Scintigraphicaspect of Rotor's Disease with Technetium-99M-.Mebrofemn
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
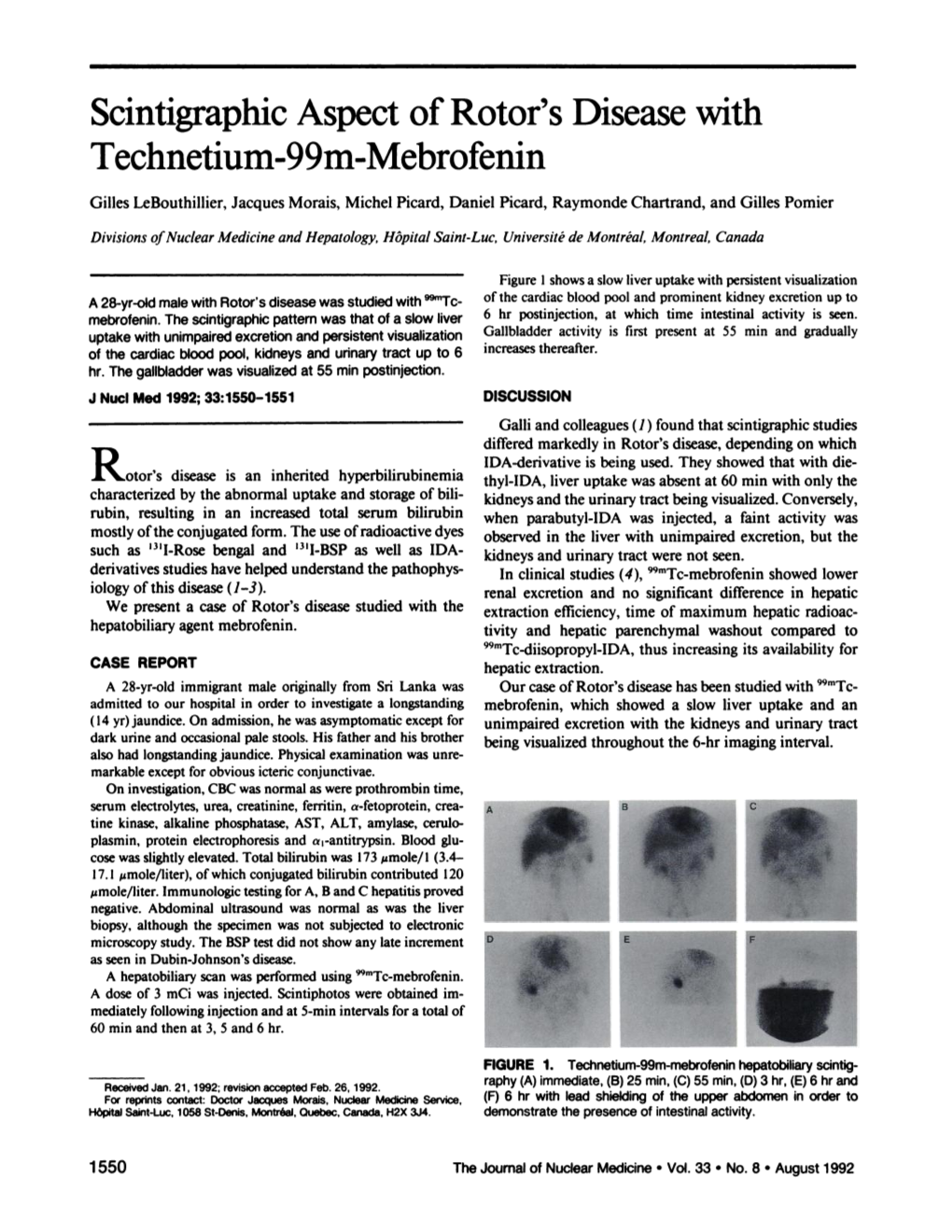
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia
Clinical Chemistry Trainee Council Pearls of Laboratory Medicine www.traineecouncil.org TITLE: Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia PRESENTER: Linnea M. Baudhuin, Ph.D., DABMG Slide 1: Title slide Slide 2: Bilirubin is an orange‐yellow pigment derived from the degradation of the heme moiety of hemoproteins, particularly the hemoglobin of mature circulating erythrocytes. Hemo oxygenase is the enzyme initially responsible for the degradation of hemoglobin, producing biliverdin and carbon monoxide. Biliverdin reductase reduces the green‐pigmented biliverdin to bilirubin. Bilirubin production primarily occurs in the liver, but also can occur in the spleen and bone marrow, and as it is produced in the unconjugated form, bilirubin is highly insoluble. Bilirubin is conjugated in the liver, which allows excretion in the bile and urine. Bilirubin is mainly conjugated to glucuronic acid by uridine diphosphate glucuronosyl transferase 1A1, or UGT1A1. Slide 3: Bilirubin is photosensitive because light causes configurational and structural changes to unconjugated bilirubin. The structure of bilirubin, as established by x‐ray crystallography, is a ridge‐tiled configuration stabilized by six intramolecular hydrogen bonds. These six intramolecular hydrogen bonds stabilize the Z‐Z structure of unconjugated bilirubin, rendering it insoluble. Rotation and/or breakage of the bonds on carbon atoms 5 and 15 lead to more open E‐Z‐ and Z‐E‐bilirubin structures, which are more water soluble. The sensitivity of bilirubin to light is the basis for phototherapy in individuals with unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Clinical measurement of bilirubin can also be affected due to this light sensitivity. Slide 4: Four fractions of bilirubin can be revealed upon open‐column chromatographic separation that does not involve deproteinization. -

Inherited Disorders of Bilirubin Clearance N
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Hofstra Northwell Academic Works (Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine) Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine Journal Articles Academic Works 2015 Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance N. Memon B. I. Weinberger Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell T. Hegyi L. M. Aleksunes Follow this and additional works at: https://academicworks.medicine.hofstra.edu/articles Part of the Pediatrics Commons Recommended Citation Memon N, Weinberger B, Hegyi T, Aleksunes L. Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance. 2015 Jan 01; 79(3):Article 2776 [ p.]. Available from: https://academicworks.medicine.hofstra.edu/articles/2776. Free full text article. This Article is brought to you for free and open access by Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine Academic Works. It has been accepted for inclusion in Journal Articles by an authorized administrator of Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine Academic Works. For more information, please contact [email protected]. HHS Public Access Author manuscript Author ManuscriptAuthor Manuscript Author Pediatr Manuscript Author Res. Author manuscript; Manuscript Author available in PMC 2016 April 05. Published in final edited form as: Pediatr Res. 2016 March ; 79(3): 378–386. doi:10.1038/pr.2015.247. Inherited Disorders of Bilirubin Clearance Naureen Memon1,*, Barry I Weinberger2, Thomas Hegyi1, and Lauren M Aleksunes3 1Department of Pediatrics, Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, New Brunswick, NJ, USA 2Department of Pediatrics, Cohen Children’s Medical Center of New York, New Hyde Park, NY, USA 3Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, Rutgers University, Piscataway, NJ, USA Abstract Inherited disorders of hyperbilirubinemia may be caused by increased bilirubin production or decreased bilirubin clearance. -

