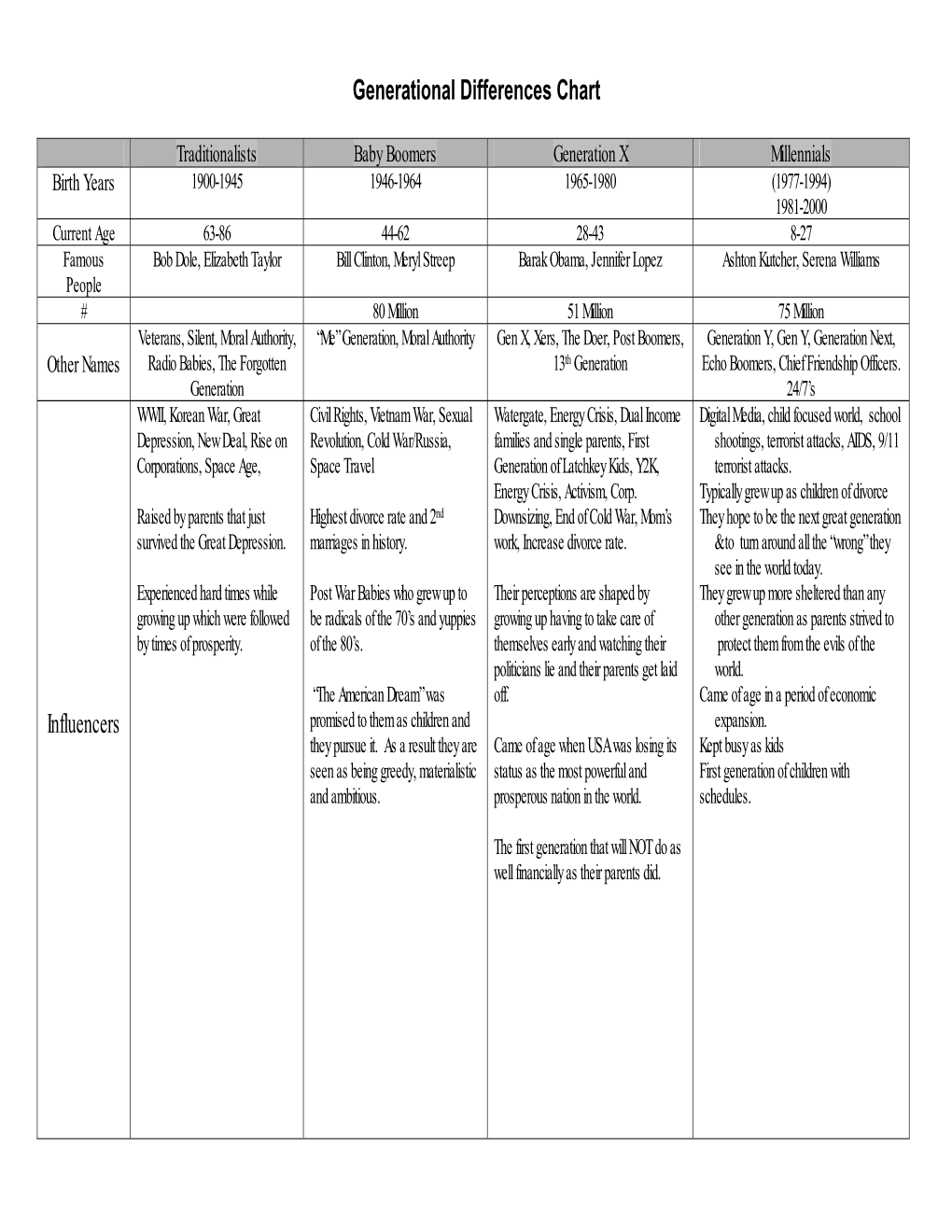
Generational Differences Chart
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Journal of Leadership in Organizations Vol.1, No
Journal of Leadership in Organizations Vol.1, No. 2 (2019) 96-111 JOURNAL OF LEADERSHIP IN ORGANIZATIONS Journal homepage: https://jurnal.ugm.ac.id/leadership HOW TO LEAD THE MILLENNIALS: A REVIEW OF 5 MAJOR LEADERSHIP THEORY GROUPS Bernadeta Cahya Kumala Putriastuti1*, Alessandro Stasi2 1 Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Gadjah Mada, Indonesia 2 Mahidol University International College, Thailand ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Millennials are currently taking over the global workforce. While Keywords: practitioners and scholars have recognized their different work values from previous generations, research on this topic is still Millennials; scarce. Furthermore, the current leadership theories have tended Neo-charismatic to focus mainly on the characteristics of leaders without Leadership; Leadership and adequately examining the leadership styles that work best for the information millennials. Using a literature review from the top tier leadership processing; journals, this paper aims to provide a more comprehensive Social exchange; framework to provide new directions for the development of Ethical leadership; leadership theory by understanding the millennials’ perspective E-leadership. on leadership. This study thus contributes to the current literatures by using five thematic leadership groups to develop the most Article History: optimum leadership style for leading the Millennials. The Received 2019-06-16 advantages and disadvantages of using neo-charismatics, Revised 2019-08-04 leadership and information processing, social exchange/relational Revised 2019-08-09 Revised 2019-08-13 leadership, ethical/moral leadership, and e-leadership theories in Accepted 2019-08-12 leading millennials are assessed. Results show that no single leadership theory is adequate for leading the millennials optimally. Hence, mixing the dimensions of different leadership theory groups is suggested. -

