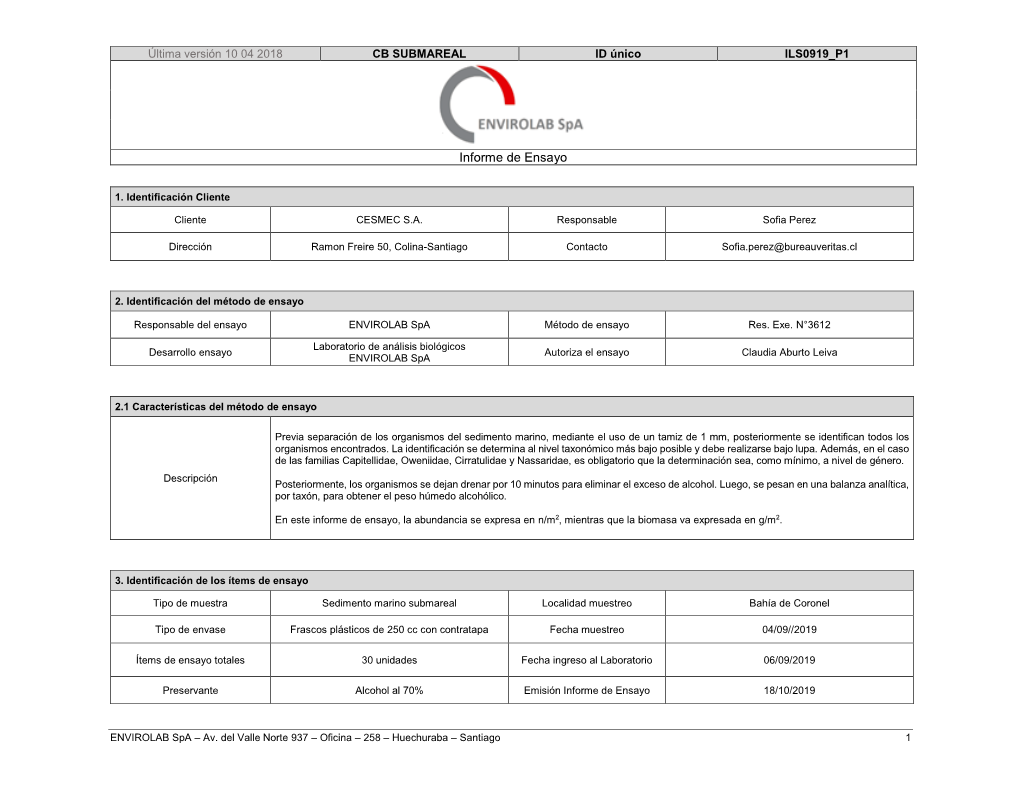
Informe De Ensayo
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Articulo De E Tarifeño
Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía 43(1): 51-61, abril de 2008 Efecto de la temperatura en el desarrollo embrionario y larval del mejillón, Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819) Temperature effect in the embryonic and larval development of the mussel, Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck, 1819) Maryori Ruiz1,2, Eduardo Tarifeño2,3, Alejandra Llanos-Rivera3, Christa Padget3 y Bernardita Campos4 1 Programa de Magíster en Ciencias, Departamento Zoología, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Oceanográficas, Universidad de Concepción. Casilla 160-C, Concepción, Chile 2 Departamento de Zoología, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Oceanográficas, Universidad de Concepción, Casilla 160-C, Concepción, Chile 3 Grupo ProMytilus. Proyecto FONDEF D03-1095, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Oceanográficas, Universidad de Concepción, Chile 4 Facultad de Ciencias del Mar y de Recursos Naturales, Universidad de Valparaíso, Valparaíso, Chile Casilla 5080, Reñaca, Viña del Mar, Chile [email protected] Abstract.- The Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus Resumen.- El mejillón del Mediterráneo (Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) has been recently registered galloprovincialis Lamarck, 1819) ha sido registrado for the Chilean coast, from Concepcion (36ºS) to the Magellan recientemente en las costas chilenas, desde Concepción (36ºS) Strait (54ºS). To determine the feasibility of the massive culture hasta el Estrecho de Magallanes (54ºS). En el estudio de factibilidad de su cultivo masivo en Chile (Proyecto FONDEF of M. galloprovincialis in Chile, a study of the temperature D05I-10258) se evaluó el efecto de la temperatura sobre su effects on the early development was carried out. Embryos and desarrollo temprano para modular empíricamente las tasas de larvae were raised at 12, 16 and 20ºC in laboratory facilities at crecimiento larval. -

Species Identification in Mussels
Elsevier Editorial System(tm) for Food Control Manuscript Draft Manuscript Number: Title: Species identification in mussels (Mytilus spp.): a case study on products sold on the Italian market underlines issues and suggests strategies to face a not still solved problem Article Type: Short Communication Keywords: Mytilus chilensis, Mytilus galloprovincialis, Choromytilus chorus, seafood labelling, traceability, species identification, DNA- based methods Corresponding Author: Dr. Andrea Armani, Corresponding Author's Institution: University of Pisa First Author: Alice Giusti Order of Authors: Alice Giusti; Federica Tosi; Lara Tinacci; Lisa Guardone; Giuseppe Arcangeli; Andrea Armani Abstract: Based on a case study concerning mussel products suspected to be mislabelled, this work wants to highlight the difficulties encountered in their molecular identification and propose new strategies for solving these issues. In November 2019, the FishLab (Department of Veterinary Sciences) was consulted by a wholesaler for identifying products labelled as "Chilean mussels" (Mytilus chilensis). The batch had been molecularly identified first as M. chilensis by an external private lab and, subsequently, as Choromytilus chorus following a second analysis entrusted to another external lab by the customer company. In this work, the samples could only be identified as Mytilus spp by sequencing the mtDNA COI gene. The amplification of the Polyphenolic Adhesive Protein (PAP) gene, a nuclear marker reported as more informative for mussel allowed to suppose the presence of M. chilensis and M. galloprovincialis based on the length of the obtained fragment. In fact, both the species, which are reported as inhabiting Chilean waters, present the same 123 bp amplicon. The low sequences quality obtained for this short fragment, however, did not allow a discrimination of the aforesaid species as this is based on a single mutation point. -

