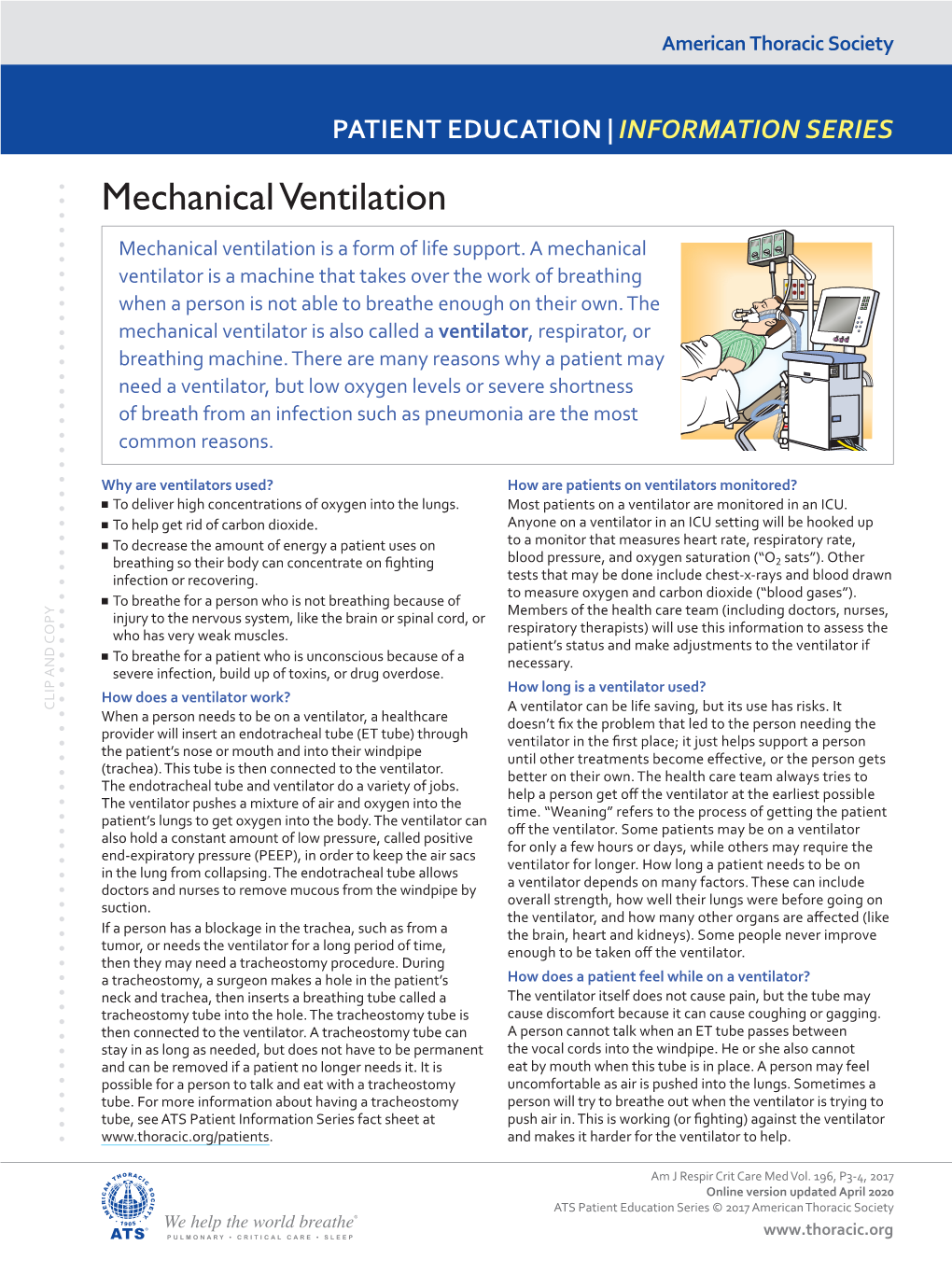
Mechanical Ventilation Mechanical Ventilation Is a Form of Life Support
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

