The Liver Is Surrounded by a Fibrous Capsule and Completely Covered by Peritoneum (Except the Bare Areas)
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Te2, Part Iii
TERMINOLOGIA EMBRYOLOGICA Second Edition International Embryological Terminology FIPAT The Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology A programme of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) TE2, PART III Contents Caput V: Organogenesis Chapter 5: Organogenesis (continued) Systema respiratorium Respiratory system Systema urinarium Urinary system Systemata genitalia Genital systems Coeloma Coelom Glandulae endocrinae Endocrine glands Systema cardiovasculare Cardiovascular system Systema lymphoideum Lymphoid system Bibliographic Reference Citation: FIPAT. Terminologia Embryologica. 2nd ed. FIPAT.library.dal.ca. Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology, February 2017 Published pending approval by the General Assembly at the next Congress of IFAA (2019) Creative Commons License: The publication of Terminologia Embryologica is under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-ND 4.0) license The individual terms in this terminology are within the public domain. Statements about terms being part of this international standard terminology should use the above bibliographic reference to cite this terminology. The unaltered PDF files of this terminology may be freely copied and distributed by users. IFAA member societies are authorized to publish translations of this terminology. Authors of other works that might be considered derivative should write to the Chair of FIPAT for permission to publish a derivative work. Caput V: ORGANOGENESIS Chapter 5: ORGANOGENESIS -

Accessory Organs of the Gastrointestinal Tract ـــ ھــــــــ دي
.د ـــ ھــــــــدي ـــــــن Accessory Organs of the Gastrointestinal Tract Liver The liver is the largest gland in the body and lies mainly in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen (occupies most of the right hypochondrium and upper epigastrium and extends into the left hypochondrium ) where it is protected by the thoracic cage (lies deep to ribs 7-11 on the right side) and diaphragm and crosses the midline toward the left nipple. The liver may be divided into a large right lobe and a small left lobe by the attachment of the peritoneum of the falciform ligament . The right lobe is further divided into a quadrate lobe and a caudate lobe by the presence of the gallbladder, the fissure for the ligamentum teres, the inferior vena cava, and the fissure for the ligamentum venosum. Experiments have shown that, in fact, the quadrate and caudate lobes are a functional part of the left lobe of the liver. The porta hepatis, or hilum of the liver, is found on the posteroinferior surface and lies between the caudate and quadrate lobes . The upper part of the free edge of the lesser omentum is attached to its margins. In it lie the right and left hepatic ducts, the right and left branches of the hepatic artery, the portal vein, and sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve fibers . A few hepatic lymph nodes lie here; they drain the liver and gallbladder and send their efferent vessels to the celiac lymph nodes. The liver is completely surrounded by a fibrous capsule but only partially covered by peritoneum. -

Vascular Architecture in Anomalous Right-Sided Ligamentum Teres: Three-Dimensional Analyses in 35 Patients
DOI:10.1111/j.1477-2574.2011.00398.x HPB ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vascular architecture in anomalous right-sided ligamentum teres: three-dimensional analyses in 35 patients Junichi Shindoh1, Masaaki Akahane2, Shoichi Satou1, Taku Aoki1, Yoshifumi Beck1, Kiyoshi Hasegawa1, Yasuhiko Sugawara1, Kuni Ohtomo2 & Norihiro Kokudo1 1Hepato-biliary-pancreatic Surgery Division, Department of Surgery and 2Department of Radiology, Graduate School of Medicine, University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan Abstracthpb_398 32..41 Background: Right-sided ligamentum teres (RSLT) is a congenital anomaly that is sometimes encoun- tered during hepatobiliary surgeries. However, a valid protocol for describing the segmental anatomy of livers with RSLT has not been established, and confusions or anatomic misunderstandings have been a major problem. Methods: The vascular architecture and morphological characteristics were investigated in 35 livers with RSLT using three-dimensional (3D) simulations. Results: Couinaud's four sectors and three hepatic veins were clearly distinguished in the liver with RSLT using 3D simulations. The ligamentum teres was connected with the right paramedian portal pedicle, and the long axis of the cystic fossa was always observed on the left of the ligamentum teres in all 35 livers. However, when the main portal scissura was visualized using 3D simulation, the gallbladder was always located on the border of either side of the hemilivers, and the malposition of the gallbladder was not confirmed. Conclusions: Although the right-sided components of the livers are well developed as a result of the right-dominant distribution of the feeding vessels in livers with RSLT, the basic segmental structure defined by the four sectors and the three hepatic veins are as well preserved as those in the typical liver anatomy. -

