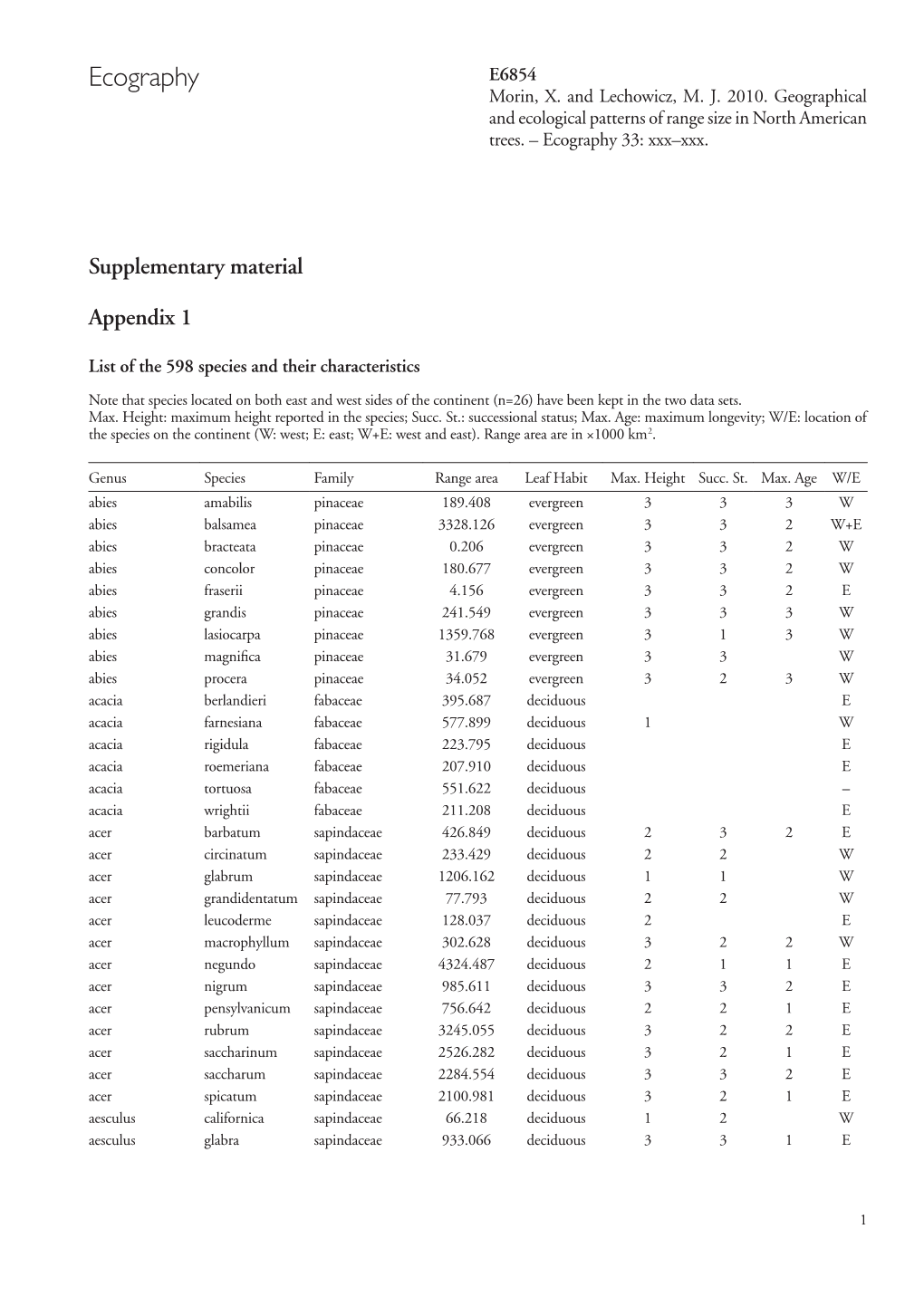
Ecography E6854 Morin, X
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Outline of Angiosperm Phylogeny
Outline of angiosperm phylogeny: orders, families, and representative genera with emphasis on Oregon native plants Priscilla Spears December 2013 The following listing gives an introduction to the phylogenetic classification of the flowering plants that has emerged in recent decades, and which is based on nucleic acid sequences as well as morphological and developmental data. This listing emphasizes temperate families of the Northern Hemisphere and is meant as an overview with examples of Oregon native plants. It includes many exotic genera that are grown in Oregon as ornamentals plus other plants of interest worldwide. The genera that are Oregon natives are printed in a blue font. Genera that are exotics are shown in black, however genera in blue may also contain non-native species. Names separated by a slash are alternatives or else the nomenclature is in flux. When several genera have the same common name, the names are separated by commas. The order of the family names is from the linear listing of families in the APG III report. For further information, see the references on the last page. Basal Angiosperms (ANITA grade) Amborellales Amborellaceae, sole family, the earliest branch of flowering plants, a shrub native to New Caledonia – Amborella Nymphaeales Hydatellaceae – aquatics from Australasia, previously classified as a grass Cabombaceae (water shield – Brasenia, fanwort – Cabomba) Nymphaeaceae (water lilies – Nymphaea; pond lilies – Nuphar) Austrobaileyales Schisandraceae (wild sarsaparilla, star vine – Schisandra; Japanese -

