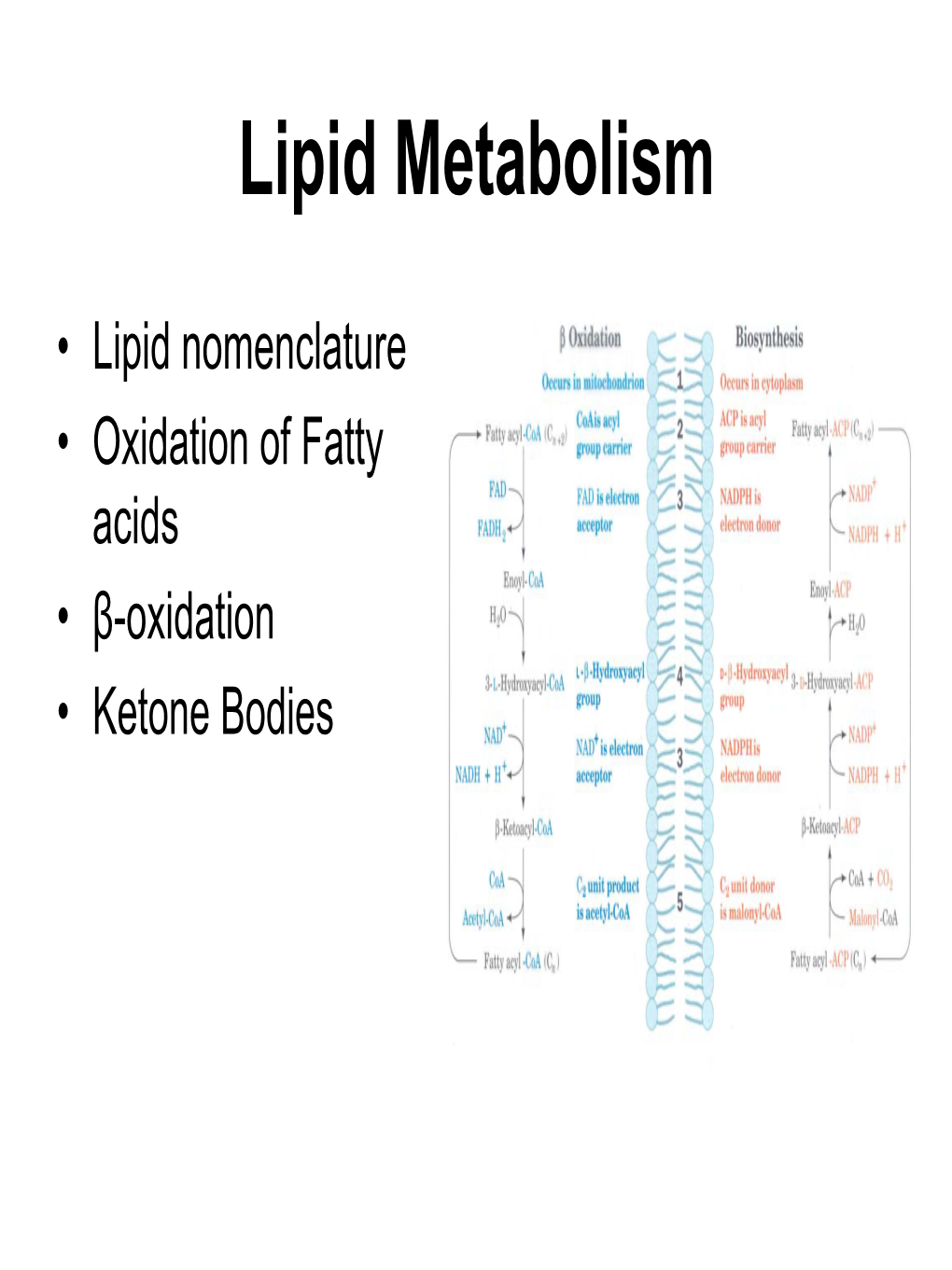
Lipid Metabolism
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Corticosteroid Treatment, Serum Lipids and Coronary Artery Disease D. B. JEFFERYS M
Postgrad Med J: first published as 10.1136/pgmj.56.657.491 on 1 July 1980. Downloaded from Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 491-493 Corticosteroid treatment, serum lipids and coronary artery disease D. B. JEFFERYS M. H. LESSOF B.Sc., M.R.C.P. M.D., F.R.C.P. M. B. MATTOCK Ph.D. Department of Medicine, Guy's Hospital, London Bridge SE] 9RT Summary cholesterol out of the tissue and back into the general Serum lipids and the cholesterol concentrations in the metabolic pool, where it may be catabolized. high density lipoprotein (HDL) fractions were meas- In this study the authors have looked at the long- ured in patients receiving long-term corticosteroid term effects of corticosteroids on HDL cholesterol. treatment for connective tissue disorders and asthma. They have studied 3 groups: patients who are receiv- Patients who were not receiving corticosteroid ing corticosteroids; age-, sex- and disease-matched treatment had blood lipid levels which did not differ patients who are not receiving such treatment; and from those of healthy people. However, female (but healthy age- and sex-matched controls. not male) patients who had received prednisolone for a mean period of 3-1 years had a significant elevation Patients and methods in total cholesterol and a large decrease in HDL Subjects cholesterol. It seems possible that high levels of The serum total cholesterol, triglycerides and copyright. corticosteroids may increase the incidence of pre- HDL cholesterol were measured for 16 pre-meno- menopausal ischaemic heart disease in females. pausal female patients (age range 18-34 years) and 15 males (ages 24-38 years) who were all receiving Introduction long-term corticosteroid treatment. -

