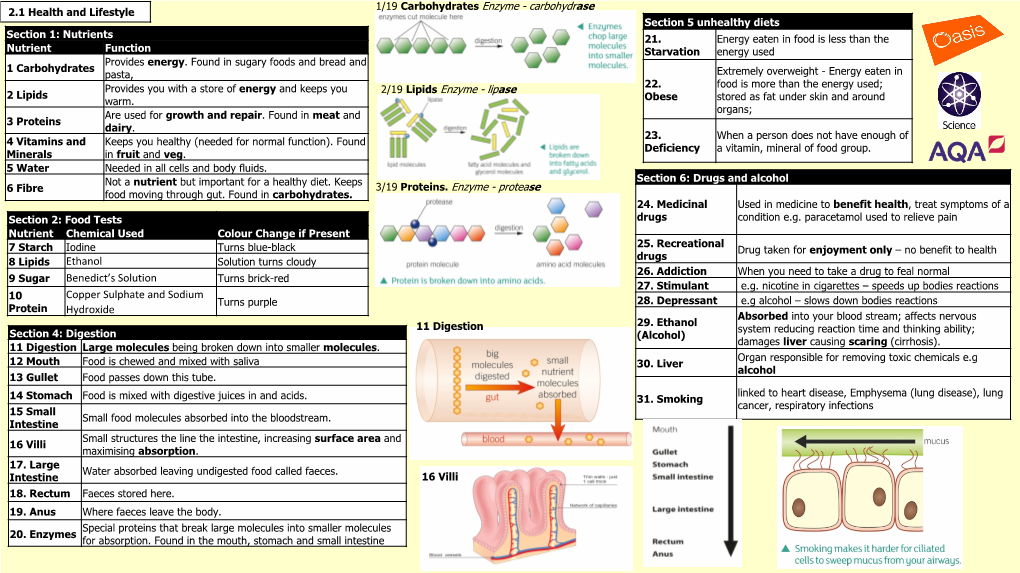
Ethanol Benedict's Solution Copper Sulphate and Sodium Hydroxide
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

SODIUM HYDROXIDE @Lye, Limewater, Lyewater@
Oregon Department of Human Services Office of Environmental Public Health (503) 731-4030 Emergency 800 NE Oregon Street #604 (971) 673-0405 Portland, OR 97232-2162 (971) 673-0457 FAX (971) 673-0372 TTY-Nonvoice TECHNICAL BULLETIN HEALTH EFFECTS INFORMATION Prepared by: ENVIRONMENTAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION OCTOBER, 1998 SODIUM HYDROXIDE @Lye, limewater, lyewater@ For More Information Contact: Environmental Toxicology Section (971) 673-0440 Drinking Water Section (971) 673-0405 Technical Bulletin - Health Effects Information Sodium Hydroxide Page 2 SYNONYMS: Caustic soda, sodium hydrate, soda lye, lye, natrium hydroxide CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: - Molecular Formula: NaOH - White solid, crystals or powder, will draw moisture from the air and become damp on exposure - Odorless, flat, sweetish flavor - Pure solid material or concentrated solutions are extremely caustic, immediately injurious to skin, eyes and respiratory system WHERE DOES IT COME FROM? Sodium hydroxide is extracted from seawater or other brines by industrial processes. WHAT ARE THE PRINCIPLE USES OF SODIUM HYDROXIDE? Sodium hydroxide is an ingredient of many household products used for cleaning and disinfecting, in many cosmetic products such as mouth washes, tooth paste and lotions, and in food and beverage production for adjustment of pH and as a stabilizer. In its concentrated form (lye) it is used as a household drain cleaner because of its ability to dissolve organic solids. It is also used in many industries including glassmaking, paper manufacturing and mining. It is used widely in medications, for regulation of acidity. Sodium hydroxide may be used to counteract acidity in swimming pool water, or in drinking water. IS SODIUM HYDROXIDE NATURALLY PRESENT IN DRINKING WATER? Yes, because sodium and hydroxide ions are common natural mineral substances, they are present in many natural soils, in groundwater, in plants and in animal tissues. -