Carpinus Betulus - European Hornbeam (Betulaceae) ------Carpinus Betulus Is a Columnar to Teardrop-Shaped Tree
Carpinus betulus - European Hornbeam (Betulaceae) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Carpinus betulus is a columnar to teardrop-shaped tree. Twigs European Hornbeam is noted for fine and dense texture, -olive-brown and lenticeled, with ornamental winter ornamental winter bark and buds, dense summer foliage, buds that are long and partially curving around the twigs pendulous spring catkins, and unusual autumn fruits. -the twigs are similar to those of the European Beech, but the latter has winter buds that extend straight out of FEATURES the stem at a 45 degree angle. Form Trunk -medium-sized deciduous tree; the -smooth and steel gray, but having a muscled character rarely available species form maturing to its appearance at 40' tall x 30' wide, with the common cultivars more compact; USAGE species form an upright oval growth Function habit in youth, quickly becoming a -specimen or focal point tree of great symmetrical and spreading oval (low-branched teardrop architectural value; can also be an effective year-round shape) with maturity screen or tall, wide hedge when used in rows -medium growth rate Culture Texture -full sun to partial sun; prefers a well-drained soil but is -fine texture in foliage and when bare; thick density in adaptable to various soils and soil pHs; if transplanted foliage and when bare, with many ascending twigs and in autumn, use amended soil, fertilize, mulch liberally, branches forming a thick canopy even in winter and avoid winter salt spray Assets -cultivars -

Flora of South Australia 5Th Edition | Edited by Jürgen Kellermann
Flora of South Australia 5th Edition | Edited by Jürgen Kellermann KEY TO FAMILIES1 J.P. Jessop2 The sequence of families used in this Flora follows closely the one adopted by the Australian Plant Census (www.anbg.gov. au/chah/apc), which in turn is based on that of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG III 2009) and Mabberley’s Plant Book (Mabberley 2008). It differs from previous editions of the Flora, which were mainly based on the classification system of Engler & Gilg (1919). A list of all families recognised in this Flora is printed in the inside cover pages with families already published highlighted in bold. The up-take of this new system by the State Herbarium of South Australia is still in progress and the S.A. Census database (www.flora.sa.gov.au/census.shtml) still uses the old classification of families. The Australian Plant Census web-site presents comparison tables of the old and new systems on family and genus level. A good overview of all families can be found in Heywood et al. (2007) and Stevens (2001–), although these authors accept a slightly different family classification. A number of names with which people using this key may be familiar but are not employed in the system used in this work have been included for convenience and are enclosed on quotation marks. 1. Plants reproducing by spores and not producing flowers (“Ferns and lycopods”) 2. Aerial shoots either dichotomously branched, with scale leaves and 3-lobed sporophores or plants with fronds consisting of a simple or divided sterile blade and a simple or branched spikelike sporophore .................................................................................. -

