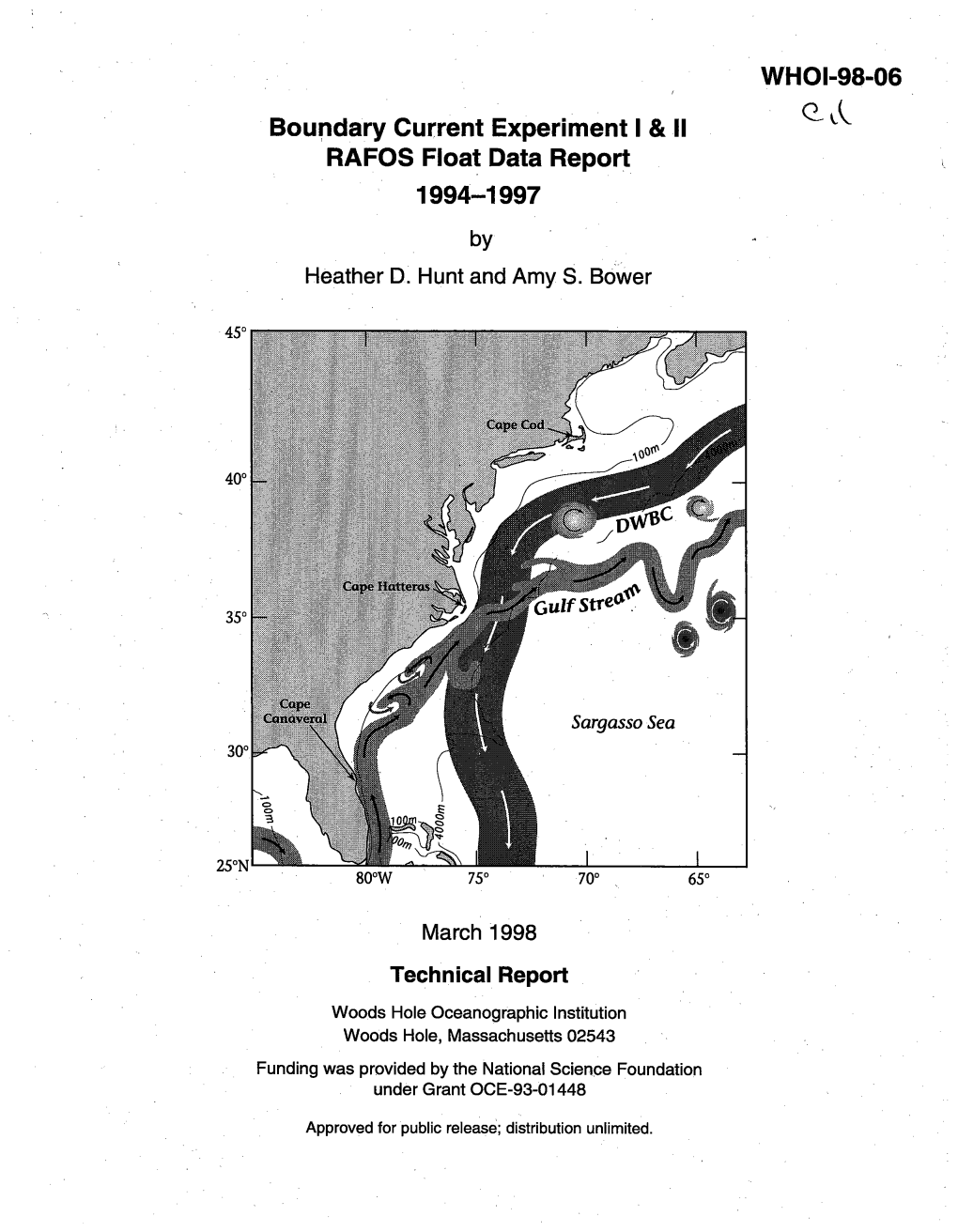
Boufldary Current Experiment I & II RAFOS Float Data Report
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Chinese Mooring and Buoy Observations in the Open-Ocean
Chinese mooring and buoy observations in the open-ocean Chujin Liang Second Institute of Oceanography, SOA May 28, 2013 Seoul Main oceanographic institutions of China First Institute of Oceanography Qingdao State Oceanic Administration Second Institute of Oceanography Hangzhou /SOA Third Institute of Oceanography Xiamen Polar Institute of China ShanghaiFirst Institute of Oceanography, FIO Institute of Oceanography Qingdao Chinese Academy of Science /CAS South China Sea Institute of Oceanography GuangzhouSecond Institute of Oceanography, SIO China Ocean University, Xiamen University Qingdao/Third Institute of Oceanography,Ministry of Education TIO Xiamen Tongji University, East China Normal university, Shanghai/ Tsinghua University, Peiking University, etc. Beijing Second Institute of Oceanography State Oceanic Administration State Oceanic Administration, SOA First Institute of Oceanography, FIO Second Institute of Oceanography, SIO Third Institute of Oceanography, TIO Second Institute of Oceanography State Oceanic Administration FIO is operating 2 buoy stations and 1 mooring at 2 sites Long-term buoy station in eastern Indian Ocean operated by FIO FIO-AMFR 中国 海洋一所 FIO Progress Report 1. Surface buoy at (100E, 8S) • In place since 30 May 2010 • Daily data will be posted on PMEL and FIO website soon • Data includes the meteorological parameters: wind speed and direction, air temperature, relative humidity, air pressure, shortwave radiation, long wave radiation, unfortunately precipitation missed due to damage in the deployment • Data includes -

