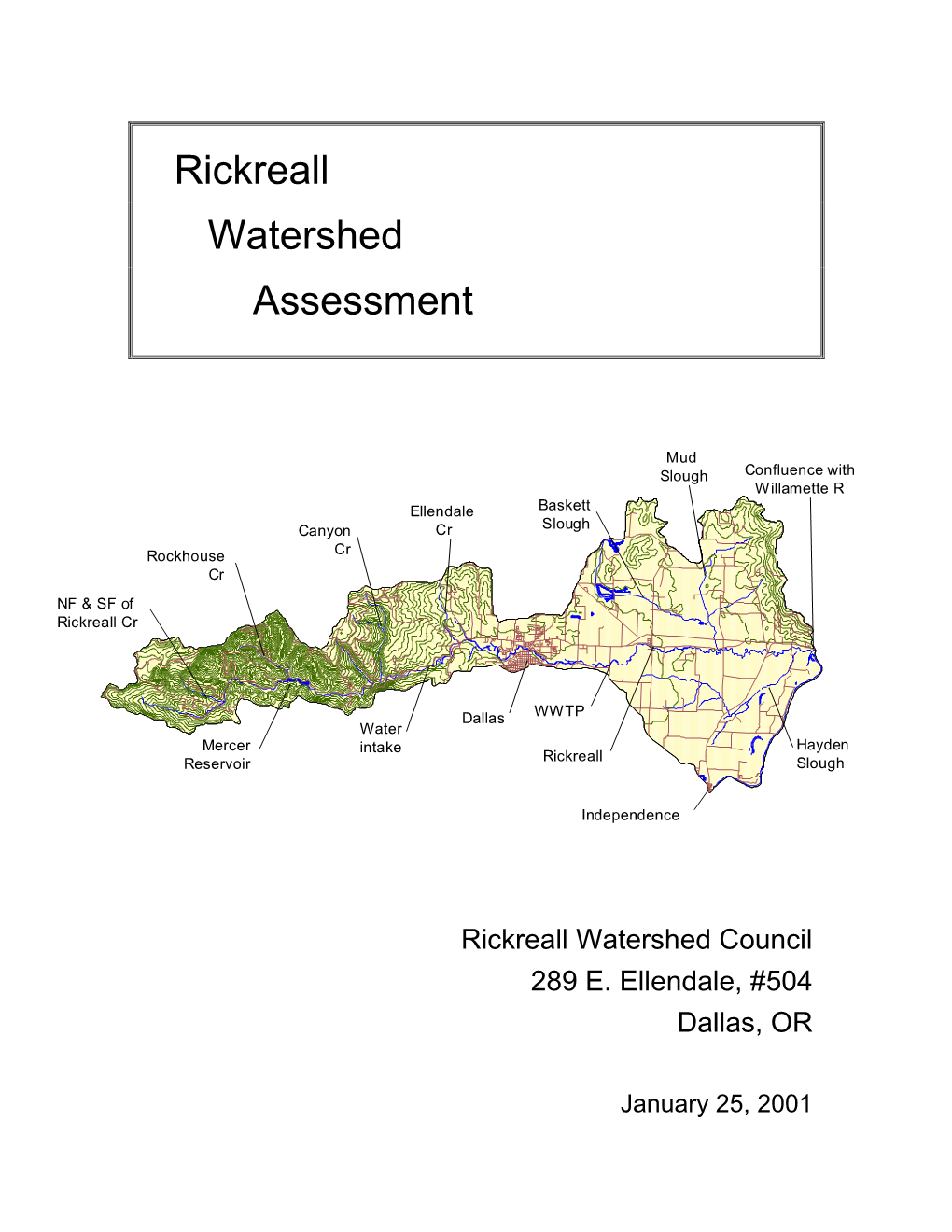
Rickreall Watershed Assessment
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Oregon Historic Trails Report Book (1998)
i ,' o () (\ ô OnBcox HrsroRrc Tnans Rpponr ô o o o. o o o o (--) -,J arJ-- ö o {" , ã. |¡ t I o t o I I r- L L L L L (- Presented by the Oregon Trails Coordinating Council L , May,I998 U (- Compiled by Karen Bassett, Jim Renner, and Joyce White. Copyright @ 1998 Oregon Trails Coordinating Council Salem, Oregon All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording, or any information storage or retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Printed in the United States of America. Oregon Historic Trails Report Table of Contents Executive summary 1 Project history 3 Introduction to Oregon's Historic Trails 7 Oregon's National Historic Trails 11 Lewis and Clark National Historic Trail I3 Oregon National Historic Trail. 27 Applegate National Historic Trail .41 Nez Perce National Historic Trail .63 Oregon's Historic Trails 75 Klamath Trail, 19th Century 17 Jedediah Smith Route, 1828 81 Nathaniel Wyeth Route, t83211834 99 Benjamin Bonneville Route, 1 833/1 834 .. 115 Ewing Young Route, 1834/1837 .. t29 V/hitman Mission Route, 184l-1847 . .. t4t Upper Columbia River Route, 1841-1851 .. 167 John Fremont Route, 1843 .. 183 Meek Cutoff, 1845 .. 199 Cutoff to the Barlow Road, 1848-1884 217 Free Emigrant Road, 1853 225 Santiam Wagon Road, 1865-1939 233 General recommendations . 241 Product development guidelines 243 Acknowledgements 241 Lewis & Clark OREGON National Historic Trail, 1804-1806 I I t . .....¡.. ,r la RivaÌ ï L (t ¡ ...--."f Pðiräldton r,i " 'f Route description I (_-- tt |". -