Corylus Colurna (Turkish Hazel)
Corylus colurna Turkish Hazel Corylus colurna is a large tree which is native to South East Europe and South West Asia. The crown is columnar when young but broadens with age, forming a beautiful pyramidal shape ideally suited to avenue planting. Seasonal interest is provided by elegant long yellow catkins in spring, clusters of edible nuts in frilly cups and good yellow autumn foliage colour. The pale brown corky bark is also very attractive throughout the year. Corylus colurna is very tough and will thrive in nearly all soils including both clay and chalk. It is also extremely tolerant of exposure and paved areas which make it a perfect candidate for urban planting. August 2013 Corylus colurna 20-25-30cm girth field grown trees Plant Profile Name: Corylus colurna Common Name: Turkish Hazel Family: Betulaceae Height: 20m+ Demands: Grows well in all soils, including chalk and clay. Bark: Attractive, pale brown corky bark Foliage: Dark green, shiny leaves Flower: Long yellow catkins in spring Fruit: Clusters of hazelnuts in large frilly cups Summer leaf of Turkish Hazel Deepdale Trees Ltd., Tithe Farm, Hatley Road, Potton, Sandy, Beds. SG19 2DX. Tel: 01767 26 26 36 www.deepdale-trees.co.uk Corylus colurna Turkish Hazel Corylus colurna is the largest species of hazel reaching 25 m in height Summer leaf 25-30cm girth standards in Air-pot Corylus colurna 40-45 girth standards Attractive corky bark Turkish Hazelnuts Deepdale Trees Ltd., Tithe Farm, Hatley Road, Potton, Sandy, Beds. SG19 2DX. Tel: 01767 26 26 36 www.deepdale-trees.co.uk. -

Corylus Colurna
Corylus colurna - Turkish Filbert (Betulaceae) ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- Corylus colurna is a large shade tree noted for bold autumn and attracting squirrels texture, pyramidal form, ornamental winter -cross-pollination between different trees is needed bark/stems/catkins, dense shade from dark green for good fruit set shiny foliage, and urban tolerance. Turkish Filbert is Twigs underutilized in modern landscapes. It's an excellent -buds are pronounced on the stems, which are often substitute for other pyramidally-shaped shade trees fissured or corky by their second year of growth, with such as Pin Oak or Littleleaf Linden. a bold texture on young branches Trunk FEATURES -the light brown, flaky outer bark is quite attractive Form when viewed up-close in winter, while the inner bark -large shade tree is slightly orange but often unnoticed -maturing at about -trees maintain a strong central leader to maturity, 60' tall x 30' wide with symmetrical branching that forms a broadly -upright pyramidal pyramidal outline growth habit -some specimens are allowed to branch to the ground, -medium growth but most trees are limbed up with maturity to yield a rate stately shade tree character Culture -full sun to partial USAGE sun Function -very urban stress -shade, focal point, specimen, or winter accent tree tolerant, including Texture adaptability to heat, -bold texture in foliage and when bare (medium drought, pollution, poor soils, compacted soils, dry texture when in flower) soils, and soils of -