Dubin-Johnson Syndrome with Some Unusual Features in a Chinese Family
Arch Dis Child: first published as 10.1136/adc.54.7.529 on 1 July 1979. Downloaded from Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1979, 54, 529-533 Dubin-Johnson syndrome with some unusual features in a Chinese family N. S. LO, C. W. CHAN, AND J. H. HUTCHISON University Departments ofPaediatrics and Pathology, Queen Mary Hospital, Hong Kong SUMMARY Three cases of chronic nonhaemolytic jaundice with conjugated bilirubin in the serum an described in a Chinese family. Bromsulphthalein excretion tests gave results typical of the Dubin- Johnson syndrome. Liver histology in the proband showed cytoplasmic pigment of the lipofuscin- melanin variety, and intravenous cholecystography failed to show visualisation of the gallbladder. Unusual findings included onset during the neonatal period in the proband and the presence of some iron pigment in the hepatic cells with a little canalicular cholestasis. It is suggested that the infant may have had a concomitant nonspecific hepatitis. These cases are regarded as belonging to a disease group in which the Dubin-Johnson syndrome is at one end of a spectrum. The mode of inheritance is discussed. The hereditary defects in bilirubin metabolism are United Christian Hospital, Hong Kong on 22 rare and incompletely understood causes ofjaundice. March 1978. The birthweight was 3 58 kg. There They can be divided into two groups according to was no history of maternal illness, drug ingestion, or whether the raised serum bilirubin level occurs only in x-irradiation. Jaundice was noted on day 2 when the unconjugated form as in Gilbert's disease (Berk the total serum bilirubin (SB) level was 225 * 7 ,tmol/l et al., 1970) and Crigler-Najjar disease (Crigler and (13 2 mg/100 ml). -

ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries
18 PRACTICE GUIDELINES CME ACG Clinical Guideline: Evaluation of Abnormal Liver Chemistries P a u l Y. K w o , M D , F A C G , F A A S L D 1 , Stanley M. Cohen , MD, FACG, FAASLD2 and Joseph K. Lim , MD, FACG, FAASLD3 Clinicians are required to assess abnormal liver chemistries on a daily basis. The most common liver chemistries ordered are serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin. These tests should be termed liver chemistries or liver tests. Hepatocellular injury is defi ned as disproportionate elevation of AST and ALT levels compared with alkaline phosphatase levels. Cholestatic injury is defi ned as disproportionate elevation of alkaline phosphatase level as compared with AST and ALT levels. The majority of bilirubin circulates as unconjugated bilirubin and an elevated conjugated bilirubin implies hepatocellular disease or cholestasis. Multiple studies have demonstrated that the presence of an elevated ALT has been associated with increased liver-related mortality. A true healthy normal ALT level ranges from 29 to 33 IU/l for males, 19 to 25 IU/l for females and levels above this should be assessed. The degree of elevation of ALT and or AST in the clinical setting helps guide the evaluation. The evaluation of hepatocellular injury includes testing for viral hepatitis A, B, and C, assessment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic liver disease, screening for hereditary hemochromatosis, autoimmune hepatitis, Wilson’s disease, and alpha-1 antitrypsin defi ciency. In addition, a history of prescribed and over-the-counter medicines should be sought. For the evaluation of an alkaline phosphatase elevation determined to be of hepatic origin, testing for primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis should be undertaken. -

