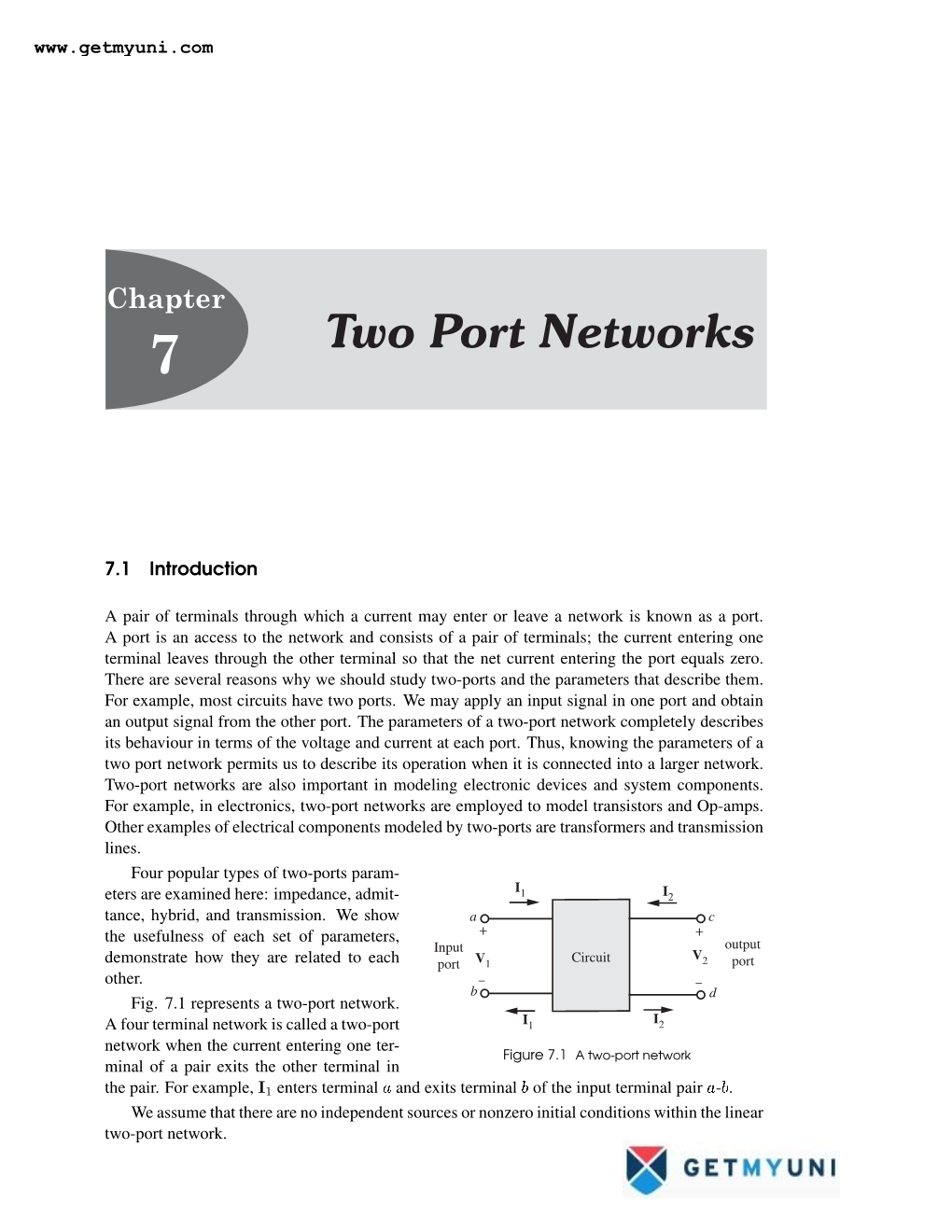
Two Port Networks
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Chapter 6 Two-Port Network Model
Chapter 6 Two-Port Network Model 6.1 Introduction In this chapter a two-port network model of an actuator will be briefly described. In Chapter 5, it was shown that an automated test setup using an active system can re- create various load impedances over a limited range of frequencies. This test set-up can therefore be used to automatically reproduce any load impedance condition (related to a possible application) and apply it to a test or sample actuator. It is then possible to collect characteristic data from the test actuator such as force, velocity, current and voltage. Those characteristics can then be used to help to determine whether the tested actuator is appropriate or not for the case simulated. However versatile and easy to use this test set-up may be, because of its limitations, there is some characteristic data it will not be able to provide. For this reason and the fact that it can save a lot of measurements, having a good linear actuator model can be of great use. Developed for transduction theory [29], the linear model presented in this chapter is 77 called a Two-Port Network model. The automated test set-up remains an essential complement for this model, as it will allow the development and verification of accuracy. This chapter will focus on the two-port network model of the 1_3 tube array actuator provided by MSI (Cf: Figure 5.5). 6.2 Theory of the Two–Port Network Model As a transducer converts energy from electrical to mechanical forms, and vice- versa, it can be modelled as a Two-Port Network that relates the electrical properties at one port to the mechanical properties at the other port. -