Review of the Literature on Bivalve Cytogenetics in the Last Ten Years
Cah. Biol. Mar. (2002) 43 : 17-26 Review of the literature on bivalve cytogenetics in the last ten years Catherine THIRIOT-QUIEVREUX Observatoire Océanologique, Université P. et M. Curie – CNRS - INSU, BP 28, 06230 Villefranche-sur-Mer, France Fax: (33) 4 93 76 38 48; E-mail: [email protected] Abstract: This paper provides a review of the studies on bivalve chromosomes since 1992, in order to gather available data and to highlight the recent progress in different fields of cytogenetics: karyotype and chromosome markers, genome size, aneuploidy, natural and induced polyploidy, and hybridization. Résumé: Revue des travaux des dix dernières années sur l’étude cytogénétique des bivalves. Cet article présente une revue sur l’étude des chromosomes des bivalves depuis 1992 afin de rassembler les données disponibles et de souligner les pro- grès récents dans les différents domaines de la cytogénétique : caryotype et marqueurs chromosomiques, taille du génome, aneuploïdie, polyploïdie naturelle et induite, et hydridisation. Keywords: Bivalvia, Chromosomes, Cytogenetics Introduction review, 1985). Later, the development of banding techniques which allowed chromosome identification in Cytogenetic studies encompass different levels of biological karyotypes began to be applied in bivalves (see Thiriot- organization ranging from the morphological to the Quiévreux review, 1994). Since these reviews, the study of molecular, depending on the applicable technology. bivalve chromosomes has greatly progressed in Chromosomes can be studied as a morphological karyological as well as molecular information, as a result of manifestation of the genome in terms of their routine application of several banding techniques and the microscopically visible size, shape, number and behaviour development of techniques for in situ hybridization. -

And Babylonia Zeylanica (Bruguiere, 1789) Along Kerala Coast, India
ECO-BIOLOGY AND FISHERIES OF THE WHELK, BABYLONIA SPIRATA (LINNAEUS, 1758) AND BABYLONIA ZEYLANICA (BRUGUIERE, 1789) ALONG KERALA COAST, INDIA Thesis submitted to Cochin University of Science and Technology in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Under the faculty of Marine Sciences By ANJANA MOHAN (Reg. No: 2583) CENTRAL MARINE FISHERIES RESEARCH INSTITUTE Indian Council of Agricultural Research KOCHI 682 018 JUNE 2007 ®edi'catec[ to My Tarents. Certificate This is to certify that this thesis entitled “Eco-biology and fisheries of the whelk, Babylonia spirata (Linnaeus, 1758) and Babylonia zeylanica (Bruguiere, 1789) along Kerala coast, India” is an authentic record of research work carried out by Anjana Mohan (Reg.No. 2583) under my guidance and supervision in Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the Ph.D degree in Marine science of the Cochin University of Science and Technology and no part of this has previously formed the basis for the award of any degree in any University. Dr. V. ipa (Supervising guide) Sr. Scientist,\ Mariculture Division Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute. Date: 3?-95' LN?