Bioenergy Harvest, Climate Change, and Forest Carbon in the Oregon Coast Range
Portland State University PDXScholar Environmental Science and Management Faculty Publications and Presentations Environmental Science and Management 3-2016 Bioenergy Harvest, Climate Change, and Forest Carbon in the Oregon Coast Range Megan K. Creutzburg Portland State University, [email protected] Robert M. Scheller Portland State University, [email protected] Melissa S. Lucash Portland State University, [email protected] Louisa B. Evers Bureau of Land Management Stephen D. LeDuc United States Environmental Protection Agency See next page for additional authors Follow this and additional works at: https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/esm_fac Part of the Forest Biology Commons Let us know how access to this document benefits ou.y Citation Details Creutzburg, M. K., Scheller, R. M., Lucash, M. S., Evers, L. B., LeDuc, S. D., & Johnson, M. G. (2015). Bioenergy harvest, climate change, and forest carbon in the Oregon Coast Range. GCB Bioenergy. This Article is brought to you for free and open access. It has been accepted for inclusion in Environmental Science and Management Faculty Publications and Presentations by an authorized administrator of PDXScholar. Please contact us if we can make this document more accessible: [email protected]. Authors Megan K. Creutzburg, Robert M. Scheller, Melissa S. Lucash, Louisa B. Evers, Stephen D. LeDuc, and Mark G. Johnson This article is available at PDXScholar: https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/esm_fac/118 GCB Bioenergy (2016) 8, 357–370, doi: 10.1111/gcbb.12255 Bioenergy harvest, climate change, and forest carbon in the Oregon Coast Range MEGAN K. CREUTZBURG1 , ROBERT M. SCHELLER1 , MELISSA S. LUCASH1 , LOUISA B. EVERS2 , STEPHEN D. LEDUC3 and MARK G. -

Terrestrial Hibernation in the Northern Cricket Frog, Acris Cnepitans
1240 Terrestrial hibernation in the northern cricket frog, Acris cnepitans Jason T. hwin, Jon P. Gostanzo, and Rlchard E. Lee, Jr. Abstract: We used laboratory experiments and field observations to explore overwintering in the northern cricket frog, Acris crepitans, in southern Ohio and Indiana. Cricket frogs died within 24 h when submerged in simulated pond warer that was anoxic or hypoxic, but lived 8-10 days when the water was oxygenatedinitially. Habitat selectionexperiments indicated that cricket frogs prefer a soil substrate to water as temperature decreasesfrom 8 to 2"C. These data suggested that cricket frogs hibernate terrestrially. However, unlike sympatric hylids, this species does not tolerate extensive freezing: only 2 of 15 individuals survived freezing in the -0.8 to -2.6"C range (duration 24-96 h). Cricket fiogs supercooledwhen dry (mean supercoolingpoint -5.5"C; range from -4.3 to -6.8'C), but were easily inoculated by external ice at temperatures between -0.5 and -0.8"C. Our data suggested that cricket frogs hibernate terrestrially but are not freeze tolerant, are not fossorial, and are incapable of supercooling in the presence of external ice. Thus we hypothesized that cricket frogs must hibernate in terrestrial sites that adequately protect against freezing. Indeed, midwinter surveys revealed cricket frogs hibernating in crayfish burrows and cracks of the pond bank, where wet soils buff'ered against extensive freezing of the soil. R6sum6 : Nous avons proc6d6 i des expdriences en laboratoire et A des observations sur le terrain pour 6tudier le sort de la Rainettegrillon, Acris crepitans,en hiver dans le sud de I'Ohio et de I'Indiana. -

