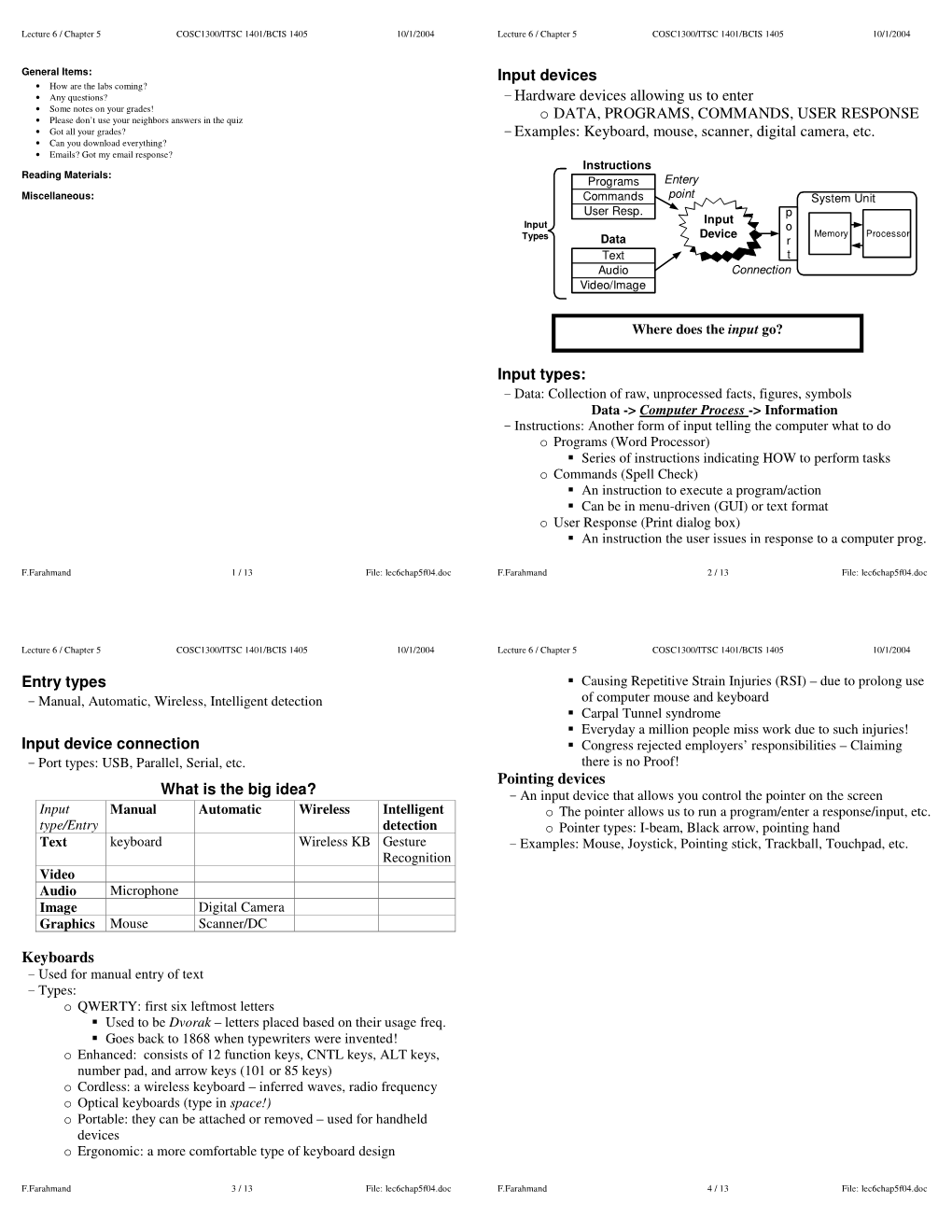
Hardware Devices Allowing Us to Enter O DATA, PROGRAMS
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