‘ Declaration I hereby declare that the thesis entitled “Eco-biology and fisheries of the whelk, Babylonia spirata (Linnaeus, 1758) and Babylonia zeylanica (Bruguiere, 1789) along Kerala coast, India” is an authentic record of research work carried out by me under the guidance and supervision of Dr. V. Kripa, Sr. Scientist, Mariculture Division, Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, in partial fulfillment for the Ph.D degree in Marine science of the Cochin University of Science and Technology and no part thereof has been previously formed the basis for the award of any degree in any University. -

Chilean Marine Mollusca of Northern Patagonia Collected During the Cimar-10 Fjords Cruise
Gayana 72(2):72(2), 202-240,2008 2008 CHILEAN MARINE MOLLUSCA OF NORTHERN PATAGONIA COLLECTED DURING THE CIMAR-10 FJORDS CRUISE MOLUSCOS MARINOS CHILENOS DEL NORTE DE LA PATAGONIA RECOLECTADOS DURANTE EL CRUCERO DE FIORDOS CIMAR-10 Javiera Cárdenas1,2, Cristián Aldea1,3 & Claudio Valdovinos2,4* 1Center for Quaternary Studies (CEQUA), Casilla 113-D, Punta Arenas, Chile. 2Unit of Aquatic Systems, EULA-Chile Environmental Sciences Centre, Universidad de Concepción, Casilla 160-C, Concepción, Chile. [email protected] 3Departamento de Ecología y Biología Animal, Facultad de Ciencias del Mar, Campus Lagoas Marcosende, 36310, Universidad de Vigo, España. 4Patagonian Ecosystems Research Center (CIEP), Coyhaique, Chile. ABSTRACT The tip of the South American cone is one of the most interesting Subantarctic areas, both biogeographically and ecologically. Nonetheless, knowledge of the area’s biodiversity, in particular that of the subtidal marine habitats, remains poor. Therefore, in 2004, a biodiversity research project was carried out as a part of the cruise Cimar-10 Fjords, organized and supported by the Chilean National Oceanographic Committee (CONA). The results of the subtidal marine mollusk surveys are presented herein. The samples were collected aboard the Agor 60 “Vidal Gormaz” in winter 2004. The study area covered the northern Chilean Patagonia from Seno de Relocanví (41º31’S) to Boca del Guafo (43º49’S), on the continental shelf from 22 to 353 m depth. The Mollusca were collected at 23 sampling sites using an Agassiz trawl. In total, 67 -

The Evolution of Extreme Longevity in Modern and Fossil Bivalves
Syracuse University SURFACE Dissertations - ALL SURFACE August 2016 The evolution of extreme longevity in modern and fossil bivalves David Kelton Moss Syracuse University Follow this and additional works at: https://surface.syr.edu/etd Part of the Physical Sciences and Mathematics Commons Recommended Citation Moss, David Kelton, "The evolution of extreme longevity in modern and fossil bivalves" (2016). Dissertations - ALL. 662. https://surface.syr.edu/etd/662 This Dissertation is brought to you for free and open access by the SURFACE at SURFACE. It has been accepted for inclusion in Dissertations - ALL by an authorized administrator of SURFACE. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Abstract: The factors involved in promoting long life are extremely intriguing from a human perspective. In part by confronting our own mortality, we have a desire to understand why some organisms live for centuries and others only a matter of days or weeks. What are the factors involved in promoting long life? Not only are questions of lifespan significant from a human perspective, but they are also important from a paleontological one. Most studies of evolution in the fossil record examine changes in the size and the shape of organisms through time. Size and shape are in part a function of life history parameters like lifespan and growth rate, but so far little work has been done on either in the fossil record. The shells of bivavled mollusks may provide an avenue to do just that. Bivalves, much like trees, record their size at each year of life in their shells. In other words, bivalve shells record not only lifespan, but also growth rate. -