ABCDE Approach
The ABCDE and SAMPLE History Approach Basic Emergency Care Course Objectives • List the hazards that must be considered when approaching an ill or injured person • List the elements to approaching an ill or injured person safely • List the components of the systematic ABCDE approach to emergency patients • Assess an airway • Explain when to use airway devices • Explain when advanced airway management is needed • Assess breathing • Explain when to assist breathing • Assess fluid status (circulation) • Provide appropriate fluid resuscitation • Describe the critical ABCDE actions • List the elements of a SAMPLE history • Perform a relevant SAMPLE history. Essential skills • Assessing ABCDE • Needle-decompression for tension • Cervical spine immobilization pneumothorax • • Full spine immobilization Three-sided dressing for chest wound • • Head-tilt and chin-life/jaw thrust Intravenous (IV) line placement • • Airway suctioning IV fluid resuscitation • • Management of choking Direct pressure/ deep wound packing for haemorrhage control • Recovery position • Tourniquet for haemorrhage control • Nasopharyngeal (NPA) and oropharyngeal • airway (OPA) placement Pelvic binding • • Bag-valve-mask ventilation Wound management • • Skin pinch test Fracture immobilization • • AVPU (alert, voice, pain, unresponsive) Snake bite management assessment • Glucose administration Why the ABCDE approach? • Approach every patient in a systematic way • Recognize life-threatening conditions early • DO most critical interventions first - fix problems before moving on -

Airway Pressures and Volutrauma
Airway Pressures and Volutrauma Airway Pressures and Volutrauma: Is Measuring Tracheal Pressure Worth the Hassle? Monitoring airway pressures during mechanical ventilation is a standard of care.1 Sequential recording of airway pressures not only provides information regarding changes in pulmonary impedance but also allows safety parameters to be set. Safety parameters include high- and low-pressure alarms during positive pressure breaths and disconnect alarms. These standards are, of course, based on our experience with volume control ventilation in adults. During pressure control ventilation, monitoring airway pressures remains important, but volume monitoring and alarms are also required. Airway pressures and work of breathing are also important components of derived variables, including airway resistance, static compliance, dynamic compliance, and intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure (auto-PEEP), measured at the bedside.2 The requisite pressures for these variables include peak inspiratory pressure, inspiratory plateau pressure, expiratory plateau pressure, and change in airway pressure within a breath. Plateau pressures should be measured at periods of zero flow during both volume control and pressure control ventilation. Change in airway pressure should be measured relative to change in volume delivery to the lung (pressure-volume loop) to elucidate work of breathing. See the related study on Page 1179. Evidence that mechanical ventilation can cause and exacerbate acute lung injury has been steadily mounting.3-5 While most of this evidence has originated from laboratory animal studies, recent clinical reports appear to support this concept.6,7 Traditionally, ventilator-induced lung injury brings to mind the clinical picture of tension pneumothorax. Barotrauma (from the root word baro, which means pressure) is typically associated with excessive airway pressures. -

Pre and Post-Thoracostomy Chest X-Ray Taking; Do We Must Do?
www.revhipertension.com Revista Latinoamericana de Hipertensión. Vol. 15 - Nº 1, 2020 Pre and post-thoracostomy chest x-ray taking; do we must do? 71 Radiografía de tórax antes y después de la toracostomía; Qué debemos hacer? Salaminia, Shirvan; Talebi, Shadi; Mehrabi, Saadat 1Assistant Professor of Cardiac Surgery, Clinical Research Development Unit Beheshti Hospital, Yasuj University of Medical Sciences, Yasuj, Iran. [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]. 2General Practitioner, Clinical Research Development Unit Beheshti Hospital, Yasuj University of Medical Sciences, Yasuj, Iran. 3Assistant Professor of Thoracic Surgery, Clinical Research Development Unit Beheshti Hospital, Yasuj University of Medical Sciences, Yasuj, Iran *corresponding author: Saadat Mehrabi, Assistant Professor of Thoracic Surgery, Clinical Research Development Unit Beheshti Hospital, Yasuj University of Medical Sciences, Yasuj, Iran. Email: [email protected] https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4074244 Abstract he prevalence of collision accidents is high in Results: Of the 58 chest tubes with the indication for re- Iran, a developing country. Currently, a plain moval, only one patient needed further observation clini- chest radiograph is routine 6 to 8 hours af- cally after removal. The coincident chest x-ray (CXR) led to ter chest tube removal. In recent years, there have been recurrent chest tube insertion. All thoracostomies had per- doubts about the necessity of routine post-removal chest formed by a trained resident or surgeon. Considering vari- x-ray (CXR) in the absence of clinical symptoms. In chil- able clinical decisions, a comparison of the diagnostic value dren, this is especially imperative because they are more of chest x-ray (CXR) to clinical examination did not differ sensitive to radiation exposure. -

