Brass Alloys
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

NZCCC DARFIELD AGM AUCTION, Saturday 9 March, 2019 Darfield Recreation Centre, North Terrace, Darfield
NZCCC DARFIELD AGM AUCTION, Saturday 9 March, 2019 Darfield Recreation Centre, North Terrace, Darfield. The following items will be offered for sale on behalf of the vendors following the AGM at the Darfield Meeting. The AGM starts after lunch. 1. The NZCCC accepts no responsibility for any incorrect description of any lot. Viewing opportunity will precede the auction. Any vendor reserve is indicated by the $ amount at the end of each lot description. 2. Bids, starting at $5, will be accepted only from currently financial members or their approved guests and the Auctioneer’s decision will be final. 3. An NZCCC vendor commission rate of 10% (minimum $1) will apply to each lot offered for sale. No commission applies to buyers. 4. All lots sold will be delivered to the purchaser or postal bid coordinator as appropriate at the time of sale. 5. A full accounting of sales will be recorded and a list of auction results will be published with the AGM report. 6. Overseas bidders must make private arrangements for the delivery of ammunition. Postal Bids: Please ensure that postal (absentee) bids are in the Editor’s hands by Monday March 4. Post to Kevan Walsh 4 Milton Road, Northcote Point, or email [email protected] . A scan of the postal bid form would be good, but simply emailing the editor with your bids will also be fine. For postal bids a payment of $5 is required. Either make a bank deposit ( BNZ account 02-0214-0052076-00) and let the Treasurer Kevan Walsh know, or post your bids with a cheque or cash to Kevan. -

Pof Catalogue
Force Behind the Forces Lt. Gen. Ali Amir Awan, HI(M) Chairman POF Board Message from the Chairman Pakistan Ordnance Factories is country’s premier defence production organization. We warmly welcome our international clients from friendly countries and offer a broad range of defence products manufactured on highest level of quality standards at most competitive prices. Established in 1951, POF is the largest state owned defence manufacturer in Pakistan. Besides being the main supplier of Pakistan Armed Forces and the law enforcement agencies, POF exports to a number of countries across the globe. Having a work force of over 27,000 skilled employees in 14 defence industrial units and a number of commercial subsidiary companies POF employees more than 20,000 plants scattered in the gigantic industrial complex located at Wah Cantonment in Pakistan. Our product range is exquisitely portrayed in this catalogue. We display it in most of the international defence exhibitions. POF’s Exports Division employees experts who take care of customer requirements in professional manner with utmost promptness. You may send all of your inquiries to us on [email protected] with my personal assurance of excellent assistance from POF. Disclaimer The technical values mentioned in the catalogue / website are average values which have been established in trials under customary conditions. We reserve the right to deviations within normal end-user practice. These specifications do not constitute a warranty and do not release the end-user from undertaking suitability tests under reigning ambient conditions. All the illustrations shown and offered are non-binding, in particular as regards design, size and color of the products. -

Here Normal Communication (1100 Mm X 1100 Mm)
IN THE BATTLE SINCE 1888 AUSTRALIAN MUNITIONS PRODUCT RANGE AND SPECIFICS www.australian-munitions.com.au AUSTRALIAN MUNITIONS - A FORMIDABLE FORCE Small Calibre Ammunition ..................................................................................................................... 3 Medium Calibre ................................................................................................................................... 13 Large Calibre ...................................................................................................................................... 15 Grenades and Demolition Stores .......................................................................................................... 17 High Explosives .................................................................................................................................... 19 Military Propellants ............................................................................................................................... 21 Pyrotechnics and Simulators ................................................................................................................. 22 Bombs ................................................................................................................................................. 24 Commercial Powders and Ammunition .................................................................................................. 26 SMALL CALIBRE AMMUNITION 5.56 mm F1 BALL AMMUNITION Consistent performance in varying -

Table of Contents Standard Reloading Dies (Group A-E)
HUNTINGTON DIE SPECIALTIES - 2014 rcbs dies table oF contents Standard Reloading Dies (Group A-E) ................. 35-36, 74-76 AR Series Dies / TC Seating Dies ........................................ 37 Competition Die Sets ...................................................... 39, 78 Cowboy Action Shooting Dies (CAS) .............................. 38, 78 Cowboy Shotshell Dies ......................................................... 38 Legacy Series Dies ......................................................... 37, 78 reloading presses Safari Series Dies ............................................................ 37, 79 Reloading Presses, Kits, & Accessories ..............................1-5 50 bmg, 416 Barrett, 460 Steyr Dies, Large Caliber ........ 38, 76 Compac Press, HDS ............................................................... 5 Neck Die Sets / Neck Sizer Dies ......................................41-42 Specialty Merchandise Information ...................................... 51 Small Base Sets / Small Base Sizers ...............................42-43 powder handling tools Die Replacement Parts ......................................................... 43 Reloading Scales, Electronic / Beam...................................5-6 Expander-Decap Units ..............................................43, 74-79 Powder Measures / Tools ....................................................6-9 Hornady Carbide Expander Assy. ......................................... 43 Bullet Feeding Systems ......................................................... -

