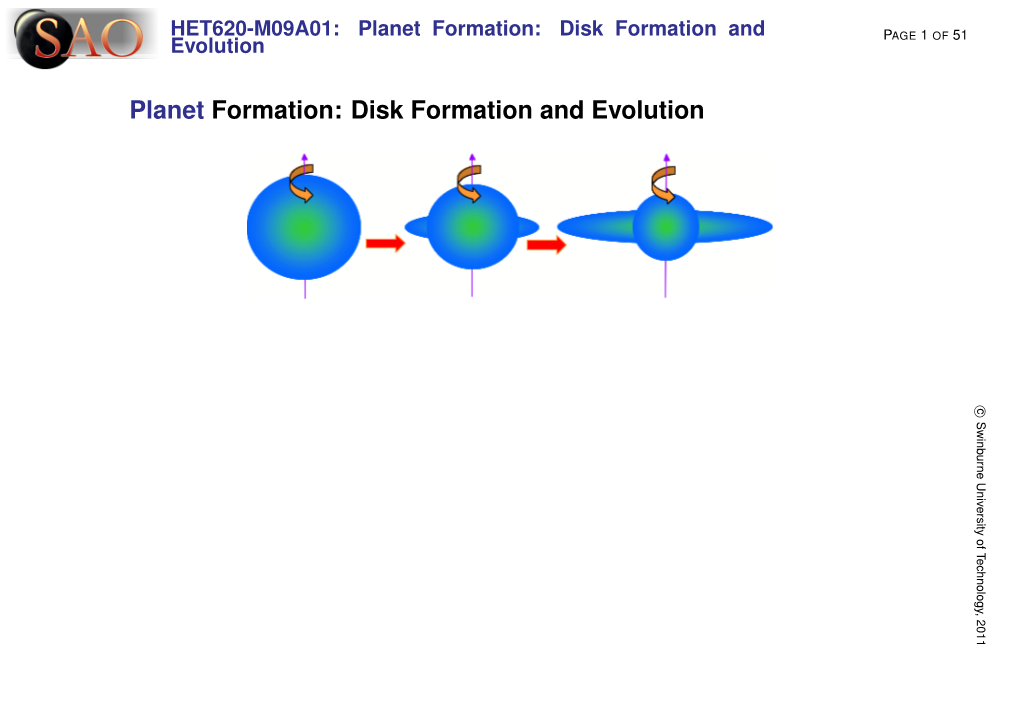
Planet Formation
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Angular Momentum of Condensations Within Elephant Trunks
A&A 503, 477–482 (2009) Astronomy DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/200912238 & c ESO 2009 Astrophysics The angular momentum of condensations within elephant trunks V. L ora 1,A.C.Raga2, and A. Esquivel2 1 Instituto de Astronomía, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Ap. 70-468, 04510, D.F México 2 Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Ap. 70-543, 04510, D.F México e-mail: [email protected] Received 31 March 2009 / Accepted 22 May 2009 ABSTRACT Aims. The radiation from newly born stars photoevaporates their parental neutral cloud, leading to the formation of dense clumps that will eventually form stars. Methods. We present 3D simulations of the interaction of a neutral cloud with an external ionising radiation field, and compute the angular momenta of these collapsing clumps. Results. The angular momenta of these collapsing clumps show that they have preferential orientations mostly perpendicular to the direction of the incident ionising photon field. Therefore, the axes of the jet systems that will be eventually ejected (from the star+accretion disk systems that will form) will be oriented approximately perpendicular to the direction to the photoionising source. Key words. ISM: kinematics and dynamics – ISM: clouds – ISM: HII regions – stars: formation 1. Introduction of elephant trunks is quite small, their alignment approximately perpendicular to the direction to the ionising photon source The radiation from newly born stars photoionises and erodes the might be indicative of a systematic alignment. This alignment parental cloud, producing structures such as the so-called ele- implies that the angular momenta of the low mass star+disk sys- phant trunks. -