Carbon Dioxide Capture from Atmospheric Air Using Sodium
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2728–2735 Carbon Dioxide Capture from Nearly all current research on CCS focuses on capturing CO2 from large, stationary sources such as power plants. Atmospheric Air Using Sodium Such plans usually entail separating CO2 from flue gas, compressing it, and transporting it via pipeline to be Hydroxide Spray sequestered underground. In contrast, the system described in this paper captures CO2 directly from ambient air (“air § capture”). This strategy will be expensive compared to capture JOSHUAH K. STOLAROFF, from point sources, but may nevertheless act as an important DAVID W. KEITH,‡ AND complement, since CO emissions from any sector can be GREGORY V. LOWRY*,† 2 captured, including emissions from diffuse sources such as Chemical and Petroleum Engineering, University of Calgary, aircraft or automobiles, where on-board carbon capture is and Departments of Civil and Environmental Engineering very difficult and the cost of alternatives is high. Additionally, and Engineering and Public Policy, Carnegie Mellon in a future economy with low carbon emissions, air capture University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania 15213 might be deployed to generate negative net emissions (1). This ability to reduce atmospheric CO2 concentrations faster Received October 15, 2007. Revised manuscript received than natural cycles allow would be particularly desirable in February 05, 2008. Accepted February 06, 2008. scenarios where climate sensitivity is on the high end of what is expected, resulting in unacceptable shifts in land usability and stress to ecosystems. In contrast to conventional carbon capture systems for Previous research has shown that air capture is theoreti- cally feasible in terms of thermodynamic energy require- power plants and other large point sources, the system described ments, land use (2), and local atmospheric transport of CO2 in this paper captures CO2 directly from ambient air. -

United States Patent Office Patented Nov
3,352,642 United States Patent Office Patented Nov. 14, 1967 2 stabilized during storage for long periods of time with 3,352,642 out degradation of its oxidizing properties. STABLZATION OF OZONE Lawrence J. Heidt, Arlington, and Vincent R. Landi, In accordance with these and other objects, the present rookine, Mass., assignors to Massachusetts in invention involves the stabilization of ozone through the stitute of Technology, Cambridge, Mass., a corpo use of base, and in particular, sodium hydroxide and ration of Massachusetts other sources of hydroxyl-ion. This is a wholly new and No Drawing. Fied June 29, 1964, Ser. No. 378,990 Surprising approach to the problem of stabilizing ozone. 15 Clains. (Cl. 23-222) In fact, it has heretofore been generally believed that sodium hydroxide would have the opposite effect upon This invention relates to a method for the stabilization O oZone. For example, the Encyclopedia of Chemical Tech of ozone and in particular to a method whereby ozone nology, vol. 9, p. 735, reports that the ozone decomposi can be stored and transported with a much slower rate tion reaction is greatly accelerated by increasing the of decomposition than was heretofore thought possible. hydroxyl-ion concentration. Other references are made Ozone (O3) is an unstable blue gas which is formed in the same volume and article on ozone to the supposedly photochemically in nature in the earth's stratosphere but 5 detrimental effect of sodium hydroxide on the stability which exists only in great dilution with air or oxygen at of ozone. It is also reported in the article that the de ground levels. -

Experimental Study on Capture of Carbon Dioxide and Production of Sodium Bicarbonate from Sodium Hydroxide
Environ. Eng. Res. 2016 Research Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4491/eer.2016.042 pISSN 1226-1025 eISSN 2005-968X In Press, Uncorrected Proof Experimental study on capture of carbon dioxide and production of sodium bicarbonate from sodium hydroxide † Jae-Goo Shim , Dong Woog Lee, Ji Hyun Lee, No-Sang Kwak KEPCO Research Institute, 105 Munji-ro, Yuseong-gu, Daejeon, 54056, Korea Abstract Global warming due to greenhouse gases is an issue of great concern today. Fossil fuel power plants, especially coal-fired thermal power plants, are a major source of carbon dioxide emission. In this work, carbon capture and utilization using sodium hydroxide was studied experimentally. Application for flue gas of a coal-fired power plant is considered. Carbon dioxide, reacting with an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, could be converted to sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). A bench-scale unit of a reactor system was designed for this experiment. The capture scale of the reactor system was 2 kg of carbon dioxide per day. The detailed operational condition could be determined. The purity of produced sodium bicarbonate was above 97% and the absorption rate of CO2 was above 95% through the experiment using this reactor system. The results obtained in this experiment contain useful information for the construction and operation of a commercial-scale plant. Through this experiment, the possibility of carbon capture for coal power plants using sodium hydroxide could be confirmed. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms Received March 14, 2016 Accepted May 10, 2016 of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial Li- † cense (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) Corresponding Author which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and repro- E-mail: [email protected] duction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -