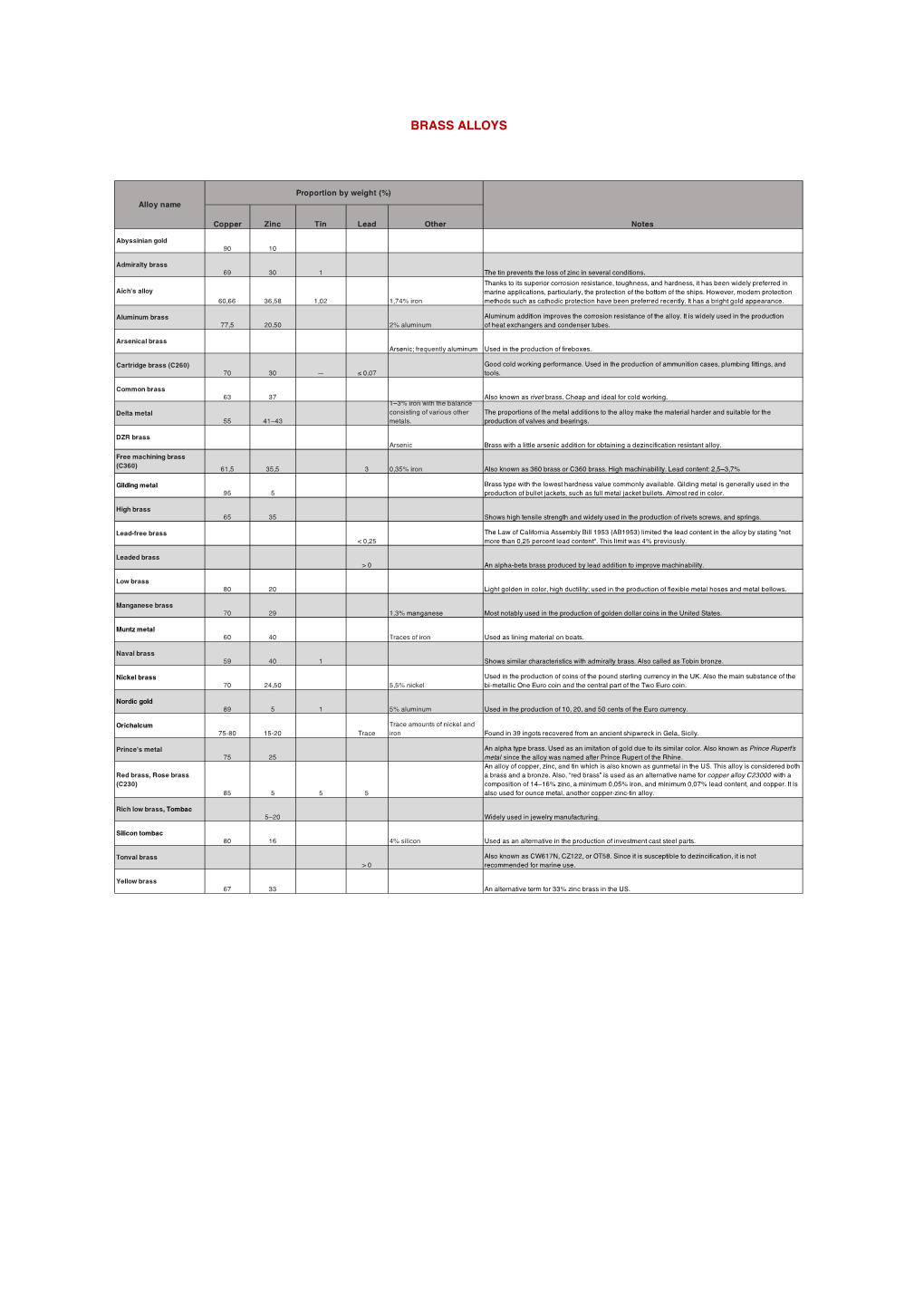
2015 Common Brass Alloys.Pdf
Brass Alloys Alloy Composition and Use Admiralty brass 30% zinc and 1% tin, used to inhibit dezincification 60.66% copper, 36.58% zinc, 1.02% tin, and 1.74% iron. Corrosion resistance, hardness and toughness Aich's alloy make it useful for marine applications. Less than 35% zinc, malleable, can be worked cold, used in pressing, forging, or similar applications. Alpha brass Alpha brasses have only one phase, with face-centered cubic crystal structure. alpha brass containing 75% copper and 25% zinc. Named for Prince Rupert of the Rhine and used to Prince's metal or Prince Rupert's metal imitate gold. 35–45% zinc and is suited for hot working. It contains both α and β' phase; the β'-phase is body- Alpha-beta brass or Muntz metal or duplex brass centered cubic and is harder and stronger than α. Alpha-beta brasses are usually worked hot. contains aluminium, which improves its corrosion resistance. Used for seawater service and in Euro Aluminium brass coins (Nordic gold). Arsenical brass contains an addition of arsenic and frequently aluminium and is used for boiler fireboxes. 45–50% zinc content. Can only be worked hot producing a hard strong metal that is suitable for Beta brass casting. Cartridge brass 30% zinc brass with good cold working properties. Used for ammunition cases. Common brass, or rivet brass 37% zinc brass, standard for cold working DZR brass dezincification resistant brass with a small percentage of arsenic Gilding metal 95% copper and 5% zinc, softest type of common brass, used for ammunition jackets High brass 65% copper -