Analysis of Microwave Networks
! a b L • ! t • h ! 9/ a 9 ! a b • í { # $ C& $'' • L C& $') # * • L 9/ a 9 + ! a b • C& $' D * $' ! # * Open ended microstrip line V + , I + S Transmission line or waveguide V − , I − Port 1 Port Substrate Ground (a) (b) 9/ a 9 - ! a b • L b • Ç • ! +* C& $' C& $' C& $ ' # +* & 9/ a 9 ! a b • C& $' ! +* $' ù* # $ ' ò* # 9/ a 9 1 ! a b • C ) • L # ) # 9/ a 9 2 ! a b • { # b 9/ a 9 3 ! a b a w • L # 4!./57 #) 8 + 8 9/ a 9 9 ! a b • C& $' ! * $' # 9/ a 9 : ! a b • b L+) . 8 5 # • Ç + V = A V + BI V 1 2 2 V 1 1 I 2 = 0 V 2 = 0 V 2 I 1 = CV 2 + DI 2 I 2 9/ a 9 ; ! a b • !./5 $' C& $' { $' { $ ' [ 9/ a 9 ! a b • { • { 9/ a 9 + ! a b • [ 9/ a 9 - ! a b • C ) • #{ • L ) 9/ a 9 ! a b • í !./5 # 9/ a 9 1 ! a b • C& { +* 9/ a 9 2 ! a b • I • L 9/ a 9 3 ! a b # $ • t # ? • 5 @ 9a ? • L • ! # ) 9/ a 9 9 ! a b • { # ) 8 -

Scattering Parameters
Scattering Parameters Motivation § Difficult to implement open and short circuit conditions in high frequencies measurements due to parasitic L’s and C’s § Potential stability problems for active devices when measured in non-operating conditions § Difficult to measure V and I at microwave frequencies § Direct measurement of amplitudes/ power and phases of incident and reflected traveling waves 1 Prof. Andreas Weisshaar ― ECE580 Network Theory - Guest Lecture ― Fall Term 2011 Scattering Parameters Motivation § Difficult to implement open and short circuit conditions in high frequencies measurements due to parasitic L’s and C’s § Potential stability problems for active devices when measured in non-operating conditions § Difficult to measure V and I at microwave frequencies § Direct measurement of amplitudes/ power and phases of incident and reflected traveling waves 2 Prof. Andreas Weisshaar ― ECE580 Network Theory - Guest Lecture ― Fall Term 2011 1 General Network Formulation V + I + 1 1 Z Port Voltages and Currents 0,1 I − − + − + − 1 V I V = V +V I = I + I 1 1 k k k k k k V1 port 1 + + V2 I2 I2 V2 Z + N-port 0,2 – port 2 Network − − V2 I2 + VN – I Characteristic (Port) Impedances port N N + − + + VN I N Vk Vk Z0,k = = − + − Z0,N Ik Ik − − VN I N Note: all current components are defined positive with direction into the positive terminal at each port 3 Prof. Andreas Weisshaar ― ECE580 Network Theory - Guest Lecture ― Fall Term 2011 Impedance Matrix I1 ⎡V1 ⎤ ⎡ Z11 Z12 Z1N ⎤ ⎡ I1 ⎤ + V1 Port 1 ⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥ - V2 Z21 Z22 Z2N I2 ⎢ ⎥ = ⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥ I2 + ⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥ V2 Port 2 ⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥ - V Z Z Z I N-port ⎣ N ⎦ ⎣ N1 N 2 NN ⎦ ⎣ N ⎦ Network I N [V]= [Z][I] V + Port N N + - V Port i i,oc- Open-Circuit Impedance Parameters Port j Ij N-port Vi,oc Zij = Network I j Port N Ik =0 for k≠ j 4 Prof. -