Ammonia Solution
AMMONIA SOLUTION Prepared at the 46th JECFA (1996), published in FNP 52 Add 4 (1996) superseding specifications prepared at the 19 th JECFA (1975), published in NMRS 55B (1976) and in FNP 52 (1992) under the name Ammonium Hydroxide. Metals and arsenic specifications revised at the 59th JECFA (2002) An ADI 'not limited' was established at the 9th JECFA (1965) SYNONYMS Ammonium hydroxide, strong ammonia solution, aqueous ammonia, INS No. 527 DEFINITION Chemical names Ammonia solution C.A.S. number 7664-41-7 (ammonia) 1336-21-6 (aqueous ammonia) Chemical formula NH3 (aqueous) Formula weight 17.03 Assay Not less than 27% and not more than 30% DESCRIPTION Clear, colourless liquid having an exceedingly pungent, characteristic odour. Upon exposure to air it loses ammonia rapidly FUNCTIONAL USES Acidity regulator CHARACTERISTICS IDENTIFICATION Test for ammonia Hold a glass rod, wet with hydrochloric acid, near the sample. Dense white fumes are produced. Specific gravity (Vol. 4) d (25,25): about 0.90 PURITY Non-volatile residue Not more than 0.02% by the following procedure: Evaporate 11 ml (10 g) of the sample in a tared platinum or porcelain dish to dryness, dry at 105o for 1 h, cool and weigh Readily oxidizable Dilute 4 ml of the sample with 6 ml of water, and add a slight excess of dilute substances sulfuric acid TS and 0.1 ml of 0.1N potassium permanganate. The pink colour does not completely disappear within 10 min. Lead Not more than 2 mg/kg Determine using an atomic absorption technique appropriate to the specified level. -

Japanese Insecticide
WAR DEPARTMENT INTELLT nPJKClS JAPANESE TT^CTICIDE 27 MARCH 19h7 5250th TECHNICAL INTELLIGENCE COMPANY WDI DIV, G-2 GHQ FEC AP0 500 31 March 1947 SUBJECT; Report of Investigation - Japanese Insecticide (Supplementary Report) TO : Director, WDI DIV 1. AUTHORITY: G-2 X.O.M., from Director, WDI DIV to 5250th TIC, subject: n Japanese Insecticide", dated 7 February 1947, 2. REFERENCES: a. Letter, War Department General Staff, Intelligence Division, MIT File No, 070, subject: "Japanese Insecticide", dated 24 January 1947 (Control No. MD-610), b. Report of Investigation - Japanese Insecticide, by 5250th 7 Technical Intelligence Company, dated 18 February 194' * This report forwarded all data then available in reply torequest for information from War Department (reference a) and recommended further investigation along indicated lines. 3. DETAILS OF INVESTIGATION: a. Investigators visited the Central Laboratory of the Kanegafuchi Spinning Co., Ltd., Osaka 12 March 1947. Yoshio MIKAMI, Jr* charge of the chemical branch of the company, was interviewedand dis- closed that he had worked for six months with Professor SHISHIDO, Kyoto Imperial University, on research of insecticides, and that the company and SHISHIDO has jointly applied for a oatent on the manufacture of f BHC ! KANEB0 , andinsect powder consisting of 10% benezenc hexachlcride and 90% talc or clay. Copy of Translation of Patent Application received from MIKAMI is inclosed (Incl 1). MIKAMI stated that the comoany had manufactured two tons of the product; one ton, packed in 20 kg. paper -

SODIUM METHOXIDE, 30% in Methanol
AKS761.5 - SODIUM METHOXIDE, 30% in methanol SODIUM METHOXIDE, 30% in methanol Safety Data Sheet AKS761.5 Date of issue: 10/26/2016 Version: 1.0 SECTION 1: Identification 1.1. Product identifier Product name : SODIUM METHOXIDE, 30% in methanol Product code : AKS761.5 Product form : Mixture Physical state : Liquid Formula : CH3NaO Synonyms : SODIUM METHYLATE METHANOL, SODIUM SALT Chemical family : METAL ALCOHOLATE 1.2. Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use Recommended use : Chemical intermediate For research and industrial use only 1.3. Details of the supplier of the safety data sheet GELEST, INC. 11 East Steel Road Morrisville, PA 19067 USA T 215-547-1015 - F 215-547-2484 - (M-F): 8:00 AM - 5:30 PM EST [email protected] - www.gelest.com 1.4. Emergency telephone number Emergency number : CHEMTREC: 1-800-424-9300 (USA); +1 703-527-3887 (International) SECTION 2: Hazard(s) identification 2.1. Classification of the substance or mixture GHS-US classification Flammable liquids Category 3 H226 Acute toxicity (oral) Category 3 H301 Acute toxicity (dermal) Category 3 H311 Acute toxicity (inhalation:vapor) Category 3 H331 Skin corrosion/irritation Category 1B H314 Serious eye damage/eye irritation Category 1 H318 Specific target organ toxicity (single exposure) Category 1 H370 Specific target organ toxicity (single exposure) Category 3 H336 Full text of H statements : see section 16 2.2. Label elements GHS-US labeling Hazard pictograms (GHS-US) : GHS02 GHS05 GHS06 GHS07 GHS08 Signal word (GHS-US) : Danger Hazard statements (GHS-US) : H226 - Flammable liquid and vapor H301+H311+H331 - Toxic if swallowed, in contact with skin or if inhaled H314 - Causes severe skin burns and eye damage H318 - Causes serious eye damage H336 - May cause drowsiness or dizziness H370 - Causes damage to organs Precautionary statements (GHS-US) : P280 - Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection P307 + P311 - If exposed: Call a poison center/doctor P210 - Keep away from heat, open flames, sparks. -