The Vital Metal
Copper Development Association Copper – The Vital Metal CDA Publication 121, 1998 Copper – The Vital Metal CDA Publication 121 April 1998 (This book replaces CDA Book 1 ‘Introduction to Copper’, 1988) Members as at 1st January 1998 ASARCO Inc Boliden MKM Ltd Thomas Bolton Ltd The British Non-Ferrous Metals Federation Chile Copper Ltd Gecamines IMI plc Inco Europe Ltd Noranda Sales Corporation of Canada Ltd Rio Tinto London Ltd Southern Peru Copper Corporation Acknowledgements This publication is financed by the members of Copper Development Association, European Copper Institute, British Non-Ferrous Metals Federation and Aalco. CDA is glad to acknowledge with thanks the provision of illustrations where noted. Copper Development Association Copper Development Association is a non-trading organisation sponsored by the copper producers and fabricators to encourage the use of copper and copper alloys and to promote their correct and efficient application. Its services, which include the provision of technical advice and information, are available to those interested in the utilisation of copper in all its aspects. The Association also provides a link between research and user industries and maintains close contact with other copper development associations throughout the world. Website: www.cda.org.uk Email: [email protected] Copyright: All information in this document is the copyright of Copper Development Association Disclaimer: Whilst this document has been prepared with care, Copper Development Association can give no warranty regarding -

Copper Commando, World War II Copper Commando
Montana Tech Library Digital Commons @ Montana Tech All Issues, Copper Commando, World War II Copper Commando July 16, 1943 Copper Commando - vol. 1, no. 24 Victory Labor-Management Production Committees of Butte, Anaconda and Great Falls Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.mtech.edu/copper_commando Part of the American Politics Commons, History Commons, Mining Engineering Commons, Photography Commons, Place and Environment Commons, and the Rhetoric Commons Recommended Citation Victory Labor-Management Production Committees of Butte, Anaconda and Great Falls, "Copper Commando - vol. 1, no. 24" (1943). http://digitalcommons.mtech.edu/copper_commando/24 This Book is brought to you for free and open access by the Copper Commando at Digital Commons @ Montana Tech. It has been accepted for inclusion in All Issues, Copper Commando, World War II by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons @ Montana Tech. For more information, please contact [email protected]. sec. 562, P. 1.. '" R. ~. U. S. POSTAGE I Paiel Butte. Mont. Permit No. 139 • \ , :u' Vol. 1 July 16, 1943 No. 2.4 _.. .. Lovely To Look At - . I HE may not be your son, Itut he's tomebody's. And if we tum our heads at the pitiful sight .f this kid, because the spectacle of "'e blood aftd gore bothers us, it's the best evi- dence in the world that we can't ~ake it. We expect him to be able to, .but we can't do it ourselves. There oughtn't to be anything so shocking about the sight of a youngster who is I probably banged up for the rest of his life. -