Ebb and Flow Tides and Life on Our Once and Future Planet
This article has This been published in or collective redistirbution of any portion of this article by photocopy machine, reposting, or other means is permitted only with the approval of The approval portionthe ofwith any permitted articleonly photocopy by is machine, of this reposting, means or collective or other redistirbution BOOK REVIEWS Ebb and Flow Oceanography Tides and Life on Our Once and Future Planet , V By Tom Koppel, The Dundurn Group, which is the loss of much of the fleet of olume 21, Number 2, a quarterly journal of journal The olume 21, Number 2, a quarterly 2007, 296 pages, ISBN 9781550027266, Alexander the Great due to a tidal bore), Paperback, $26.99 US coastal ecosystems, modern analysis, and extracting energy from tides. Chapter 1 REVIEWED BY JOHN L. LuiCK contains an account of the ancient tidal dockyards at Lothal, India—surely a can- Ebb and Flow: Tides and Life on Our didate for “Engineering Wonders of the Once and Future Planet is well titled. It Ancient World.” The most ambitious and O tells the story of tides, why they matter, original chapter is the final one, whose ceanography Society. Society. ceanography what causes them, and how they have three subheadings are Sea Level Change changed over time. The author, Tom Causes Intertidal Zones to Migrate; Giant all sorts of ammonia and phosphoric Koppel, is not an analyst or theoretician Ancient Tides and Earth’s Rotation; and salts.” Again, tides are shown to play a C of tides but a man of inquisitive mind The Origin, Evolution, and Future of Life crucial role in both the origin and the opyright 2008 by The 2008 by opyright and substantial beachcombing and on Earth. -

The Evolution and Demise of North Brazil Current Rings*
VOLUME 36 JOURNAL OF PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY JULY 2006 The Evolution and Demise of North Brazil Current Rings* DAVID M. FRATANTONI Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Massachusetts PHILIP L. RICHARDSON Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceeanographic Institution, and Associated Scientists at Woods Hole, Woods Hole, Massachusetts (Manuscript received 27 May 2004, in final form 26 October 2005) ABSTRACT Subsurface float and surface drifter observations illustrate the structure, evolution, and eventual demise of 10 North Brazil Current (NBC) rings as they approached and collided with the Lesser Antilles in the western tropical Atlantic Ocean. Upon encountering the shoaling topography east of the Lesser Antilles, most of the rings were deflected abruptly northward and several were observed to completely engulf the island of Barbados. The near-surface and subthermocline layers of two rings were observed to cleave or separate upon encountering shoaling bathymetry between Tobago and Barbados, with the resulting por- tions each retaining an independent and coherent ringlike vortical circulation. Surface drifters and shallow (250 m) subsurface floats that looped within NBC rings were more likely to enter the Caribbean through the passages of the Lesser Antilles than were deeper (500 or 900 m) floats, indicating that the regional bathymetry preferentially inhibits transport of intermediate-depth ring components. No evidence was found for the wholesale passage of rings through the island chain. 1. Introduction ration from the NBC, anticyclonic rings with azimuthal speeds approaching 100 cm sϪ1 move northwestward a. Background toward the Caribbean Sea on a course parallel to the The North Brazil Current (NBC) is an intense west- South American coastline (Johns et al. -