Porta Hepatis) - Bile Ducts, Portal Vein, Hepatic Arteries
10 Al-Mohtaseb Faisal Nimri Shada gharaibeh The Liver continued The superior surface of the liver You can see * The right and left lobes. * Cut edge of the Falciform ligament. * The coronary ligament, continues on both sides as: * The left triangular ligament * The right triangular ligament * Between the edges of the coronary ligament is the Bare area of the liver (where there is no peritoneum covering the liver). * Groove for the inferior vena cava and the 3 hepatic veins that drain in it. * Cut edge of the Falciform ligament. * Caudate lobe of the liver more or less wrapping around the groove of the inferior vena cava * Fundus of gall bladder * Ligamentum teres → Relations of the superior surface • Diaphragm (the diaphragm is above the liver and is related to the anterior, superior and posterior surfaces of the liver but the visceral surface of the liver doesn’t have relations with the diaphragm). The diaphragm separates the Pleura & lung and the Pericardium & heart from the liver. 1 | P a g e → Relations of the liver anteriorly • Diaphragm • Rt & Lt pleura and lung (separated from the liver by the diaphragm) • Costal cartilage • Xiphoid process • Anterior abdominal wall → Relations of the liver posteriorly • Diaphragm • Rt. Kidney • Supra renal gland • Transverse colon (hepatic flexure) • Duodenum • Gall bladder • I.V.C • Esophagus • Fundus of stomach (pay attention to the impressions in the picture they are important) → lobes of the liver • Right Lobe • Left lobe • Quadrate lobe • Caudate lobe (the quadrate and caudate lobes are similar -

Falciform Ligament
It is largest gland in body, soft & pliable . Location: RT hypochondrium just beneath diaphragm which separates from the liver from thoracic cavity. Surfaces of liver: Superioanterior surface (diaphragmatic): its a convex upper surface of liver is molded to domes of diaphragm. Posteroinferior (visceral) :its irregular in shape molded to adjacent viscera 1)Large RT lobe & small LT lobe form by attachment of peritoneum of falciform ligament . 2)RT lobe is further subdivided into a quadrate lobe & caudate lobe by presence of gallbladder , ligamentum teres, inferior vena cava & ligamentum venosum . It found on visceral surface & lies between caudate & quadrate lobes . It containes : RT & LT hepatic ducts. RT& LT branches of hepatic artery. Portal vein. Sympathetic & parasympathetic nerve fibers . Hepatic lymph nodes. Peritoneal relation: Falciform Ligament: which is two-layered fold of peritoneum ascends from umbilicus to liver. It contain ligamentum teres ( remains of umbilical vein). Falciform ligament passes on to anterior & then superior surfaces of liver& then splits into two layers. The right upper layer forms coronary ligament. left upper layer of falciform ligament forms left triangular ligament . The right extremity of coronary ligament is known as right triangular ligament. ligamentum venosum ( remains of the ductus venosus) a fibrous band is attached to left branch of portal vein and inferior vena cava. lesser omentum arises from lesser curvature of stomach till edges of porta hepatis. It be noted that the peritoneal layers forming the coronary ligament are widely separated leaving an area of liver devoid of peritoneum. Diaphragm. RT & LT costal margins. RT & LT pleura . Lower margins of both lungs. Xiphoid process. -

