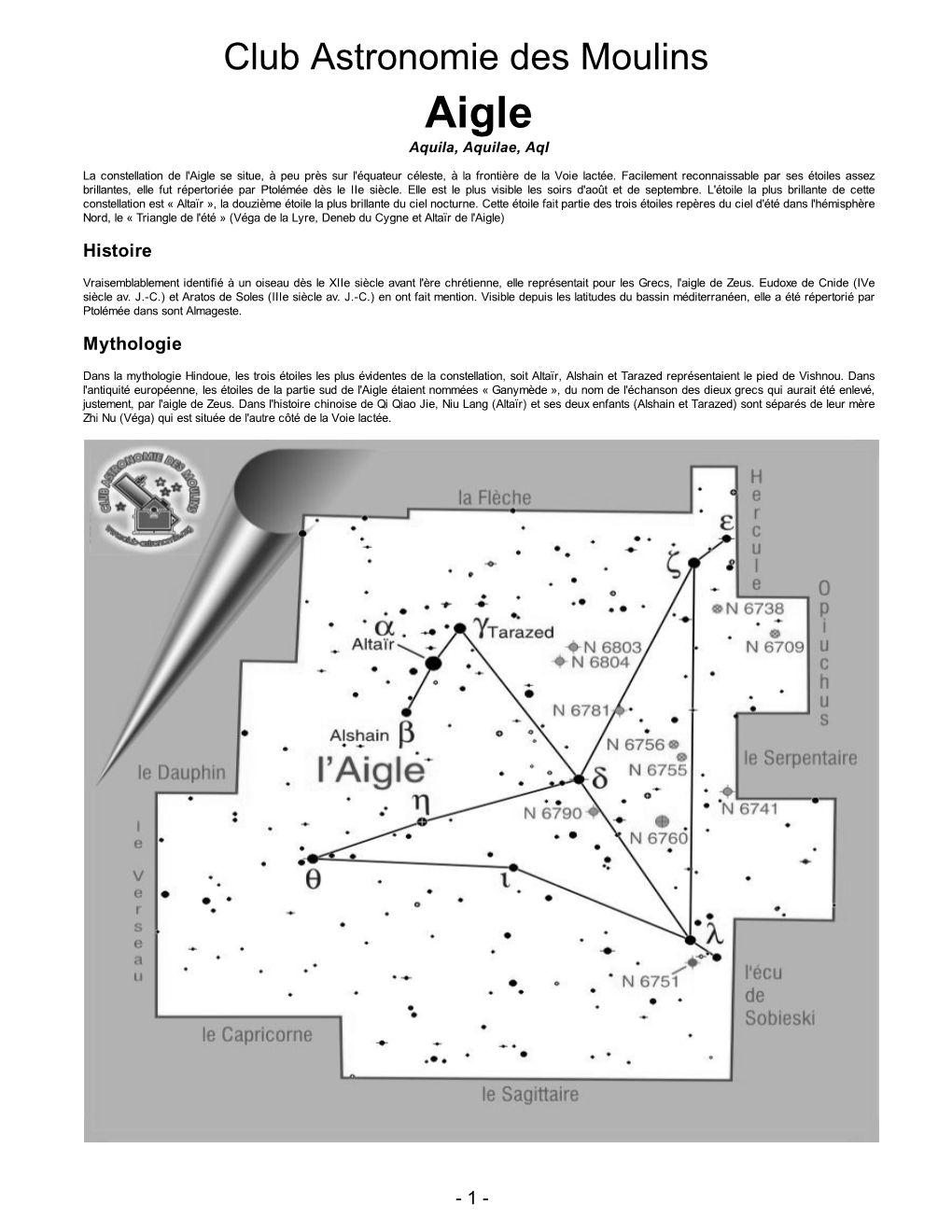
Aigle Aquila, Aquilae, Aql
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

I N S I D E T H I S I S S
Publications from February/février 1998 Volume/volume 92 Number/numero 1 [669] The Royal Astronomical Society of Canada The Beginner’s Observing Guide This guide is for anyone with little or no experience in observing the night sky. Large, easy to read star maps are provided to acquaint the reader with the constellations and bright stars. Basic information on observing the moon, planets and eclipses through the year 2000 is provided. There The Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada Le Journal de la Société royale d’astronomie du Canada is also a special section to help Scouts, Cubs, Guides and Brownies achieve their respective astronomy badges. Written by Leo Enright (160 pages of information in a soft-cover book with a spiral binding which allows the book to lie flat). Price: $12 (includes taxes, postage and handling) Looking Up: A History of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada Published to commemorate the 125th anniversary of the first meeting of the Toronto Astronomical Club, “Looking Up — A History of the RASC” is an excellent overall history of Canada’s national astronomy organization. The book was written by R. Peter Broughton, a Past President and expert on the history of astronomy in Canada. Histories on each of the centres across the country are included as well as dozens of biographical sketches of the many people who have volunteered their time and skills to the Society. (hard cover with cloth binding, 300 pages with 150 b&w illustrations) Price: $43 (includes taxes, postage and handling) Observers Calendar — 1998 This calendar was created by members of the RASC. -

Planetary Nebulae
Planetary Nebulae A planetary nebula is a kind of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from old red giant stars late in their lives. The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer that originated in the 1780s with astronomer William Herschel because when viewed through his telescope, these objects appeared to him to resemble the rounded shapes of planets. Herschel's name for these objects was popularly adopted and has not been changed. They are a relatively short-lived phenomenon, lasting a few tens of thousands of years, compared to a typical stellar lifetime of several billion years. The mechanism for formation of most planetary nebulae is thought to be the following: at the end of the star's life, during the red giant phase, the outer layers of the star are expelled by strong stellar winds. Eventually, after most of the red giant's atmosphere is dissipated, the exposed hot, luminous core emits ultraviolet radiation to ionize the ejected outer layers of the star. Absorbed ultraviolet light energizes the shell of nebulous gas around the central star, appearing as a bright colored planetary nebula at several discrete visible