A Spitzer Survey of Protoplanetary Disk Dust in the Young Serpens Cloud: How Do Dust Characteristics Evolve with Time?
The Astrophysical Journal, 714:778–798, 2010 May 1 doi:10.1088/0004-637X/714/1/778 C 2010. The American Astronomical Society. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A. A SPITZER SURVEY OF PROTOPLANETARY DISK DUST IN THE YOUNG SERPENS CLOUD: HOW DO DUST CHARACTERISTICS EVOLVE WITH TIME? Isa Oliveira1,2, Klaus M. Pontoppidan2, Bruno Mer´ın3, Ewine F. van Dishoeck1,4, Fred Lahuis1,5, Vincent C. Geers6, Jes K. Jørgensen7, Johan Olofsson8, Jean-Charles Augereau8, and Joanna M. Brown4 1 Leiden Observatory, Leiden University, P.O. Box 9513, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands; [email protected] 2 California Institute of Technology, Division for Geological and Planetary Sciences, MS 150-21, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA 3 Herschel Science Center, European Space Agency (ESA), P.O. Box 78, 28691 Villanueva de la Canada˜ (Madrid), Spain 4 Max-Planck Institut fur¨ Extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstrasse 1, 85748 Garching, Germany 5 SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research, P.O. Box 800, 9700 AV Groningen, The Netherlands 6 University of Toronto, 50 St. George St., Toronto, ON M5R 2W9, Canada 7 Centre for Star and Planet Formation, Natural History Museum of Denmark, University of Copenhagen, Øster Voldgade 5-7, DK-1350 Copenhagen, Denmark 8 Laboratoire d’Astrophysique de Grenoble, Universite´ Joseph Fourier, CNRS, UMR 5571, Grenoble, France Received 2009 December 28; accepted 2010 March 16; published 2010 April 14 ABSTRACT We present Spitzer InfraRed Spectrograph (IRS) mid-infrared (5–35 μm) spectra of a complete flux-limited sample (3mJyat8μm) of young stellar object (YSO) candidates selected on the basis of their infrared colors in the Serpens Molecular Cloud. -

The Potential to Form Planets in the Orion Nebula ! Rita Mann Plaskett Fellow NRC-Herzberg
The Potential to Form Planets in the Orion Nebula ! Rita Mann Plaskett Fellow NRC-Herzberg ! James Di Francesco, Sean Andrews, Jonathan Williams, Doug Johnstone, John Bally, Meredith Hughes, Luca Ricci, Brenda Matthews Protoplanetary Disks in the Orion Nebula Most stars form in rich clusters Our Solar System formed in a massive star forming environment. To understand planet formation, we need to study disk properties in massive star forming regions! HST images of protostars in Orion Orion Nebula Cluster Trapezium Cluster • Thousands of protostars • Ages ~ 1-2 Myr • Distance ~ 400 pc 1 • θ Ori C, 40M¤, O6 SpT Orion Nebula Cluster Massive Stars • Hostile environment • Many low mass stars near ϑ1C have teardrop shaped morphologies Low Mass Stars PROPLYDS: PROtoPLanetarY DiskS Photoevaporating Proplyds -7 VLA mass-loss rate of 10 M¤/yr Churchwell et al. (1987) Mdisk < 0.1 M¤ Evaporation Timescales < 1 Myr Material removed too quickly! C.R. O’Dell Is planet formation inhibited in rich clusters? Disk Masses in Orion: Previous Attempts Millimeter Wavelength Interferometers (clustered disks) BIMA OVRO PdBI Mundy et al. (1995) Bally et al. (1998) Lada (1999) λ = 3.5 mm λ = 1.3 mm λ = 1.3 mm low sensitivity no detections never published Mdisk ≲ 15 MJUP Radio-Submillimeter SED -0.1 2-4 Ffree-free ~ ν + Fdust ~ ν λ = 1 cm Radio-Submillimeter SED -0.1 2-4 Ffree-free ~ ν + Fdust ~ ν λ = 1 cm 1 mm Radio-Submillimeter SED -0.1 2-4 Ffree-free ~ ν + Fdust ~ ν λ = 1 cm 1 mm Higher frequency observations: more sensitive to dust emission! Interferometry with -