Field Identification of the 50 Most Common Plant Families in Temperate Regions
Field identification of the 50 most common plant families in temperate regions (including agricultural, horticultural, and wild species) by Lena Struwe [email protected] © 2016, All rights reserved. Note: Listed characteristics are the most common characteristics; there might be exceptions in rare or tropical species. This compendium is available for free download without cost for non- commercial uses at http://www.rci.rutgers.edu/~struwe/. The author welcomes updates and corrections. 1 Overall phylogeny – living land plants Bryophytes Mosses, liverworts, hornworts Lycophytes Clubmosses, etc. Ferns and Fern Allies Ferns, horsetails, moonworts, etc. Gymnosperms Conifers, pines, cycads and cedars, etc. Magnoliids Monocots Fabids Ranunculales Rosids Malvids Caryophyllales Ericales Lamiids The treatment for flowering plants follows the APG IV (2016) Campanulids classification. Not all branches are shown. © Lena Struwe 2016, All rights reserved. 2 Included families (alphabetical list): Amaranthaceae Geraniaceae Amaryllidaceae Iridaceae Anacardiaceae Juglandaceae Apiaceae Juncaceae Apocynaceae Lamiaceae Araceae Lauraceae Araliaceae Liliaceae Asphodelaceae Magnoliaceae Asteraceae Malvaceae Betulaceae Moraceae Boraginaceae Myrtaceae Brassicaceae Oleaceae Bromeliaceae Orchidaceae Cactaceae Orobanchaceae Campanulaceae Pinaceae Caprifoliaceae Plantaginaceae Caryophyllaceae Poaceae Convolvulaceae Polygonaceae Cucurbitaceae Ranunculaceae Cupressaceae Rosaceae Cyperaceae Rubiaceae Equisetaceae Rutaceae Ericaceae Salicaceae Euphorbiaceae Scrophulariaceae -

Betulaceae Birch Family
Betulaceae Birch Family Betulaceae is a family of trees and shrubs included in six genera; four of which contain species native to Page | 317 Nova Scotia. Mostly ranging throughout the northern hemisphere, 120 species are found worldwide, generally in temperate climates. Flowers are unisexual; species are monoecious. Staminate catkins are pendulous; pistillate catkins are erect or pendulous, usually firm and often woody. Petals are lacking; sepals tend to be tiny. Fruit is a samara or a nut with a single seed. Leaves are simple, alternate and mostly serrate. Venation is straight and pinnate. Key to species A. Bark of older twigs and trunk without lenticels; fruit not winged, enclosed in an B involucre. B. Shrub, wiry with creeping stems; mature fruits 1–2 nuts, 1cm thick, Corylus the involucre long-beaked, bristly when immature; leaves with 5–8 pairs of veins, doubly serrate; winter buds velutinous, ovate. bb. Small tree; nutlets enclosed in a loose sac; leaves with 9 or more Ostrya pairs of veins, merely serrate; winter buds dark brown. aa. Bark of twigs with elongated lenticels; fruit small, exposed in the axils of the C scales, winged. C. Scales of pistillate catkins, thin and papery, deciduous, usually 3 Betula lobed; bark of mature specimens white to yellowish, often peeling; stamens 2; fruit a tiny samara, with thin wings. cc. Scales of pistillate catkins woody, 3–5 lobed at the tip, persistent; Alnus bark not white nor yellowish, never peeling; stamens 4;tiny nuts with thick wings. Alnus Miller alder Three of 30 species of alders are found in NS. -

On the Flora of Australia
L'IBRARY'OF THE GRAY HERBARIUM HARVARD UNIVERSITY. BOUGHT. THE FLORA OF AUSTRALIA, ITS ORIGIN, AFFINITIES, AND DISTRIBUTION; BEING AN TO THE FLORA OF TASMANIA. BY JOSEPH DALTON HOOKER, M.D., F.R.S., L.S., & G.S.; LATE BOTANIST TO THE ANTARCTIC EXPEDITION. LONDON : LOVELL REEVE, HENRIETTA STREET, COVENT GARDEN. r^/f'ORElGN&ENGLISH' <^ . 1859. i^\BOOKSELLERS^.- PR 2G 1.912 Gray Herbarium Harvard University ON THE FLORA OF AUSTRALIA ITS ORIGIN, AFFINITIES, AND DISTRIBUTION. I I / ON THE FLORA OF AUSTRALIA, ITS ORIGIN, AFFINITIES, AND DISTRIBUTION; BEIKG AN TO THE FLORA OF TASMANIA. BY JOSEPH DALTON HOOKER, M.D., F.R.S., L.S., & G.S.; LATE BOTANIST TO THE ANTARCTIC EXPEDITION. Reprinted from the JJotany of the Antarctic Expedition, Part III., Flora of Tasmania, Vol. I. LONDON : LOVELL REEVE, HENRIETTA STREET, COVENT GARDEN. 1859. PRINTED BY JOHN EDWARD TAYLOR, LITTLE QUEEN STREET, LINCOLN'S INN FIELDS. CONTENTS OF THE INTRODUCTORY ESSAY. § i. Preliminary Remarks. PAGE Sources of Information, published and unpublished, materials, collections, etc i Object of arranging them to discuss the Origin, Peculiarities, and Distribution of the Vegetation of Australia, and to regard them in relation to the views of Darwin and others, on the Creation of Species .... iii^ § 2. On the General Phenomena of Variation in the Vegetable Kingdom. All plants more or less variable ; rate, extent, and nature of variability ; differences of amount and degree in different natural groups of plants v Parallelism of features of variability in different groups of individuals (varieties, species, genera, etc.), and in wild and cultivated plants vii Variation a centrifugal force ; the tendency in the progeny of varieties being to depart further from their original types, not to revert to them viii Effects of cross-impregnation and hybridization ultimately favourable to permanence of specific character x Darwin's Theory of Natural Selection ; — its effects on variable organisms under varying conditions is to give a temporary stability to races, species, genera, etc xi § 3. -