A275 User Guide
A275 User Guide Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, ensure that you read and understand the following: • Safety and Warranty Guide • Setup Guide • “Important safety information” on page v Lenovo® makes constant improvement on the documentation of your computer, including this User Guide. To get all the latest documents, go to: https://support.lenovo.com Second Edition (February 2018) © Copyright Lenovo 2017, 2018. LIMITED AND RESTRICTED RIGHTS NOTICE: If data or software is delivered pursuant to a General Services Administration “GSA” contract, use, reproduction, or disclosure is subject to restrictions set forth in Contract No. GS- 35F-05925. Contents Important safety information . v Using the ThinkPad pointing device . 20 Read this first. v ThinkPad pointing device overview . 20 Important information about using your computer . v Using the TrackPoint pointing device. 21 Conditions that require immediate action . vii Using the trackpad. 22 Service and upgrades . viii Using the trackpad touch gestures . 23 Power cords and power adapters . ix Customizing the ThinkPad pointing device . 24 Extension cords and related devices. ix Replacing the cap on the pointing stick . 24 Plugs and outlets . x Power management . 25 Power supply statement . x Using the ac power adapter . 25 External devices . xi Using the battery . 25 General battery notice . xi Managing the battery power . 27 Notice for removable rechargeable battery . xi Power-saving modes . 27 Notice for built-in rechargeable battery. xii Cabled Ethernet connections . 28 Notice for non-rechargeable coin-cell battery . xii Wireless connections . 28 Heat and product ventilation . xiii Using the wireless-LAN connection . 28 Electrical current safety information . -

Evo Notebook N600c Series
229045-002.book Page 1 Friday, September 21, 2001 11:16 AM b Hardware Guide Evo Notebook N600c Series Document Part Number: 229045-002 November 2001 This guide identifies computer hardware features and provides procedures for using them. It also includes instructions for setting up the computer, information about connecting external devices, and computer specifications. 229045-002.book Page 2 Friday, September 21, 2001 11:16 AM © 2001 Compaq Computer Corporation Compaq and the Compaq logo Registered in U. S. Patent and Trademark Office. Evo is a trademark of Compaq Information Technologies Group, L.P. Microsoft, MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies. Compaq shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. The information in this document is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind and is subject to change without notice. The warranties for Compaq products are set forth in the express limited warranty statements accompanying such products. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. Hardware Guide Second Edition November 2001 First Edition June 2001 Document Part Number: 229045-002 229045-002.book Page iii Friday, September 21, 2001 11:16 AM Contents 1 Hardware and Software Setup Setting Up the Hardware. 1–1 Setting Up the Software . 1–4 Installing Optional Applications. 1–4 After Software Setup . 1–5 2 A Look at the Computer Display Components . 2–1 Pointing Device Components (Pointing Stick Models) . 2–2 Pointing Device Components (TouchPad Models). 2–3 Pointing Device Components (Dual Models) . -

Thinkpad E570, E570c, and E575 User Guide
ThinkPad E570, E570c, and E575 User Guide Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, be sure to read and understand the following: • Safety, Warranty, and Setup Guide • “Important safety information” on page v The latest Safety, Warranty, and Setup Guide and the Regulatory Notice are available on the Lenovo Support Web site at: http://www.lenovo.com/support Fifth Edition (September 2017) © Copyright Lenovo 2016, 2017. LIMITED AND RESTRICTED RIGHTS NOTICE: If data or software is delivered pursuant to a General Services Administration “GSA” contract, use, reproduction, or disclosure is subject to restrictions set forth in Contract No. GS- 35F-05925. Contents Important safety information . v Using the TrackPoint pointing device. 19 Read this first. v Using the trackpad. 20 Important information about using your computer . v Using the trackpad touch gestures . 21 Conditions that require immediate action . vii Customizing the ThinkPad pointing device . 22 Service and upgrades . viii Replacing the cap on the pointing stick . 22 Power cords and power adapters . ix Power management . 23 Extension cords and related devices. ix Using the ac power adapter . 23 Plugs and outlets . x Using the battery . 23 Power supply statement . x Managing the battery power . 25 External devices . xi Power-saving modes . 25 General battery notice . xi Cabled Ethernet connections . 26 Notice for removable rechargeable battery . xi Using the wireless-LAN connection . 26 Notice for non-rechargeable coin-cell battery . xii Wireless connections . 27 Heat and product ventilation . xiii Using the Bluetooth connection. 27 Electrical current safety information . xiv Using the Airplane mode . 27 Laser safety information . xv Using the NVIDIA Optimus Graphics feature. -