Respiratory Examination Cardiac Examination Is an Essential Part of the Respiratory Assessment and Vice Versa
Respiratory examination Cardiac examination is an essential part of the respiratory assessment and vice versa. # Subject steps Pictures Notes Preparation: Pre-exam Checklist: A Very important. WIPE Be the one. 1 Wash your hands. Wash your hands in Introduce yourself to the patient, confirm front of the examiner or bring a sanitizer with 2 patient’s ID, explain the examination & you. take consent. Positioning of the patient and his/her (Position the patient in a 3 1 2 Privacy. 90 degree sitting position) and uncover Exposure. full exposure of the trunk. his/her upper body. 4 (if you could not, tell the examiner from the beginning). 3 4 Examination: General appearance: B (ABC2DEVs) Appearance: young, middle aged, or old, Begin by observing the and looks generally ill or well. patient's general health from the end of the bed. Observe the patient's general appearance (age, Around the bed I can't state of health, nutritional status and any other see any medications, obvious signs e.g. jaundice, cyanosis, O2 mask, or chest dyspnea). 1 tube(look at the lateral sides of chest wall), metered dose inhalers, and the presence of a sputum mug. 2 Body built: normal, thin, or obese The patient looks comfortable and he doesn't appear short of breath and he doesn't obviously use accessory muscles or any heard Connections: such as nasal cannula wheezes. To determine this, check for: (mention the medications), nasogastric Dyspnea: Assess the rate, depth, and regularity of the patient's 3 tube, oxygen mask, canals or nebulizer, breathing by counting the respiratory rate, range (16–25 breaths Holter monitor, I.V. -

Mechanisms of Pulmonary Gas Exchange Abnormalities During Experimental Group B Streptococcal Infusion
003 I -3998/85/1909-0922$02.00/0 PEDIATRIC RESEARCH Vol. 19, No. 9, I985 Copyright 0 1985 International Pediatric Research Foundation, Inc. Printed in (I.S. A. Mechanisms of Pulmonary Gas Exchange Abnormalities during Experimental Group B Streptococcal Infusion GREGORY K. SORENSEN, GREGORY J. REDDING, AND WILLIAM E. TRUOG ABSTRACT. Group B streptococcal sepsis in newborns obtained from GBS (5, 6). Arterial Poz fell by 9 torr in association produces pulmonary arterial hypertension and hypoxemia. with the increase in pulmonary arterial pressure (4). In contrast, The purpose of this study was to investigate the mecha- the neonatal piglet infused with GBS demonstrated both pul- nisms by which hypoxemia occurs. Ten anesthetized, ven- monary arterial hypertension and profound arterial hypoxemia tilated piglets were infused with 2 x lo9 colony forming (7). These results suggest that the neonatal pulmonary vascula- unitstkg of Group B streptococci over a 30-min period. ture may respond to bacteremia differently from that of adults. Pulmonary arterial pressure rose from 14 ? 2.8 to 38 ? The relationship between Ppa and the matching of alveolar 6.7 torr after 20 min of the bacterial infusion (p< 0.01). ventilation and pulmonary perfusion, a major determinant of During the same period, cardiac output fell from 295 to arterial oxygenation during room air breathing (8), has not been 184 ml/kg/min (p< 0.02). Arterial Po2 declined from 97 studied in newborns. The predictable rise in Ppa with an infusion 2 7 to 56 2 11 torr (p< 0.02) and mixed venous Po2 fell of group B streptococcus offers an opportunity to delineate the from 39.6 2 5 to 28 2 8 torr (p< 0.05). -