Wilson Disease Α1-Anti Antitrypsin Deficiency Hereditary Hyperbilirubinemia
Wilson Disease α1-Anti Antitrypsin Deficiency Hereditary Hyperbilirubinemia NEIL CRITTENDEN OCTOBER 29, 2015 Wilson Disease Wilson Disease: Autosomal Recessive Disorder of copper overload Incidence 1 in 30,000 Copper accumulation in the liver, brain, kidney and cornea Related to the gene ATP7B -> mutated ATP7B protein (an ATPase that can’t excrete Cu) Symptom onset range 3 to 55 years May present with isolated elevation of LFT’s, progressive neurologic/psychiatric disorder or isolated acute hemolysis With fulminant hepatic failure, acute intravascular hemolysis is usually present Wilson Disease: Diagnosis J. Korman Hepatology 2008; 48:1167-1174 J. Korman Hepatology 2008; 48:1167-1174 J. Korman Hepatology 2008; 48:1167-1174 Wilson Disease: Chronic Diagnosis, Initial Clues Hepatic Inflammation, AST:ALT usually >2 CBC may show anemia, (Coombs-Negative hemolytic anemia) Low serum copper concentration Low serum uric acid and phosphate (renal tubular dysfunction) Wilson Disease: Chronic Diagnosis Ocular Slit-Lamp Examination Ceruloplasmin < 20 mg/dL DDx: Wilson (homozygous vs. heterozygous, other chronic liver disease, intestinal malabsorption, nephrosis, malnutrition, hereditary aceruloplasminemia) 24-hour urinary copper excretion (preferably 3 separate), usually 2-3 x Normal, or 100 ug/day Hepatic tissue copper concentration > 250 ug/g dry weight of liver is diagnostic of Wilson disease Aside on Liver Biopsy Require Cu Free Needle (BioPince used at UofL and Jewish Hospital) Collect in a plastic container which has been rinsed -

The First Turkish Family with Rotor Syndrome Diagnosed at the Molecular Level Moleküler Düzeyde Tanısı Konulmuş Olan Ilk Türk Rotor Sendromlu Aile
Case Report / Olgu Sunumu The first Turkish family with Rotor syndrome diagnosed at the molecular level Moleküler düzeyde tanısı konulmuş olan ilk Türk Rotor sendromlu aile Evren Gümüş1, Meryem Karaca2, Uğur Deveci3, Milan Jirsa4 1Department of Medical Genetics, Harran University Faculty of Medicine, Şanlıurfa, Turkey 2Department of Pediatrics, Harran University Faculty of Medicine, Şanlıurfa, Turkey 3Department of Pediatrics, Şanlıurfa Training and Research Hospital, Şanlıurfa, Turkey 4Experimental Hepatology Laboratory, Clinical and Experimental Medicine Institute, Prag, Czechia The known about this topic Although Rotor syndrome is a disease that has been known for about 70 years, its genetic background was elucidated only after the 2010s. Contribution of the study The individuals presented in our study are the first Turkish patients with Rotor syndrome whose diagnoses were demonstrated using molecular methods. Abstract Öz Rotor syndrome is defined as a self-limiting hyperbilirubinemia Rotor sendromu, tedaviye gereksinim göstermeyen, kendi kendini characterized by jaundice that does not need treatment, cause any sınırlayabilen, sarılık ile seyreden, herhangi bir morbiditeye neden morbidity or affect life expectancy. As far as the literature is evalu- olmayan, beklenen yaşam süresini etkilemeyen, hiperbilirubinemi ated, the number of patients with Rotor syndrome diagnosed at the olarak tanımlanmaktadır. Dizinde değerlendirilebildiği kadarı ile bu- molecular level is less than 20 until today. In this case presentation, güne kadar moleküler temeli gösterilmiş Rotor sendromu hasta sayısı we aimed to present two siblings with Rotor syndrome who were 20’den azdır. Bu olgu takdiminde moleküler temeli gösterilmiş Rotor diagnosed at the molecular level. To the nest of our knowledge, these sendromu olan iki kardeşi sunmayı amaçladık. -