42 Papers Human Origin Sites and the World Heritage Convention In
42 World Heritage papers42 World Heritage papers HEADWORLD HERITAGES 5 NIO M O UN IM D R T IA A L • P • W L O A I R D L D N H O E M R I E TA IN G O E • PATRIM United Nations World Educational, Scientific and Heritage Cultural Organization Convention Human Origin Sites and the GOBIERNO DE World Heritage Convention in the Americas PUEBLAACCIONES QUE TRANSFORMAN In support of UNESCO’s 70th Anniversary Celebrations United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization VOLUME I Human Origin Sites and the Heritage World in the Convention Americas. I Volume For more information contact: UNESCO World Heritage Centre papers NIO M O UN IM D R T IA A L • P • W L O A I 7, place Fontenoy R D L D N H O E M 75352 Paris 07 SP France R E I TA IN G O Tel: 33 (0)1 45 68 24 96 E • PATRIM Fax: 33 (0)1 45 68 55 70 United Nations World Educational, Scientific and Heritage 9 789231 001406 http://whc.unesco.org HeritageWorld Cultural Organization Convention Human Origin Sites and the World Heritage Convention in the Americas HEADS 5 VOLUME I Published in 2015 by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization, 7, place de Fontenoy, 75352 Paris 07 SP, France and the UNESCO Office in Mexico, Presidente Masaryk 526, Polanco, Miguel Hidalgo, 11550 Ciudad de Mexico, D.F., Mexico. © UNESCO 2015 ISBN 978-92-3-100140-6 This publication is available in Open Access under the Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 IGO (CC-BY-SA 3.0 IGO) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/igo/). -
Diversity of Benthic Marine Mollusks of the Strait of Magellan, Chile
ZooKeys 963: 1–36 (2020) A peer-reviewed open-access journal doi: 10.3897/zookeys.963.52234 DATA PAPER https://zookeys.pensoft.net Launched to accelerate biodiversity research Diversity of benthic marine mollusks of the Strait of Magellan, Chile (Polyplacophora, Gastropoda, Bivalvia): a historical review of natural history Cristian Aldea1,2, Leslie Novoa2, Samuel Alcaino2, Sebastián Rosenfeld3,4,5 1 Centro de Investigación GAIA Antártica, Universidad de Magallanes, Av. Bulnes 01855, Punta Arenas, Chile 2 Departamento de Ciencias y Recursos Naturales, Universidad de Magallanes, Chile 3 Facultad de Ciencias, Laboratorio de Ecología Molecular, Departamento de Ciencias Ecológicas, Universidad de Chile, Santiago, Chile 4 Laboratorio de Ecosistemas Marinos Antárticos y Subantárticos, Universidad de Magallanes, Chile 5 Instituto de Ecología y Biodiversidad, Santiago, Chile Corresponding author: Sebastián Rosenfeld ([email protected]) Academic editor: E. Gittenberger | Received 19 March 2020 | Accepted 6 June 2020 | Published 24 August 2020 http://zoobank.org/9E11DB49-D236-4C97-93E5-279B1BD1557C Citation: Aldea C, Novoa L, Alcaino S, Rosenfeld S (2020) Diversity of benthic marine mollusks of the Strait of Magellan, Chile (Polyplacophora, Gastropoda, Bivalvia): a historical review of natural history. ZooKeys 963: 1–36. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.963.52234 Abstract An increase in richness of benthic marine mollusks towards high latitudes has been described on the Pacific coast of Chile in recent decades. This considerable increase in diversity occurs specifically at the beginning of the Magellanic Biogeographic Province. Within this province lies the Strait of Magellan, considered the most important channel because it connects the South Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. These characteristics make it an interesting area for marine research; thus, the Strait of Magellan has histori- cally been the area with the greatest research effort within the province. -