Corylus Americana, American Hazelnut
Of interest this week at Beal... American Hazelnut Corylus americana Family: the Birch family, Betulaceae Also called American filbert W. J. Beal This nut-bearing member of the birch family is not as well known as its commercial Botanical Garden European counterpart, Corylus avellana. Ours are located on the hill overlooking the north side of the pond. Just as the European filbert has a long history of use in Europe, the American hazelnut has a long history of being harvested for food by the Indigenous First Nations peoples of Eastern North America. The fruit of the American hazelnut is comparable to the fruit of the cultivated European hazelnut, except significantly smaller. American hazelnut ranges from Maine west to Saskatchewan, south to eastern Oklahoma, east to northern Florida. In Michigan, American hazelnut is common throughout the southerly counties of the Lower Peninsula, but at the approximate latitude of the town of Clare, it is replaced by the more northerly distribution of beaked hazelnut, Corylus cornuta. American hazelnut flowers a few days after temperatures are consistently above 40 degrees. Male flowers are catkins that expand upon opening to release massive quantities of pollen. The unexpanded male catkins comprise one of its most recognizable winter features. Female flowers are striking but tiny sprays of bright red stigmata up to three millimeters in length. Flowers of both sexes are born on the same stems. American hazelnut forms thickets some 6-10 feet (2-3.3 m) in height especially along forest trails and edges. After pollination, the female flowers expand and wrap themselves in large frilly bracts that are the hallmark of their presence. -

Betulaceae - Birch Family Betula Papyrifera Paper Birch
Betulaceae - birch family Betula papyrifera paper birch Sight ID characteristics Vegetative Features: • Leaf: alternate, 2-4" long, ovate, obtuse base, acute to acuminate apex, doubly serrate margin. • Twig: dull red-brown, numerous lenticels, lacking wintergreen smell when cut; terminal bud absent. • Bark: brown and smooth (young trees), but turning cinnamon to creamy white with papery, peeling (exfoliating) outer layers at maturity. Older trees become black and furrowed at the base. Reproductive Features: • Monoecious, male and female flowers borne in catkins. Fruits are laterally winged nutlets borne in pendant cone-like structures that are 1 1/2-2" long with a persistent axis and 3- lobed bracts that are deciduous at maturity. 29 NOTES AND SKETCHES 30 Betulaceae - birch family Betula occidentallis water birch Sight ID characteristics Vegetative Features: • Leaf: alternate, 1-2" long, ovate with a variably toothed, doubly serrate margin. • Twig: green and sticky when young, becoming reddish brown and resin-dotted (yellow, crystalline). • Bark: smooth, shiny and reddish brown in color. Not exfoliating. Often has a several-trunked form. Reproductive Features: • Monoecious, male and female flowers borne in catkins. Fruits are laterally winged nutlets borne in cone-like structures 1-1 1/4" long with a persistent axis and 3-lobed bracts that are deciduous at maturity. 31 NOTES AND SKETCHES 32 Betulaceae - birch family COMMON Betula pendula ORNAMENTAL European white birch many cultivars Sight ID characteristics Vegetative Features: • Leaf: alternate, commonly 1-2 3/4" long, ovate to deltoid, doubly serrate to divided or lobed - size, shape and structure are variable in different cultivars (a cultivar with divided leaves is very common). -