APPROACH to ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Mitchell L Shiffman, MD
APPROACH TO ABNORMAL LIVER TESTS Mitchell L Shiffman, MD Liver Institute of Virginia Bon Secours Health System Richmond and Newport News, VA CATAGORIES OF LIVER FUNCTION TESTS: What are commonly referred to as liver function tests (LFTs) do not actually measure liver function. Liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase are utilized to assess injury to the liver but can still be normal in patients with liver disease. True liver function tests measure the metabolic and synthetic function of the liver. Other “non-liver” tests can be utilized to estimate hepatic fibrosis and mortality in patients with advanced liver disease. Liver chemistries: Aspartate aminotransferase Reflect injury to the liver Alanine aminotransferase Alkaline phosphatase Gamma glutamyl transferase 5’ nucleotidase Tests which assess liver function Albumin INR (factor 7) Tests which assess hepatic metabolism Total bilirubin Direct and indirect bilirubin Non-Liver function tests Platelet count Serum creatinine LIVER TRANSAMINASES: Transaminases are enzymes that convert amino acids to alpha-keto acids. During this reaction an amino acid is metabolized to its alpha-keto acid by removing the amino group and leaving an alpha-keto group. Alpha-keto-acids are produced from amino acids by the reverse reaction. The liver contains several transaminases. The two that are typically measured to assess for the presence of liver cell injury are alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). ALT is a cytoplasmic enzyme. AST is a mitochondrial based enzyme. Injury to liver cells release ALT into serum in higher concentrations than AST. For this reason, ALT is always higher than AST in all forms of chronic liver disease except for those diseases which selectively injure the mitochondria. -

A Rare Case Report of Crigler Najjar Syndrome Type II
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12669 A Rare Case Report of Crigler Najjar Syndrome Type II Eusha Abdul Raffay 1 , Ayesha Liaqat 1 , Maria Khan 2 , Ali I. Awan 3 , Bakhat Mand 1 1. Internal Medicine, Services Institute of Medical Sciences, Lahore, PAK 2. Internal Medicine, King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital, Lahore, PAK 3. Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital, Lahore, PAK Corresponding author: Eusha Abdul Raffay, [email protected] Abstract Crigler-Najjar syndrome is an inborn error of metabolism caused by a point mutation in one of the five exons of UGT1A1 gene, the product of which is responsible for elimination of bilirubin via bile. A number of hyperbilirubinemia disorders similar to Crigler-Najjar syndrome are reported, but they differ in their level of unconjugated bilirubin and responses to the treatment. Here we report a 14-year-old male patient admitted to hospital with the complaint of vomiting and frequent tonsillitis. Further examination revealed that he was jaundiced since birth and had a family history of similar disorder. This report is about an extremely rare case of Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II and also management of the condition to provide the patient with a healthy lifestyle. Categories: Genetics, Internal Medicine, Gastroenterology Keywords: crigler-najjar syndrome, phenobarbital, ugt1a1 gene, hyperbilirubinemia, unconjugated bilirubin Introduction Crigler-Najjar syndrome type II (CN-II) is a rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in the UGT1A1 gene. The mode of inheritance of this disorder is autosomal recessive. Mutations in the same gene could alternatively cause other disorders like Crigler-Najjar Syndrome type I and Gilbert syndrome. -