Lagrangian Measurement of Subsurface Poleward Flow Between 38 Degrees N and 43 Degrees N Along the West Coast of the United States During Summer, 1993
CORE Metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk Provided by Calhoun, Institutional Archive of the Naval Postgraduate School Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive Faculty and Researcher Publications Faculty and Researcher Publications 1996-09-01 Lagrangian Measurement of subsurface poleward Flow between 38 degrees N and 43 degrees N along the West Coast of the United States during Summer, 1993 Collins, Curtis A. Geophysical Research Letters, Vol. 23, No. 18, pp. 2461-2464, September 1, 1996 http://hdl.handle.net/10945/45730 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 23, NO. 18, PAGES 2461-2464, SEPTEMBER 1, 1996 Lagrangian Measurement of subsurface poleward Flow between 38øN and 43øN along the West Coast of the United States during Summer, 1993 CurtisA. Collins,Newell Garfield, Robert G. Paquette,and Everett Carter 1 Departmentof Oceanography,Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California Abstract. SubsurfaceLagrangian measurementsat about Undercurrentalong the coastsof California and Oregon. We 140 m showedthat the pathof the CaliforniaUndercurrent lay are using quasi-isobaric(float depth controlled primarily by next to the continentalslope betweenSan Francisco(37.80N) the pressureeffect on density)RAFOS floats (Rossby et al., and St. GeorgeReef (41.8øN) duringmid-summer 1993. The 1986) to make these measurements. A RAFOS float consists meanspeed along this 500 km pathwas 8 cms-1. Theflow at of a hydrophonemounted in a glasstube that is about2 meters this depth was not disturbedby upwelling centersat Point long. These hydrophonesreceive signals from three sound Reyesor CapeMendocino. Restfits also demonstratethe abil- sources that were moored 400 km offshore between 34.3øN and ity to acousticallytrack floats located well above the sound 40.4øN.The sound sources emit 15 W, 80 s signalsa•t 260 Hz channelaxis along the California coast. -

MBARI's Buoy Based Seafloor Observatory Design (PDF)
MBARI’s Buoy Based Seafloor Observatory Design Mark Chaffey, Larry Bird, Jon Mike Kelley, Lance McBride, Tom O’Reilly, Walter Paul*, Erickson, John Graybeal, Andy Ed Mellinger, Tim Meese, Mike Risi, and Wayne Hamilton, Kent Headley, Radochonski Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute * Dept. of Applied Ocean Physics and Engineering 7700 Sandholdt Road Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution Moss Landing CA 95039 Woods Hole, MA 02543 Abstract - There has been considerable discussion and planning in the oceanographic community toward the installation of long-term seafloor sites for scientific observation in the deep ocean. The Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI) has designed a portable mooring system for deep ocean deployment that provides data and power connections to both seafloor and ocean surface instruments. The surface mooring collects solar and wind energy for powering instruments and transmits data to shore-side researchers using a satellite communications modem. A specialty anchor cable connects the surface mooring to a network of benthic instrumentation, providing the required data and power transfer. Design details and results of laboratory and field testing of the completed portions of the observatory system are described. I. INTRODUCTION Fig. 1 Buoy and seafloor network. MBARI has undertaken a major effort to develop the technology and techniques for building deep ocean of reliability, fault tolerance, and remote diagnostic seafloor observatories under the in-house Monterey capability. Ocean Observing System (MOOS) program. A key The overall functional and design requirements of the component of the overall observatory technology effort is MOOS mooring have previously been described in detail a moored surface buoy connected to the seafloor using [1] and can be summarized as a portable system, an anchor cable that incorporates mechanical strength configurable to a wide range of experiments, providing elements, copper conductors for power transfer, and episodic event response using on-board processing, and optical elements for communications. -