Ancient & Historic
Ancient & Historic METALS CONSERVATION AND SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Ancient & Historic METALS CONSERVATION AND SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH Proceedings of a Symposium Organized by the J. Paul Getty Museum and the Getty Conservation Institute November 1991 Edited by DAVID A. SCOTT, JERRY PODANY, BRIAN B. CONSIDINE THE GETTY CONSERVATION INSTITUTE Symposium editors: David A. Scott, the Getty Conservation Institute; Jerry Podany and Brian B. Considine, the-J. Paul Getty Museum Publications coordination: Irina Averkieff, Dinah Berland Editing: Dinah Berland Art director: Jacki Gallagher Design: Hespenheide Design, Marilyn Babcock / Julian Hills Design Cover design: Marilyn Babcock / Julian Hills Design Production coordination: Anita Keys © 1994 The J. Paul Getty Trust © 2007 Electronic Edition, The J. Paul Getty Trust All rights reserved Printed in Singapore Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Ancient & historic metals : conservation and scientific research : proceedings of a symposium organized by the J.-Paul Getty Museum and the Getty Conservation Institute, November 1991 / David A. Scott, Jerry Podany, Brian B. Considine, editors. p. cm. Includes bibliographical references. ISBN 0-89236-231-6 (pbk.) 1. Art metal-work—Conservation and restoration—Congresses. I. Scott, David A. II. Podany, Jerry. III. Considine, Brian B. IV. J. Paul Getty Museum. V. Getty Conservation Institute. VI. Title: Ancient and historic metals. NK6404.5.A53 1995 730’.028—dc20 92-28095 CIP Every effort has been made to contact the copyright holders of the photographs and illustrations in this book to obtain permission to publish. Any omissions will be corrected in future editions if the publisher is contacted in writing. Cover photograph: Bronze sheathing tacks from the HMS Sirius. -

2012 Blue Press
September 2014 theBlueBlue PressPress$2.95 U.S./$3.95 Canada WhichWhich DillonDillon isis Just In, Special RightRight Purchases, forfor Bargains YOU?YOU? and PagePage 66 Close Outs Page 65 DP Dillon’sDillon’s RFRF 100100 3 AutomaticAutomatic PrimerPrimer FillerFiller Eliminates the need illon’s RF 100 Automatic Primer DFiller eliminates the task of fill- for primer pick-up tubes! ing primer pick up tubes. Now you simply pour your primers from their Fills the primer tube box into the top, press the blue but- ton and watch it run! while you reload! In about two minutes the primers are inside the protective metal hous- Clear polycarbonate shield ing. That’s about 30 rounds you can load while the RF 100 is doing your and protective housing work for you! The RF 100 is available for either large or small primers, and conver- sion kits are available at one low price of $47.95 each. Lg. Primer Filler K84-97077 $317.95 Sm. Primer Filler K84-97111 317.95 Lg. (Euro. 220v) K84-97112 327.95 Sm. (Euro. 220v) K84-97113 327.95 Sm. Conversion K84-17903 47.95 Lg. Conversion K84-17902 47.95 Nylon Packcloth Dust Cover K84-11143 14.95 4 What’s Inside: We READ Our Mail! would like to thank John Marshall for his article about ONE SHOT, Ithe Savage Model 99 rifle in the July 2014 issue of The Blue Press. My Dad, Elmer, owns just such a rifle, in .300 ONE Savage, that he bought in the late 1950s for the exorbitant price of $85. -

Copper Commando, World War II Copper Commando
Montana Tech Library Digital Commons @ Montana Tech All Issues, Copper Commando, World War II Copper Commando July 16, 1943 Copper Commando - vol. 1, no. 24 Victory Labor-Management Production Committees of Butte, Anaconda and Great Falls Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.mtech.edu/copper_commando Part of the American Politics Commons, History Commons, Mining Engineering Commons, Photography Commons, Place and Environment Commons, and the Rhetoric Commons Recommended Citation Victory Labor-Management Production Committees of Butte, Anaconda and Great Falls, "Copper Commando - vol. 1, no. 24" (1943). http://digitalcommons.mtech.edu/copper_commando/24 This Book is brought to you for free and open access by the Copper Commando at Digital Commons @ Montana Tech. It has been accepted for inclusion in All Issues, Copper Commando, World War II by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons @ Montana Tech. For more information, please contact [email protected]. sec. 562, P. 1.. '" R. ~. U. S. POSTAGE I Paiel Butte. Mont. Permit No. 139 • \ , :u' Vol. 1 July 16, 1943 No. 2.4 _.. .. Lovely To Look At - . I HE may not be your son, Itut he's tomebody's. And if we tum our heads at the pitiful sight .f this kid, because the spectacle of "'e blood aftd gore bothers us, it's the best evi- dence in the world that we can't ~ake it. We expect him to be able to, .but we can't do it ourselves. There oughtn't to be anything so shocking about the sight of a youngster who is I probably banged up for the rest of his life. -