The Oregon Coast Range- Considerations for Ecological Restoration Joe Means Tom Spies Shu-Huei Chen Jane Kertis Pete Teensma
Forests of the Oregon Coast Range- Considerations for Ecological Restoration Joe Means Tom Spies Shu-huei Chen Jane Kertis Pete Teensma The Oregon Coast Range supports some of the most dense Ocean, so they are warm and often highly productive, com- and productive forests in North America. In the pre-harvest- pared to the Cascade Range and central Oregon forests. ing period these forests arose as a result of large fires-the Isaac's (1949) site index map shows much more site class I largest covering 330,000 ha (Teensma and others 1991). and I1 land in the Coast Range than in the Cascades. In the These fires occurred mostly at intervals of 150 to 300 years. summers, humid maritime air creates a moisture gradient The natural disturbance regime supported a diverse fauna from the coastal western hemlock-Sitka spruce (Tsuga and large populations of anadromous salmonids (salmon heterophylla-Piceasitchensis) zone with periodic fog extend- and related fish). In contrast, the present disturbance re- ing 4 to 10 km inland, through Douglas-fir (Pseudotsuga gime is dominated by patch clearcuts of about 10-30 ha menziesii var. rnenziesii)-western hemlock forests in the superimposed on most of the forest land with agriculture on central zone to the drier interior-valley foothill zone of the flats near rivers. Ages of most managed forests are less Douglas-fir, bigleaf maple (Acer rnacrophyllum)and Oregon than 60 years. This logging has coincided with significant oak (Quercus garryana). declines in suitable habitat and populations of some fish and wildlife species. Some of these species have been nearly extirpated. -

Mill Creek Watershed Assessment
Yamhill Basin Council Mill Watershed Assessment December 30, 1999 Funding for the Mill Assessment was provided by the Oregon Watershed Enhancement Board and Resource Assistance for Rural Environments. Mill Assessment Project Manager: Robert J. Bower, Principal Author Co-authors: Chris Lupoli, Linfield College intern, for Riparian section and assisted with Wetlands Conditions section. Tamara Quandt, Linfield College intern, for Sensitive Species section. Editors: Melissa Leoni, Yamhill Basin Council, McMinnville, OR Alison Bower, Forest Ecologist, Corvallis, OR Contributors: Bill Ferber, Salem, Water Resources Department (WRD) Chester Novak, Salem, Bureau Land Management (BLM) Dan Upton, Dallas, Willamette Industries David Anderson, Monmouth, Boise Cascade Dean Anderson, Dallas, Polk County Geographical Information Systems (GIS) Dennis Ades, Salem, Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) Gary Galovich, Corvallis, Oregon Department Fish and Wildlife (ODFW) Mark Koski, Salem, Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Patrick Hawe, Salem, Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Rob Tracey, McMinnville, Natural Resource and Conservation Service (NRCS) Stan Christensen, McMinnville, Yamhill Soil Water Conservation District Susan Maleki, Corvallis, Oregon Watershed Enhancement Board (OWEB) Warren Tausch, Tillamook Bureau of Land Management (BLM) Special Thanks: ! John Cruickshank, Gooseneck Creek resident for his assistance with the Historical, and Channel Modification sections and in the gathering of historical photographs. ! Gooseneck Creek Watershed Group for their support and guidance. ! John Caputo, Yamhill County GIS. ! BLM and Polk County GIS for providing some of the GIS base layers used to create the maps in this assessment. ! USDA Service Center, Natural Resource Conservation Service, McMinnville, for copying and office support. ! Polk and Yamhill Soil and Water Conservation Districts. ! Nick Varnum, PNG Environmental Inc., Tigard, for assisting with the Hydrology and Channel Habitat Typing sections. -