Porphyrin Metabolism and Haem Biosynthesis in Gilbert's Syndrome
Gut: first published as 10.1136/gut.28.2.125 on 1 February 1987. Downloaded from Gut, 1987, 28, 125-130 Porphyrin metabolism and haem biosynthesis in Gilbert's syndrome K E L McCOLL, G G THOMPSON, E EL OMAR, M R MOORE, AND A GOLDBERG From the University Dept. Medicine, Gardiner Institute, Western Infirmary, Glasgow SUMMARY Studies in 14 patients with unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia caused by Gilbert's syndrome have revealed abnormalities of the enzymes of haem biosynthesis measured in peripheral blood cells. The activity of the penultimate enzyme of haem biosynthesis protopor- phyrinogen (PROTO) oxidase was reduced at 3-1±2.6 nmol PROTO/g protein/h (mean±ISD) compared with 8*2±5-1 in controls (p<0.005). This was associated with a compensatory increase in the activity of the initial and rate controlling enzyme of the pathway delta-aminolaevulinic acid (ALA) synthase at 866±636 nmol ALA/g/protein/h compared with 156±63 in controls (p<0.001). Unlike variegate porphyria in which there is a genetic deficiency of PROTO oxidase there was no increased excretion of porphyrins or their precursors in Gilbert's syndrome. Accentuation and subsequent correction of the unconjugated hyperbilirubinaemia with rifampicin produced reciprocal changes in PROTO oxidase activity indicating that bilirubin may be inhibiting the activity of this enzyme. http://gut.bmj.com/ Gilbert's syndrome originally described in 1901 by ferase activity.`8 Gilbert's syndrome may be a Gilbert and Lereboullet' is a benign disorder affect- heterogenous disorder.9 We wish to report a pre- ing 2-5% of the population. -
Dubin-Johnson Syndrome Aziz-Un-Nisa and Zubair Ahmad
CASE REPORT Dubin-Johnson Syndrome Aziz-un-Nisa and Zubair Ahmad ABSTRACT A young man presented with recurrent episodes of mild jaundice. Apart from conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, other liver function tests were always normal. Clinical suspicion of Dubin-Johnson syndrome was raised. Liver biopsy showed diffuse deposition of coarse granular dark brown pigment in hepatocytes. Dubin-Johnson syndrome is a benign condition, which results from a hereditary defect in biliary secretion of bilirubin pigments, and manifests as recurrent jaundice with conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The defect is due to the absence of the canalicular protein MRP2 located on chromosomes 10q 24, which is responsible for the transport of biliary glucuronides and related organic anions into bile. No treatment is necessary and patients have a normal life expectancy. Key words: Dubin-Johnson syndrome. Conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Liver biopsy. Brown pigment. INTRODUCTION The patient at that time had a copy of blood tests performed earlier. That also showed increased serum Dubin-Johnson syndrome is a benign autosomal bilirubin and increased conjugated bilirubin, while all recessive condition in which biliary secretion of bilirubin other liver function tests were negative. Diagnosis of pigment is defective. The defect is due to the absence of conjugated hyperbilirubinemia was made, and with a the canalicular protein MRP2 located on chromosomes suspicion of Dubin-Johnson syndrome, liver biopsy was 10q 24, which is responsible for the transport of biliary performed. glucuronides and related organic anions into bile.1 The hepatocytes contain diffusely a coarsely granular dark We received the single linear core of liver tissue brown pigment.2 The liver is otherwise normal. -