Exors and the Stellar Birthline Mackenzie S
A&A 600, A133 (2017) Astronomy DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/201630196 & c ESO 2017 Astrophysics EXors and the stellar birthline Mackenzie S. L. Moody1 and Steven W. Stahler2 1 Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA e-mail: [email protected] 2 Astronomy Department, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA e-mail: [email protected] Received 6 December 2016 / Accepted 23 February 2017 ABSTRACT We assess the evolutionary status of EXors. These low-mass, pre-main-sequence stars repeatedly undergo sharp luminosity increases, each a year or so in duration. We place into the HR diagram all EXors that have documented quiescent luminosities and effective temperatures, and thus determine their masses and ages. Two alternate sets of pre-main-sequence tracks are used, and yield similar results. Roughly half of EXors are embedded objects, i.e., they appear observationally as Class I or flat-spectrum infrared sources. We find that these are relatively young and are located close to the stellar birthline in the HR diagram. Optically visible EXors, on the other hand, are situated well below the birthline. They have ages of several Myr, typical of classical T Tauri stars. Judging from the limited data at hand, we find no evidence that binarity companions trigger EXor eruptions; this issue merits further investigation. We draw several general conclusions. First, repetitive luminosity outbursts do not occur in all pre-main-sequence stars, and are not in themselves a sign of extreme youth. They persist, along with other signs of activity, in a relatively small subset of these objects. -

Správa O Činnosti Organizácie SAV Za Rok 2017
Astronomický ústav SAV Správa o činnosti organizácie SAV za rok 2017 Tatranská Lomnica január 2018 Obsah osnovy Správy o činnosti organizácie SAV za rok 2017 1. Základné údaje o organizácii 2. Vedecká činnosť 3. Doktorandské štúdium, iná pedagogická činnosť a budovanie ľudských zdrojov pre vedu a techniku 4. Medzinárodná vedecká spolupráca 5. Vedná politika 6. Spolupráca s VŠ a inými subjektmi v oblasti vedy a techniky 7. Spolupráca s aplikačnou a hospodárskou sférou 8. Aktivity pre Národnú radu SR, vládu SR, ústredné orgány štátnej správy SR a iné organizácie 9. Vedecko-organizačné a popularizačné aktivity 10. Činnosť knižnično-informačného pracoviska 11. Aktivity v orgánoch SAV 12. Hospodárenie organizácie 13. Nadácie a fondy pri organizácii SAV 14. Iné významné činnosti organizácie SAV 15. Vyznamenania, ocenenia a ceny udelené organizácii a pracovníkom organizácie SAV 16. Poskytovanie informácií v súlade so zákonom o slobodnom prístupe k informáciám 17. Problémy a podnety pre činnosť SAV PRÍLOHY A Zoznam zamestnancov a doktorandov organizácie k 31.12.2017 B Projekty riešené v organizácii C Publikačná činnosť organizácie D Údaje o pedagogickej činnosti organizácie E Medzinárodná mobilita organizácie F Vedecko-popularizačná činnosť pracovníkov organizácie SAV Správa o činnosti organizácie SAV 1. Základné údaje o organizácii 1.1. Kontaktné údaje Názov: Astronomický ústav SAV Riaditeľ: Mgr. Martin Vaňko, PhD. Zástupca riaditeľa: Mgr. Peter Gömöry, PhD. Vedecký tajomník: Mgr. Marián Jakubík, PhD. Predseda vedeckej rady: RNDr. Luboš Neslušan, CSc. Člen snemu SAV: Mgr. Marián Jakubík, PhD. Adresa: Astronomický ústav SAV, 059 60 Tatranská Lomnica http://www.ta3.sk Tel.: 052/7879111 Fax: 052/4467656 E-mail: [email protected] Názvy a adresy detašovaných pracovísk: Astronomický ústav - Oddelenie medziplanetárnej hmoty Dúbravská cesta 9, 845 04 Bratislava Vedúci detašovaných pracovísk: Astronomický ústav - Oddelenie medziplanetárnej hmoty prof. -