Brief Study of Two Port Network and Its Parameters
© 2014 IJIRT | Volume 1 Issue 6 | ISSN : 2349-6002 Brief study of two port network and its parameters Rishabh Verma, Satya Prakash, Sneha Nivedita Abstract- this paper proposes the study of the various ports (of a two port network. in this case) types of parameters of two port network and different respectively. type of interconnections of two port networks. This The Z-parameter matrix for the two-port network is paper explains the parameters that are Z-, Y-, T-, T’-, probably the most common. In this case the h- and g-parameters and different types of relationship between the port currents, port voltages interconnections of two port networks. We will also discuss about their applications. and the Z-parameter matrix is given by: Index Terms- two port network, parameters, interconnections. where I. INTRODUCTION A two-port network (a kind of four-terminal network or quadripole) is an electrical network (circuit) or device with two pairs of terminals to connect to external circuits. Two For the general case of an N-port network, terminals constitute a port if the currents applied to them satisfy the essential requirement known as the port condition: the electric current entering one terminal must equal the current emerging from the The input impedance of a two-port network is given other terminal on the same port. The ports constitute by: interfaces where the network connects to other networks, the points where signals are applied or outputs are taken. In a two-port network, often port 1 where ZL is the impedance of the load connected to is considered the input port and port 2 is considered port two. -

Introduction to Transmission Lines
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSMISSION LINES DR. FARID FARAHMAND FALL 2012 http://www.empowermentresources.com/stop_cointelpro/electromagnetic_warfare.htm RF Design ¨ In RF circuits RF energy has to be transported ¤ Transmission lines ¤ Connectors ¨ As we transport energy energy gets lost ¤ Resistance of the wire à lossy cable ¤ Radiation (the energy radiates out of the wire à the wire is acting as an antenna We look at transmission lines and their characteristics Transmission Lines A transmission line connects a generator to a load – a two port network Transmission lines include (physical construction): • Two parallel wires • Coaxial cable • Microstrip line • Optical fiber • Waveguide (very high frequencies, very low loss, expensive) • etc. Types of Transmission Modes TEM (Transverse Electromagnetic): Electric and magnetic fields are orthogonal to one another, and both are orthogonal to direction of propagation Example of TEM Mode Electric Field E is radial Magnetic Field H is azimuthal Propagation is into the page Examples of Connectors Connectors include (physical construction): BNC UHF Type N Etc. Connectors and TLs must match! Transmission Line Effects Delayed by l/c At t = 0, and for f = 1 kHz , if: (1) l = 5 cm: (2) But if l = 20 km: Properties of Materials (constructive parameters) Remember: Homogenous medium is medium with constant properties ¨ Electric Permittivity ε (F/m) ¤ The higher it is, less E is induced, lower polarization ¤ For air: 8.85xE-12 F/m; ε = εo * εr ¨ Magnetic Permeability µ (H/m) Relative permittivity and permeability -