Forgotten Ligaments of the Anterior Abdominal Wall: Have You Heard Their Voices?
Japanese Journal of Radiology (2019) 37:750–772 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-019-00869-5 INVITED REVIEW Four “fne” messages from four kinds of “fne” forgotten ligaments of the anterior abdominal wall: have you heard their voices? Toshihide Yamaoka1 · Kensuke Kurihara1 · Aki Kido2 · Kaori Togashi2 Received: 28 July 2019 / Accepted: 3 September 2019 / Published online: 14 September 2019 © Japan Radiological Society 2019 Abstract On the posterior aspect of the anterior abdominal wall, there are four kinds of “fne” ligaments. They are: the round ligament of the liver, median umbilical ligament (UL), a pair of medial ULs, and a pair of lateral ULs. Four of them (the round liga- ment, median UL, and paired medial ULs) meet at the umbilicus because they originate from the contents of the umbilical cord. The round ligament of the liver originates from the umbilical vein, the medial ULs from the umbilical arteries, and the median UL from the urachus. These structures help radiologists identify right-sided round ligament (RSRL) (a rare, but surgically important normal variant), as well as to diferentiate groin hernias. The ligaments can be involved in infamma- tion; moreover, tumors can arise from them. Unique symptoms such as umbilical discharge and/or location of pathologies relating to their embryology are important in diagnosing their pathologies. In this article, we comprehensively review the anatomy, embryology, and pathology of the “fne” abdominal ligaments and highlight representative cases with emphasis on clinical signifcance. Keywords Hepatic round ligament · Right-sided round ligament · Umbilical ligament · Groin hernia Introduction Anatomy On the posterior wall of the anterior abdominal wall, there Four “fne” ligaments of the posterior aspect of the anterior are forgotten ligaments. -

26 April 2010 TE Prepublication Page 1 Nomina Generalia General Terms
26 April 2010 TE PrePublication Page 1 Nomina generalia General terms E1.0.0.0.0.0.1 Modus reproductionis Reproductive mode E1.0.0.0.0.0.2 Reproductio sexualis Sexual reproduction E1.0.0.0.0.0.3 Viviparitas Viviparity E1.0.0.0.0.0.4 Heterogamia Heterogamy E1.0.0.0.0.0.5 Endogamia Endogamy E1.0.0.0.0.0.6 Sequentia reproductionis Reproductive sequence E1.0.0.0.0.0.7 Ovulatio Ovulation E1.0.0.0.0.0.8 Erectio Erection E1.0.0.0.0.0.9 Coitus Coitus; Sexual intercourse E1.0.0.0.0.0.10 Ejaculatio1 Ejaculation E1.0.0.0.0.0.11 Emissio Emission E1.0.0.0.0.0.12 Ejaculatio vera Ejaculation proper E1.0.0.0.0.0.13 Semen Semen; Ejaculate E1.0.0.0.0.0.14 Inseminatio Insemination E1.0.0.0.0.0.15 Fertilisatio Fertilization E1.0.0.0.0.0.16 Fecundatio Fecundation; Impregnation E1.0.0.0.0.0.17 Superfecundatio Superfecundation E1.0.0.0.0.0.18 Superimpregnatio Superimpregnation E1.0.0.0.0.0.19 Superfetatio Superfetation E1.0.0.0.0.0.20 Ontogenesis Ontogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.21 Ontogenesis praenatalis Prenatal ontogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.22 Tempus praenatale; Tempus gestationis Prenatal period; Gestation period E1.0.0.0.0.0.23 Vita praenatalis Prenatal life E1.0.0.0.0.0.24 Vita intrauterina Intra-uterine life E1.0.0.0.0.0.25 Embryogenesis2 Embryogenesis; Embryogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.26 Fetogenesis3 Fetogenesis E1.0.0.0.0.0.27 Tempus natale Birth period E1.0.0.0.0.0.28 Ontogenesis postnatalis Postnatal ontogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.29 Vita postnatalis Postnatal life E1.0.1.0.0.0.1 Mensurae embryonicae et fetales4 Embryonic and fetal measurements E1.0.1.0.0.0.2 Aetas a fecundatione5 Fertilization -