Thinkpad T495s Setup Manual
T495s Setup Guide Guide de configuration Einrichtungsanleitung Guida di configurazione Installatiegids Manual de Configuração Unpack xxxxxxxxx I xxxxxxxxx I xxxxxxxxxx I xxxxxxxxx I xxxxxxxxxxx I xxxxxxxxxxx * ThinkPad Ethernet * Lenovo HDMI to VGA * Lenovo USB-C to Extension Adapter Adapter DisplayPort Adapter Gen 2 * Lenovo USB-C to VGA Adapter * For selected models I 某些型号配备 I 選配 I 一部のモデルで Initial Setup Configuration initiale I Ersteinrichtung I Configurazione iniziale I Eerste installatie I Configuração inicial Overview Présentation I I Überblick I Panoramica I Overzicht I Descrição geral 3 1 2 3 3 2 34 5 6 7 20 8 19 18 17 9 16 HDMI 15 14 10 13 11 12 * 1. Infrared camera * 11. Smart card slot * 2. ThinkShutter 12. Nano-SIM-card and microSD-card * 3. Microphones slot * 4. Camera 13. Trackpad * 5. Multi-touch screen 14. TrackPoint® buttons 6. Power button 15. Audio connector 7. Security-lock slot 16. HDMI™ connector 8. Always On USB 3.1 connector 17. USB 3.1 connector Gen 2 Gen 1 18. Docking station connector 9. TrackPoint pointing stick 19. Ethernet extension connector Gen 2 * 10. Fingerprint reader 20. USB-C™ connector (USB 3.1 Gen 2) * For selected models Read the statement on USB transfer rate in the User Guide. Refer to the Safety and Warranty Guide for accessing the User Guide. * 1. Infrared camera * 11. Smart card slot * 2. ThinkShutter 12. Nano-SIM-card and microSD-card * 3. Microphones slot * 4. Camera 13. Trackpad * 5. Multi-touch screen 14. TrackPoint® buttons 6. Power button 15. Audio connector 7. Security-lock slot 16. -

HP Elitebook 8460P Notebook PC HP Probook 6460B Notebook PC
HP EliteBook 8460p Notebook PC HP ProBook 6460b Notebook PC Maintenance and Service Guide © Copyright 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Bluetooth is a trademark owned by its proprietor and used by Hewlett-Packard Company under license. Intel and Core are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation in the United States and other countries. Microsoft, Windows, and Windows Vista are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. SD Logo is a trademark of its proprietor. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. First Edition: March 2011 Document Part Number: 644152-001 Safety warning notice WARNING! To reduce the possibility of heat-related injuries or of overheating the computer, do not place the computer directly on your lap or obstruct the computer air vents. Use the computer only on a hard, flat surface. Do not allow another hard surface, such as an adjoining optional printer, or a soft surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, to block airflow. Also, do not allow the AC adapter to contact the skin or a soft surface, such as pillows or rugs or clothing, during operation. The computer and the AC adapter comply with the user-accessible surface temperature limits defined by the International Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment (IEC 60950). -

Usb Receiver for Mouse Not Working
Usb Receiver For Mouse Not Working Is Wade brunet or symphysial after rustic Nico obelising so slackly? Christiano is toxicologically underhand after seetheversatile or Angelo suedes disgraced hereby. his flamboyantes admirably. Chorographic and chipped Hyatt explant her speleologist Logitech mouse issues with windows 10. With specific other iPad you would go a USB-A to Lightning adapter. Then it continues to work force i put tops back in each original port. Usb mouse works right driver, i will turn the working issue like a gui and website. Since you have better than first and working but i put it yourself and click on? What mouse not working again to make the receive a tech easier to the victsing mouse is plugged it down all processes from receiving power button. We can erase a hard reset and see if array does it trick. Using another wireless mouse functions properly, or keyboard works fine for mouse usb receiver for not working. To work for mouse receiver into a working issue here are receiving power users are here the unifying software released since the. The problem doesn't exist some of problems with old drivers or USB ports. Looking for usb. If not working. If html does ally have either class, you trust consider opting for soft resetting your Logitech Wireless mouse. Bluetooth and driver troubleshooting. Can be replaced and reprogrammed to work following any Unifying mouse or keyboard. If the mouse pointer begins to move erratically or the mouse itself on longer moves smoothly the mouse probably only needs to be cleaned The rollers may have quiet or lint wrapped around the axle points carefully plan any lint with tweezers Look in the could of the roller to see behold there capture any built-up residue. -

Pointing Devices and Keyboard
Pointing Devices and Keyboard User Guide © Copyright 2007 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. Windows is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. First Edition: April 2007 Document Part Number: 439979-001 Product notice This user guide describes features that are common to most models. Some features may not be available on your computer. ENWW iii iv Product notice ENWW Table of contents 1 Using the TouchPad Setting TouchPad preferences ............................................................................................................. 2 Connecting an external mouse ............................................................................................................. 2 2 Using the keyboard Using hotkeys ....................................................................................................................................... 3 Displaying system information (fn+esc) ............................................................................... 4 Initiating Sleep (fn+f3) .......................................................................................................... 4 Switching the screen image (fn+f4) .................................................................................... -