Particle Pathways in the Gulf Stream
Particle Pathways and P-T Shaw2 in the Gulf Stream Abstract East of Cape Hatteras, the Gulf Stream front separates two water masses: Sargasso Sea water to the south and the An experiment is under way to study the kinematics, dynamics, and cold slope waters to its north. The sharpness of the water mass path evolution of the Gulf Stream front between Cape Hatteras and boundary along the current's cyclonic edge and its coincidence 60°W. The Rafos float, which can track the true motion of water with the stream suggests that the front is impermeable to parcels along density surfaces which slope steeply across the Gulf Stream, has recently been developed for this study. These instruments cross-stream exchange of water. (It should be noted that this are launched in the center of the Gulf Stream every 5-15 days for a distinction of separate water masses loses validity below the 30-day mission. Each float provides a trajectory and a continuous midthermocline, where increasing uniformity of water prop- record of temperature and pressure along the trajectory. Our results erties suggests greater cross-stream exchange.) The Gulf so far show that: a) cross-stream motion has a significant vertical -1 Stream is not so isolated from the Sargasso Sea, however. Be- component (ranging to some 0.1 cm • s ) compared to vertical veloc- ities in midocean; b) floats systematically shoal (upwell) as they ap- tween the Florida Straits and Cape Hatteras the transport of proach anticyclonic meanders and deepen (downwell) as they ap- water more than doubles, with nearly all the new water coming proach cyclonic meanders; c) more than half of the floats launched from the Sargasso Sea. -

The Official Magazine of The
OceTHE OFFICIALa MAGAZINEn ogOF THE OCEANOGRAPHYra SOCIETYphy CITATION Smith, L.M., J.A. Barth, D.S. Kelley, A. Plueddemann, I. Rodero, G.A. Ulses, M.F. Vardaro, and R. Weller. 2018. The Ocean Observatories Initiative. Oceanography 31(1):16–35, https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2018.105. DOI https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2018.105 COPYRIGHT This article has been published in Oceanography, Volume 31, Number 1, a quarterly journal of The Oceanography Society. Copyright 2018 by The Oceanography Society. All rights reserved. USAGE Permission is granted to copy this article for use in teaching and research. Republication, systematic reproduction, or collective redistribution of any portion of this article by photocopy machine, reposting, or other means is permitted only with the approval of The Oceanography Society. Send all correspondence to: [email protected] or The Oceanography Society, PO Box 1931, Rockville, MD 20849-1931, USA. DOWNLOADED FROM HTTP://TOS.ORG/OCEANOGRAPHY SPECIAL ISSUE ON THE OCEAN OBSERVATORIES INITIATIVE The Ocean Observatories Initiative By Leslie M. Smith, John A. Barth, Deborah S. Kelley, Al Plueddemann, Ivan Rodero, Greg A. Ulses, Michael F. Vardaro, and Robert Weller ABSTRACT. The Ocean Observatories Initiative (OOI) is an integrated suite of instrumentation used in the OOI. The instrumented platforms and discrete instruments that measure physical, chemical, third section outlines data flow from geological, and biological properties from the seafloor to the sea surface. The OOI ocean platforms and instrumentation to provides data to address large-scale scientific challenges such as coastal ocean dynamics, users and discusses quality control pro- climate and ecosystem health, the global carbon cycle, and linkages among seafloor cedures. -