The History of Carbon Monoxide Intoxication
medicina Review The History of Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Ioannis-Fivos Megas 1 , Justus P. Beier 2 and Gerrit Grieb 1,2,* 1 Department of Plastic Surgery and Hand Surgery, Gemeinschaftskrankenhaus Havelhoehe, Kladower Damm 221, 14089 Berlin, Germany; fi[email protected] 2 Burn Center, Department of Plastic Surgery and Hand Surgery, University Hospital RWTH Aachen, Pauwelsstrasse 30, 52074 Aachen, Germany; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] Abstract: Intoxication with carbon monoxide in organisms needing oxygen has probably existed on Earth as long as fire and its smoke. What was observed in antiquity and the Middle Ages, and usually ended fatally, was first successfully treated in the last century. Since then, diagnostics and treatments have undergone exciting developments, in particular specific treatments such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy. In this review, different historic aspects of the etiology, diagnosis and treatment of carbon monoxide intoxication are described and discussed. Keywords: carbon monoxide; CO intoxication; COHb; inhalation injury 1. Introduction and Overview Intoxication with carbon monoxide in organisms needing oxygen for survival has probably existed on Earth as long as fire and its smoke. Whenever the respiratory tract of living beings comes into contact with the smoke from a flame, CO intoxication and/or in- Citation: Megas, I.-F.; Beier, J.P.; halation injury may take place. Although the therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide has Grieb, G. The History of Carbon also been increasingly studied in recent history [1], the toxic effects historically dominate a Monoxide Intoxication. Medicina 2021, 57, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ much longer period of time. medicina57050400 As a colorless, odorless and tasteless gas, CO is produced by the incomplete combus- tion of hydrocarbons and poses an invisible danger. -