WAVEGUIDE ATTENUATORS : in Order to Control Power Levels in a Microwave System by Partially Absorbing the Transmitted Microwave Signal, Attenuators Are Employed
UNIT II MICROWAVE COMPONENTS Waveguide Attenuators- Resistive card, Rotary Vane types. Waveguide Phase Shifters : Dielectric, Rotary Vane types. Waveguide Multi port Junctions- E plane and H plane Tees, Magic Tee, Hybrid Ring. Directional Couplers- 2 hole, Bethe hole types. Ferrites-Composition and characteristics, Faraday Rotation. Ferrite components: Gyrator, Isolator, Circulator. S-matrix calculations for 2 port junction, E & H plane Tees, Magic Tee, Directional Coupler, Circulator and Isolator WAVEGUIDE ATTENUATORS : In order to control power levels in a microwave system by partially absorbing the transmitted microwave signal, attenuators are employed. Resistive films (dielectric glass slab coated with aquadag) are used in the design of both fixed and variable attenuators. A co-axial fixed attenuator uses the dielectric lossy material inside the centre conductor of the co-axial line to absorb some of the centre conductor microwave power propagating through it dielectric rod decides the amount of attenuation introduced. The microwave power absorbed by the lossy material is dissipated as heat. 1 In waveguides, the dielectric slab coated with aquadag is placed at the centre of the waveguide parallel to the maximum E-field for dominant TEIO mode. Induced current on the lossy material due to incoming microwave signal, results in power dissipation, leading to attenuation of the signal. The dielectric slab is tapered at both ends upto a length of more than half wavelength to reduce reflections as shown in figure 5.7. The dielectric slab may be made movable along the breadth of the waveguide by supporting it with two dielectric rods separated by an odd multiple of quarter guide wavelength and perpendicular to electric field. -

Solutions to Problems
Solutions to Problems Chapter l 2.6 1.1 (a)M-IC3T3/2;(b)M-IL-3y4J2; (c)ML2 r 2r 1 1.3 (a) 102.5 W; (b) 11.8 V; (c) 5900 W; (d) 6000 w 1.4 Two in series connected in parallel with two others. The combination connected in series with the fifth 1.5 6 V; 16 W 1.6 2 A; 32 W; 8 V 1.7 ~ D.;!b n 1.8 in;~ n 1.9 67.5 A, 82.5 A; No.1, 237.3 V; No.2, 236.15 V; No. 3, 235.4 V; No. 4, 235.65 V; No.5, 236.7 V Chapter 2 2.1 3il + 2i2 = 0; Constraint equation, 15vl - 6v2- 5v3- 4v4 = 0 i 1 - i2 = 5; i 1 = 2 A; i2 = - 3 A -6v1 + l6v2- v3- 2v4 = 0 2.2 va\+va!=-5;va=2i2;va=-3il; -5vl- v2 + 17v3- 3v4 = 0 -4vl - 2vz- 3v3 + l8v4 = 0 i1 = 2 A;i2 = -3 A 2.7 (a) 1 V ±and 2.4 .!?.; (b) 10 V +and 2.3 v13 + v2 2 = 0 (from supernode 1 + 2); 10 n; (c) 12 V ±and 4 n constraint equation v1- v2 = 5; v1 = 2 V; v2=-3V 2.8 3470 w 2.5 2.9 384 000 w 2.10 (a) 1 .!?., lSi W; (b) Ra = 0 (negative values of Ra not considered), 162 W 2.11 (a) 8 .!?.; (b),~ W; (c) 4 .!1. 2.12 ! n. By the principle of superposition if 1 A is fed into any junction and taken out at infinity then the currents in the four branches adjacent to the junction must, by symmetry, be i A. -