wavelengths. Planetary nebulae may play a crucial role in the chemical evolution of the Milky Way, returning material to the interstellar medium from stars where elements, the products of nucleosynthesis (such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and neon), have been created. Planetary nebulae are also observed in more distant galaxies, yielding useful information about their chemical abundances. In recent years, Hubble Space Telescope images have revealed many planetary nebulae to have extremely complex and varied morphologies. -

A Basic Requirement for Studying the Heavens Is Determining Where In
Abasic requirement for studying the heavens is determining where in the sky things are. To specify sky positions, astronomers have developed several coordinate systems. Each uses a coordinate grid projected on to the celestial sphere, in analogy to the geographic coordinate system used on the surface of the Earth. The coordinate systems differ only in their choice of the fundamental plane, which divides the sky into two equal hemispheres along a great circle (the fundamental plane of the geographic system is the Earth's equator) . Each coordinate system is named for its choice of fundamental plane. The equatorial coordinate system is probably the most widely used celestial coordinate system. It is also the one most closely related to the geographic coordinate system, because they use the same fun damental plane and the same poles. The projection of the Earth's equator onto the celestial sphere is called the celestial equator. Similarly, projecting the geographic poles on to the celest ial sphere defines the north and south celestial poles. However, there is an important difference between the equatorial and geographic coordinate systems: the geographic system is fixed to the Earth; it rotates as the Earth does . The equatorial system is fixed to the stars, so it appears to rotate across the sky with the stars, but of course it's really the Earth rotating under the fixed sky. The latitudinal (latitude-like) angle of the equatorial system is called declination (Dec for short) . It measures the angle of an object above or below the celestial equator. The longitud inal angle is called the right ascension (RA for short). -

September 2020 BRAS Newsletter
A Neowise Comet 2020, photo by Ralf Rohner of Skypointer Photography Monthly Meeting September 14th at 7:00 PM, via Jitsi (Monthly meetings are on 2nd Mondays at Highland Road Park Observatory, temporarily during quarantine at meet.jit.si/BRASMeets). GUEST SPEAKER: NASA Michoud Assembly Facility Director, Robert Champion What's In This Issue? President’s Message Secretary's Summary Business Meeting Minutes Outreach Report Asteroid and Comet News Light Pollution Committee Report Globe at Night Member’s Corner –My Quest For A Dark Place, by Chris Carlton Astro-Photos by BRAS Members Messages from the HRPO REMOTE DISCUSSION Solar Viewing Plus Night Mercurian Elongation Spooky