BETULACEAE Christine Pang, Darla Chenin, and Amber M
Comparative Seed Manual: BETULACEAE Christine Pang, Darla Chenin, and Amber M. VanDerwarker (Completed, April 19, 2019) This seed manual consists of photos and relevant information on plant species housed in the Integrative Subsistence Laboratory at the Anthropology Department, University of California, Santa Barbara. The impetus for the creation of this manual was to enable UCSB graduate students to have access to comparative materials when making in-field identifications. Most of the plant species included in the manual come from New World locales with an emphasis on Eastern North America, California, Mexico, Central America, and the South American Andes. Published references consulted1: 1998. Moerman, Daniel E. Native American ethnobotany. Vol. 879. Portland, OR: Timber press. 2009. Moerman, Daniel E. Native American medicinal plants: an ethnobotanical dictionary. OR: Timber Press. 2010. Moerman, Daniel E. Native American food plants: an ethnobotanical dictionary. OR: Timber Press. Species included herein: Alnus rhombifolia Alnus serrulata 1 Disclaimer: Information on relevant edible and medicinal uses comes from a variety of sources, both published and internet-based; this manual does NOT recommend using any plants as food or medicine without first consulting a medical professional. Alnus rhombifolia Family: Betulaceae Common Names: White alder, California Alder, Sierra Alder Habitat and Growth Habit: This plant is native to California. It is confined to Western North America and grows in rocky soil, canyons, chaparral, forests, and riparian. Human Uses: There are edible parts, which include the flowers and inner bark. Notably, the bark can be used as an astringent. Medicinal usages include diaphoretic, emetic, hemostatic, stomachic, and tonic. Used in treatment of stomach aches and diarrhea. -

Corylus Avellana: a New Biotechnological Source of Anticancer Agents
Corylus avellana: a new biotechnological source of anticancer agents Ana Gallego Palacios TESI DOCTORAL UPF / 2015 Thesis Directors: Dr. Elisabet Moyano Claramunt, Departament de Ciències Experimentals i de la Salut, Universitat Pompeu Fabra. Dr. Mercedes Bonfill Baldrich, Departament de Productes Naturals, Biologia Vegetal i Edafologia, Universitat de Barcelona. DEPARTAMENT DE CIENCIES EXPERIMENTALS I DE LA SALUT ii “Mira a la derecha y a la izquierda del tiempo y que tu corazón aprenda a estar tranquilo” Federico García Lorca iii Agraïments/Agradecimientos/Acknowledgement En primer lugar quería agradecer a los organismos que han apoyado económicamente el trabajo plasmado en esta tesis, al Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia de España (BIO2011-29856-C02-1) y a Generalitat de Catalunya (2014SGR215). También a la Universidad Pompeu Fabra por proporcionarme la beca pre-doctoral que me ha permitido realizar este doctorado y la Universidad de Barcelona donde he realizado todo el trabajo experimental. Hay muchas personas que han contribuido, tanto directa como indirectamente, en este proyecto y a las cuales quiero agradecer. En primer lloc volia agrair a les meves directores de tesi, la Dr. Elisabeth Moyano i la Dr. Mercedes Bonfill per l’ajuda, la dedicació i el suport que m’han donat durant tots aquest anys. Eli he pogut aprendre molt de tu, no només a nivell científic sinó també a nivell personal. Gracies pel teu temps, pel teu positivisme i per les teves reflexions. A la Mercè perquè sempre has tingut la porta del teu despatx oberta per qualsevol dubte i perquè sempre m’has donat la llibertat i la independència necessària per millorar.