Working Pack Dog Titles 2017-0119
Working Pack Dog issued number registeredname owners regnum sire sireregnum dam damregnum 1 Shadak’s Sastan Taka Keith & Lynne Hurrell WC786190 Lobito's Caballero of Kiska WC257803 Shadak's Shukeenyuk WB579440 2 Shadak’s Tich-A-Luk Keith & Lynne Hurrell 3 Shadak’s Artic Sonrise Keith & Lynne Hurrell WB650563 Pak N Pulls Kingak WA764822 Pak N Pulls Arctic Shadow WA524342 4 Arken’s Nakina Cheryll Arkins 5 Shadak’s Wicked Winter Keith & Lynne Hurrell WD543192 Witch 6 Czarina Anastasia Nicolle Pat Paulding WD625393 Wyvern Alyeska Arkah of Jo- WB547353 Wyvern's Heather WC990172 Jan 7 Kamai’s Alaluk Of Inuit Ralph Coppola WD686604 Inuit's Driftwood WD252511 Kamai's Artica of Inuit WC738866 8 Suak’s Brite Artic Dawn Paula & Louis Perdoni WE020543 Wyvern's Invictus WD609383 Suak's Aksoah of Brandy WD222764 9 Sno King’s Northern Light Jackai Szuhai WD932145 Tigara's Apollo of Totemtok WC367473 Tamerak's Mist of Cougar Cub WC980864 10 Nicole Ohtahyon Jackai Szuhai WC010823 Athabascan King WB386373 Nicole of Athabasca WB495979 11 Storm King Of Berkeley Gale Castro WE266354 12 Maska Bull Of Rushing Waters Jeff Rolfson WD233138 Gypsy King WC791246 Cricket Lady Under the Pine WC423794 13 Avalanche At Snow Castle Helen Brockmeyer WD598136 Aristeed's Frost Shadow WB496698 Storm Kloud's Happy Nequivik WC510192 14 Maska’s Sure-Foot Sheba Jeff Rolfson WE707239 Maska Bull of Rushing Waters WD233138 Beauty Queen of Swamp WD701391 Hollow 15 Hi-De-Ho’s Royal Heritage Of Sue Worley WE333340 Northwood's Lord Kipnuk WB475489 Eldor's Starr Von Hi-De-Ho WD490983 -

"Preserve Analysis : Saddle Mountain"
PRESERVE ANALYSIS: SADDLE MOUNTAIN Pre pare d by PAUL B. ALABACK ROB ERT E. FRENKE L OREGON NATURAL AREA PRESERVES ADVISORY COMMITTEE to the STATE LAND BOARD Salem. Oregon October, 1978 NATURAL AREA PRESERVES ADVISORY COMMITTEE to the STATE LAND BOARD Robert Straub Nonna Paul us Governor Clay Myers Secretary of State State Treasurer Members Robert Frenkel (Chairman), Corvallis Bill Burley (Vice Chainnan), Siletz Charles Collins, Roseburg Bruce Nolf, Bend Patricia Harris, Eugene Jean L. Siddall, Lake Oswego Ex-Officio Members Bob Maben Wi 11 i am S. Phe 1ps Department of Fish and Wildlife State Forestry Department Peter Bond J. Morris Johnson State Parks and Recreation Branch State System of Higher Education PRESERVE ANALYSIS: SADDLE MOUNTAIN prepared by Paul B. Alaback and Robert E. Frenkel Oregon Natural Area Preserves Advisory Committee to the State Land Board Salem, Oregon October, 1978 ----------- ------- iii PREFACE The purpose of this preserve analysis is to assemble and document the significant natural values of Saddle Mountain State Park to aid in deciding whether to recommend the dedication of a portion of Saddle r10untain State Park as a natural area preserve within the Oregon System of I~atural Areas. Preserve management, agency agreements, and manage ment planning are therefore not a function of this document. Because of the outstanding assemblage of wildflowers, many of which are rare, Saddle r·1ountain has long been a mecca for· botanists. It was from Oregon's botanists that the Committee initially received its first documentation of the natural area values of Saddle Mountain. Several Committee members and others contributed to the report through survey and documentation. -