Sensation Great Martian Opposition Observing Notes: Aquila – The Eagle Like this newsletter? See PAST ISSUES online back to 2009 Visit us on Facebook – Baton Rouge Astronomical Society Baton Rouge Astronomical Society Newsletter, Night Visions Page 2 of 27 September 2020 President’s Message Welcome to September. You may have noticed that this newsletter is showing up a little bit later than usual, and it’s for good reason: release of the newsletter will now happen after the monthly business meeting so that we can have a chance to keep everybody up to date on the latest information. Sometimes, this will mean the newsletter shows up a couple of days late. But, the upshot is that you’ll now be able to see what we discussed at the recent business meeting and have time to digest it before our general meeting in case you want to give some feedback. Now that we’re on the new format, business meetings (and the oft neglected Light Pollution Committee Meeting), are going to start being open to all members of the club again by simply joining up in the respective chat rooms the Wednesday before the first Monday of the month—which I encourage people to do, especially if you have some ideas you want to see the club put into action. -

La Porte Des Étoiles Le Journal Des Astronomes Amateurs Du Nord De La France
la porte des étoiles le journal des astronomes amateurs du nord de la France Numéro 39 - hiver 2018 39 À la une Les environs de la grande nébuleuse d’Orion Auteur : F. Lefebvre et D. Fayolle Date : 16/10/2017 Lieu : Saint-Véran (05) GROUPEMENT D’ASTRONOMES Matériel : APN Canon 1000D et AMATEURS COURRIEROIS astrographe Boren-Simon 8'' F2.8 Adresse postale GAAC - Simon Lericque Édito 12 lotissement des Flandres 62128 WANCOURT On avait déjà raconté beaucoup de choses sur Saint-Véran et son Internet observatoire... On pensait même avoir tout dit... On ne voulait pas Site : http://www.astrogaac.fr se répéter... Et pourtant, la mission Astroqueyras 2017 du GAAC Facebook : https://www.facebook.com/GAAC62 a encore repoussé les limites... Imaginez, une fine équipe de 20 E-mail : [email protected] astronomes amateurs venus de l’ensemble des Hauts-de-France (et même au-delà) envahissant pour une semaine le plus bel Les auteurs de ce numéro observatoire astronomique ouvert aux amateurs ; parmi eux, des Philippe Nonckelynck - membre du GAAC contemplateurs, des dessinateurs, des photographes. Les résultats, E-mail : [email protected] fort nombreux, de cette mission historique nous ont poussé à nouveau à prendre la plume pour causer de ce coin de paradis, Simon Lericque - membre du GAAC E-mail : [email protected] de son ciel, de son observatoire et de ses instruments, et surtout de l’ambiance extraordinaire d’une semaine à 3000 mètres sous Yann Picco - membre du GAAC les étoiles... La belle histoire entre le GAAC et Saint-Véran se E-mail : [email protected] poursuit donc avec cet épais numéro de la porte des étoiles.. -

Proto-Planetary Nebula Observing Guide