From Baby Boomers to Generation Y Millennials: Structure Classes For
From Baby Boomers to Generation Y Millennials: Ideas on How Professors Might Structure Classes for this Media Conscious Generation Marilyn Koeller National University New techniques for matching instructional strategies for the Millennial generation have been researched and discussed in this article. Some comparisons with previous generations have been outlined. These strategies are meant to meet the learning needs of Generation Y Millennial students in order to make their education more meaningful in both the on ground and online teaching and learning environment. Specific examples have been provided for both venues with a focus on the online environment. Hopefully, these strategies will not only support learner centered instruction and interactivity, but will address the communication preferences of Millennials in today’s colleges and universities. INTRODUCTION Four groups were compared in various categories to make the transition to what is valued by the Millennials. Through these comparisons, various instructional strategies will be outlined to produce an effective learning environment for today’s students (Wilson & Gerber, 2008). The Generational Divide The traditionalists generation was born between 1925 and 1945. There were about seventy five million traditionalists. This group was considered loyal to their teachers and authority in general. They valued logic and discipline and teachers used lectures, memorization and one way communication to deliver content in teaching. The instructional strategies used were based on processing information and learning basic skills that were given to students by teachers. There was one right answer that did not allow for change or thinking “outside the box”. It was important for students to learn basic facts and to be able to spell correctly, use correct grammar, and compute without using a calculator (Wilson & Gerber, 2008). -

Presentation
AIM Leadership Development Conference Sheraton New Orleans Hotel April 23‐24, 2015 This event is made possible through a Merck educational grant and with support from our partners at South Central Public Health Partnership and the Louisiana Public Health Institute. Thank YOU! Diane Thielfoldt Learning Strategist and Co‐ Founder The Learning Café 2 Leading a Multigenerational Workforce AIM Leadership Development Conference Diane Thielfoldt The Learning Cafe ©2015 The Learning Café meet the 4 generation workforce Silent Boomers Gen X Millennials 1933 - 1945 1946 - 1964 1965 - 1976 1977 - 1998 Cuspers 1960 - 1968 “Each generation has a shared history, common biases, and core beliefs.” 4 ©2015 The Learning Café shifting demographics Silents are past the traditional retirement age of 65. the labor force of those 65 to 75 is growing at a rate of 80% Silents are the most likely generation to read a daily newspaper and watch the news on television. 5 ©2015 The Learning Café shifting demographics Baby Boomers were the largest generation of children born in the US. The last 4.5 million Baby Boomers turned 50. 75 million Baby Boomers are redefining consumerism during the “Golden Years.” Boomers @65 AARP 6 ©2015 The Learning Café shifting demographics 65 % of Gen X is currently employed in full-time jobs. Gen X is the emerging management class in American Companies. Gen X is firmly in position as the leader of American parenting philosophy. 7 ©2015 The Learning Café shifting demographics The Millennials are now officially the largest and most influential adult population in American history. 8 ©2015 The Learning Café shifting demographics Professionals interact 85% with at least 3 other generations at work. -