3. Extraction
© Professor Kathleen V. Kilway and Robert Clevenger, Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri – Kansas City, 2006 3. Extraction J.R. Mohrig, Chapters 11 (extraction) and 12 (drying agents) C.N. Hammond, 113-118 (general introduction) and P.F. Schatz: 120 (acid-base) 115 (partition/distribution coefficient) 122-127 (microscale extraction and general information) 127-132 (density, sources of confusion) 132-137 (drying agents) Vocabulary: Miscible Two or more compounds, which dissolve in one another to form a homogenous solution. Aqueous contains water. Organic non-aqueous (does not contain water), usually hydrophobic. Emulsion No separation of the organic and aqueous layers (usually cloudy). Partition coefficient the same as the distribution coefficient. It is the relationship between the solubility ratios of two different layers for a compound, which is soluble in both solvents. Workup is a generic term used for any step or series of steps performed at the end of a reaction to isolate and/or purify the product. It may include filtration, extraction, and/or chromatography. Background What is extraction? There are several listings for extraction in the American Heritage Dictionary (p. 466) but in its simplest form, extraction is the separation of something from another. There are numerous examples in our everyday lives. Vanilla extract is used in cooking. The essence of perfume is extracted from flowers and plants, for example. For the organic chemist, extraction is part of the normal work up of a reaction. Sometimes, it is referred to an aqueous workup in the text or manuscript. We wash the organic reaction mixture with water (acidic, neutral and/or basic) to remove any byproducts or inorganic material. -

Incompatible Chemical Groups.Pdf
Incompatible Chemical Hazard Groups (and some common examples) Mineral Acids Do NOT Store with… Hydrochloric acid Hydrogen peroxide Acetone Sulfuric Acid Sodium hydroxide Methanol Phosphoric Acid Calcium hydroxide Nitric Acid (keep separate) Chloroform Acetic Acid Strong Organic Acids Do NOT Store with… Acetic Acid3, 4 Hydrogen peroxide Acetone Acetonitrile Formic Acid Sodium hydroxide Methanol Benzene Sulfuric Acid Chloroform Special 1. Organic acids are varied and may be incompatible with each other. Notes: Check MSDSs for specifics 2. Store nitric acid separately in its own secondary container. It is a strong oxidizer. 3. Store acetic acid away from oxidizing agents — especially nitric acid. 4. Acetic acid may be stored with some inorganic acids and most flammable solvents but keep in a separate secondary container. (>70% acetic acid is combustible). Weak These are typically not corrosive and not strongly reactive and can be Organic Acids stored with general liquid lab chemicals. Examples include butyric, maleic, and benzoic acids. Non-Flammable Do NOT Store with… Chlorinated Solvents Methylene chloride Acetone Hexane Chloroform Methanol Nitric Acid Trichloroethane Ethanol Hydrogen Peroxide Carbon tetrachloride Organic Solvents Do NOT Store with… Acetone Hydrogen peroxide Nitric Acid Methanol Sodium hydroxide Chromic Acid Phenol Calcium hydroxide Sulfuric Acid Xylene Trichlorfluoromethane Hydrochloric Acid Oxidizers Do NOT Store with… Nitric Acid Sodium metal Paper and oily rags Hydrogen peroxide Isopropyl Alcohol Xylene Chromic Acid Acetone Sodium nitrate Perchloric Acid Ethyl ether Bromate salts . -