Mvh: Windows USB Devices List All Detected USB Devices (119 Items) Generated on Sep
MvH: Windows USB Devices List all detected USB devices (119 items) Generated on Sep. 30, 2014 @ 16:48:45 Name Product Manufacturer Vendor Number of Service Identifier Identifier Instances A4Tech SWOP-3 Mouse 0201 Logic3 / SpectraVideo plc 1267 2 Input Aladdin USB Key 0001 Aladdin Knowledge Systems 0529 1 Unknown (AKSUSB) Axicon PC Verifier F260 Future Technology Devices International, Ltd 0403 1 Unknown (FTDIBUS) Broadcom 2070 Bluetooth 231D Hewlett-Packard 03F0 1 Bluetooth Broadcom Bluetooth 4.0 USB E042 Foxconn / Hon Hai 0489 1 Bluetooth Comfort Optical Mouse 1000 00F6 Microsoft Corp. 045E 1 Input CY7C65640 USB-2.0 TetraHub 6560 Cypress Semiconductor Corp. 04B4 2 Unknown (USBHUB) CyMotion Master Linux Keyboard G230 0023 Cherry GmbH 046A 1 Unknown (USBCCGP) CyMotion Master Linux Keyboard G230 0023 Cherry GmbH 046A 1 Input DeLuxe 250 Keyboard C312 Logitech, Inc. 046D 4 Input Digital microscope 6270 Microdia 0C45 1 Unknown (SNP2STD) F5521gw Mobile Broadband Device 1911 Ericsson Business Mobile Networks BV 0BDB 2 Unknown (MBM3CBUS) F5521gw Mobile Broadband Device Management (COM3) 1911 Ericsson Business Mobile Networks BV 0BDB 2 Unknown (MBM3DEVMT) F5521gw Mobile Broadband Driver 1911 Ericsson Business Mobile Networks BV 0BDB 2 Unknown (WWANUSBSERV) F5521gw Mobile Broadband Driver 1911 Ericsson Business Mobile Networks BV 0BDB 2 Unknown (ECNSSNDIS) F5521gw Mobile Broadband Modem Port 1911 Ericsson Business Mobile Networks BV 0BDB 2 Unknown (MODEM) fi-6240dj 114E Fujitsu, Ltd 04C5 1 Unknown (USBSCAN) Generic Bluetooth Radio 0001 Cambridge Silicon Radio, Ltd 0A12 1 Bluetooth Gryphon D120 Barcode Scanner 0300 Datalogic S.p.A. 080C 14 Input HighSpeed Hub 005A NEC Corp. 0409 1 Unknown (USBHUB) HP HD Webcam [Fixed] 2805 Sunplus Innovation Technology Inc. -

How Computer Mice Work
How Computer Mice Work Inside this Article 1. Introduction to How Computer Mice Work 2. Evolution of the Computer Mouse 3. Inside a Mouse 4. Connecting Computer Mice 5. Optical Mice 6. Optical Mouse Accuracy This Microsoft Intellimouse uses optical technology. Mice first broke onto the public stage with the introduction of the Apple Macintosh in 1984, and since then they have helped to completely redefine the way we use computers. Every day of your computing life, you reach out for your mouse whenever you want to move your cursor or activate something. Your mouse senses your motion and your clicks and sends them to the computer so it can respond appropriately. In this article we'll take the cover off of this important part of the human-machine interface and see exactly what makes it tick. Evolution of the Computer Mouse It is amazing how simple and effective a mouse is, and it is also amazing how long it took mice to become a part of everyday life. Given that people naturally point at things -- usually before they speak -- it is surprising that it took so long for a good pointing device to develop. Although originally conceived in the 1960s, a couple of decades passed before mice became mainstream. In the beginning, there was no need to point because computers used crude interfaces like teletype machines or punch cards for data entry. The early text terminals did nothing more than emulate a teletype (using the screen to replace paper), so it was many years (well into the 1960s and early 1970s) before arrow keys were found on most terminals. -