The Post-80S Generation in Beijing: Collective Memory and Generational Identity
SANDRA VALéRIE CONSTANTIN. The post-80s generation in Beijing 5 DOI: 10.2478/ijas-2013-0001 Sandra Valérie ConStantin UniVerSitY oF GeneVa The post-80s generation in Beijing: collective memory and generational identity Abstract This article questions the relevance of the notion of generation to describe the cohort who lives in Beijing and who was born in the 1980s and early 1990s, after the implementation of the reforms and opening-up policy in China. The analysis relies on 627 questionnaires collected in Beijing in 2010. The sample was stratified by age and sex, and, based on quotas; it was split into five age groups (18-26 year-olds, 33-41 year-olds, 48-56 year-olds, 63-71 year-olds and 78-86 year-olds). The respondents were questioned on their perception of turning points and socio-historical changes that occurred during their lifetime. After having analysed the data in a comparative perspective, we came to conclusion that the word generation is suitable to describe the young people from Beijing born in the 1980s and early 1990s not only because they do share autobiographical and collective historical memories, but also because these memories have by and large taken place between their adolescence and entry into adulthood (supporting the hypothesis of the existence of a reminiscence bump). Keywords: China, collective memory, generation, identity, life course, youth Theoretical framework Individual life course and History are strongly imbedded. Since the middle of the last century, sociologists have been seeking to understand the mechanics of this embedded-ness on micro-, meso-, and macro-socioeconomic levels. -

THE PROBLEM of GENERATIONS As to Be Capable of Choosing Rationally the Form of Government Most Suitable for Himself
HOW THE PROBLEM STANDS AT THE MOMENT 277 forms of historical being. But if the ultimate human relationships are changed, the existence of man as we have come to understand it must cease altogether-culture, creativeness, tradition must all disappear, or must at least appear in a totally different light. Hume actually experimented with the idea of a modification of such ultimate data. Suppose, he said, the type of succession of human generations to be completely altered to resemble that of CHAPTER VII a butterfly or caterpillar, so that the older generation disappears at one stroke and the new one is born all at once. Further, suppose man to be of such a high degree of mental development THE PROBLEM OF GENERATIONS as to be capable of choosing rationally the form of government most suitable for himself. (This, of course, was the main problem I. HOW THE PROBLEM STANDS AT THE MOMENT of Hume's time.) These conditions given, he said, it would be both possible and proper for each generation, without reference A. THE POSITIVIST FORMULATION OF THE PROBLEM to the ways of its ancestors, to choose afresh its own particular form of state. Only because mankind is as it is-generation follow• of investigation into his problem. All too often it falls to ing generation in a continuous stream, so that whenever one THEhis lotfirsttotaskdealofwiththe sociologiststray problemsis to toreviewwhichtheallgeneralthe sciencesstate person dies off, another is b-9rn to replace him-do we find it in turn have made their individual contribution without anyone necessary to preserve the continuity of our forms of government. -

Trend Hacking: How to Make Trends Work #IRL
MARCH 22, 2018 Trend Hacking: How to Make Trends Work #IRL PRESENTED BY Scarlett Rosier / Co-Founder & Director of Operations, Rhyme & Reason Design Heather Daniel / TMP Business Development, Rhyme & Reason Design 9 seconds 8 seconds What does this mean for marketing? Squirrel Engagement is elusive Everyone wants a unicorn Budgets are made from shoestring Womp Womp Fret not. We’re here to help you hack the trends for real life application. Going Viral DEFINITION: Any technique that induces websites or users to pass on a marketing message to other sites or users, creating a potentially exponential growth in the message’s visibility and effect. TREND #1 GOING VIRAL - EXAMPLE 1 Oreo’s You can still dunk in the dark tweet GOING VIRAL - EXAMPLE 2 JJ Watt’s Hurricane Harvey Relief GOING VIRAL - EXAMPLE 3 KFC’s Twitter following of 11 “herbs & spices” GOING VIRAL - EXAMPLE 4 Spotify’s 2018 Goals campaign: BY THE NUMBERS: • Five billion items of content are posted each day on Facebook • 1% of Twitter messages are shared more than seven times • 95% of news people see on Twitter comes directly from its original source or from one degree of separation • Internet popularity is mostly driven by a handful of one- to-one-million blasts not by a million one-to-one shares SOURCE: http://time.com/4672540/go-viral-on-internet/ https://www.forbes.com/sites/robertwynne/2017/07/31/why-its-so-hard-to-go-viral/#348737e60623 Hack it WE ALL CAN’T BE KARDASHIANS… AND THAT’S REALLY OKAY. Social Media Algorithms, they are a-changing • Facebook diminishes posts shown by marketers • Engagement bait tactics are getting the hook PRO TIP: Use your organization’s nimble size to your advantage Experiential Marketing Experiential Marketing DEFINITION: A marketing strategy that directly engages consumers and invites and encourages them to participate in the evolution of a brand or brand experience. -