Proto-Planetary Nebula Observing Guide www.reinervogel.net RA Dec CRL 618 Westbrook Nebula 04h 42m 53.6s +36° 06' 53" PK 166-6 1 HD 44179 Red Rectangle 06h 19m 58.2s -10° 38' 14" V777 Mon OH 231.8+4.2 Rotten Egg N. 07h 42m 16.8s -14° 42' 52" Calabash N. IRAS 09371+1212 Frosty Leo 09h 39m 53.6s +11° 58' 54" CW Leonis Peanut Nebula 09h 47m 57.4s +13° 16' 44" Carbon Star with dust shell M 2-9 Butterfly Nebula 17h 05m 38.1s -10° 08' 33" PK 10+18 2 IRAS 17150-3224 Cotton Candy Nebula 17h 18m 20.0s -32° 27' 20" Hen 3-1475 Garden-sprinkler Nebula 17h 45m 14. 2s -17° 56' 47" IRAS 17423-1755 IRAS 17441-2411 Silkworm Nebula 17h 47m 13.5s -24° 12' 51" IRAS 18059-3211 Gomez' Hamburger 18h 09m 13.3s -32° 10' 48" MWC 922 Red Square Nebula 18h 21m 15s -13° 01' 27" IRAS 19024+0044 19h 05m 02.1s +00° 48' 50.9" M 1-92 Footprint Nebula 19h 36m 18.9s +29° 32' 50" Minkowski's Footprint IRAS 20068+4051 20h 08m 38.5s +41° 00' 37" CRL 2688 Egg Nebula 21h 02m 18.8s +36° 41' 38" PK 80-6 1 IRAS 22036+5306 22h 05m 30.3s +53° 21' 32.8" IRAS 23166+1655 23h 19m 12.6s +17° 11' 33.1" Southern Objects ESO 172-7 Boomerang Nebula 12h 44m 45.4s -54° 31' 11" Centaurus bipolar nebula PN G340.3-03.2 Water Lily Nebula 17h 03m 10.1s -47° 00' 27" PK 340-03 1 IRAS 17163-3907 Fried Egg Nebula 17h 19m 49.3s -39° 10' 37.9" Finder charts measure 20° (with 5° circle) and 5° (with 1° circle) and were made with Cartes du Ciel by Patrick Chevalley (http://www.ap-i.net/skychart) Images are DSS Images (blue plates, POSS II or SERCJ) and measure 30’ by 30’ (http://archive.stsci.edu/cgi- bin/dss_plate_finder) and STScI Images (Hubble Space Telescope) Downloaded from www.reinervogel.net version 12/2012 DSS images copyright notice: The Digitized Sky Survey was produced at the Space Telescope Science Institute under U.S. -

The 2011 Observers Challenge List
TMSP OBSERVER'S CHALLENGE 2011 By Kreig McBride and Tom Masterson All observations must be made at TMSP and 25 out of 30 objects must be viewed to earn a unique TMSP Observer's Award lapel pin. You must create a record of your observations which include date, time, instruments used and a brief description and/or sketch of the object. Your records will be returned to you. Size or ID Number V Magnitude Object Type Constellation RA Dec Description Separation The Sun! View 2 days noting changes. H-alpha, white 1 Sol -28m ½ degree Star Cancer 08h 39' +27d 07' light or projection is OK North Galactic Astronomical Catch this one before it sets. Next to the double star 31 2 N/A N/A Coma Berenices 12h 51' +27d 07' Pole Reference point Comae Berenices Omicron-2 a wide 4.9m, 9m double lies close by as does 3 U Cygni 5.9 – 12.1m N/A Carbon Star Cygnus 19.6h +47d 54' 6” diameter, 12.6m Planetary nebula NGC6884 4 M22 5.1m 7.8' Globular Cluster Sagittarius 18h 36.4' -23d 54' Rich, large and bright 5 NGC 6629 11.3m 15” Planetary Nebula Sagittarius 18h 25.7' -23d 12' Stellar at low powers. Central Star is 12.8m 6 Barnard 86 N/A 5' Dark Nebula Sagittarius 18h 03' -27d 53' “Ink Spot” Imbedded in spectacular star field Faint 1' glow surrounding 9.5m star w/a faint companion 7 NGC 6589-90 N/A 5' x 3' Reflection Nebula Sagittarius 18h 16.9'' -19d 47' 25” to its SW A 3.2m, B Reddish/Orange primary, B white, C is 10m companion 8 ETA Sagittarii 3.6m, C 10m, AB pair 3.6” Quadruple Star Sagittarius 18h 17.6' -36d 46' 93” distant at PA303d and D is 13m star 33” -