The Child with Altered Respiratory Status
Path: K:/LWW-BOWDEN-09-0101/Application/LWW-BOWDEN-09-0101-016.3d Date: 3rd July 2009 Time: 16:31 User ID: muralir 1BlackLining Disabled CHAPTER 16 The Child With Altered Respiratory Status Do you remember the Diaz fam- Case History leave Lela, the baby sister, ily from Chapter 9, in which with Claudia’s mother, Selma, Jose has trouble taking his asthma medication, and head to the hospital. and in Chapter 4, in which Jose’s little sister, At the hospital the emergency department Lela, expresses her personality even as a new- nurse observes Jose sitting cross-legged and born? Jose is 4 years old and was diagnosed leaning forward on his hands. His mouth is with asthma this past fall, about 6 months ago. open and he is breathing hard with an easily Since that time Claudia, his mother, has audible inspiratory wheeze. He is using his noticed several factors that trigger his asthma subclavicular accessory muscles with each including getting sick, pollen, and cold air. breath. His respiratory rate is 32 breaths per One evening following a warm early-spring minute, his pulse is 112 beats per minutes, day, Jose is outside playing as the sun sets and and he is afebrile. Claudia explains that he the air cools. When he comes inside he was fine; he was outside running and playing, begins to cough. Claudia sets up his nebulizer and then came in and began coughing and and gives him a treatment of albuterol, which wheezing, and she gave him an albuterol lessens his coughing. Within an hour, Jose is treatment. -

Assessment Report COVID-19 Vaccine Astrazeneca EMA/94907/2021
29 January 2021 EMA/94907/2021 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Assessment report COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca Common name: COVID-19 Vaccine (ChAdOx1-S [recombinant]) Procedure No. EMEA/H/C/005675/0000 Note Assessment report as adopted by the CHMP with all information of a commercially confidential nature deleted. Official address Domenico Scarlattilaan 6 ● 1083 HS Amsterdam ● The Netherlands Address for visits and deliveries Refer to www.ema.europa.eu/how-to-find-us Send us a question Go to www.ema.europa.eu/contact Telephone +31 (0)88 781 6000 An agency of the European Union © European Medicines Agency, 2021. Reproduction is authorised provided the source is acknowledged. Table of contents 1. Background information on the procedure .............................................. 7 1.1. Submission of the dossier ..................................................................................... 7 1.2. Steps taken for the assessment of the product ........................................................ 9 2. Scientific discussion .............................................................................. 12 2.1. Problem statement ............................................................................................. 12 2.1.1. Disease or condition ........................................................................................ 12 2.1.2. Epidemiology and risk factors ........................................................................... 12 2.1.3. Aetiology and pathogenesis ............................................................................. -

Breathing Sounds – Determination of Extremely Low Spl
MATEC Web of Conferences 217, 03001 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/201821703001 ICVSSD 2018 BREATHING SOUNDS – DETERMINATION OF EXTREMELY LOW SPL M. Harun1*, R. Teoh Y. S1, M. ‘A. A. Ahmad, M. Mohd. Mokji1, You K. Y1, S. A. R. Syed Abu Bakar1, P. I. Khalid1, S. Z. Abd. Hamid1 and R. Arsat1 1 School of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, *Email: [email protected] Phone: +6075535358 ABSTRACT Breathing sound is an extremely low SPL that results from inspiration and expiration process in the lung. Breathing sound can be used to diagnose persons with complications with breathing. Also, the sound can indicate the effectiveness of treatment of lung disease such as asthma. The purpose of this study was to identify SPL of breathing sounds, over six one octave center frequencies from 63 Hz to 4000 Hz, from the recorded breathing sounds in .wav files. Breathing sounds of twenty participants with normal weight BMI had been recorded in an audiometry room. The breathing sound was acquired in two states: at rest and after a 300 meters walk. Matlab had been used to process the breathing sounds that are in .wav files to come up with SPL (in dB). It has been found out that the SPL of breathing sound of all participants are positive at frequencies 63 Hz and 125 Hz. On the other hand, the SPL are all negatives at frequency 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz and 4000 Hz. In conclusion, SPL of breathing sounds of the participants, at frequencies 250 Hz and 500 Hz that have both positive and negative values are viable to be studied further for physiological and medicinal clues. -

