Movement Pull your arm back, bringing your hand behind you. Return to the starting position and repeat. STEP 1 STEP 2 Standing Single Arm Shoulder Abduction with Resistance REPS: 15 | SETS: 2 | WEEKLY: 5x | Setup Begin in a standing upright position holding one end of a resistance band anchored under your feet with your thumb pointing up. Movement Lift your arm straight out to your side, to shoulder height, then lower it back down and repeat. Tip Make sure to maintain good posture and do not shrug your shoulder during the exercise. STEP 1 STEP 2 Shoulder Adduction with Anchored Resistance REPS: 15 | SETS: 2 | WEEKLY: 5x | Setup Begin in a standing upright position holding the end of a resistance band in one hand with your arm straight and palm facing downward, to the side of the anchor point. Movement Pull your arm down against the resistance band to your side, then slowly return to the starting position and repeat. STEP 1 STEP 2 Shoulder External Rotation with Anchored Resistance REPS: 15 | SETS: 2 | WEEKLY: 5x | Setup Begin standing upright with your elbow bent at 90 degrees and a towel roll tucked under your arm, holding a resistance band that is anchored out to your opposite side. -

REVIEW ARTICLE Osteoarthritis of the Wrist
REVIEW ARTICLE Osteoarthritis of the Wrist Krista E. Weiss, Craig M. Rodner, MD From Harvard College, Cambridge, MA and Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, CT. Osteoarthritis of the wrist is one of the most common conditions encountered by hand surgeons. It may result from a nonunited or malunited fracture of the scaphoid or distal radius; disruption of the intercarpal, radiocarpal, radioulnar, or ulnocarpal ligaments; avascular necrosis of the carpus; or a developmental abnormality. Whatever the cause, subsequent abnormal joint loading produces a spectrum of symptoms, from mild swelling to considerable pain and limitations of motion as the involved joints degenerate. A meticulous clinical and radiographic evaluation is required so that the pain-generating articulation(s) can be identi- fied and eliminated. This article reviews common causes of wrist osteoarthritis and their surgical treatment alternatives. (J Hand Surg 2007;32A:725–746. Copyright © 2007 by the American Society for Surgery of the Hand.) Key words: Wrist, osteoarthritis, arthrodesis, carpectomy, SLAC. here are several different causes, both idio- of events is analogous to SLAC wrist and has pathic and traumatic, of wrist osteoarthritis. been termed scaphoid nonunion advanced collapse Untreated cases of idiopathic carpal avascular (SNAC). Wrist osteoarthritis can also occur second- T 1 2 necrosis, as in Kienböck’s or Preiser’s disease, may ary to an intra-articular fracture of the distal radius or result in radiocarpal arthritis. Congenital wrist abnor- ulna or from an extra-articular fracture resulting in malities, such as Madelung’s deformity,3,4 can lead malunion and abnormal joint loading. -

Wrist and Hand Examina[On
Wrist and Hand Examinaon Daniel Lueders, MD Assistant Professor Physical Medicine and Rehabilitaon Objecves • Understand the osseous, ligamentous, tendinous, and neural anatomy of the wrist and hand • Outline palpable superficial landmarks in the wrist and hand • Outline evaluaon of and differen.aon between nerves to the wrist and hand • Describe special tes.ng of wrist and hand Wrist Anatomy • Radius • Ulna • Carpal bones Wrist Anatomy • Radius • Ulna • Carpal bones Wrist Anatomy • Radius • Ulna • Carpal bones Wrist Anatomy • Radius • Ulna • Carpal bones Inspec.on • Ecchymosis • Erythema • Deformity • Laceraon Inspec.on • Common Finger Deformies • Swan Neck Deformity • Boutonniere Deformity • Hypertrophic nodules • Heberden’s, Bouchard’s Inspec.on • Swan Neck Deformity • PIP hyperextension, DIP flexion • Pathology is at PIP joint • Insufficiency of volar/palmar plate and suppor.ng structures • Distally, the FDP tendon .ghtens from PIP extension causing secondary DIP flexion • Alternavely, extensor tendon rupture produces similar deformity Inspec.on • Boutonniere Deformity • PIP flexion, DIP hyperextension • Pathology is at PIP joint • Commonly occurs from insufficiency of dorsal and lateral suppor.ng structures at PIP joint • Lateral bands migrate volar/palmar, creang increased flexion moment • Results in PIP “buTon hole” effect dorsally Inspec.on • Nodules • Osteoarthri.c • Hypertrophic changes of OA • PIP - Bouchard’s nodule • DIP - Heberden’s nodule • Rheumatoid Arthri.s • MCP joints affected most • Distal radioulnar joint can also be affected -