Geologic History of Siletzia, a Large Igneous Province in the Oregon And
Geologic history of Siletzia, a large igneous province in the Oregon and Washington Coast Range: Correlation to the geomagnetic polarity time scale and implications for a long-lived Yellowstone hotspot Wells, R., Bukry, D., Friedman, R., Pyle, D., Duncan, R., Haeussler, P., & Wooden, J. (2014). Geologic history of Siletzia, a large igneous province in the Oregon and Washington Coast Range: Correlation to the geomagnetic polarity time scale and implications for a long-lived Yellowstone hotspot. Geosphere, 10 (4), 692-719. doi:10.1130/GES01018.1 10.1130/GES01018.1 Geological Society of America Version of Record http://cdss.library.oregonstate.edu/sa-termsofuse Downloaded from geosphere.gsapubs.org on September 10, 2014 Geologic history of Siletzia, a large igneous province in the Oregon and Washington Coast Range: Correlation to the geomagnetic polarity time scale and implications for a long-lived Yellowstone hotspot Ray Wells1, David Bukry1, Richard Friedman2, Doug Pyle3, Robert Duncan4, Peter Haeussler5, and Joe Wooden6 1U.S. Geological Survey, 345 Middlefi eld Road, Menlo Park, California 94025-3561, USA 2Pacifi c Centre for Isotopic and Geochemical Research, Department of Earth, Ocean and Atmospheric Sciences, 6339 Stores Road, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada 3Department of Geology and Geophysics, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 1680 East West Road, Honolulu, Hawaii 96822, USA 4College of Earth, Ocean, and Atmospheric Sciences, Oregon State University, 104 CEOAS Administration Building, Corvallis, Oregon 97331-5503, USA 5U.S. Geological Survey, 4210 University Drive, Anchorage, Alaska 99508-4626, USA 6School of Earth Sciences, Stanford University, 397 Panama Mall Mitchell Building 101, Stanford, California 94305-2210, USA ABSTRACT frames, the Yellowstone hotspot (YHS) is on southern Vancouver Island (Canada) to Rose- or near an inferred northeast-striking Kula- burg, Oregon (Fig. -

Dr John Glen Interviewed by Paul Merchant
NATIONAL LIFE STORIES AN ORAL HISTORY OF BRITISH SCIENCE Dr John Glen Interviewed by Dr Paul Merchant C1379/26 © The British Library Board http://sounds.bl.uk This interview and transcript is accessible via http://sounds.bl.uk . © The British Library Board. Please refer to the Oral History curators at the British Library prior to any publication or broadcast from this document. Oral History The British Library 96 Euston Road London NW1 2DB United Kingdom +44 (0)20 7412 7404 [email protected] Every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of this transcript, however no transcript is an exact translation of the spoken word, and this document is intended to be a guide to the original recording, not replace it. Should you find any errors please inform the Oral History curators. © The British Library Board http://sounds.bl.uk The British Library National Life Stories Interview Summary Sheet Title Page Ref no: C1379/26 Collection title: An Oral History of British Science Interviewee’s surname: Glen Title: Dr Interviewee’s forename: John W Sex: M Occupation: Physicist Date and place of birth: 6/11/1927; Putney, London Mother’s occupation: Father’s occupation: ‘Day Publisher’, Times Newspaper Dates of recording, Compact flash cards used, tracks (from – to): 28/7/10 (track 1-3); 29/7/10 (track 4-10) Location of interview: Interviewee’s home, Birmingham Name of interviewer: Dr Paul Merchant Type of recorder: Marantz PMD661 Recording format : WAV 24 bit 48kHz Total no. of tracks: 10 Stereo Total Duration: 8:12:10 Additional material: Small collection of digitised photographs, referred to in recording. -