Rotor-Syndrome.Pdf
Rotor syndrome Description Rotor syndrome is a relatively mild condition characterized by elevated levels of a substance called bilirubin in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia). Bilirubin is produced when red blood cells are broken down. It has an orange-yellow tint, and buildup of this substance can cause yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice). In people with Rotor syndrome, jaundice is usually evident shortly after birth or in childhood and may come and go; yellowing of the whites of the eyes (also called conjunctival icterus) is often the only symptom. There are two forms of bilirubin in the body: a toxic form called unconjugated bilirubin and a nontoxic form called conjugated bilirubin. People with Rotor syndrome have a buildup of both unconjugated and conjugated bilirubin in their blood, but the majority is conjugated. Frequency Rotor syndrome is a rare condition, although its prevalence is unknown. Causes The SLCO1B1 and SLCO1B3 genes are involved in Rotor syndrome. Mutations in both genes are required for the condition to occur. The SLCO1B1 and SLCO1B3 genes provide instructions for making similar proteins, called organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1) and organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B3 (OATP1B3) , respectively. Both proteins are found in liver cells; they transport bilirubin and other compounds from the blood into the liver so that they can be cleared from the body. In the liver, bilirubin is dissolved in a digestive fluid called bile and then excreted from the body. The SLCO1B1 and SLCO1B3 gene mutations that cause Rotor syndrome lead to abnormally short, nonfunctional OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 proteins or an absence of these proteins. -

Clinical Chemistry Trainee Council Pearls of Laboratory Medicine
Clinical Chemistry Trainee Council Pearls of Laboratory Medicine www.traineecouncil.org TITLE: Porphyrias PRESENTER: M. Laura Parnas Slide 1: Hello, my name is Dr. Laura Parnas. I am the Associate Medical Director of Laboratory Services at the Palo Alto Medical Foundation. Welcome to this discussion on porphyrias. The porphyrias are a group of rare inborn errors of metabolism associated with defects in the heme biosynthetic pathway. Enzymatic deficiencies during heme biosynthesis result in accumulation and excretion of pathway precursors and intermediates, causing unique biochemical features and disease symptoms. Slide 2: Heme Heme is a crucial component of cellular hemoproteins that fulfill essential functions, including oxygen transport and storage, electron transport, and oxidation-reduction reactions. Heme biosynthesis occurs in all nucleated cells in the human body, primarily in developing red blood cells of the bone marrow where hemoglobin is produced, and to a lesser extent in hepatocytes, where cytochromes and other heme-containing enzymes are generated. Slide 3: Heme Biosynthesis Heme is enzymatically produced in sequential steps that occur in two cellular compartments; the first and last three steps occur in the mitochondrion and the intermediate steps take place in the cytosol. Eight enzymes catalyze formation of protoporphyrin IX and iron chelation to form heme. The initial and rate-limiting step is the condensation of glycine and succinyl-CoA to form δ- aminolevulinic acid (ALA). Then, condensation and polymerization reactions occur to form hydroxymethylbilane. Cyclization of hydroxymethylbilane can occur spontaneously to generate type I isomers, but the enzymatically-generated type III isomers are most abundant and physiological. The last steps include decarboxylation, oxidation, and insertion of iron to complete the cycle.