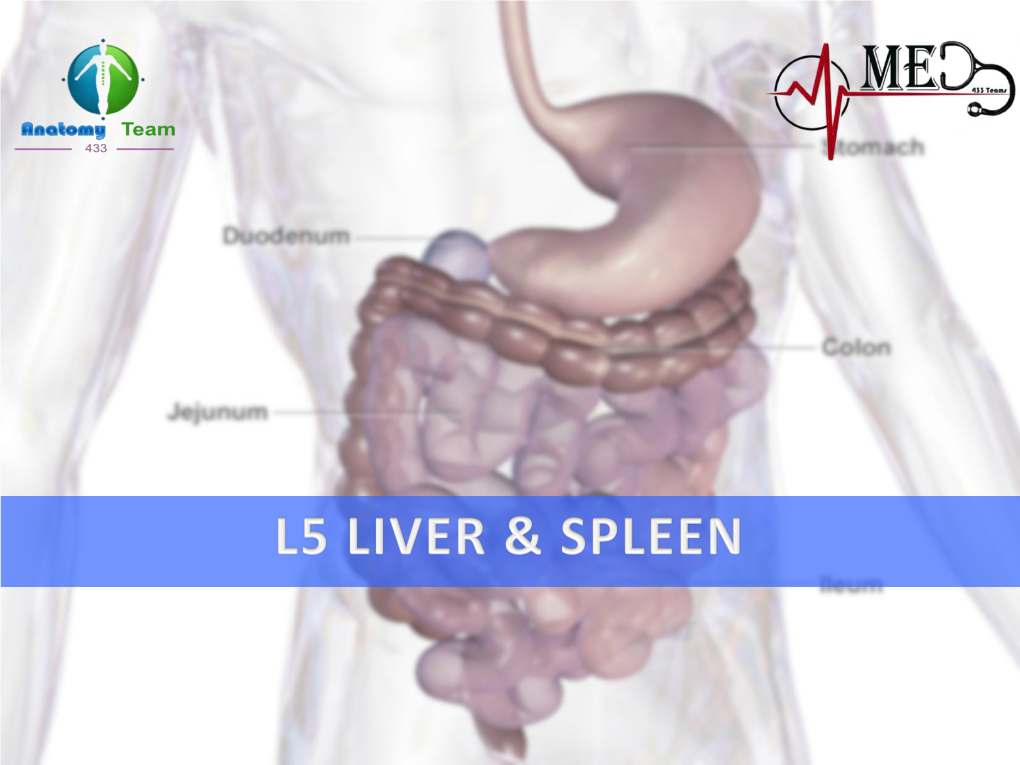
Anatomy of Liver and Spleen
Liver & Spleen 1 Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to describe the: • Location, subdivisions and relations and peritoneal reflection of liver. • Blood supply, nerve supply and lymphatic drainage of liver. • Location, subdivisions and relations and peritoneal reflection of spleen. • Blood supply, nerve supply and lymphatic drainage of spleen. 2 • The largest gland in the body. Liver • Weighs approximately 1500 g. (2.5% of adult body weight). • Lies mainly in: • Right hypochondrium, • Epigastrium and Epigastric • Left hypochondrium. • Protected by the thoracic cage and diaphragm, lies deep to ribs 7-11 on the right side and crosses the midline toward the left nipple. • Moves with the diaphragm and Hypogastric is located more inferiorly in erect posture because of gravity. 3 • Anterior: 1. Diaphragm, Relations of Liver 2. Right and left costal margins, 3. Right and left pleura, 4. Right and left lungs, 5. Xiphoid process, 6. Anterior abdominal wall. • Posterior: 1. Diaphragm, 2. Right kidney, 3. Right suprarenal land, 4. Right colic (hepatic ) flexure, 5. Duodenum, 6. Gallbladder, 7. Inferior vena cava, 8. Esophagus and 9. Fundus of the stomach. 4 Peritoneal Reflection Ø The liver is completely surrounded by a fibrous capsule. Superior Diaphragm layer of Ø It is partially covered by peritoneum. coronary Peritoneum ligament Ø The bare area of the liver is an area lying on the diaphragmatic surface Inferior Anterior layer of abdominal (on posterior surface of right lobe) where there is no coronary wall peritoneum between the liver and the ligament diaphragm. Posterior abdominal Ø Boundaries of Bare area: wall Ø Anterior: Superior layer of coronary ligament. -