The Brasses Properties & Applications
Copper Development Association Publication 117 The Brasses properties & applications CDA Publication No. 117, 1996 by Vin Callcut Revised 2005 by Peter Webster COPPER DEVELOPMENT ASSOCIATION (Limited by guarantee) MEMBERS, as at April 2005 BrazeTec Codelco Services Ltd Ecosea Ltd IBP Conex Mueller Europe Copper Tube & Fittings Noranda Islandi ehf Outokumpu Copper Metal Supplies Ltd Rio Tinto London Ltd SANHA UK Ltd Southern Peru Copper Corporation The British Non-Ferrous Metals Federation Wieland–Werke (UK) Ltd WMC Resources Ltd Yorkshire Copper Tube Ltd Yorkshire Fittings Ltd COPPER DEVELOPMENT ASSOCIATION is a non-trading organisation sponsored by the copper producers and fabricators to encourage the use of copper and copper alloys and to promote their correct and efficient application. Its services, which include the provision of technical advice and information, are available to those interested in the utilisation of copper in all its aspects. The Association also provides a link between research and the user industries and maintains close contact with other copper development organisations throughout the world. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This revision was financed by International Copper Association, European Copper Institute and Rio Tinto London Ltd. In the preparation of the 1996 text CDA is pleased to acknowledge with thanks significant help given by Hector Campbell, John Nicholson and John Westlake. For the 2005 revision thanks are due to: Vin Callcut Sean Hammond (Tungum Ltd) Keith Ingram (Consultant) Ken Kempson Roger Thompson (Armack Chemicals Ltd) Mark Thomson-Tur (Cole & Swallow Materials Ltd) Mike Treadwell (Outokumpu Copper MKM Ltd) Copper Development Association 5 Grovelands Business Centre PHOTOGRAPHY Boundary Way All photography by Vin Callcut unless otherwise credited. -

Metal Techniques for Craftsmen
METAL TECHNIQUES FOR CRAFTSMEN : A Basic Manual,for Craftsmen 1 on the Methods of Forming and Decorating Metals By OPPI UNTRACHT ROBERT HALE LONDON Contents Introduction xiii Aluminum Aluminum alloys. Soldering aluminum. Brazing aluminum. Casting aluminum. Sand casting of aluminum. Plaster mold Part One casting of aluminum. Other casting METALS : BASIC INFORMATION procedures with aluminum Nickel METALS : ORIGIN, BEHAVIOR, ' , Considerations in working nickel. AND MANUFACTURE l Soldering and joining nickel. Polishing Origin nickel and its alloys Metallurgy 3 Nickel alloys Characteristic Physical Properties of Nickel silver. Monel Metal. Nichrome Metals 4 wire. Invar The Behavior of Metals: Their Mechanical Mercury Properties C Amalgam gold plating. Preparing gola Hardness. Malleability. Ductility. Tensile amalgam. Applying the amalgam strength. Compressi n : Shear. Toughness. Elasticity. Torsion. pBgttleness. Impact Ferrous Metals resistance. Rigiditv Iron Steel CLASSIFICATION OF METALS Carbon steel. Alloy steel Nonferrous Precious Metals THE MANUFACTURE OF METALS Gold Gold alloys. Karat gold. Karat gold Manufacture of Sterling Silver Sheet solders. Purchasing gold. IJsing karat Metal gold: General considerations. Testing for Wire Drawing gold with acid Procedure for hand drawing wire Annealing the wire. Using the Silver l1 drawplate Silver alloys. Purchasing silver. General considerations in the use of silver. Mechanical wire drawing Testing for silver. Cleaning silverware The flat rolling mill by electrolytic action Adjusting the rolling mill. Using the Platinum rolling mill Base Metals 16 Sheet and Wire Gauge Measuring Copper 16 Systems Copper-based alloys 18 Extruded Metals Shotting Brass l8 Annealing Bronze l8 Texture of Metal Surfaces Lead 19 Toxicity of Metals Forms of lead. Casting lead. Soldering lead. Lead welding.