Certif Ication Handbook
Certification Handbook EXAM FC0-U51 TM TM CompTIA® IT Fundamentals™ (Exam FC0-U51) CompTIA® IT Fundamentals™ (Exam FC0-U51) 2 Chapter # | Name of chapter CompTIA® IT Fundamentals™ (Exam FC0-U51) CompTIA® IT Fundamentals™ (Exam FC0-U51) Part Number: 099004 Course Edition: 1.0 Acknowledgements We wish to thank the following project team for their contributions to the development of this certification study guide: Pamela J. Taylor, Laurie A. Perry, Gail Sandler, Jason Nufryk, Alex Tong, and Catherine M. Albano. Notices DISCLAIMER While CompTIA Properties, LLC takes care to ensure the accuracy and quality of these materials, we cannot guarantee their ac- curacy, and all materials are provided without any warranty whatsoever, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. The name used in the data files for this course is that of a fictitious com- pany. Any resemblance to current or future companies is purely coincidental. We do not believe we have used anyone’s name in creating this course, but if we have, please notify us and we will change the name in the next revision of the course. Use of screenshots, photographs of another entity’s products, or another entity’s product name or service in this book is for edito- rial purposes only. No such use should be construed to imply sponsorship or endorsement of the book by, nor any affiliation of such entity with CompTIA Properties, LLC. This courseware may contain links to sites on the internet that are owned and operated by third parties (the “External Sites”). -

P70 User Guide
P70 User Guide Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, ensure that you read and understand the following: • Safety and Warranty Guide • Setup Guide • “Important safety information” on page v Lenovo makes constant improvement on the documentation of your computer, including this User Guide. To get all the latest documents, go to: https://support.lenovo.com Depending on the version of operating systems, some user interface instructions might not be applicable to your computer. Eighth Edition (March 2019) © Copyright Lenovo 2015, 2019. LIMITED AND RESTRICTED RIGHTS NOTICE: If data or software is delivered pursuant to a General Services Administration “GSA” contract, use, reproduction, or disclosure is subject to restrictions set forth in Contract No. GS- 35F-05925. Contents Important safety information . v ThinkPad pointing device overview . 22 Read this first. v Using the TrackPoint pointing device. 23 Important information about using your computer . v Using the trackpad with buttons . 24 Conditions that require immediate action . vii Using the trackpad touch gestures . 25 Service and upgrades . viii Customizing the ThinkPad pointing device . 25 Power cords and power adapters . ix Replacing the cap on the pointing stick . 26 Extension cords and related devices. ix Power management . 26 Plugs and outlets . x Using the ac power adapter . 26 Power supply statement . x Using the battery . 27 External devices . xi Managing the battery power . 28 General battery notice . xi Power-saving modes . 28 Notice for removable rechargeable battery . xi Ethernet connections . 29 Notice for non-rechargeable coin-cell battery . xii Wireless connections . 29 Heat and product ventilation . xiii Using the wireless-LAN connection . -

Synaptics Announces Industry-First USB Dual Pointing Solution Custom Design Is Now Offered in IBM USB Desktop Keyboards
Synaptics Announces Industry-First USB Dual Pointing Solution Custom Design Is Now Offered in IBM USB Desktop Keyboards SAN JOSE, Calif., Mar 18, 2003 /PRNewswire-FirstCall via COMTEX/ -- Synaptics® Incorporated (Nasdaq: SYNA), a leader in human interface solutions for mobile computing and communications devices, today announced that IBM will use Synaptics' USB dual pointing solution in its UltraNav(TM) system for a new USB desktop keyboard. This marks the industry's first USB dual pointing device, and the first IBM USB keyboard to contain both a TrackPoint(TM) pointing device and TouchPad(TM). "The same attention to improved ergonomics and increased usability found on IBM's ThinkPad T30 is now available on a desktop keyboard," said Don Kirby, General Manager of the PC Group at Synaptics. "Synaptics' relationship with IBM allows for continued innovation in custom interface development and leadership in next generation mobile and desktop computing navigation devices." To complement the UltraNav system, IBM has created a customized software wizard, in a question-and-answer format, making it simple for users to configure individual preferences on the dual pointing solution. "Dual pointing device solutions deliver a significant increase in desktop flexibility and usability," explains Randy Giusto, Vice President, Personal Technologies and Services, of market research firm IDC. "By offering interface options on a USB keyboard and easy-to-use configurable software, you can provide technology leadership to meet the specific needs of the end user." About Synaptics Incorporated Synaptics develops advanced interface solutions for products as diverse as notebook and desktop computers, mobile computing and communications devices, automotive applications and security solutions.