Lecture 3 - Minimum Mass Model of Solar Nebula
Lecture 3 - Minimum mass model of solar nebula o Topics to be covered: o Composition and condensation o Surface density profile o Minimum mass of solar nebula PY4A01 Solar System Science Minimum Mass Solar Nebula (MMSN) o MMSN is not a nebula, but a protoplanetary disc. Protoplanetary disk Nebula o Gives minimum mass of solid material to build the 8 planets. PY4A01 Solar System Science Minimum mass of the solar nebula o Can make approximation of minimum amount of solar nebula material that must have been present to form planets. Know: 1. Current masses, composition, location and radii of the planets. 2. Cosmic elemental abundances. 3. Condensation temperatures of material. o Given % of material that condenses, can calculate minimum mass of original nebula from which the planets formed. • Figure from Page 115 of “Physics & Chemistry of the Solar System” by Lewis o Steps 1-8: metals & rock, steps 9-13: ices PY4A01 Solar System Science Nebula composition o Assume solar/cosmic abundances: Representative Main nebular Fraction of elements Low-T material nebular mass H, He Gas 98.4 % H2, He C, N, O Volatiles (ices) 1.2 % H2O, CH4, NH3 Si, Mg, Fe Refractories 0.3 % (metals, silicates) PY4A01 Solar System Science Minimum mass for terrestrial planets o Mercury:~5.43 g cm-3 => complete condensation of Fe (~0.285% Mnebula). 0.285% Mnebula = 100 % Mmercury => Mnebula = (100/ 0.285) Mmercury = 350 Mmercury o Venus: ~5.24 g cm-3 => condensation from Fe and silicates (~0.37% Mnebula). =>(100% / 0.37% ) Mvenus = 270 Mvenus o Earth/Mars: 0.43% of material condensed at cooler temperatures. -

Impact of Supernovae on Molecular Cloud Evolution Dynamics and Structure
Impact of Supernovae on Molecular Cloud Evolution Dynamics and Structure Bastian K¨ortgen1, Daniel Seifried1, and Robi Banerjee1 1Hamburger Sternwarte, Gojenbergsweg 112, 21029 Hamburg, Germany [email protected] Introduction We perform numerical simulations of colliding streams of the WNM, including magnetic fields and self{gravity, to analyse the formation and evolution of molecular clouds subject to supernova feedback from massive stars. Simulation Setup The Supernova Subgrid Model The equations of MHD together with selfgravity and heating and cooling are evolved in time using the The supernova feedback is included into the model by means of a Sedov blast FLASH code [Fryxell et al., 2000]. We use a constant heating rate Γ and the cooling function Λ according to wave solution. We define a volume of radius R = 1 pc centered on the sink [Koyama and Inutsuka, 2000] and [V´azquez-Semadeni et al., 2007]. The table below lists the initial conditions. particle. Within this volume each grid cell is assigned a certain radial veloc- ity vc. This velocity depends on the kinetic energy input. Additionally we U Sink Particle Parameter Value Parameter Value inject thermal energy, which then gives the total amount of injected energy of E = 1051 erg with 65 % thermal and 35 % kinetic energy according to the Flow Mach number Mf 2.0 Alfv´en velocity va [km/s] 5.8 sn Sedov solution. The cell velocity is Turbulent Mach number Ms 0.5 Alfv´enic Mach number Ma 1.96 r vc = Ush Temperature [K] 5000 Plasma Beta β = Pth=PB 1.93 R Number density n cm−3 1.0 Flow Length [pc] 112 Figure 1: Schematic of the where U is the shock velocity, depending on the kinetic energy input. -