Arenicola Marina During Low Tide
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Published June 15 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Sulfide stress and tolerance in the lugworm Arenicola marina during low tide Susanne Volkel, Kerstin Hauschild, Manfred K. Grieshaber Institut fiir Zoologie, Lehrstuhl fur Tierphysiologie, Heinrich-Heine-Universitat, Universitatsstr. 1, D-40225 Dusseldorf, Germany ABSTRACT: In the present study environmental sulfide concentrations in the vicinity of and within burrows of the lugworm Arenicola marina during tidal exposure are presented. Sulfide concentrations in the pore water of the sediment ranged from 0.4 to 252 pM. During 4 h of tidal exposure no significant changes of pore water sulfide concentrations were observed. Up to 32 pM sulfide were measured in the water of lugworm burrows. During 4 h of low tide the percentage of burrows containing sulfide increased from 20 to 50% in July and from 36 to 77% in October A significant increase of median sulfide concentrations from 0 to 14.5 pM was observed after 5 h of emersion. Sulfide and thiosulfate concentrations in the coelomic fluid and succinate, alanopine and strombine levels in the body wall musculature of freshly caught A. marina were measured. During 4 h of tidal exposure in July the percentage of lugworms containing sulfide and maximal sulfide concentrations increased from 17 % and 5.4 pM to 62% and 150 pM, respectively. A significant increase of median sulfide concentrations was observed after 2 and 3 h of emersion. In October, changes of sulfide concentrations were less pronounced. Median thiosulfate concentrations were 18 to 32 FM in July and 7 to 12 ~.IMin October No significant changes were observed during tidal exposure. -

Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle Intermediates: Regulators of Immune Responses
life Review Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle Intermediates: Regulators of Immune Responses Inseok Choi , Hyewon Son and Jea-Hyun Baek * School of Life Science, Handong Global University, Pohang, Gyeongbuk 37554, Korea; [email protected] (I.C.); [email protected] (H.S.) * Correspondence: [email protected]; Tel.: +82-54-260-1347 Abstract: The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) is a series of chemical reactions used in aerobic organisms to generate energy via the oxidation of acetylcoenzyme A (CoA) derived from carbohydrates, fatty acids and proteins. In the eukaryotic system, the TCA cycle occurs completely in mitochondria, while the intermediates of the TCA cycle are retained inside mitochondria due to their polarity and hydrophilicity. Under cell stress conditions, mitochondria can become disrupted and release their contents, which act as danger signals in the cytosol. Of note, the TCA cycle intermediates may also leak from dysfunctioning mitochondria and regulate cellular processes. Increasing evidence shows that the metabolites of the TCA cycle are substantially involved in the regulation of immune responses. In this review, we aimed to provide a comprehensive systematic overview of the molecular mechanisms of each TCA cycle intermediate that may play key roles in regulating cellular immunity in cell stress and discuss its implication for immune activation and suppression. Keywords: Krebs cycle; tricarboxylic acid cycle; cellular immunity; immunometabolism 1. Introduction The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA, also known as the Krebs cycle or the citric acid Citation: Choi, I.; Son, H.; Baek, J.-H. Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) Cycle cycle) is a series of chemical reactions used in aerobic organisms (pro- and eukaryotes) to Intermediates: Regulators of Immune generate energy via the oxidation of acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) derived from carbohydrates, Responses. -

Fatty Acid Synthesis ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid Synthesis I
Handout 5 Fatty Acid Synthesis ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid Synthesis I. Overall concepts A. Definitions 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose and lactate) 1) De novo fatty acid synthesis uses glucose absorbed from the diet rather than glucose synthesized by the liver. 2) De novo fatty acid synthesis uses lactate derived primarily from glucose metabolism in muscle and red blood cells. b. Amino acid precursors (e.g., alanine, branched-chain amino acids) 1) De novo fatty acid synthesis from amino acids is especially important during times of excess protein intake. 2) Use of amino acids for fatty acid synthesis may result in nitrogen overload (e.g., the Atkins diet). c. Short-chain organic acids (e.g., acetate, butyrate, and propionate) 1) The rumen of ruminants is a major site of short-chain fatty acid synthesis. 2) Only small amounts of acetate circulate in non-ruminants. 2. Lipogenesis = fatty acid or triacylglycerol synthesis a. From preformed fatty acids (from diet or de novo fatty acid synthesis) b. Requires source of carbon (from glucose or lactate) for glycerol backbone 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes at confluence. No lipid 3T3-L1 Adipocytes after 6 days of filling has yet occurred. differentiation. Dark spots are lipid droplets. 1 Handout 5 Fatty Acid Synthesis B. Tissue sites of de novo fatty acid biosynthesis 1. Liver. In birds, fish, humans, and rodents (approx. 50% of fatty acid biosynthesis). 2. Adipose tissue. All livestock species synthesize fatty acids in adipose tissue; rodents synthesize about 50% of their fatty acids in adipose tissue. -