S-Parameter Techniques – HP Application Note 95-1
H Test & Measurement Application Note 95-1 S-Parameter Techniques Contents 1. Foreword and Introduction 2. Two-Port Network Theory 3. Using S-Parameters 4. Network Calculations with Scattering Parameters 5. Amplifier Design using Scattering Parameters 6. Measurement of S-Parameters 7. Narrow-Band Amplifier Design 8. Broadband Amplifier Design 9. Stability Considerations and the Design of Reflection Amplifiers and Oscillators Appendix A. Additional Reading on S-Parameters Appendix B. Scattering Parameter Relationships Appendix C. The Software Revolution Relevant Products, Education and Information Contacting Hewlett-Packard © Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company, 1997. 3000 Hanover Street, Palo Alto California, USA. H Test & Measurement Application Note 95-1 S-Parameter Techniques Foreword HEWLETT-PACKARD JOURNAL This application note is based on an article written for the February 1967 issue of the Hewlett-Packard Journal, yet its content remains important today. S-parameters are an Cover: A NEW MICROWAVE INSTRUMENT SWEEP essential part of high-frequency design, though much else MEASURES GAIN, PHASE IMPEDANCE WITH SCOPE OR METER READOUT; page 2 See Also:THE MICROWAVE ANALYZER IN THE has changed during the past 30 years. During that time, FUTURE; page 11 S-PARAMETERS THEORY AND HP has continuously forged ahead to help create today's APPLICATIONS; page 13 leading test and measurement environment. We continuously apply our capabilities in measurement, communication, and computation to produce innovations that help you to improve your business results. In wireless communications, for example, we estimate that 85 percent of the world’s GSM (Groupe Speciale Mobile) telephones are tested with HP instruments. Our accomplishments 30 years hence may exceed our boldest conjectures. -

A Unified State-Space Approach to Rlct Two-Port
A UNIFIED STATE-SPACE APPROACH TO RLCT TWO-PORT TRANSFER FUNCTION SYNTHESIS By EDDIE RANDOLPH FOWLER Bachelor of Science Kan,sas State University Manhattan, Kansas 1957 Master of Science Kansas State University Manhattan, Kansas 1965 Submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate Col.lege of the Oklahoma State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY May, 1969 OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY LIBRARY SEP 2l1 l969 ~ A UNIFIED STATE-SPACE APPROACH TO RLCT TWO-PORT TRANSFER FUNCTION SYNTHESIS Thesis Approved: Dean of the Graduate College ii AC!!..NOWLEDGEMENTS Only those that have had children in school all during their graduate studies know the effort and sacrifice that my wife, Pat, has endured during my graduate career. I appreciate her accepting this role without complainL Also I am deeply grateful that she was willing to take on the horrendous task of typing this thesis. My heartfelt thanks to Dr. Rao Yarlagadda, my thesis advisor, who was always available for $Uidance and help during the research and writing of this thesis. I appreciate the assistance and encouragement of the other members of my graduate comruitteei, Dr. Kenneth A. McCollom, Dr. Charles M. Bacon ar1d Dr~ K.ar 1 N.... ·Re id., I acknowledge Paul Howell, a fellow Electrical Engineering grad uate student, whose Christian Stewardship has eased the burden during these last months of thesis preparation~ Also Dwayne Wilson, Adminis trative Assistant, has n1y gratitude for assisting with the financial and personal problems of the Electrical Engineering graduate students. My thanks to Dr. Arthur M. Breipohl for making available the assistant ship that was necessary before it was financially possible to initiate my doctoral studies. -