SAC's 110 Best of the NGC
SAC's 110 Best of the NGC by Paul Dickson Version: 1.4 | March 26, 1997 Copyright °c 1996, by Paul Dickson. All rights reserved If you purchased this book from Paul Dickson directly, please ignore this form. I already have most of this information. Why Should You Register This Book? Please register your copy of this book. I have done two book, SAC's 110 Best of the NGC and the Messier Logbook. In the works for late 1997 is a four volume set for the Herschel 400. q I am a beginner and I bought this book to get start with deep-sky observing. q I am an intermediate observer. I bought this book to observe these objects again. q I am an advance observer. I bought this book to add to my collect and/or re-observe these objects again. The book I'm registering is: q SAC's 110 Best of the NGC q Messier Logbook q I would like to purchase a copy of Herschel 400 book when it becomes available. Club Name: __________________________________________ Your Name: __________________________________________ Address: ____________________________________________ City: __________________ State: ____ Zip Code: _________ Mail this to: or E-mail it to: Paul Dickson 7714 N 36th Ave [email protected] Phoenix, AZ 85051-6401 After Observing the Messier Catalog, Try this Observing List: SAC's 110 Best of the NGC [email protected] http://www.seds.org/pub/info/newsletters/sacnews/html/sac.110.best.ngc.html SAC's 110 Best of the NGC is an observing list of some of the best objects after those in the Messier Catalog. -

Catalogue of Excitation Classes P for 750 Galactic Planetary Nebulae
Catalogue of Excitation Classes p for 750 Galactic Planetary Nebulae Name p Name p Name p Name p NeC 40 1 Nee 6072 9 NeC 6881 10 IC 4663 11 NeC 246 12+ Nee 6153 3 NeC 6884 7 IC 4673 10 NeC 650-1 10 Nee 6210 4 NeC 6886 9 IC 4699 9 NeC 1360 12 Nee 6302 10 Nee 6891 4 IC 4732 5 NeC 1501 10 Nee 6309 10 NeC 6894 10 IC 4776 2 NeC 1514 8 NeC 6326 9 Nee 6905 11 IC 4846 3 NeC 1535 8 Nee 6337 11 Nee 7008 11 IC 4997 8 NeC 2022 12 Nee 6369 4 NeC 7009 7 IC 5117 6 NeC 2242 12+ NeC 6439 8 NeC 7026 9 IC 5148-50 6 NeC 2346 9 NeC 6445 10 Nee 7027 11 IC 5217 6 NeC 2371-2 12 Nee 6537 11 Nee 7048 11 Al 1 NeC 2392 10 NeC 6543 5 Nee 7094 12 A2 10 NeC 2438 10 NeC 6563 8 NeC 7139 9 A4 10 NeC 2440 10 NeC 6565 7 NeC 7293 7 A 12 4 NeC 2452 10 NeC 6567 4 Nee 7354 10 A 15 12+ NeC 2610 12 NeC 6572 7 NeC 7662 10 A 20 12+ NeC 2792 11 NeC 6578 2 Ie 289 12 A 21 1 NeC 2818 11 NeC 6620 8 IC 351 10 A 23 4 NeC 2867 9 NeC 6629 5 Ie 418 1 A 24 1 NeC 2899 10 Nee 6644 7 IC 