Biotransformation: Basic Concepts (1)
Chapter 5 Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Elimination of Toxics Biotransformation: Basic Concepts (1) • Renal excretion of chemicals Biotransformation: Basic Concepts (2) • Biological basis for xenobiotic metabolism: – To convert lipid-soluble, non-polar, non-excretable forms of chemicals to water-soluble, polar forms that are excretable in bile and urine. – The transformation process may take place as a result of the interaction of the toxic substance with enzymes found primarily in the cell endoplasmic reticulum, cytoplasm, and mitochondria. – The liver is the primary organ where biotransformation occurs. Biotransformation: Basic Concepts (3) Biotransformation: Basic Concepts (4) • Interaction with these enzymes may change the toxicant to either a less or a more toxic form. • Generally, biotransformation occurs in two phases. – Phase I involves catabolic reactions that break down the toxicant into various components. • Catabolic reactions include oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis. – Oxidation occurs when a molecule combines with oxygen, loses hydrogen, or loses one or more electrons. – Reduction occurs when a molecule combines with hydrogen, loses oxygen, or gains one or more electrons. – Hydrolysis is the process in which a chemical compound is split into smaller molecules by reacting with water. • In most cases these reactions make the chemical less toxic, more water soluble, and easier to excrete. Biotransformation: Basic Concepts (5) – Phase II reactions involves the binding of molecules to either the original toxic molecule or the toxic molecule metabolite derived from the Phase I reactions. The final product is usually water soluble and, therefore, easier to excrete from the body. • Phase II reactions include glucuronidation, sulfation, acetylation, methylation, conjugation with glutathione, and conjugation with amino acids (such as glycine, taurine, and glutamic acid). -

Anomalies in Coral Reef Community Metabolism and Their Potential Importance in the Reef CO2 Source-Sink Debate
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 95, pp. 6566–6569, May 1998 Population Biology Anomalies in coral reef community metabolism and their potential importance in the reef CO2 source-sink debate JOHN R. M. CHISHOLM* AND DAVID J. BARNES Australian Institute of Marine Science, Private Mail Bag No. 3, Mail Centre, Townsville, Queensland 4810, Australia Communicated by Andrew A. Benson, University of California, San Diego, CA, March 20, 1998 (received for review September 23, 1997) ABSTRACT It is not certain whether coral reefs are ratio of photosynthesis to respiration on unperturbed reefs sources of or sinks for atmospheric CO2. Air–sea exchange of over 24 h is considered to be close to unity (10). CO2 over reefs has been measured directly and inferred from In March 1996, we made an expedition to Lizard Island, changes in the seawater carbonate equilibrium. Such mea- northern Great Barrier Reef, Australia (Fig. 1), to measure surements have provided conflicting results. We provide changes in the O2 concentration and pH of seawater flowing community metabolic data that indicate that large changes in across a 300-m section of the reef flat by using a floating CO2 concentration can occur in coral reef waters via biogeo- instrument package (11–14). Measurements were made in chemical processes not directly associated with photosynthe- March when tides permitted the instrument package to float sis, respiration, calcification, and CaCO3 dissolution. These freely over the reef flat, a short distance above the benthos. processes can significantly distort estimates of reef calcifica- On arriving at Lizard Island, we encountered environmental tion and net productivity and obscure the contribution of coral conditions that we had not anticipated. -