(Mooring – Tide Gauge) Is ~22 Mm
Updated Results from the In Situ Calibration Site in Bass Strait, Australia Christopher Watson1 , Neil White2,, John Church2 Reed Burgette1, Paul Tregoning 3, Richard Coleman 4 1 University of Tasmania ([email protected]) 2 Centre for Australian Weather and Climate Research, A partnership between CSIRO and the Australian Bureau of Meteorology 3 The Australian National University 4 The Institute of Marine and Antarctic Studies, UTAS OSTM/Jason-2 OST Science Team Meeting Updated Data Stream Presentation 1 San Diego OSTST Meeting October 2011 Impossible d'afficher l'image. Votre ordinateur manque peut-être de mémoire pour ouvrir l'image ou l'image est endommagée. Redémarrez l'ordinateur, puis ouvrez à nouveau le fichier. Si le x rouge est toujours affiché, vous devrez peut-être supprimer l'image avant de la réinsérer. Methods Recap Bass Strait • Primary site is located on Pass 088 in Bass Strait. Contributing bias estimates to the SWT/OSTST since the launch of T/P . • Secondary site along track in Storm Bay Storm Bay 2 Methods Recap • We adopt a purely geometric technique for determination of absolute bias. • The method is centred around the use of GPS buoys to define the datum ofhihf high preci si on ocean moori ngs. • Outside of available mooring data, all available mooring SSH data are used to correct tide gauge SSH to the comparison point. 3 Instrumentation (Bass Strait): Tide Gauge and CGPS • Tide gauge part of the Australian baseline array, located in Burnie. • Vertical velocity not significantly different from zero. • CGPS time series shows a quasi-annual periodic signal (amplitude ~3-4 mm). -

2021 Connecticut Boater's Guide Rules and Resources
2021 Connecticut Boater's Guide Rules and Resources In The Spotlight Updated Launch & Pumpout Directories CONNECTICUT DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION HTTPS://PORTAL.CT.GOV/DEEP/BOATING/BOATING-AND-PADDLING YOUR FULL SERVICE YACHTING DESTINATION No Bridges, Direct Access New State of the Art Concrete Floating Fuel Dock Offering Diesel/Gas to Long Island Sound Docks for Vessels up to 250’ www.bridgeportharbormarina.com | 203-330-8787 BRIDGEPORT BOATWORKS 200 Ton Full Service Boatyard: Travel Lift Repair, Refit, Refurbish www.bridgeportboatworks.com | 860-536-9651 BOCA OYSTER BAR Stunning Water Views Professional Lunch & New England Fare 2 Courses - $14 www.bocaoysterbar.com | 203-612-4848 NOW OPEN 10 E Main Street - 1st Floor • Bridgeport CT 06608 [email protected] • 203-330-8787 • VHF CH 09 2 2021 Connecticut BOATERS GUIDE We Take Nervous Out of Breakdowns $159* for Unlimited Towing...JOIN TODAY! With an Unlimited Towing Membership, breakdowns, running out GET THE APP IT’S THE of fuel and soft ungroundings don’t have to be so stressful. For a FASTEST WAY TO GET A TOW year of worry-free boating, make TowBoatU.S. your backup plan. BoatUS.com/Towing or800-395-2628 *One year Saltwater Membership pricing. Details of services provided can be found online at BoatUS.com/Agree. TowBoatU.S. is not a rescue service. In an emergency situation, you must contact the Coast Guard or a government agency immediately. 2021 Connecticut BOATER’S GUIDE 2021 Connecticut A digest of boating laws and regulations Boater's Guide Department of Energy & Environmental Protection Rules and Resources State of Connecticut Boating Division Ned Lamont, Governor Peter B. -