(Antarctica) Glacial, Basal, and Accretion Ice
CHARACTERIZATION OF ORGANISMS IN VOSTOK (ANTARCTICA) GLACIAL, BASAL, AND ACCRETION ICE Colby J. Gura A Thesis Submitted to the Graduate College of Bowling Green State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE December 2019 Committee: Scott O. Rogers, Advisor Helen Michaels Paul Morris © 2019 Colby Gura All Rights Reserved iii ABSTRACT Scott O. Rogers, Advisor Chapter 1: Lake Vostok is named for the nearby Vostok Station located at 78°28’S, 106°48’E and at an elevation of 3,488 m. The lake is covered by a glacier that is approximately 4 km thick and comprised of 4 different types of ice: meteoric, basal, type 1 accretion ice, and type 2 accretion ice. Six samples were derived from the glacial, basal, and accretion ice of the 5G ice core (depths of 2,149 m; 3,501 m; 3,520 m; 3,540 m; 3,569 m; and 3,585 m) and prepared through several processes. The RNA and DNA were extracted from ultracentrifugally concentrated meltwater samples. From the extracted RNA, cDNA was synthesized so the samples could be further manipulated. Both the cDNA and the DNA were amplified through polymerase chain reaction. Ion Torrent primers were attached to the DNA and cDNA and then prepared to be sequenced. Following sequencing the sequences were analyzed using BLAST. Python and Biopython were then used to collect more data and organize the data for manual curation and analysis. Chapter 2: As a result of the glacier and its geographic location, Lake Vostok is an extreme and unique environment that is often compared to Jupiter’s ice-covered moon, Europa. -

Chapter 5 State(S): Oregon Recovery Unit Name: Willamette River
Chapter 5 State(s): Oregon Recovery Unit Name: Willamette River Recovery Unit Region 1 U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service Portland, Oregon DISCLAIMER Recovery plans delineate reasonable actions that are believed necessary to recover and protect listed species. Plans are prepared by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and, in this case, with the assistance of recovery unit teams, contractors, State and Tribal agencies, and others. Objectives will be attained and any necessary funds made available subject to budgetary and other constraints affecting the parties involved, as well as the need to address other priorities. Recovery plans do not necessarily represent the views or the official positions or indicate the approval of any individuals or agencies involved in the plan formulation, other than the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Recovery plans represent the official position of the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service only after they have been signed by the Director or Regional Director as approved. Approved recovery plans are subject to modification as dictated by new findings, changes in species status, and the completion of recovery tasks. Literature Cited: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. 2002. Chapter 5, Willamette River Recovery Unit, Oregon. 96 p. In: U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Bull Trout (Salvelinus confluentus) Draft Recovery Plan. Portland, Oregon. ii ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Two working groups are active in the Willamette River Recovery Unit: the Upper Willamette (since 1989) and Clackamas Bull Trout Working Groups. In 1999, these groups were combined, and, along with representation from the Santiam subbasin, comprise the Willamette River Recovery Unit Team. -

North Santiam Canyon (Please Forward Documented Corrections Or Additions to PO Box 574, Gates OR 97346.)
1 Timeline--North Santiam Canyon (Please forward documented corrections or additions to PO Box 574, Gates OR 97346.) 1844 “The story is told that three French-Canadian trappers from the Gervais area trapped for furs in the Santiam canyon” in 1844 (from Lawrence E. "Bud" George, Oregon State Highway Division retiree, in talk given in April, 1989 at North Santiam Historical society meeting.) 1845 By 1845, the price of furs dropped, the Santiam area had been trapped out, and few or no people used the trail up the Canyon above Mehama for several years. (Bud George) 1846 A public meeting was held in Salem in 1846 and elected a committee to "make an examination of the trail" up the Santiam toward eastern Oregon. They apparently went not up the river but "over the top of some of the broken and jagged part of the range." Col. Gilliam reported that it was "absolutely impossible for wagons up there" and returned to Salem. From 1846- 1873, the pass was not used and "was sort of forgotten." (Bud George) 1850 Senator L.F. Linn of Missouri was credited with passage of the Donation Land Claim (DLC) Law, September 27, 1850, which allowed individuals over 18 to claim 320 acres 1852 1)About 1852, Fox Valley, a cove on the south side of the North Santiam River 3.2 miles east of Lyons, was named for John Fox.. (see Santiam Lyons, Lyons Methodist Church from 1893 to 1963 by Earl B.Cotton, published jointly by North Santiam Historical Society and the Lyons Methodist Church in 1993.