Star Formation in the “Gulf of Mexico”
A&A 528, A125 (2011) Astronomy DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/200912671 & c ESO 2011 Astrophysics Star formation in the “Gulf of Mexico” T. Armond1,, B. Reipurth2,J.Bally3, and C. Aspin2, 1 SOAR Telescope, Casilla 603, La Serena, Chile e-mail: [email protected] 2 Institute for Astronomy, University of Hawaii at Manoa, 640 N. Aohoku Place, Hilo, HI 96720, USA e-mail: [reipurth;caa]@ifa.hawaii.edu 3 Center for Astrophysics and Space Astronomy, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309, USA e-mail: [email protected] Received 9 June 2009 / Accepted 6 February 2011 ABSTRACT We present an optical/infrared study of the dense molecular cloud, L935, dubbed “The Gulf of Mexico”, which separates the North America and the Pelican nebulae, and we demonstrate that this area is a very active star forming region. A wide-field imaging study with interference filters has revealed 35 new Herbig-Haro objects in the Gulf of Mexico. A grism survey has identified 41 Hα emission- line stars, 30 of them new. A small cluster of partly embedded pre-main sequence stars is located around the known LkHα 185-189 group of stars, which includes the recently erupting FUor HBC 722. Key words. Herbig-Haro objects – stars: formation 1. Introduction In a grism survey of the W80 region, Herbig (1958) detected a population of Hα emission-line stars, LkHα 131–195, mostly The North America nebula (NGC 7000) and the adjacent Pelican T Tauri stars, including the little group LkHα 185 to 189 located nebula (IC 5070), both well known for the characteristic shapes within the dark lane of the Gulf of Mexico, thus demonstrating that have given rise to their names, are part of the single large that low-mass star formation has recently taken place here. -

Pulsar Physics Without Magnetars
Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. Vol.8 (2008), Supplement, 213–218 Chinese Journal of (http://www.chjaa.org) Astronomy and Astrophysics Pulsar Physics without Magnetars Wolfgang Kundt Argelander-Institut f¨ur Astronomie der Universit¨at, Auf dem H¨ugel 71, D-53121 Bonn, Germany Abstract Magnetars, as defined some 15 yr ago, are inconsistent both with fundamental physics, and with the (by now) two observed upward jumps of the period derivatives (of two of them). Instead, the class of peculiar X-ray sources commonly interpreted as magnetars can be understood as the class of throttled pulsars, i.e. of pulsars strongly interacting with their CSM. This class is even expected to harbour the sources of the Cosmic Rays, and of all the (extraterrestrial) Gamma-Ray Bursts. Key words: magnetars — throttled pulsars — dying pulsars — cavity — low-mass disk 1 DEFINITION AND PROPERTIES OF THE MAGNETARS Magnetars have been defined by Duncan and Thompson some 15 years ago, as spinning, compact X-ray sources - probably neutron stars - which are powered by the slow decay of their strong magnetic field, of strength 1015 G near the surface, cf. (Duncan & Thompson 1992; Thompson & Duncan 1996). They are now thought to comprise the anomalous X-ray pulsars (AXPs), soft gamma-ray repeaters (SGRs), recurrent radio transients (RRATs), or ‘stammerers’, or ‘burpers’, and the ‘dim isolated neutron stars’ (DINSs), i.e. a large, fairly well defined subclass of all neutron stars, which has the following properties (Mereghetti et al. 2002): 1) They are isolated neutron stars, with spin periods P between 5 s and 12 s, and similar glitch behaviour to other neutron-star sources, which correlates with their X-ray bursting. -

Kuchner, M. & Seager, S., Extrasolar Carbon Planets, Arxiv:Astro-Ph
Extrasolar Carbon Planets Marc J. Kuchner1 Princeton University Department of Astrophysical Sciences Peyton Hall, Princeton, NJ 08544 S. Seager Carnegie Institution of Washington, 5241 Broad Branch Rd. NW, Washington DC 20015 [email protected] ABSTRACT We suggest that some extrasolar planets . 60 ML will form substantially from silicon carbide and other carbon compounds. Pulsar planets and low-mass white dwarf planets are especially good candidate members of this new class of planets, but these objects could also conceivably form around stars like the Sun. This planet-formation pathway requires only a factor of two local enhancement of the protoplanetary disk’s C/O ratio above solar, a condition that pileups of carbonaceous grains may create in ordinary protoplanetary disks. Hot, Neptune- mass carbon planets should show a significant paucity of water vapor in their spectra compared to hot planets with solar abundances. Cooler, less massive carbon planets may show hydrocarbon-rich spectra and tar-covered surfaces. The high sublimation temperatures of diamond, SiC, and other carbon compounds could protect these planets from carbon depletion at high temperatures. arXiv:astro-ph/0504214v2 2 May 2005 Subject headings: astrobiology — planets and satellites, individual (Mercury, Jupiter) — planetary systems: formation — pulsars, individual (PSR 1257+12) — white dwarfs 1. INTRODUCTION The recent discoveries of Neptune-mass extrasolar planets by the radial velocity method (Santos et al. 2004; McArthur et al. 2004; Butler et al. 2004) and the rapid development 1Hubble Fellow –2– of new technologies to study the compositions of low-mass extrasolar planets (see, e.g., the review by Kuchner & Spergel 2003) have compelled several authors to consider planets with chemistries unlike those found in the solar system (Stevenson 2004) such as water planets (Kuchner 2003; Leger et al. -