972 10 A 30 12+ NeC 3132 9 NeC 6720 10 IC 1295 10 A 33 11 NeC 3195 9 NeC 6741 9 IC 1297 9 A 35 1 NeC 3211 10 NeC 6751 9 Ie 1454 10 A 36 12+ NeC 3242 9 Nee 6765 10 IC1747 9 A 40 2 NeC 3587 8 NeC 6772 9 IC 2003 10 A 41 1 NeC 3699 9 NeC 6778 9 IC 2149 2 A 43 2 NeC 3918 9 NeC 6781 8 IC 2165 10 A 46 2 NeC 4071 11 NeC 6790 4 IC 2448 9 A 49 4 NeC 4361 12+ NeC 6803 5 IC 2501 3 A 50 10 NeC 5189 10 NeC 6804 12 IC 2553 8 A 51 12 NeC 5307 9 NeC 6807 4 IC 2621 9 A 54 12 NeC 5315 2 NeC 6818 10 Ie 3568 3 A 55 4 NeC 5873 10 NeC 6826 11 Ie 4191 6 A 57 3 NeC 5882 6 NeC 6833 2 Ie 4406 4 A 60 2 NeC 5879 12 NeC 6842 2 IC 4593 6 A -

Skytools Chart
22 Aquila - Scutum SkyTools 3 / Skyhound.com 7006 γ2 α IC 4997 γ1 δ ρ ε β ζ ζ Delphinus 6891 NGC 6738 ε δ γ γ NGC 6709 κ 6803 +10° ξ 6934 μ Blue Racquetball 6781 NGC 6633 β IC 4665 IC 4756 NGC 6755 θ1 Aquila θ2 Equuleus δ γ Collinder 359 6852 6790 Collinder 350 η 6760 ν Collinder 401 Phantom Streak +0° θ 6535 ι Serpens Cauda ζ λ β NGC 6704 6751 η NGC 6683 κ Wild Duck Cluster IC 1276 NGC 6664 6539 6712 ε α τ IC 4846 μ δ ζ 6517 ε M 26 ν -10° Scutum ν Saturn Nebula NGC 6625 2 NGC 6604 M 73 M72 ν α α1 Eagle Nebula Little Gem Star Queen Barnard's Galaxy γ β NGC 6605 τ h 8 υ Omega Nebula 1 M 17 52° x 34° 19h30m00.0s +00°00'00" (Skymark) Open Cl. Nebula Galaxy 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Globular Cl. Dark Neb. Quasar Globule Planetary 22 Aquila - Scutum GALASSIE Sigla Nome Cost. A.R. Dec. Mv. Dim. Tipo Distanza 200/4 80/11,5 20x60 NGC 6822 Barnard's Gal. Sgr 19h 47m 58s -14° 48' 11" +9,40 13',5x12',3 IB 4,4 Mly Er 20 (dif.) Er 20 (v. c.) (v. c.) AMMASSI APERTI Sigla Nome Cost. A.R. Dec. Mv. Dim. N° Æ Distanza 200/4 80/11,5 20x60 IC 4665 Oph 17h 46m 18s +05° 43' 00" +5,30 70',0 29 1.100 ly Er 20 (det.) Er 15,5 (det.) (dif.) Cr 350 Oph 17h 48m 06s +01° 18' 00" +6,10 39',0 --- 930 ly Er 12,4 (det.) Er 20 (det.) (dif.) Cr 359 Oph 18h 01m 06s +02° 54' 00" +3,00 240',0 --- 810 ly Er 20 (det.) Er 20 (det.) (det.) NGC 6604 Ser 18h 18m 04s -12° 14' 30" +7,50 5',0 30 5.500 ly Er 20 (easy) Er 20 (easy) (det.) NGC 6605 Ser 18h 18m 21s -14° 56' 42" +6,00 15',0 12 --- Er 20 (dif.) Er 20 (cha.) (cha.) M 16 Star Queen Ser 18h 18m 48s -13° 48' 24" +6,50 6',0 60 5.700 ly Er 20 (obv.) Er 20 (easy) (easy) M 17 Sgr 18h 20m 47s -16° 10' 18" +7,30 25',0 --- 4.200 Or 6 (dif.) Er 20 (cha.) (v. -

Planetary Nebula 168 Planetary Nebula 168
Planetary nebula 168 Planetary Nebula 168 Pagina 1 Planetary nebula 168 . o ) . ) . R N ' x e e g c n n m t A i B z z a . a r e i i o Object Other o Class NGC Description U m a m R S S h D C ( M S h ( C 14 NGC 7662 PK 106-17.1 AND 23 25.9 +42 32 8,6 5,6 17 s 14 s 4(3) !!! Planetary or annular neb,vB,pS,R,blue 138 PK 315-13.1 He2-131 APS 15 37.2 -71 55 11,8 6,8 4.9 s 138 PK 308-12.1 He2-105 APS 14 15.5 -74 13 12 12 35 s 66 IC 4846 PK 27-9.1 AQL 19 16.5 -09 03 12 4,5 2 s 2 stellar 66 NGC 6790 PK 37-6.1 AQL 19 23.0 +01 31 11,4 5,9 2 s 2 B,eS,stell=9.5m 66 NGC 6803 PK 46-4.1 AQL 