Transmission Line and Lumped Element Quadrature Couplers
High Frequency Design From November 2009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright © 2009 Summit Technical Media, LLC QUADRATURE COUPLERS Transmission Line and Lumped Element Quadrature Couplers By Gary Breed Editorial Director uadrature cou- This month’s tutorial article plers are used for reviews the basic design Qpower division and operation of power and combining in circuits divider/combiners with where the 90º phase shift ports that have a 90- between the two coupled degree phase difference ports will result in a desirable performance characteristic. Common uses of quadrature couplers include: Antenna feed systems—The combination of power division/combining and 90º phase shift can simplify the feed network of phased array antenna systems, compared to alternative net- Figure 1 · The branch line quadrature works using delay lines, other types of com- hybrid, implemented using λ/4 transmission biners and impedance matching networks. It line sections. is especially useful for feeding circularly polarized arrays. Test and measurement systems—The phase each module has active devices in push-pull shift performance performance may be suffi- (180º combined), both even- and odd-order ciently accurate for phase comparisons over a harmonics can be reduced, which simplifies substantial fraction of an octave. A less critical output filtering. use is to resolve phase ambiguity in test cir- In an earlier tutorial [1], I introduced a cuits. A number of measurement techniques range of 90º coupler types without much anal- have a discontinuity at 180º—as this value is ysis. In this article, we focus on the two main approached, a 90º phase “rotation” moves the coupler types—the branch-line and coupled- system away from that point. -

2-PORT CIRCUITS Objectives
Notes for course EE1.1 Circuit Analysis 2004-05 TOPIC 10 – 2-PORT CIRCUITS Objectives: . Introduction . Re-examination of 1-port sub-circuits . Admittance parameters for 2-port circuits . Gain and port impedance from 2-port admittance parameters . Impedance parameters for 2-port circuits . Hybrid parameters for 2-port circuits 1 INTRODUCTION Amplifier circuits are found in a large number of appliances, including radios, TV, video, audio, telephony (mobile and fixed), communications and instrumentation. The applications of amplifiers are practically unlimited. It is clear that an amplifier circuit has an input signal and an output signal. This configuration is represented by a device called a 2-port circuit, which has an input port for the input signal and an output port for the output signal. In this topic, we look at circuits from this point of view. To develop the idea of 2-port circuits, consider a general 1-port sub-circuit of the type we are very familiar with: The basic passive elements, resistor, inductor and capacitor, and the independent sources, are the simplest 1-port sub-circuits. A more general 1-port sub-circuit contains any number of interconnected resistors, capacitors, inductors, and sources and could have many nodes. Sometimes, perhaps when we have finished designing a circuit, we become less interested in the detail of the elements interconnected in the circuit and are happy to represent the 1-port circuit by how it behaves at its terminals. This is achieved by use of circuit analysis to determine the relationship between the voltage V1 across the terminals and the current I1 flowing through the terminals which leads to a Thevenin or Norton equivalent circuit, which can be used as a simpler replacement for the original complex circuit. -

The Dreaded “2-Port Parameters”
The dreaded “2-port parameters” Aims: – To generalise the Thevenin an Norton Theorems to devices with 3 terminals – Develop efficient computational tools to handle feedback connections of non ideal devices L5 Autumn 2009 E2.2 Analogue Electronics Imperial College London – EEE 1 Generalised Thevenin + Norton Theorems • Amplifiers, filters etc have input and output “ports” (pairs of terminals) • By convention: – Port numbering is left to right: left is port 1, right port 2 – Output port is to the right of input port. e.g. output is port 2. – Current is considered positive flowing into the positive terminal of port – The two negative terminals are usually considered connected together • There is both a voltage and a current at each port – We are free to represent each port as a Thevenin or Norton • Since the output depends on the input (and vice-versa!) any Thevenin or Norton sources we use must be dependent sources. • General form of amplifier or filter: I1 I2 Port 1 + Thevenin Thevenin + Port 2 V1 V2 (Input) - or Norton or Norton - (Output) Amplifier L5 Autumn 2009 E2.2 Analogue Electronics Imperial College London – EEE 2 How to construct a 2-port model • Decide the representation (Thevenin or Norton) for each of: – Input port – Output port • Remember the I-V relations for Thevenin and Norton Circuits: – A Thevenin circuit has I as the independent variable and V as the dependent variable: V=VT + I RT – A Norton circuit has V as the independent variable and I as the dependent variable: I = IN + V GN • The source of one port is controlled by the independent variable of the other port.