Sodium Hydride-Based Hydrogen Storage System
Analysis of the Sodium Hydride-based Hydrogen Storage System being developed by PowerBall Technologies, LLC Prepared for The US Department of Energy Office of Power Technologies Hydrogen Program Prepared by J. Philip DiPietro and Edward G. Skolnik, Energetics, Incorporated October 29, 1999 v Analysis of the Sodium Hydride-Based Hydrogen Storage System being developed by PowerBall Technologies, LLC We considered the viability of a system for storing hydrogen on-board a vehicle in the form of plastic-encapsulated sodium hydride (NaH) pellets. Hydrogen is produced when the pellets are cut and immersed in water. The exposed NaH surface reacts with water, releasing hydrogen and forming sodium hydroxide (NaOH) as a byproduct. Later, in an off-board activity, the hydroxide is recycled to hydride via a multi-step regeneration process that relies on methane as both a fuel and a reactant. This is a preliminary analysis that required the development of conceptual designs for several of the process steps and the need to make several assumptions in order to complete the overall systems analysis. The analysis was peer reviewed by several members of their hydrogen community, and their comments were taken into account in the preparation of this document. Executive Summary The reaction of sodium hydride with water to form hydrogen and sodium hydroxide can be utilized onboard a vehicle to deliver hydrogen to an onboard power system. PowerBall Technologies, LLC has developed a novel means of controlling the reaction: they encapsulate small amounts of sodium hydride in plastic balls. These balls are sliced open one at a time onboard the vehicle to deliver hydrogen as needed. -

Carbon Dioxide Capture Using Sodium Hydroxide Solution: Comparison Between an Absorption Column and a Membrane Contactor
Carbon dioxide capture using sodium hydroxide solution: comparison between an absorption column and a membrane contactor Dissertation presented by Nicolas CAMBIER for obtaining the master's degree in Chemical and Materials Engineering Supervisor Patricia LUIS ALCONERO Tutor Israel RUIZ SALMON Readers Juray DE WILDE, Joris PROOST Academic year 2016-2017 Acknowledgements Before beginning this report, I would like to address my acknowledgements to the people who helped me throughout the realisation of my master thesis. First of all, nothing would have been possible without the support and advices of my promoter, the professor Patricia Luis. The working environment provided by her team and the meetings along the year were good opportunities to evolve for the best. Secondly, I would like to thank Israel Ruiz Salmon who was a major actor of my work. He always helped me with my numerous questions and uncertainties. Without him, I certainly would not have managed to overcome the numerous challenges encountered during this work. His precious advices and corrections are certainly what helped me to finish this master thesis. For their help with the preparation of solutions and in the lab, I thank Luc Wautier, Frédéric Van Wonterghem, Ronny Santoro and Nadine Deprez. In addition, I would like to express my gratitude to Professors J. De Wilde and J. Proost who have accepted to be the readers of this thesis. List of symbols Symbols Signification Units 푎 Specific area of packing per unit volume of column m2⁄m³ 퐴 Cross sectional area of the column m² -

Glibenclamide (Glibenclamidum)
The International Pharmacopoeia - Sixth Edition, 2016 Glibenclamide (Glibenclamidum) Glibenclamide (Glibenclamidum) Molecular formula. C H ClN O S 23 28 3 5 Relative molecular mass. 494.0 Graphic formula. Chemical name. 1-[[p-[2-(5-Chloro-o-anisamido)ethyl]phenyl]sulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea; 5-chloro-N-[2-[4- [[[(cyclohexylamino)carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]-ethyl]-2-methoxybenzamide; 1-[4-[2-(5-chloro-2-methoxybenzamido)ethyl]- phenylsulfonyl]-3-cyclohexylurea; CAS Reg. No. 10238-21-8. Other name. Glyburide. Description. A white or almost white, crystalline powder; odourless or almost odourless. Solubility. Practically insoluble in water and ether R; slightly soluble in ethanol (~750 g/l) TS and methanol R. Category. Antidiabetic agent. Storage. Glibenclamide should be kept in a well-closed container. Requirements Definition. Glibenclamide contains not less than 98.5% and not more than 101.0% of C23H28ClN3O5S, calculated with reference to the dried substance. Identity tests • Either test A alone or tests B and C may be applied. A. Carry out the examination as described under 1.7 Spectrophotometry in the infrared region. The infrared absorption spectrum is concordant with the spectrum obtained from glibenclamide RS or with the reference spectrum of glibenclamide. B. The absorption spectrum of a 0.10 mg/mL solution in hydrochloric acid/ methanol (0.01 mol/l) VS, when observed between 230 nm and 350 nm, exhibits a maximum at about 300 nm and a less intense maximum at about 275 nm; the absorbance of a 1-cm layer at 300 nm is about 0.63. C. Melting temperature, about 172 °C. Heavy metals. Use 1.0 g for the preparation of the test solution as described under 2.2.3 Limit test for heavy metals, Procedure 3; not more than 20 μg/g.