The Effects of Warm and Cold Water Scuba Finning on Cardiorespiratory Responses and Energy Expenditure
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESISOF in Caron Lee Louise Shake for the degreeof Doctor of Philosophy Education presented on April 5, 1989. Scuba Finning on Title: The Effects of Warm and Cold Water Cardiorespiratory Responses and EnergyExpenditure Redacted for privacy Abstract approved: cardiorespiratory and energy This study was designed to determine finning at expenditure responses elicited byrecreational divers while and warm (29°C) water a submaximal intensity(35% max) in cold (18°C) to par- with and without wet suits. Male divers (15) volunteered exercise ticipate in five experimentalprocedures. A maximal graded in 29°C tethered finning test, two submaximal(30 min.) finning tests tests with and without wet suits, and twosubmaximal (30 min.) finning The variables in 18°C with and without wetsuits were performed. (VE), measured were: breathing frequency(BF), minute ventilation (RER), heart rate oxygen consumption (V02)respiratory exchange ratio (HR), and core temperature (CT). Caloric expenditure (kcal) was calculated from RER and V02. A Four-Way ANOVA andrepeated measures 0.05) Two-Way design was used to analyze the data. A significant (p < A significant (p < (suit x time) interaction wasrevealed for BF. 0.01) Three-Way (suit x temp. x time)interaction was revealed forVE, V02, RER, HR, and CT. An inverse relationship exists betweenBF and VE when comparing dives with and without suits. Diving in 18°C with suitselicited higher BF and lower VE than diving in 29°Cwithout suits. V02 increased significantly during threeof the four dives. Diving without suits elicited higher V02values though this was not significant in every case. Diving in a cold environmentelicited lower RER re- higher V02 and VE. -

Can't Catch My Breath! a Study of Metabolism in Fish. Subjects
W&M ScholarWorks Reports 2017 Can’t Catch My Breath! A Study of Metabolism in Fish. Subjects: Environmental Science, Marine/Ocean Science, Life Science/ Biology Grades: 6-8 Gail Schweiterman Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.wm.edu/reports Part of the Marine Biology Commons, and the Science and Mathematics Education Commons Recommended Citation Schweiterman, G. (2017) Can’t Catch My Breath! A Study of Metabolism in Fish. Subjects: Environmental Science, Marine/Ocean Science, Life Science/Biology Grades: 6-8. VA SEA 2017 Lesson Plans. Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary. https://doi.org/10.21220/V5414G This Report is brought to you for free and open access by W&M ScholarWorks. It has been accepted for inclusion in Reports by an authorized administrator of W&M ScholarWorks. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Can’t catch my breath! A study of metabolism in fish Gail Schwieterman Virginia Institute of Marine Science Grade Level High School Subject area Biology, Environmental, or Marine Science This work is sponsored by the National Estuarine Research Reserve System Science Collaborative, which supports collaborative research that addresses coastal management problems important to the reserves. The Science Collaborative is funded by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and managed by the University of Michigan Water Center. 1. Activity Title: Can’t Catch My Breath! A study of metabolism in fish 2. Focus: Metabolism (Ecological drivers); The Scientific Method (Formulating Hypothesis) 3. Grade Levels/ Subject: HS Biology, HS Marine Biology 4. VA Science Standard(s) addressed: BIO.1. The student will demonstrate an understanding of scientific reasoning, logic, and the nature of science by planning and conducting investigations (including most Essential Understandings and nearly all Essential Knowledge and Skills) BIO.4a. -