Trombose Da Veia Porta Em Animais De Companhia: a Importância Do Exame Ecográfico No Diagnóstico
UNIVERSIDADE DE LISBOA Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária TROMBOSE DA VEIA PORTA EM ANIMAIS DE COMPANHIA: A IMPORTÂNCIA DO EXAME ECOGRÁFICO NO DIAGNÓSTICO INÊS ALEXANDRA PINTO DA SILVA CONSTITUIÇÃO DO JÚRI ORIENTADOR Doutor José Manuel Chéu Limão Oliveira Dr. Rui Domingos da Mata Lemos Doutora Maria Teresa da Costa Mendes Vítor Ferreira Villa de Brito Dr. Rui Domingos da Mata Lemos Ferreira CO-ORIENTADOR Doutora Maria Manuela Grave Rodeia Espada Niza 2015 LISBOA UNIVERSIDADE DE LISBOA Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária TROMBOSE DA VEIA PORTA EM ANIMAIS DE COMPANHIA: A IMPORTÂNCIA DO EXAME ECOGRÁFICO NO DIAGNÓSTICO INÊS ALEXANDRA PINTO DA SILVA DISSERTAÇÃO DE MESTRADO INTEGRADO EM MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA CONSTITUIÇÃO DO JÚRI ORIENTADOR Doutor José Manuel Chéu Limão Oliveira Dr. Rui Domingos da Mata Lemos Doutora Maria Teresa da Costa Mendes Vítor Ferreira Villa de Brito Dr. Rui Domingos da Mata Lemos Ferreira CO-ORIENTADOR Doutora Maria Manuela Grave Rodeia Espada Niza 2015 LISBOA Agradecimentos À Professora Doutora Manuela Rodeia, por me ter concedido a possibilidade de estagiar na sua clínica e por todos os conhecimentos transmitidos enquanto professora e coorientadora ao longo de todo este percurso. Ao Dr. Rui Lemos Ferreira, meu orientador, por todo o apoio que me prestou, quer ao longo do estágio, quer na elaboração deste trabalho, por todos os ensinamentos partilhados e por ter incutido em mim o gosto pela ecografia. É, sem dúvida, um exemplo de dedicação e profissionalismo, pelo qual nutro uma grande admiração. A toda a restante equipa da Azevet, Dra. Helena Guerreiro, Dra. Ivana Coimbra e Dra. Sílvia Spínola, com quem tanto aprendi. À Paula e à Rita, por todos os momentos de risada, por me terem feito sentir “em casa”. -

Anatomy of Liver and Spleen Doctors Notes Notes/Extra Explanation Please View Our Editing File Before Studying This Lecture to Check for Any Changes
Color Code Important Anatomy of Liver and Spleen Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: ✓ Location, subdivisions ,relations and peritoneal reflection of liver. ✓ Blood supply, nerve supply and lymphatic drainage of liver. ✓ Location, subdivisions and relations and peritoneal reflection of spleen. ✓ Blood supply, nerve supply and lymphatic drainage of spleen. Liver o The largest gland in the body. o Weighs approximately 1500 g (approximately 2.5% of adult body weight). o Lies mainly in the right hypochondrium and epigastrium and extends into the left hypochondrium. o Protected by the thoracic cage and diaphragm, its greater part lies deep to ribs 7-11 on the right side and crosses the midline toward the left below the nipple. o Moves with the diaphragm and is located more inferiorly when on is erect (standing) because of gravity. Liver Relations 10:07 Anterior: Extra o Diaphragm o Right & left pleura and lower margins of both lungs o Right and left costal margins o Xiphoid process o Anterior abdominal wall in the subcostal angle Extra Posterior: o Diaphragm o Inferior vena cava o Right kidney and right suprarenal gland o Hepatic flexure of the colon o Duodenum (beginning), gallbladder, esophagus and fundus of the stomach Liver Posterior surface of liver Peritoneal Reflection o The liver is completely surrounded by a fibrous capsule and completely covered by peritoneum (except the bare areas). o The bare area of the liver is a triangular area on the posterior (diaphragmatic) surface of right lobe where there is no intervening peritoneum between the liver and the diaphragm. -