19 31.3 +10 03 11 6,4 4 s 2a stellar 66 NGC 6741 PK 33-2.1 AQL 19 02.6 -00 27 12 7 9 s 7 s 4 Planetary,stellar 42 PK 52- 2.2 Merrill 1-1 AQL 19 39.1 +15 56 11,8 7,7 3 s 4 13''-pF,vS,R,BM at 165X, averted viz helps 66 NGC 6751 PK 29-5.1 AQL 19 05.9 -06 00 12 9,2 20 s 3 pB,S 66 NGC 6804 PK 45-4.1 AQL 19 31.6 +09 14 12,4 11 63 s 50 s 4(2) cB,S,iR,rrr 65 NGC 6852 PK 42-14.1 AQL 20 00.7 +01 44 11.4p 11,2 28 s 4 F neb,am st 66 NGC 6781 PK 41-2.1 AQL 19 18.5 +06 32 11,8 12,8 111 s 109 s 3b(3) F,L,R,vsbM disc 66 NGC 6772 PK 33-6.1 AQL 19 14.6 -02 42 14 99,9 75 s 55 s 3b(2) vF,L,R,vvlBM,r 66 PK 31-10.1 M3-34 AQL 19 27.1 -06 35 12,4 99,9 6.0 s 5.1 s 2 66 PK 37- 3.2 Abell 56 AQL 19 13.1 +02 53 12,4 99,9 188 s 174 s 4 64 NGC 7009 PK 37-34.1 AQR 21 04.2 -11 22 8,3 6,2 28 s 23 s 4(6) !!! vB,S,elliptic 87 NGC 7293 PK 36-57.1 AQR 22 29.6 -20 50 6,3 13,6 960 s 720 s 4(3) !,pF,vL,E or biN 116 IC 4642 PK 334-9.1 ARA 17 11.8 -55 24 12,4 9,6 15 s 4 stellar 115 PK 342-14.1 Shapley 3 ARA 18 07.4 -51 03 11,9 12,4 36 s 116 IC 1266 PK 345-8.1 ARA 17 45.6 -46 05 12,3 99,9 13 s 4 stellar,gaseous spectrum-Pickering 56 PK 173- 5.1 K2-1;SS 38 AUR 05 08.1 +30 48 12 15,5 132 s 3 13''-pF,pL,R,nBM at 165X, 3* invol 32 IC 2149 PK 166+10.1 AUR 05 56.4 +46 06 10 99,9 12 s 6 s 3b(2) S,vB 32 PK 169-0.1 AUR 05 19.2 +38 11 12 99,9 32 s Pagina 2 Planetary nebula 168 . -

108 Afocal Procedure, 105 Age of Globular Clusters, 25, 28–29 O
Index Index Achromats, 70, 73, 79 Apochromats (APO), 70, Averted vision Adhafera, 44 73, 79 technique, 96, 98, Adobe Photoshop Aquarius, 43, 99 112 (software), 108 Aquila, 10, 36, 45, 65 Afocal procedure, 105 Arches cluster, 23 B1620-26, 37 Age Archinal, Brent, 63, 64, Barkhatova (Bar) of globular clusters, 89, 195 catalogue, 196 25, 28–29 Arcturus, 43 Barlow lens, 78–79, 110 of open clusters, Aricebo radio telescope, Barnard’s Galaxy, 49 15–16 33 Basel (Bas) catalogue, 196 of star complexes, 41 Aries, 45 Bayer classification of stellar associations, Arp 2, 51 system, 93 39, 41–42 Arp catalogue, 197 Be16, 63 of the universe, 28 Arp-Madore (AM)-1, 33 Beehive Cluster, 13, 60, Aldebaran, 43 Arp-Madore (AM)-2, 148 Alessi, 22, 61 48, 65 Bergeron 1, 22 Alessi catalogue, 196 Arp-Madore (AM) Bergeron, J., 22 Algenubi, 44 catalogue, 197 Berkeley 11, 124f, 125 Algieba, 44 Asterisms, 43–45, Berkeley 17, 15 Algol (Demon Star), 65, 94 Berkeley 19, 130 21 Astronomy (magazine), Berkeley 29, 18 Alnilam, 5–6 89 Berkeley 42, 171–173 Alnitak, 5–6 Astronomy Now Berkeley (Be) catalogue, Alpha Centauri, 25 (magazine), 89 196 Alpha Orionis, 93 Astrophotography, 94, Beta Pictoris, 42 Alpha Persei, 40 101, 102–103 Beta Piscium, 44 Altair, 44 Astroplanner (software), Betelgeuse, 93 Alterf, 44 90 Big Bang, 5, 29 Altitude-Azimuth Astro-Snap (software), Big Dipper, 19, 43 (Alt-Az) mount, 107 Binary millisecond 75–76 AstroStack (software), pulsars, 30 Andromeda Galaxy, 36, 108 Binary stars, 8, 52 39, 41, 48, 52, 61 AstroVideo (software), in globular clusters, ANR 1947