LIST of PUBLICATIONS Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences ARIES (An Autonomous Scientific Research Institute
LIST OF PUBLICATIONS Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences ARIES (An Autonomous Scientific Research Institute of Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India) Manora Peak, Naini Tal - 263 129, India (1955−2020) ABBREVIATIONS AA: Astronomy and Astrophysics AASS: Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series ACTA: Acta Astronomica AJ: Astronomical Journal ANG: Annals de Geophysique Ap. J.: Astrophysical Journal ASP: Astronomical Society of Pacific ASR: Advances in Space Research ASS: Astrophysics and Space Science AE: Atmospheric Environment ASL: Atmospheric Science Letters BA: Baltic Astronomy BAC: Bulletin Astronomical Institute of Czechoslovakia BASI: Bulletin of the Astronomical Society of India BIVS: Bulletin of the Indian Vacuum Society BNIS: Bulletin of National Institute of Sciences CJAA: Chinese Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics CS: Current Science EPS: Earth Planets Space GRL : Geophysical Research Letters IAU: International Astronomical Union IBVS: Information Bulletin on Variable Stars IJHS: Indian Journal of History of Science IJPAP: Indian Journal of Pure and Applied Physics IJRSP: Indian Journal of Radio and Space Physics INSA: Indian National Science Academy JAA: Journal of Astrophysics and Astronomy JAMC: Journal of Applied Meterology and Climatology JATP: Journal of Atmospheric and Terrestrial Physics JBAA: Journal of British Astronomical Association JCAP: Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics JESS : Jr. of Earth System Science JGR : Journal of Geophysical Research JIGR: Journal of Indian -

Progenitors of Magnetars and Hyperaccreting Magnetized Disks
Feeding Compact Objects: Accretion on All Scales Proceedings IAU Symposium No. 290, 2012 c International Astronomical Union 2013 C. M. Zhang, T. Belloni, M. M´endez & S. N. Zhang, eds. doi:10.1017/S1743921312020340 Progenitors of Magnetars and Hyperaccreting Magnetized Disks Y. Xie1 andS.N.Zhang1,2 1 National Astronomical Observatories, Chinese Academy Of Sciences, Beijing, 100012, P. R.China email: [email protected] 2 Key Laboratory of Particle Astrophysics, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100012, P. R. China email: [email protected] Abstract. We propose that a magnetar could be formed during the core collapse of massive stars or coalescence of two normal neutron stars, through collecting and inheriting the magnetic fields magnified by hyperaccreting disk. After the magnetar is born, its dipole magnetic fields in turn have a major influence on the following accretion. The decay of its toroidal field can fuel the persistent X-ray luminosity of either an SGR or AXP; however the decay of only the poloidal field is insufficient to do so. Keywords. Magnetar, accretion disk, gamma ray bursts, magnetic fields 1. Introduction Neutron stars (NSs) with magnetic field B stronger than the quantum critical value, 2 3 13 Bcr = m c /e ≈ 4.4 × 10 G, are called magnetars. Observationally, a magnetar may appear as a soft gamma-ray repeater (SGR) or an anomalous X-ray pulsar (AXP). It is believed that its persistent X-ray luminosity is powered by the consumption of their B- decay energy (e.g. Duncan & Thompson 1992; Paczynski 1992). However, the formation of strong B of a magnetar remains unresolved, and the possible explanations are divided into three classes: (i) B is generated by a convective dynamo (Duncan & Thompson 1992); (ii) B is essentially of fossil origin (e.g.