Anatomy of the Liver from the fissures of the Porta Hepatis and the Ligamentum Venosum to Attach Along the Lesser Curvature of the Stomach
BASIC SCIENCE fissure for the ligamentum venosum. The lesser omentum arises Anatomy of the liver from the fissures of the porta hepatis and the ligamentum venosum to attach along the lesser curvature of the stomach. Harold Ellis Anatomical subdivisions (Figure 2) The superior aspect of the liver is divided by the falciform liga- Abstract ment into an anatomical right and smaller left lobe. Postero- The liver is the largest organ in the body. Its gross anatomical divisions inferiorly it bears an H-shaped arrangement of fossae: comprise the right, left, caudate and quadrate lobes, which do not corre- Anteriorly and to the right e the fossa for the gall bladder. spond with its functional division into eight hepatic segments, each with Posteriorly and to the right e the groove for the inferior vena their own blood supply and biliary drainage. The porta hepatis transmits cava. the hepatic artery, portal vein and right and left hepatic ducts (the portal Anteriorly and to the left e the groove for the ligamentum triad), together with lymphatic and autonomic nerves. The venous teres (often partially bridged by liver tissue). drainage of the liver, directly into the inferior vena cava, comprises the Posteriorly and to the left e the fissure for the ligamentum right, left and middle hepatic veins, together with the small accessory venosum. This represents the obliterated fetal ductus veno- hepatic veins. sus, which shunts oxygenated blood from the umbilical vein to the inferior vena cava, short-circuiting the liver. Keywords bile ducts; hepatic artery; hepatic lobes (right, left, quadrate The cross-bar of the H is the porta hepatis. -

Surgical Importance of Variant Hepatic Blood Vessels
CASE REPORT Surgical importance of variant hepatic blood vessels: a case report Importância cirúrgica de variações em vasos sangüíneos hepáticos: relato de caso Thejodhar Pulakunta,1 Bhagath Kumar Potu,1 Vasavi Rakesh Gorantla,2 Venkata Ramana Vollala,3 Jency Thomas2 Abstract Resumo This report describes a variation in blood vessels of the liver and Este relato descreve uma variação nos vasos hepáticos e uma abnormal entry of hepatic arteries into the liver found during routine entrada anormal de artérias hepáticas no fígado, encontradas durante dissection in an approximately 43-year-old male cadaver. An accessory uma dissecção de rotina em um cadáver masculino de hepatic artery arose from the superior mesenteric artery and entered aproximadamente 43 anos. Uma artéria hepática acessória surgiu da artéria mesentérica superior e entrou no fígado no porta hepatis, ao the liver at the porta hepatis, whereas the proper hepatic artery was passo que se constatou que a artéria hepática própria entrava no lobo seen entering the left liver lobe at the fissure for ligamentum venosum. hepático na fissura do ligamento venoso. Implicações clínicas desta Clinical implications of such variation are discussed in the article. variação são discutidas neste artigo. Keywords: Hepatic artery, accessory hepatic artery, liver Palavras-chave: Artéria hepática, artéria hepática acessória, transplantation. transplante hepático. Introduction We are reporting this case to create awareness in sur- Various types of vascular anomalies are frequently geons to take care and identify arterial variations before found in human abdominal viscera in dissection labora- visceral resection. tories and during radiological imaging. Literature describes incidence of “normal”hepatic arterial anatomy Case report ranging between approximately 50-80% of individuals.1-7 During routine dissection in the Department of Patterns of arterial blood supply to the liver are vari- Anatomy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, a able.