Oxygenation and Oxygen Therapy
Rules on Oxygen Therapy: Physiology: 1. PO2, SaO2, CaO2 are all related but different. 2. PaO2 is a sensitive and non-specific indicator of the lungs’ ability to exchange gases with the atmosphere. 3. FIO2 is the same at all altitudes 4. Normal PaO2 decreases with age 5. The body does not store oxygen Therapy & Diagnosis: 1. Supplemental O2 is an FIO2 > 21% and is a drug. 2. A reduced PaO2 is a non-specific finding. 3. A normal PaO2 and alveolar-arterial PO2 difference (A-a gradient) do NOT rule out pulmonary embolism. 4. High FIO2 doesn’t affect COPD hypoxic drive 5. A given liter flow rate of nasal O2 does not equal any specific FIO2. 6. Face masks cannot deliver 100% oxygen unless there is a tight seal. 7. No need to humidify if flow of 4 LPM or less Indications for Oxygen Therapy: 1. Hypoxemia 2. Increased work of breathing 3. Increased myocardial work 4. Pulmonary hypertension Delivery Devices: 1. Nasal Cannula a. 1 – 6 LPM b. FIO2 0.24 – 0.44 (approx 4% per liter flow) c. FIO2 decreases as Ve increases 2. Simple Mask a. 5 – 8 LPM b. FIO2 0.35 – 0.55 (approx 4% per liter flow) c. Minimum flow 5 LPM to flush CO2 from mask 3. Venturi Mask a. Variable LPM b. FIO2 0.24 – 0.50 c. Flow and corresponding FIO2 varies by manufacturer 4. Partial Rebreather a. 6 – 10 LPM b. FIO2 0.50 – 0.70 c. Flow must be sufficient to keep reservoir bag from deflating upon inspiration 5. -

Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation in the Home
Technology Assessment Program Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation in the Home Final Technology Assessment Project ID: PULT0717 2/4/2020 Technology Assessment Program Project ID: PULT0717 Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation in the Home (with addendum) Prepared for: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality U.S. Department of Health and Human Services 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, MD 20857 www.ahrq.gov Contract No: HHSA290201500013I_HHSA29032004T Prepared by: Mayo Clinic Evidence-based Practice Center Rochester, MN Investigators: Michael Wilson, M.D. Zhen Wang, Ph.D. Claudia C. Dobler, M.D., Ph.D Allison S. Morrow, B.A. Bradley Beuschel, B.S.P.H. Mouaz Alsawas, M.D., M.Sc. Raed Benkhadra, M.D. Mohamed Seisa, M.D. Aniket Mittal, M.D. Manuel Sanchez, M.D. Lubna Daraz, Ph.D Steven Holets, R.R.T. M. Hassan Murad, M.D., M.P.H. Key Messages Purpose of review To evaluate home noninvasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) in adults with chronic respiratory failure in terms of initiation, continuation, effectiveness, adverse events, equipment parameters and required respiratory services. Devices evaluated were home mechanical ventilators (HMV), bi-level positive airway pressure (BPAP) devices, and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices. Key messages • In patients with COPD, home NIPPV as delivered by a BPAP device (compared to no device) was associated with lower mortality, intubations, hospital admissions, but no change in quality of life (low to moderate SOE). NIPPV as delivered by a HMV device (compared individually with BPAP, CPAP, or no device) was associated with fewer hospital admissions (low SOE). In patients with thoracic restrictive diseases, HMV (compared to no device) was associated with lower mortality (low SOE). -