Talking About Whose Generation?
issue 6 | 2010 Complimentary article reprint Talking About Whose Generation? why western generational models can’t account for a global workforce By daVid hole, le zhong and jeff SChwartz > PhotograPhy By daVid ClugSton This publication contains general information only, and none of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, its member firms, or its and their affiliates are, by means of this publication, render- ing accounting, business, financial, investment, legal, tax, or other professional advice or services. This publication is not a substitute for such professional advice or services, nor should it be used as a basis for any decision or action that may affect your finances or your business. Before making any decision or taking any action that may affect your finances or your business, you should consult a qualified professional adviser. None of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, its member firms, or its and their respective affiliates shall be responsible for any loss whatsoever sustained by any person who relies on this publication. About Deloitte Deloitte refers to one or more of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu, a Swiss Verein, and its network of member firms, each of which is a legally separate and independent entity. Please see www.deloitte.com/about for a detailed description of the legal structure of Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu and its member firms. Copyright © 2010 Deloitte Development LLC. All rights reserved. 84 Talking About Whose Generation? Why Western generational models can’t account for a global workforce By DaviD Hole, le ZHong anD Jeff ScHwartZ > pHotograpHy By DaviD clugSton Deloitte Review deloittereview.com talking about Whose gener ation? 85 it is 8 pm in shanghai, and Kan, a marketing manager for a large global retailer has just gotten off of another call with a headhunter. -

RACIAL and GENDER IDENTITIES Sasha Shen Johfre and Aliya Saperstein
STATE OF THE UNION 7 RACIAL AND GENDER IDENTITIES Sasha Shen Johfre and Aliya Saperstein KEY FINDINGS • Millennials are more likely than previous generations to identify as multiracial. • Millennials also are more likely to adopt unconventional gender identities, such as reporting that they see themselves as equally feminine and masculine. • However, they are not outpacing previous generations in rejecting race and gender stereotypes. Their attitudes toward women’s roles and perceptions of black Americans are quite similar to those of baby boomers or Gen Xers. merican millennials have been hailed New forms of data collection also emerged as the “bridge” to a more racially diverse during this period. The oldest millennials were future and cast as pushing the boundaries on the cusp of adulthood in 1997 when the U.S. Aof gender with new forms of identity and expres- Office of Management and Budget announced sion.1 But the labeling and branding of each new that it was revising guidelines for all federal data generation often invites criticism. Are these char- collection to allow Americans to “mark one or acterizations on the mark? Are millennials indeed more” boxes when identifying their race.3 Unlike embracing a more diverse and unconventional previous cohorts, when most millennials sent off set of racial and gender identities? Are they also their college applications or applied for their first poised to challenge social norms around race and jobs, they were not forced to choose just one race gender in other ways? to describe themselves. We take on each of these questions in turn. We Millennials thus stand out from previous show that millennials do see their racial and gen- generations in two ways. -

The Deloitte Global 2021 Millennial and Gen Z Survey
A call for accountability and action T HE D ELO IT T E GLOB A L 2021 M IL LE N N IA L AND GEN Z SUR V E Y 1 Contents 01 06 11 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 2 Impact of the COVID-19 The effect on mental health pandemic on daily life 15 27 33 CHAPTER 3 CHAPTER 4 CONCLUSION How the past year influenced Driven to act millennials’ and Gen Zs’ world outlooks 2 Introduction Millennials and Generation Zs came of age at the same time that online platforms and social media gave them the ability and power to share their opinions, influence distant people and institutions, and question authority in new ways. These forces have shaped their worldviews, values, and behaviors. Digital natives’ ability to connect, convene, and create disruption via their keyboards and smartphones has had global impact. From #MeToo to Black Lives Matter, from convening marches on climate change to the Arab Spring, from demanding eco-friendly products to challenging stakeholder capitalism, these generations are compelling real change in society and business. The lockdowns resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic curtailed millennials’ and Gen Zs’ activities but not their drive or their desire to be heard. In fact, the 2021 Deloitte Global Millennial Survey suggests that the pandemic, extreme climate events, and a charged sociopolitical atmosphere may have reinforced people’s passions and given them oxygen. 01 Urging accountability Last year’s report1 reflected the results of two Of course, that’s a generality—no group of people is surveys—one taken just before the pandemic and a homogeneous. -