Gayana 73(1): 17-27, 2009 ISSN 0717-652X
Gayana 73(1): 17-27, 2009 ISSN 0717-652X MOLECULAR ANALYSIS IN CHILEAN COMMERCIAL GASTROPODS BASED ON 16S rRNA, COI AND ITS1-5.8S rDNA-ITS2 SEQUENCES ANALISIS MOLECULAR EN GASTROPODOS CHILENOS COMERCIALES BASADOS EN LAS SECUENCIAS 16S rRNA,. COI Y ITS1-5.8S rDNA-ITS2 Felipe Aguilera-Muñoz, Fabiola Lafarga-Cruz & Cristian Gallardo-Escárate* Laboratorio de Biotecnología Acuícola, Departamento de Oceanografía, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Oceanográficas, Centro de Biotecnología, Universidad de Concepción. Barrio Universitario s/n. Casilla 160-C Concepción, Chile. email: [email protected] ABSTRACT Gastropod mollusks are part of the principal marine resources cultivated and commercialized in Chile. There are native Chilean species such as loco (Concholepas concholepas), locate (Thais chocolata), trumulco snail (Chorus giganteus), keyhole limpets (Fissurella spp.), tegula snail (Tegula atra) as well as exotic species such as red abalone (Haliotis rufescens) and Japanese abalone (Haliotis discus hannai). Despite their importance as marine resources, molecular genetic studies establishing phylogenetic relationships and estimating population genetic parameters are scarce. The aim of this study is to establish a molecular approach among the main commercial gastropod species in Chile. The mitochondrial genes 16S rRNA and COI, and the nuclear ribosomal region ITS1-5.8SrDNA-ITS2 were amplified by PCR and sequencing. Alignment analysis was used to determine systematic relationships at the specific level for the species studied. The results revealed that 7 species are grouped in 4 genetically distinct families (Haliotidae, Trochidae, Muricidae and Fissurellidae). In comparison with COI sequencing, 16S rRNA and ITS1-5.8SrDNA-ITS2 sequencing were relatively more conserved with a divergence percentage for 16S rDNA and ITS1-5.8SrDNA-ITS2 of 1.2% and 1.8%, respectively, contrasting with the value of 10% obtained for COI in abalone. -

WSN Long Program 2014 FINAL
Western Society of Naturalists Meeting Program Tacoma, WA Nov. 13-16, 2014 1 Western Society of Naturalists Treasurer President ~ 2014 ~ Andrew Brooks Steven Morgan Dept of Ecology, Evolution Bodega Marine Laboratory, Website and Marine Biology UC Davis www.wsn-online.org UC Santa Barbara P.O. Box 247 Santa Barbara, CA 93106 Bodega, CA 94923 Secretariat [email protected] [email protected] Michael Graham Scott Hamilton Member-at-Large Diana Steller President-Elect Phil Levin Moss Landing Marine Laboratories Northwest Fisheries Science Gretchen Hofmann 8272 Moss Landing Rd Center Dept. Ecology, Evolution, & Moss Landing, CA 95039 Conservation Biology Division Marine Biology Seattle, WA 98112 Corey Garza UC Santa Barbara [email protected] CSU Monterey Bay Santa Barbara, CA 93106 [email protected] Seaside, CA 93955 [email protected] 95TH ANNUAL MEETING NOVEMBER 13-16, 2014 IN TACOMA, WASHINGTON Registration and Information Welcome! The registration desk will be open Thurs 1600-2000, Fri-Sat 0730-1800, and Sun 0800-1000. Registration packets will be available at the registration table for those members who have pre-registered. Those who have not pre-registered but wish to attend the meeting can pay for membership and registration (with a $20 late fee) at the registration table. Unfortunately, banquet tickets cannot be sold at the meeting because the hotel requires final counts of attendees well in advance. The Attitude Adjustment Hour (AAH) is included in the registration price, so you will only need to show your badge for admittance. WSN t-shirts and other merchandise can be purchased or picked up at the WSN Student Committee table. -