Ulnar Nerve Injury & Repair
1/8/16 Ulnar Nerve Injury & Repair: Philadelphia’s Rehabilita6on & Ortho6c Magic Gardens Intervenon 1020 South Street Jenifer M. Haines,MS,OTR /L,CHT The Philadelphia Hand Center Outcomes Following Ulnar Nerve Repair Purpose: quan4fy variables influencing outcome aer 1. Outcomes & Expectaons ulnar & median nerve repair 2. Anatomy Methods: meta-analysis, literature review, 23 ar4cles 3. Clinical presentaon ulnar Results: nerve injury 1) 45% “sasfactory motor outcome” (71% < median nerve) 4. Func4onal deficits 41% “sasfactory sensory outcome” (approx. = median 5. Acute post-operave stage nerve) 6. ReHabilitaon stage 2) HigH level injury - poor motor outcome *irreversible motor damage by 1 ½-2 years (before re- innervaon of muscle) Ruijs, 2005 Long Term Outcomes of Ulnar 3) Paents < 16 years old 4x more likely sasfactory Nerve Injury motor recovery than those > 40 * neuroplas4city Purposes: 1. assess long term outcomes of paents following 4) Delayed surgery, lower cHance motor & sensory peripHeral repair recovery 2. determine relaonsHips between measures of Hand * Improvement possible up to 3 years func4on and nerve recovery. Methods: evaluated 32 paents approx. 5 years post-op Rosen and Lundborg scale, sensory, motor, and pain/ symptom tests, and self-report measures Ruijs, 2005 MacDermid J, 2010 1 1/8/16 Results: Paents retained 82.91% global func4on: 44.48%-84.90% sensory funcon “Factors that predict outcomes aer the repair of 80.13%-89.89% motor func4on peripHeral nerve injuries of the upper limb include age, 89.75%-93.19% pain/symptom experience gender, repair 4me, repair materials, defect length, duraon of follow-up and nerve injured.” Self-report measures of Hand func4on were more closely related to nerve recovery than were pHysical measures. -

Nerve Blocks for Surgery on the Shoulder, Arm Or Hand
The Association of Regional The Royal College of Anaesthetists of Great Anaesthesia – Anaesthetists Britain and Ireland United Kingdom Nerve blocks for surgery on the shoulder, arm or hand Information for patients and families www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo First edition 2015 This leaflet is for anyone who is thinking about having a nerve block for an operation on the shoulder, arm or hand. It will be of particular interest to people who would prefer not to have a general anaesthetic. The leaflet has been written with the help of patients who have had a nerve block for their operation. You can find more information leaflets on the website www.rcoa.ac.uk/patientinfo. The leaflets may also be available from the anaesthetic department or pre-assessment clinic in your hospital. The website includes the following: ■ Anaesthesia explained (a more detailed booklet). ■ You and your anaesthetic (a shorter summary). ■ Your spinal anaesthetic. ■ Anaesthetic choices for hip or knee replacement. ■ Epidural pain relief after surgery. ■ Local anaesthesia for your eye operation. ■ Your child’s general anaesthetic. ■ Your anaesthetic for major surgery with planned high dependency care afterwards. ■ Your anaesthetic for a broken hip. Risks associated with your anaesthetic This is a collection of 14 articles about specific risks associated with having an anaesthetic or an anaesthetic procedure. It supplements the patient information leaflets listed above and is available on the website: www.rcoa.ac.uk/patients-and-relatives/risks. Throughout this leaflet and others in the series, we have used this symbol to highlight key facts. 2 NERVE BLOCKS FOR SURGERY ON THE SHOULDER, ARM OR HAND Brachial plexus block? The brachial plexus is the group of nerves that lies between your neck and your armpit. -