Characteristics of Intermediate Water Flow in the Benguela Current As
Deep-Sea Research II 50 (2003) 87–118 Characteristics of intermediate water flow in the Benguela current as measured with RAFOS floats P.L. Richardsona,*, S.L. Garzolib a Department of Physical Oceanography, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, 360 Woods Hole Road, Woods Hole, MA 02543, 3 Water Street, P.O. Box 721, USA b Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory, NOAA, 4301 Rickenbacker Causeway, Miami, FL 33149, USA Received 28 September 2001; accepted 26 July 2002 Abstract Seven floats (not launched in rings) crossed over the mid-Atlantic Ridge in the Benguela extension with a mean westward velocity of around 2 cm=s between 22S and 35S. Two Agulhas rings crossed over the mid-Atlantic Ridge with a mean velocity of 5:7cm=s toward 2851: This implies they translated at around 3:8cm=s through the background velocity field near 750 m: The boundaries of the Benguela Current extension were clearly defined from the observations. At 750 m the Benguela extension was bounded on the south by 35S and the north by an eastward current located between 18S and 21S. Other recent float measurements suggest that this eastward current originates near the Trindade Ridge close to the western boundary and extends across most of the South Atlantic, limiting the Benguela extension from flowing north of around 20S. The westward transport of the Benguela extension was estimated to be 15 Sv by integrating the mean westward velocities from 22S to 35S and multiplying by the 500 m estimated thickness of intermediate water. Roughly 1.5 Sv of this are transported by the B3 Agulhas rings that cross the mid-Atlantic Ridge each year (as observed with altimetry). -

Updated Guidelines for Seadatanet ODV Production
EMODnet Thematic Lot n° 4 - Chemistry EMODnet Phase III Updated guidelines for SeaDataNet ODV production M. Lipizer, M. Vinci, A. Giorgetti, L. Buga, M. Fichault, J. Gatti, S. Iona, M. Larsen, R. Schlitzer, D. Schaap, M. Wenzer, E. Molina Date: 12/04/2018 EMODnet Thematic Lot n° 4 - Chemistry Updated guidelines for SDN ODV production Index EMODnet Phase III............................................................................................................................1 Updated guidelines for SeaDataNet ODV producton......................................................................1 Updated guidelines for SeaDataNet ODV producton..........................................................................1 Introducton......................................................................................................................................1 SeaDataNet ODV import format.......................................................................................................1 How to check your SeaDataNet ODV fle format?............................................................................6 Vocabulary........................................................................................................................................7 How to choose the correct P01?......................................................................................................8 Flagging of Data Below Detecton Limits and Data Below Limit of Quantfcatoni.......................13 Guidelines for SeaDataNet ODV producton for sediment -

Vertical Flow in the Southern Ocean Estimated from Individual Moorings
SEPTEMBER 2015 S É VELLEC ET AL. 2209 Vertical Flow in the Southern Ocean Estimated from Individual Moorings F. SÉVELLEC,A.C.NAVEIRA GARABATO,J.A.BREARLEY,* AND K. L. SHEEN Ocean and Earth Science, National Oceanography Centre Southampton, University of Southampton, Southampton, United Kingdom (Manuscript received 14 February 2014, in final form 26 March 2015) ABSTRACT This study demonstrates that oceanic vertical velocities can be estimated from individual mooring mea- surements, even for nonstationary flow. This result is obtained under three assumptions: (i) weak diffusion (Péclet number 1), (ii) weak friction (Reynolds number 1), and (iii) small inertial terms (Rossby number 1). The theoretical framework is applied to a set of four moorings located in the Southern Ocean. For this site, the diagnosed vertical velocities are highly variable in time, their standard deviation being one to two orders of magnitude greater than their mean. The time-averaged vertical velocities are demonstrated to be largely induced by geostrophic flow and can be estimated from the time-averaged density and hori- zontal velocities. This suggests that local time-mean vertical velocities are primarily forced by the time- mean ocean dynamics, rather than by, for example, transient eddies or internal waves. It is also shown that, in the context of these four moorings, the time-mean vertical flow is consistent with stratified Taylor column dynamics in the presence of a topographic obstacle. 1. Introduction motions, and rectified mesoscale eddy flows along sloping isopycnals (Marshall and Speer 2012, and ref- Oceanic vertical flow is an important element of the erences therein). The latter two mechanisms are believed ocean circulation, playing a central role in the re- to extensively underpin vertical flow in the Southern distribution of water and tracers between (and within) Ocean, a region hosting a prominent large-scale vertical the upper-ocean mixed layer and the ocean interior.