Gen Z in the Workforce: Nuance and Success
GEN Z IN THE WORKFORCE: NUANCE AND SUCCESS Zachary N. Clark Dr. Kathleen Howley Director of Student Activities & Assessment Deputy Vice Chancellor for Academic & Student Affairs Indiana University of Pennsylvania Pennsylvania State System of Higher Education Overview In this session, you will: Acquire an overview of the different generations of Americans currently serving in the workforce, including Baby Boomers, Generation X, Millennials, and Generation Z. Explore key differences and similarities in these generations across core belief structures, including understandings of society, education, leadership, technology, and more. Identify recommendations and best practices, reinforced with research, to help find success in the multigenerational workplace, including in the first post-educational work experience. Evaluate through deep reflection how participants define student success, while also collaborating with peers to identify ‘one piece of advice’ for trustees and presidents to ensure worthwhile experiences at our universities and to support post-graduation success. Things to Keep in Mind Generational studies are not exact, and have clear limitations. These pieces of information highlight national trends, as shown in sociological and educational research. Not every member of a particular generation of college student will be a cookie-cutter image to their peers. While engaging in discussion today, keep statements broad enough so as to respect the privacy and guard the identities of individuals (students, faculty, staff, administrators, -

Are Millennials Really All That Different Than Generation X? an Analysis of Factors Contributing to Differences in Vehicle Miles of Travel
Are Millennials Really All That Different Than Generation X? An Analysis of Factors Contributing to Differences in Vehicle Miles of Travel Denise Capasso da Silva Arizona State University, School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment 660 S. College Avenue, Tempe, AZ 85287-3005 Tel: 480-727-3613; Email: [email protected] Sebastian Astroza Universidad de Concepción, Department of Industrial Engineering Edmundo Larenas 219, Concepción, Chile Tel: +56-41-220-3618; Email: [email protected] Irfan Batur Arizona State University, School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment 660 S. College Avenue, Tempe, AZ 85287-3005 Tel: 480-727-3613; Email: [email protected] Sara Khoeini Arizona State University, School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment 660 S. College Avenue, Tempe, AZ 85287-3005 Tel: 480-965-5047; Email: [email protected] Tassio B. Magassy Arizona State University, School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment 660 S. College Avenue, Tempe, AZ 85287-3005 Tel: 480-727-3613; Email: [email protected] Ram M. Pendyala Arizona State University, School of Sustainable Engineering and the Built Environment 660 S. College Avenue, Tempe, AZ 85287-3005 Tel: 480-727-4587; Email: [email protected] Chandra R. Bhat (corresponding author) The University of Texas at Austin Department of Civil, Architectural and Environmental Engineering 301 E. Dean Keeton St. Stop C1761, Austin TX 78712 Tel: 512-471-4535; Email: [email protected] and The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong August 2019 ABSTRACT This paper is motivated by a desire to understand and quantify the extent to which millennials are truly different in their activity-travel behavior when compared with Generation X that preceded them. -

GENERATION INFORMATION Adapted From: the Center for Generational Studies
GENERATION INFORMATION Adapted from: The Center for Generational Studies www.gentrends.com Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964) Baby Boomers entered a thriving economy after WWII. The US had established itself as the preeminent power in the world. Factories were pumping out new cars and appliances. Houses were being built at a record pace. The proliferation of TVs in the 1950s forever changed the way that those growing up viewed the world. Boomers grew up feeling more secure than their parents. They began to question policies, rules and practices that had been in place for years. From this emerged civil rights protests, anti-war protests and a host of other rumbling that unsettled prior generations. Because of their size, this generation has received lots of attention. Companies focused their products. Politicians focused their messages. Rock and roll music took over the air waves. As a result, Boomers have grown up thinking the world is their oyster. As boomers entered the work place, they forever changed the way business was done. Many have taken advantage of college opportunities which raised the bar for many positions. Boomers focused on efficiency, teamwork, quality, and service. These efforts have produced a thriving “self-help” industry which feeds Boomers’ optimism and quest for eternal youth. The size of this generation continues to drive the economy and they place increasing emphasis on convenience. Financial security will remain a central issue for many, forcing thousands to work well past the age at which their parents retired. Their quest to remain eternally young will alter the face of lifestyles, the work force, consumer products, entertainment and public policy.