Iatrogenic Tension Pneumothorax After Surgical Tracheostomy in a Child with Idiopathic Subglottic Stenosis - Case Report
Kosin Medical Journal 2019;34:161-167. https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2019.34.2.161 &D VH 5HSRUWV Iatrogenic Tension Pneumothorax after Surgical Tracheostomy in a Child with Idiopathic Subglottic Stenosis - case report Sang Yoong Park, Woo jae Yim, Joon Ho Jeong, Jeongho Kim, Seung-Cheol Lee, So Ron Choi, Jong-Hwan Lee, Chan Jong Chung Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea Tracheostomy is increasingly performed in children for upper airway anomalies. Here, an 18-month-old child (height 84.1 cm, weight 12.5 kg) presented to the emergency department with dyspnea, stridor, and chest retraction. However, exploration of the airways using a bronchoscope failed due to subglottic stenosis. Therefore, a surgical tracheostomy was successfully performed with manual mask ventilation. However, pneumomediastinum was found in the postoperative chest radiograph. Although an oxygen saturation of 99% was initially maintained, oxygen saturation levels dropped, due to sudden dyspnea, after 3 hours. A chest radiograph taken at this time revealed a left tension pneumothorax and small right pneumothorax. Despite a needle thoracostomy, the pneumothorax was aggravated, and cardiac arrest occurred. Car - diopulmonary-cerebral resuscitation was performed, but the patient was declared dead 30 minutes later. This study high - lights the fatal complications that can occur in children during tracheostomy. Therefore, close monitoring, immediate suspicion, recognition, and aggressive management may avoid fatal outcomes. Key Words : Pediatrics, Pneumomediastinum, Tension pneumothorax, Tracheostomy, Thoracostomy Tracheostomy is increasingly being performed swallowing problems, some of which can be in children, leading to improvements in neonatal life-threatening in children. -

Ventilation Recommendations Table
SURVIVING SEPSIS CAMPAIGN INTERNATIONAL GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF SEPTIC SHOCK AND SEPSIS-ASSOCIATED ORGAN DYSFUNCTION IN CHILDREN VENTILATION RECOMMENDATIONS TABLE RECOMMENDATION #34 STRENGTH & QUALITY OF EVIDENCE We were unable to issue a recommendation about whether to Insufficient intubate children with fluid-refractory, catecholamine-resistant septic shock. However, in our practice, we commonly intubate children with fluid-refractory, catecholamine-resistant septic shock without respiratory failure. RECOMMENDATION #35 STRENGTH & QUALITY OF EVIDENCE We suggest not to use etomidate when intubating children • Weak with septic shock or other sepsis-associated organ dysfunction. • Low-Quality of Evidence RECOMMENDATION #36 STRENGTH & QUALITY OF EVIDENCE We suggest a trial of noninvasive mechanical ventilation (over • Weak invasive mechanical ventilation) in children with sepsis-induced • Very Low-Quality of pediatric ARDS (PARDS) without a clear indication for intubation Evidence and who are responding to initial resuscitation. © 2020 Society of Critical Care Medicine and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine Care Medicine. RECOMMENDATION #37 STRENGTH & QUALITY OF EVIDENCE We suggest using high positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) • Weak in children with sepsis-induced PARDS. Remarks: The exact level • Very Low-Quality of of high PEEP has not been tested or determined in PARDS Evidence patients. Some RCTs and observational studies in PARDS have used and advocated for use of the ARDS-network PEEP to Fio2 grid though adverse hemodynamic effects of high PEEP may be more prominent in children with septic shock. RECOMMENDATION #38 STRENGTH & QUALITY OF EVIDENCE We cannot suggest for or against the use of recruitment Insufficient maneuvers in children with sepsis-induced PARDS and refractory hypoxemia.