Amici Molluscarum 2008 (16) Sociedad Malacológica De Chile
- Amici Molluscarum 2008 (16) Sociedad Malacológica de Chile AMICI MOLLUSCARUM Sociedad Malacológica de Chile Año 2008 Número 16 Año XVI Perry, 1811 Perry, Pomacea Pomacea Editorial Pág. 3 - Registro de Pomacea sp. (Gastropoda: Ampullaridae) en Chile. Sergio Letelier y Sergio Soto-Acuña 6-13 -Significancia taxonómica del complejo epipodial en especies sudamericanas del género Tegula Lesson, 1835 (Mollusca: Vetigastropoda). Gonzalo A. Collado 14-19 -Rol de las poblaciones de Diplodon (Diplodon) chilensis Gray 1828 en la Laguna Chica de San Pedro de la Paz. Carmen Fuentealba y Oscar Henríquez. 20-25 Notas, Reuniones Científicas, Congresos y Talleres 26 -34 -Homenaje de SMACH y ALMAMICI a Cecilia Osorio, MOLLUSCARUM José Stuardo, y Melbourne R. Carriker 29 - 31 Ficha Taxonómica 1: - RobsonellaSociedad fontaniana Malacológica. Sergio A. Carrasco. de Chile 35 Ficha Taxonómica 2 : -Benthoctopus longibrachus . Christian Ibáñez, M.Cecilia Pardo-Gandarillas Diana Párraga. 36 - Amici Molluscarum 2008 (16) Sociedad Malacológica de Chile Amici Molluscarum es un boletín de publicación anual, editado por la Sociedad Malacológica de Chile (SMACH), con el patrocinio del Museo Nacional de Historia Natural de Chile (MNHNCL), que tiene el propósito de comunicar notas, conferencias y artículos científicos en el área de la Malacología. ______________________________________________________________________ Presidencia Sergio Letelier (MNHNCL) Vicepresidencia Laura G. Huaquin (UNIVERSIDAD DE CHILE) Tesorería Esteban Saavedra (SOCIEDAD MALACOLOGICA DE CHILE) -

Del Mejillón Choromytilus Chorus (Molina
UNIVERSIDAD DE ANTOFAGASTA FACULTAD DE RECURSOS DEL MAR PROGRAMA DE DOCTORADO EN CIENCIAS APLICADAS, MENCIÓN SISTEMAS MARINOS COSTEROS FUNCIÓN DE LOS ESTEROIDES SEXUALES EN LA DIFERENCIACIÓN SEXUAL (GONADAL) DEL MEJILLÓN CHOROMYTILUS CHORUS (MOLINA 1782) (BIVALVIA MYTILIDAE) Tesis presentada a la Facultad de Recursos del Mar como requisito para optar al grado académico de Doctor en Ciencias Aplicadas, mención Sistemas Marinos Costeros MARYORI IVONNE RUIZ VELÁSQUEZ Profesor Patrocinante: Dr. Manuel Zapata Arcos Profesor Copatrocinante: Dra. María Teresa González Enero, 2017 Antofagasta, Chile CALIFICACIONES FACULTAD DE RECURSOS DEL MAR PROGRAMA DE DOCTORADO EN CIENCIAS APLICADAS, MENCIÓN SISTEMAS MARINOS COSTEROS FUNCIÓN DE LOS ESTEROIDES SEXUALES EN LA DIFERENCIACIÓN SEXUAL (GONADAL) DEL MEJILLÓN CHOROMYTILUS CHORUS (MOLINA 1782) (BIVALVIA MYTILIDAE) Dr. Manuel Zapata Arcos ----------------------------------------- Profesor Patrocinante Dra. María Teresa González ----------------------------------------- Profesor Co Patrocinante Dr. Eduardo Tarifeño Silva ----------------------------------------- Profesor Evaluador Externo Dr. Aldo Pacheco Velásquez ----------------------------------------- Profesor Evaluador Programa Enero, 2017 Antofagasta, Chile ii DEDICATORIA Esta tesis está dedicada al Señor, a mis amados mis padres y hermano. iii AGRADECIMIENTOS Al concluir esta etapa, deseo agradecer al Señor por su amor, ayuda y por darme la fortaleza de enfrentar este gran desafío y poder finalizarlo con éxito. A mis amados padres Ivón Velásquez