Upwelling As a Source of Nutrients for the Great Barrier Reef Ecosystems: a Solution to Darwin's Question?
Vol. 8: 257-269, 1982 MARINE ECOLOGY - PROGRESS SERIES Published May 28 Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. / I Upwelling as a Source of Nutrients for the Great Barrier Reef Ecosystems: A Solution to Darwin's Question? John C. Andrews and Patrick Gentien Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville 4810, Queensland, Australia ABSTRACT: The Great Barrier Reef shelf ecosystem is examined for nutrient enrichment from within the seasonal thermocline of the adjacent Coral Sea using moored current and temperature recorders and chemical data from a year of hydrology cruises at 3 to 5 wk intervals. The East Australian Current is found to pulsate in strength over the continental slope with a period near 90 d and to pump cold, saline, nutrient rich water up the slope to the shelf break. The nutrients are then pumped inshore in a bottom Ekman layer forced by periodic reversals in the longshore wind component. The period of this cycle is 12 to 25 d in summer (30 d year round average) and the bottom surges have an alternating onshore- offshore speed up to 10 cm S-'. Upwelling intrusions tend to be confined near the bottom and phytoplankton development quickly takes place inshore of the shelf break. There are return surface flows which preserve the mass budget and carry silicate rich Lagoon water offshore while nitrogen rich shelf break water is carried onshore. Upwelling intrusions penetrate across the entire zone of reefs, but rarely into the Lagoon. Nutrition is del~veredout of the shelf thermocline to the living coral of reefs by localised upwelling induced by the reefs. -

Ocean Life, Bioenergetics and Metabolism
Ocean life, bioenergetics and metabolism Biological Oceanography (OCN 621) Matthew Church (MSB 612) Ecosystems are hierarchically organized • Atoms → Molecules → Cells → Organisms→ Populations→ Communities • This organizational system dictates the pathways that energy and material travel through a system. • Cells are the lowest level of structure capable of performing ALL the functions of life. Classification of life Two primary cellular forms • Prokaryotes: lack internal membrane-bound organelles. Genetic information is not separated from other cell functions. Bacteria and Archaea are prokaryotes. Note however this does not imply these divisions of life are closely related. • Eukaryotes: membrane-bound organelles (nucleus, mitochrondrion, etc .). Compartmentalization (organization) of different cellular functions allows sequential intracellular activities In the ocean, microscopic organisms account for >50% of the living biomass. Controls on types of organisms, abundances, distributions • Habitat: The physical/chemical setting or characteristics of a particular environment, e.g., light vs. dark, cold vs. warm, high vs. low pressure • Each marine habitat supports a somewhat predictable assemblage of organisms that collectively make up the community, e.g., rocky intertidal community, coral reef community, abyssobenthic community • The structure and function of the individuals/populations in these communities arise from evolution and selective adaptations in response to the habitat characteristics • Niche: The role of a particular organism in an integrated community •The ocean is not homogenous: spatial and temporal variability in habitats Clearly distinguishable ocean habitats with elevated “plant” biomass in regions where nutrients are elevated The ocean is stirred more than mixed Sea Surface Temperature Chl a (°C) (mg m-3) Spatial discontinuities at various scales (basin, mesoscale, microscale) in ocean habitats play important roles in controlling plankton growth and distributions. -

Metabolic Transformation
Metabolic Transformation USE THESE TIPS TO JUMP START YOUR METABOLISM AND HELP YOU SHED THOSE EXTRA COLORIES YOU ARE WANTING RID OF! Your metabolism is your body’s way of expending energy by breaking down the food you eat to run your body how it should. The metabolism helps your body to burn calories, fat and carbohydrates. There are many things that can speed up and slow down your metabolism. SOME IDEAS TO GET YOUR METABOLISM GOING: Diet Exercise Life Practices Your Choices Metabolic Transformation Diet Breakfast—A must! Eating a good breakfast will start your metabolism off right at the start of each day. When you skip your morning meal, your body begins to slow that it may conserve energy. And don’t forget the joe! Grab a cup of caffeinated coffee to raise your heart rate, burning a few extra calories . Eating in Multiples It is researched that increasing your food intake to 5-6 times a day may lead to a faster metabolism because digestion helps speed up that Power Boosting Foods: process. Keep in mind though that those meals Chewing Gum should be small and of good quality nutrition. Coffee Power Punch with Protein Green Tea Protein is a good source to help build and Spicy Foods maintain lean muscle mass. Muscle is proven to burn more calories than fat does, even at rest. You Cold Water want to aim between 20-30 grams of protein per meal. Protein paired with the appropriate workouts can give great results. Choices, Choices, Choices! There are a lot of foods that you can start eating that will add some extra caloric burn to your day.