Readingsample
Color Atlas of Human Anatomy Vol. 1: Locomotor System Bearbeitet von Werner Platzer 6. durchges. Auflage 2008. Buch. ca. 480 S. ISBN 978 3 13 533306 9 Zu Inhaltsverzeichnis schnell und portofrei erhältlich bei Die Online-Fachbuchhandlung beck-shop.de ist spezialisiert auf Fachbücher, insbesondere Recht, Steuern und Wirtschaft. Im Sortiment finden Sie alle Medien (Bücher, Zeitschriften, CDs, eBooks, etc.) aller Verlage. Ergänzt wird das Programm durch Services wie Neuerscheinungsdienst oder Zusammenstellungen von Büchern zu Sonderpreisen. Der Shop führt mehr als 8 Millionen Produkte. 130 Upper Limb: Bones, Ligaments, Joints Radiocarpal and Midcarpal Joints Ligaments in the Region of the Wrist (A–E) (A–E) Four groups of ligaments can be distin- The radiocarpal or wrist joint is an ellip- guished: soid joint formed on one side by the radius (1) and the articular disk (2) and on the Ligaments which unite the forearm bones with other by the proximal row of carpal bones.Not the carpal bones (violet). These include the all the carpal bones of the proximal row are ulnar collateral ligament (8), the radial col- in continual contact with the socket- lateral ligament (9), the palmar radiocarpal shaped articular facet of the radius and the ligament (10), the dorsal radiocarpal liga- disk. The triquetrum (3), only makes close ment (11), and the palmar ulnocarpal liga- contact with the disk during ulnar abduc- ment (12). tion and loses contact on radial abduction. Ligaments which unite the carpal bones with The capsule of the wrist joint is lax, dorsally one another,orintercarpal ligaments (red). These comprise the radiate carpal ligament Upper Limb relatively thin, and is reinforced by numer- ous ligaments. -

Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines III. Wrist
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines III. Wrist Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen, Denmark Andrew Grainger, UK Franz Kainberger, Austria Andrea Klauser, Austria Carlo Martinoli, Italy Eugene McNally, UK Philip J. O’Connor, UK Philippe Peetrons, Belgium Monique Reijnierse, The Netherlands Philipp Remplik, Germany Enzo Silvestri, Italy Wrist Note The standard US examination of the wrist begins with evaluation of its dorsal aspect, followed by the palmar one. Depending on the specific clinical presentation, US images can be obtained in different position of the wrist (flexion and extension, radial and ulnar deviation, pronation and supination), with the patient seated in front of the examiner. 1 DORSAL WRIST: compartments of extensor tendons Place the transducer on a transverse plane over the dorsal aspect of the wrist to allow proper identification of the extensor tendons. In general, one should first recognize a given tendon and then follow it on short-axis planes down to the distal insertion. Long- axis US images of the extensor tendons are less useful: they may help to evaluate the integrity of tendons and assess their dynamic motion in detail. Dynamic scanning of the extensor tendons can be performed by placing the hand on a gel tube with the fingers hanging outside its edge to allow easy fingers movements. Legend: APL, abductor pollicis longus; EPB, extensor pollicis brevis; ECRL, extensor carpi radialis longus; EPCB, extensor carpi radialis brevis; EPL, extensor pollicis longus; EIP, extensor indicis proprius; EDC, extensor digitorum longus; EDQ, extensor digiti quinti proprius; ECU, extensor carpi ulnaris 2 first compartment Keeping the patient’s wrist halfway between pronation and supination, place the probe over the lateral aspect of the radial styloid to examine the first compartment of the extensor tendons - abductor pollicis longus (ventral) and extensor pollicis brevis (dorsal).